Compare commits
1 Commits
of/repo-st
...
mrT23-patc
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
| b9e3e5603b |
@ -1,4 +1,3 @@
|
||||
.venv/
|
||||
venv/
|
||||
pr_agent/settings/.secrets.toml
|
||||
pics/
|
||||
|
||||
38
.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/bug-report.yml
vendored
@ -1,38 +0,0 @@
|
||||
name: "\U0001FAB2 Bug Report"
|
||||
description: Submit a bug report
|
||||
labels: ["bug"]
|
||||
body:
|
||||
|
||||
- type: dropdown
|
||||
id: information-git-provider
|
||||
attributes:
|
||||
label: Git provider
|
||||
description: 'The problem arises when using:'
|
||||
options:
|
||||
- "Github Cloud"
|
||||
- "Github Enterprise"
|
||||
- "Gitlab"
|
||||
- "Bitbucket Cloud"
|
||||
- "Bitbucket Server"
|
||||
- "Azure"
|
||||
- "Other"
|
||||
validations:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
|
||||
- type: textarea
|
||||
id: system-info
|
||||
attributes:
|
||||
label: System Info
|
||||
description: Please share your system info with us.
|
||||
placeholder: model used, deployment type (action/app/cli/...), etc...
|
||||
validations:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
|
||||
- type: textarea
|
||||
id: bug-details
|
||||
attributes:
|
||||
label: Bug details
|
||||
description: Please describe the problem.
|
||||
placeholder: Describe the problem
|
||||
validations:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
10
.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/config.yml
vendored
@ -1,10 +0,0 @@
|
||||
blank_issues_enabled: false
|
||||
version: 0.1
|
||||
contact_links:
|
||||
- name: Discussions
|
||||
url: https://github.com/qodo-ai/pr-agent/discussions
|
||||
about: GitHub Discussions
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Discord community
|
||||
url: https://discord.com/channels/1057273017547378788/1126104260430528613
|
||||
about: Join our discord community
|
||||
21
.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/feature-request.yml
vendored
@ -1,21 +0,0 @@
|
||||
name: "\U0001F4A1 Feature request"
|
||||
description: Submit a proposal/request for a new PR-Agent feature
|
||||
labels: ["feature"]
|
||||
body:
|
||||
- type: textarea
|
||||
id: feature-request
|
||||
validations:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
attributes:
|
||||
label: Feature request
|
||||
description: |
|
||||
Description of the feature proposal.
|
||||
|
||||
- type: textarea
|
||||
id: motivation
|
||||
validations:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
attributes:
|
||||
label: Motivation
|
||||
description: |
|
||||
Outline the motivation for the proposal.
|
||||
36
.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/miscellaneous.yml
vendored
@ -1,36 +0,0 @@
|
||||
name: "❔ General Issue"
|
||||
description: Submit a general issue
|
||||
labels: ["general"]
|
||||
body:
|
||||
|
||||
- type: dropdown
|
||||
id: information-git-provider
|
||||
attributes:
|
||||
label: Git provider (optional)
|
||||
description: 'Git Provider:'
|
||||
options:
|
||||
- "Github Cloud"
|
||||
- "Github Enterprise"
|
||||
- "Gitlab"
|
||||
- "Bitbucket Cloud"
|
||||
- "Bitbucket Server"
|
||||
- "Azure"
|
||||
- "Other"
|
||||
|
||||
- type: textarea
|
||||
id: system-info
|
||||
attributes:
|
||||
label: System Info (optional)
|
||||
description: Please share your system info with us.
|
||||
placeholder: model used, deployment type (action/app/cli/...), etc...
|
||||
validations:
|
||||
required: false
|
||||
|
||||
- type: textarea
|
||||
id: issues-details
|
||||
attributes:
|
||||
label: Issues details
|
||||
description: Please share the issues details.
|
||||
placeholder: Describe the issue
|
||||
validations:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
8
.github/workflows/build-and-test.yaml
vendored
@ -14,15 +14,15 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- id: checkout
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
||||
|
||||
- id: dockerx
|
||||
name: Setup Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v2
|
||||
|
||||
- id: build
|
||||
name: Build dev docker
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v6
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
context: .
|
||||
file: ./docker/Dockerfile
|
||||
@ -37,3 +37,5 @@ jobs:
|
||||
name: Test dev docker
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
docker run --rm codiumai/pr-agent:test pytest -v tests/unittest
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
13
.github/workflows/code_coverage.yaml
vendored
@ -15,15 +15,15 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- id: checkout
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
||||
|
||||
- id: dockerx
|
||||
name: Setup Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v2
|
||||
|
||||
- id: build
|
||||
name: Build dev docker
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v6
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
context: .
|
||||
file: ./docker/Dockerfile
|
||||
@ -37,10 +37,11 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- id: code_cov
|
||||
name: Test dev docker
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
docker run --name test_container codiumai/pr-agent:test pytest tests/unittest --cov=pr_agent --cov-report term --cov-report xml:coverage.xml
|
||||
docker run --name test_container codiumai/pr-agent:test pytest tests/unittest --cov=pr_agent --cov-report term --cov-report xml:coverage.xml
|
||||
docker cp test_container:/app/coverage.xml coverage.xml
|
||||
docker rm test_container
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Validate coverage report
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
if [ ! -f coverage.xml ]; then
|
||||
@ -48,6 +49,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
exit 1
|
||||
fi
|
||||
- name: Upload coverage to Codecov
|
||||
uses: codecov/codecov-action@v5
|
||||
uses: codecov/codecov-action@v4.0.1
|
||||
with:
|
||||
token: ${{ secrets.CODECOV_TOKEN }}
|
||||
token: ${{ secrets.CODECOV_TOKEN }}
|
||||
6
.github/workflows/docs-ci.yaml
vendored
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
name: docs-ci
|
||||
name: docs-ci
|
||||
on:
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
@ -20,14 +20,14 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- uses: actions/setup-python@v5
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-version: 3.x
|
||||
- run: echo "cache_id=$(date --utc '+%V')" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
- run: echo "cache_id=$(date --utc '+%V')" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
- uses: actions/cache@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
key: mkdocs-material-${{ env.cache_id }}
|
||||
path: .cache
|
||||
restore-keys: |
|
||||
mkdocs-material-
|
||||
- run: pip install mkdocs-material
|
||||
- run: pip install mkdocs-material
|
||||
- run: pip install "mkdocs-material[imaging]"
|
||||
- run: pip install mkdocs-glightbox
|
||||
- run: mkdocs gh-deploy -f docs/mkdocs.yml --force
|
||||
|
||||
11
.github/workflows/e2e_tests.yaml
vendored
@ -11,14 +11,14 @@ jobs:
|
||||
name: PR-Agent E2E GitHub App Test
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout repository
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Setup Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v2
|
||||
|
||||
- id: build
|
||||
name: Build dev docker
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v6
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
context: .
|
||||
file: ./docker/Dockerfile
|
||||
@ -32,14 +32,15 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- id: test1
|
||||
name: E2E test github app
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
docker run -e GITHUB.USER_TOKEN=${{ secrets.TOKEN_GITHUB }} --rm codiumai/pr-agent:test pytest -v tests/e2e_tests/test_github_app.py
|
||||
docker run -e GITHUB.USER_TOKEN=${{ secrets.TOKEN_GITHUB }} --rm codiumai/pr-agent:test pytest -v tests/e2e_tests/test_github_app.py
|
||||
|
||||
- id: test2
|
||||
name: E2E gitlab webhook
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
docker run -e gitlab.PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN=${{ secrets.TOKEN_GITLAB }} --rm codiumai/pr-agent:test pytest -v tests/e2e_tests/test_gitlab_webhook.py
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- id: test3
|
||||
name: E2E bitbucket app
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
docker run -e BITBUCKET.USERNAME=${{ secrets.BITBUCKET_USERNAME }} -e BITBUCKET.PASSWORD=${{ secrets.BITBUCKET_PASSWORD }} --rm codiumai/pr-agent:test pytest -v tests/e2e_tests/test_bitbucket_app.py
|
||||
docker run -e BITBUCKET.USERNAME=${{ secrets.BITBUCKET_USERNAME }} -e BITBUCKET.PASSWORD=${{ secrets.BITBUCKET_PASSWORD }} --rm codiumai/pr-agent:test pytest -v tests/e2e_tests/test_bitbucket_app.py
|
||||
5
.github/workflows/pr-agent-review.yaml
vendored
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
# This workflow enables developers to call PR-Agents `/[actions]` in PR's comments and upon PR creation.
|
||||
# This workflow enables developers to call PR-Agents `/[actions]` in PR's comments and upon PR creation.
|
||||
# Learn more at https://www.codium.ai/pr-agent/
|
||||
# This is v0.2 of this workflow file
|
||||
|
||||
@ -30,3 +30,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
GITHUB_ACTION_CONFIG.AUTO_DESCRIBE: true
|
||||
GITHUB_ACTION_CONFIG.AUTO_REVIEW: true
|
||||
GITHUB_ACTION_CONFIG.AUTO_IMPROVE: true
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
17
.github/workflows/pre-commit.yml
vendored
@ -1,17 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# disabled. We might run it manually if needed.
|
||||
name: pre-commit
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
workflow_dispatch:
|
||||
# pull_request:
|
||||
# push:
|
||||
# branches: [main]
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
pre-commit:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
- uses: actions/setup-python@v5
|
||||
# SEE https://github.com/pre-commit/action
|
||||
- uses: pre-commit/action@v3.0.1
|
||||
6
.gitignore
vendored
@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
|
||||
.idea/
|
||||
.lsp/
|
||||
.vscode/
|
||||
.env
|
||||
.venv/
|
||||
venv/
|
||||
pr_agent/settings/.secrets.toml
|
||||
__pycache__
|
||||
@ -10,6 +8,4 @@ dist/
|
||||
*.egg-info/
|
||||
build/
|
||||
.DS_Store
|
||||
docs/.cache/
|
||||
.qodo
|
||||
poetry.lock
|
||||
docs/.cache/
|
||||
@ -1,46 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# See https://pre-commit.com for more information
|
||||
# See https://pre-commit.com/hooks.html for more hooks
|
||||
|
||||
default_language_version:
|
||||
python: python3
|
||||
|
||||
repos:
|
||||
- repo: https://github.com/pre-commit/pre-commit-hooks
|
||||
rev: v5.0.0
|
||||
hooks:
|
||||
- id: check-added-large-files
|
||||
- id: check-toml
|
||||
- id: check-yaml
|
||||
- id: end-of-file-fixer
|
||||
- id: trailing-whitespace
|
||||
# - repo: https://github.com/rhysd/actionlint
|
||||
# rev: v1.7.3
|
||||
# hooks:
|
||||
# - id: actionlint
|
||||
- repo: https://github.com/pycqa/isort
|
||||
# rev must match what's in dev-requirements.txt
|
||||
rev: 5.13.2
|
||||
hooks:
|
||||
- id: isort
|
||||
# - repo: https://github.com/PyCQA/bandit
|
||||
# rev: 1.7.10
|
||||
# hooks:
|
||||
# - id: bandit
|
||||
# args: [
|
||||
# "-c", "pyproject.toml",
|
||||
# ]
|
||||
# - repo: https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff-pre-commit
|
||||
# rev: v0.7.1
|
||||
# hooks:
|
||||
# - id: ruff
|
||||
# args:
|
||||
# - --fix
|
||||
# - id: ruff-format
|
||||
# - repo: https://github.com/PyCQA/autoflake
|
||||
# rev: v2.3.1
|
||||
# hooks:
|
||||
# - id: autoflake
|
||||
# args:
|
||||
# - --in-place
|
||||
# - --remove-all-unused-imports
|
||||
# - --remove-unused-variables
|
||||
@ -1,7 +1,6 @@
|
||||
## 2023-08-03
|
||||
|
||||
### Optimized
|
||||
|
||||
- Optimized PR diff processing by introducing caching for diff files, reducing the number of API calls.
|
||||
- Refactored `load_large_diff` function to generate a patch only when necessary.
|
||||
- Fixed a bug in the GitLab provider where the new file was not retrieved correctly.
|
||||
@ -9,7 +8,6 @@
|
||||
## 2023-08-02
|
||||
|
||||
### Enhanced
|
||||
|
||||
- Updated several tools in the `pr_agent` package to use commit messages in their functionality.
|
||||
- Commit messages are now retrieved and stored in the `vars` dictionary for each tool.
|
||||
- Added a section to display the commit messages in the prompts of various tools.
|
||||
@ -17,7 +15,6 @@
|
||||
## 2023-08-01
|
||||
|
||||
### Enhanced
|
||||
|
||||
- Introduced the ability to retrieve commit messages from pull requests across different git providers.
|
||||
- Implemented commit messages retrieval for GitHub and GitLab providers.
|
||||
- Updated the PR description template to include a section for commit messages if they exist.
|
||||
@ -25,10 +22,10 @@
|
||||
- Implemented this feature for both GitHub and GitLab providers.
|
||||
- Added a new configuration option 'use_repo_settings_file' to enable or disable the use of a repo-specific settings file.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 2023-07-30
|
||||
|
||||
### Enhanced
|
||||
|
||||
- Added the ability to modify any configuration parameter from 'configuration.toml' on-the-fly.
|
||||
- Updated the command line interface and bot commands to accept configuration changes as arguments.
|
||||
- Improved the PR agent to handle additional arguments for each action.
|
||||
@ -36,7 +33,6 @@
|
||||
## 2023-07-28
|
||||
|
||||
### Improved
|
||||
|
||||
- Enhanced error handling and logging in the GitLab provider.
|
||||
- Improved handling of inline comments and code suggestions in GitLab.
|
||||
- Fixed a bug where an additional unneeded line was added to code suggestions in GitLab.
|
||||
@ -44,7 +40,6 @@
|
||||
## 2023-07-26
|
||||
|
||||
### Added
|
||||
|
||||
- New feature for updating the CHANGELOG.md based on the contents of a PR.
|
||||
- Added support for this feature for the Github provider.
|
||||
- New configuration settings and prompts for the changelog update feature.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,44 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Contributor Code of Conduct
|
||||
|
||||
As contributors and maintainers of this project, and in the interest of fostering an open
|
||||
and welcoming community, we pledge to respect all people who contribute through reporting
|
||||
issues, posting feature requests, updating documentation, submitting pull requests or
|
||||
patches, and other activities.
|
||||
|
||||
We are committed to making participation in this project a harassment-free experience for
|
||||
everyone, regardless of level of experience, gender, gender identity and expression,
|
||||
sexual orientation, disability, personal appearance, body size, race, ethnicity, age,
|
||||
religion, or nationality.
|
||||
|
||||
Examples of unacceptable behavior by participants include:
|
||||
|
||||
* The use of sexualized language or imagery
|
||||
* Personal attacks
|
||||
* Trolling or insulting/derogatory comments
|
||||
* Public or private harassment
|
||||
* Publishing other's private information, such as physical or electronic addresses,
|
||||
without explicit permission
|
||||
* Other unethical or unprofessional conduct
|
||||
|
||||
Project maintainers have the right and responsibility to remove, edit, or reject comments,
|
||||
commits, code, wiki edits, issues, and other contributions that are not aligned to this
|
||||
Code of Conduct, or to ban temporarily or permanently any contributor for other behaviors
|
||||
that they deem inappropriate, threatening, offensive, or harmful.
|
||||
|
||||
By adopting this Code of Conduct, project maintainers commit themselves to fairly and
|
||||
consistently applying these principles to every aspect of managing this project. Project
|
||||
maintainers who do not follow or enforce the Code of Conduct may be permanently removed
|
||||
from the project team.
|
||||
|
||||
This Code of Conduct applies both within project spaces and in public spaces when an
|
||||
individual is representing the project or its community.
|
||||
|
||||
Instances of abusive, harassing, or otherwise unacceptable behavior may be reported by
|
||||
contacting a project maintainer at tal.r@qodo.ai . All complaints will
|
||||
be reviewed and investigated and will result in a response that is deemed necessary and
|
||||
appropriate to the circumstances. Maintainers are obligated to maintain confidentiality
|
||||
with regard to the reporter of an incident.
|
||||
|
||||
This Code of Conduct is adapted from the
|
||||
[Contributor Covenant](https://contributor-covenant.org), version 1.3.0, available at
|
||||
[contributor-covenant.org/version/1/3/0/](https://contributor-covenant.org/version/1/3/0/)
|
||||
@ -1,38 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Contributing to PR-Agent
|
||||
|
||||
Thank you for your interest in contributing to the PR-Agent project!
|
||||
|
||||
## Getting Started
|
||||
|
||||
1. Fork the repository and clone your fork
|
||||
2. Install Python 3.10 or higher
|
||||
3. Install dependencies (`requirements.txt` and `requirements-dev.txt`)
|
||||
4. Create a new branch for your contribution:
|
||||
- For new features: `git checkout -b feature/your-feature-name`
|
||||
- For bug fixes: `git checkout -b fix/issue-description`
|
||||
5. Make your changes
|
||||
6. Write or update tests as needed
|
||||
7. Run tests locally to ensure everything passes
|
||||
8. Commit your changes using conventional commit messages
|
||||
9. Push to your fork and submit a pull request
|
||||
|
||||
## Development Guidelines
|
||||
|
||||
- Keep pull requests focused on a single feature or fix
|
||||
- Follow the existing code style and formatting conventions
|
||||
- Add unit tests for any new functionality using pytest
|
||||
- Ensure test coverage for your changes
|
||||
- Update documentation as needed
|
||||
|
||||
## Pull Request Process
|
||||
|
||||
1. Ensure your PR includes a clear description of the changes
|
||||
2. Link any related issues
|
||||
3. Update the README.md if needed
|
||||
4. Wait for review from maintainers
|
||||
|
||||
## Questions or Need Help?
|
||||
|
||||
- Join our [Discord community](https://discord.com/channels/1057273017547378788/1126104260430528613) for questions and discussions
|
||||
- Check the [documentation](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/) for detailed information
|
||||
- Report bugs or request features through [GitHub Issues](https://github.com/qodo-ai/pr-agent/issues)
|
||||
@ -1,11 +1,9 @@
|
||||
FROM python:3.12.10-slim AS base
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install --no-install-recommends -y git curl && apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
|
||||
FROM python:3.12 as base
|
||||
|
||||
WORKDIR /app
|
||||
ADD pyproject.toml .
|
||||
ADD requirements.txt .
|
||||
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir . && rm pyproject.toml requirements.txt
|
||||
RUN pip install . && rm pyproject.toml requirements.txt
|
||||
ENV PYTHONPATH=/app
|
||||
ADD docs docs
|
||||
ADD pr_agent pr_agent
|
||||
|
||||
2
LICENSE
@ -199,4 +199,4 @@
|
||||
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
limitations under the License.
|
||||
limitations under the License.
|
||||
@ -1,2 +1,2 @@
|
||||
recursive-include pr_agent *.toml
|
||||
recursive-exclude pr_agent *.secrets.toml
|
||||
recursive-exclude pr_agent *.secrets.toml
|
||||
303
README.md
@ -2,154 +2,157 @@
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<picture>
|
||||
<source media="(prefers-color-scheme: dark)" srcset="https://www.qodo.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/PR-Agent-Purple-2.png">
|
||||
<source media="(prefers-color-scheme: light)" srcset="https://www.qodo.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/PR-Agent-Purple-2.png">
|
||||
<source media="(prefers-color-scheme: dark)" srcset="https://codium.ai/images/pr_agent/logo-dark.png" width="330">
|
||||
<source media="(prefers-color-scheme: light)" srcset="https://codium.ai/images/pr_agent/logo-light.png" width="330">
|
||||
<img src="https://codium.ai/images/pr_agent/logo-light.png" alt="logo" width="330">
|
||||
|
||||
</picture>
|
||||
<br/>
|
||||
|
||||
[Installation Guide](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/) |
|
||||
[Usage Guide](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/) |
|
||||
[Tools Guide](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/) |
|
||||
[Qodo Merge](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/overview/pr_agent_pro/) 💎
|
||||
|
||||
PR-Agent aims to help efficiently review and handle pull requests, by providing AI feedback and suggestions
|
||||
Qode Merge PR-Agent aims to help efficiently review and handle pull requests, by providing AI feedback and suggestions
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://chromewebstore.google.com/detail/qodo-merge-ai-powered-cod/ephlnjeghhogofkifjloamocljapahnl)
|
||||
[](https://github.com/apps/qodo-merge-pro/)
|
||||
[](https://github.com/apps/qodo-merge-pro-for-open-source/)
|
||||
[](https://discord.com/invite/SgSxuQ65GF)
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/commits/main">
|
||||
<img alt="GitHub" src="https://img.shields.io/github/last-commit/Codium-ai/pr-agent/main?style=for-the-badge" height="20">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
[](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/LICENSE)
|
||||
[](https://chromewebstore.google.com/detail/pr-agent-chrome-extension/ephlnjeghhogofkifjloamocljapahnl)
|
||||
[](https://pr-agent-docs.codium.ai/finetuning_benchmark/)
|
||||
[](https://discord.com/channels/1057273017547378788/1126104260430528613)
|
||||
[](https://twitter.com/codiumai)
|
||||
[](https://www.codium.ai/images/pr_agent/cheat_sheet.pdf)
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/commits/main">
|
||||
<img alt="GitHub" src="https://img.shields.io/github/last-commit/Codium-ai/pr-agent/main?style=for-the-badge" height="20">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
### [Documentation](https://pr-agent-docs.codium.ai/)
|
||||
- See the [Installation Guide](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/) for instructions on installing Qode Merge PR-Agent on different platforms.
|
||||
|
||||
- See the [Usage Guide](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/) for instructions on running Qode Merge PR-Agent tools via different interfaces, such as CLI, PR Comments, or by automatically triggering them when a new PR is opened.
|
||||
|
||||
- See the [Tools Guide](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/) for a detailed description of the different tools, and the available configurations for each tool.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Table of Contents
|
||||
|
||||
- [News and Updates](#news-and-updates)
|
||||
- [Overview](#overview)
|
||||
- [Example results](#example-results)
|
||||
- [Try it now](#try-it-now)
|
||||
- [Qodo Merge](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/overview/pr_agent_pro/)
|
||||
- [PR-Agent Pro 💎](https://pr-agent-docs.codium.ai/overview/pr_agent_pro/)
|
||||
- [How it works](#how-it-works)
|
||||
- [Why use PR-Agent?](#why-use-pr-agent)
|
||||
- [Data privacy](#data-privacy)
|
||||
- [Contributing](#contributing)
|
||||
- [Links](#links)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## News and Updates
|
||||
|
||||
## May 17, 2025
|
||||
### October 27, 2024
|
||||
|
||||
- v0.29 was [released](https://github.com/qodo-ai/pr-agent/releases)
|
||||
- `Qodo Merge Pull Request Benchmark` was [released](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/pr_benchmark/). This benchmark evaluates and compares the performance of LLMs in analyzing pull request code.
|
||||
- `Recent Updates and Future Roadmap` page was added to the [Qodo Merge Docs](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/recent_updates/)
|
||||
Qodo Merge PR Agent will now automatically document accepted code suggestions in a dedicated wiki page (`.pr_agent_accepted_suggestions`), enabling users to track historical changes, assess the tool's effectiveness, and learn from previously implemented recommendations in the repository.
|
||||
|
||||
## Apr 30, 2025
|
||||
This dedicated wiki page will also serve as a foundation for future AI model improvements, allowing it to learn from historically implemented suggestions and generate more targeted, contextually relevant recommendations.
|
||||
Read more about this novel feature [here](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#suggestion-tracking).
|
||||
|
||||
A new feature is now available in the `/improve` tool for Qodo Merge 💎 - Chat on code suggestions.
|
||||
<kbd><img href="https://qodo.ai/images/pr_agent/pr_agent_accepted_suggestions1.png" src="https://qodo.ai/images/pr_agent/pr_agent_accepted_suggestions1.png" width="768"></kbd>
|
||||
|
||||
<img width="512" alt="image" src="https://codium.ai/images/pr_agent/improve_chat_on_code_suggestions_ask.png" />
|
||||
|
||||
Read more about it [here](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#chat-on-code-suggestions).
|
||||
|
||||
## Apr 16, 2025
|
||||
### October 21, 2024
|
||||
**Disable publishing labels by default:**
|
||||
|
||||
New tool for Qodo Merge 💎 - `/scan_repo_discussions`.
|
||||
The default setting for `pr_description.publish_labels` has been updated to `false`. This means that labels generated by the `/describe` tool will no longer be published, unless this configuration is explicitly set to `true`.
|
||||
|
||||
<img width="635" alt="image" src="https://codium.ai/images/pr_agent/scan_repo_discussions_2.png" />
|
||||
We constantly strive to balance informative AI analysis with reducing unnecessary noise. User feedback indicated that in many cases, the original PR title alone provides sufficient information, making the generated labels (`enhancement`, `documentation`, `bug fix`, ...) redundant.
|
||||
The [`review_effort`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/review/#configuration-options) label, generated by the `review` tool, will still be published by default, as it provides valuable information enabling reviewers to prioritize small PRs first.
|
||||
|
||||
However, every user has different preferences. To still publish the `describe` labels, set `pr_description.publish_labels=true` in the [configuration file](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/).
|
||||
For more tailored and relevant labeling, we recommend using the [`custom_labels 💎`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/custom_labels/) tool, that allows generating labels specific to your project's needs.
|
||||
|
||||
<kbd></kbd>
|
||||
|
||||
→
|
||||
|
||||
<kbd></kbd>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### October 14, 2024
|
||||
Improved support for GitHub enterprise server with [GitHub Actions](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/github/#action-for-github-enterprise-server)
|
||||
|
||||
### October 10, 2024
|
||||
New ability for the `review` tool - **ticket compliance feedback**. If the PR contains a ticket number, PR-Agent will check if the PR code actually [complies](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/1279#issuecomment-2404042130) with the ticket requirements.
|
||||
|
||||
<kbd><img src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/4a2a728b-5f47-40fa-80cc-16efd296938c" width="768"></kbd>
|
||||
|
||||
Read more about it [here](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/scan_repo_discussions/).
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="text-align:left;">
|
||||
|
||||
Supported commands per platform:
|
||||
|
||||
| | | GitHub | GitLab | Bitbucket | Azure DevOps |
|
||||
| ----- |---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|:------:|:------:|:---------:|:------------:|
|
||||
| TOOLS | [Review](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/review/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Describe](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/describe/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Improve](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Ask](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/ask/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | ⮑ [Ask on code lines](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/ask/#ask-lines) | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Update CHANGELOG](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/update_changelog/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Help Docs](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/help_docs/?h=auto#auto-approval) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | [Ticket Context](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/fetching_ticket_context/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | [Utilizing Best Practices](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#best-practices) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | [PR Chat](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/chrome-extension/features/#pr-chat) 💎 | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | [Suggestion Tracking](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#suggestion-tracking) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [CI Feedback](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/ci_feedback/) 💎 | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | [PR Documentation](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/documentation/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Custom Labels](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/custom_labels/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Analyze](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/analyze/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Similar Code](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/similar_code/) 💎 | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | [Custom Prompt](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/custom_prompt/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | [Test](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/test/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Implement](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/implement/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | [Scan Repo Discussions](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/scan_repo_discussions/) 💎 | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | [Repo Statistics](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/repo_statistics/) 💎 | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | [Auto-Approve](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/?h=auto#auto-approval) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | | | | | |
|
||||
| USAGE | [CLI](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/automations_and_usage/#local-repo-cli) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [App / webhook](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/automations_and_usage/#github-app) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Tagging bot](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent#try-it-now) | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | [Actions](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/github/#run-as-a-github-action) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | | | | | |
|
||||
| CORE | [PR compression](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/compression_strategy/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | Adaptive and token-aware file patch fitting | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Multiple models support](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/changing_a_model/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Local and global metadata](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/metadata/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Dynamic context](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/dynamic_context/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Self reflection](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/self_reflection/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Static code analysis](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/static_code_analysis/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Global and wiki configurations](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | [PR interactive actions](https://www.qodo.ai/images/pr_agent/pr-actions.mp4) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Impact Evaluation](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/impact_evaluation/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Code Validation 💎](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/code_validation/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Auto Best Practices 💎](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/auto_best_practices/) | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
- 💎 means this feature is available only in [Qodo Merge](https://www.qodo.ai/pricing/)
|
||||
| | | GitHub | Gitlab | Bitbucket | Azure DevOps |
|
||||
|-------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|:--------------------:|:--------------------:|:--------------------:|:------------:|
|
||||
| TOOLS | Review | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | ⮑ Incremental | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | Describe | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | ⮑ [Inline File Summary](https://pr-agent-docs.codium.ai/tools/describe#inline-file-summary) 💎 | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | Improve | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | ⮑ Extended | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | Ask | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | ⮑ [Ask on code lines](https://pr-agent-docs.codium.ai/tools/ask#ask-lines) | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Custom Prompt](https://pr-agent-docs.codium.ai/tools/custom_prompt/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | [Test](https://pr-agent-docs.codium.ai/tools/test/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | Reflect and Review | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | Update CHANGELOG.md | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | Find Similar Issue | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | [Add PR Documentation](https://pr-agent-docs.codium.ai/tools/documentation/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Custom Labels](https://pr-agent-docs.codium.ai/tools/custom_labels/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Analyze](https://pr-agent-docs.codium.ai/tools/analyze/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [CI Feedback](https://pr-agent-docs.codium.ai/tools/ci_feedback/) 💎 | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | [Similar Code](https://pr-agent-docs.codium.ai/tools/similar_code/) 💎 | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | | | | | |
|
||||
| USAGE | CLI | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | App / webhook | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | Tagging bot | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | Actions | ✅ |✅| ✅ |✅|
|
||||
| | | | | | |
|
||||
| CORE | PR compression | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | Repo language prioritization | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | Adaptive and token-aware file patch fitting | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | Multiple models support | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Static code analysis](https://pr-agent-docs.codium.ai/core-abilities/#static-code-analysis) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | [Global and wiki configurations](https://pr-agent-docs.codium.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | [PR interactive actions](https://www.codium.ai/images/pr_agent/pr-actions.mp4) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
- 💎 means this feature is available only in [PR-Agent Pro](https://www.codium.ai/pricing/)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (- Support for additional git providers is described in [here](./docs/Full_environments.md))
|
||||
___
|
||||
|
||||
‣ **Auto Description ([`/describe`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/describe/))**: Automatically generating PR description - title, type, summary, code walkthrough and labels.
|
||||
‣ **Auto Description ([`/describe`](https://pr-agent-docs.codium.ai/tools/describe/))**: Automatically generating PR description - title, type, summary, code walkthrough and labels.
|
||||
\
|
||||
‣ **Auto Review ([`/review`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/review/))**: Adjustable feedback about the PR, possible issues, security concerns, review effort and more.
|
||||
‣ **Auto Review ([`/review`](https://pr-agent-docs.codium.ai/tools/review/))**: Adjustable feedback about the PR, possible issues, security concerns, review effort and more.
|
||||
\
|
||||
‣ **Code Suggestions ([`/improve`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/))**: Code suggestions for improving the PR.
|
||||
‣ **Code Suggestions ([`/improve`](https://pr-agent-docs.codium.ai/tools/improve/))**: Code suggestions for improving the PR.
|
||||
\
|
||||
‣ **Question Answering ([`/ask ...`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/ask/))**: Answering free-text questions about the PR.
|
||||
‣ **Question Answering ([`/ask ...`](https://pr-agent-docs.codium.ai/tools/ask/))**: Answering free-text questions about the PR.
|
||||
\
|
||||
‣ **Update Changelog ([`/update_changelog`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/update_changelog/))**: Automatically updating the CHANGELOG.md file with the PR changes.
|
||||
‣ **Update Changelog ([`/update_changelog`](https://pr-agent-docs.codium.ai/tools/update_changelog/))**: Automatically updating the CHANGELOG.md file with the PR changes.
|
||||
\
|
||||
‣ **Help Docs ([`/help_docs`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/help_docs/))**: Answers a question on any repository by utilizing given documentation.
|
||||
‣ **Find Similar Issue ([`/similar_issue`](https://pr-agent-docs.codium.ai/tools/similar_issues/))**: Automatically retrieves and presents similar issues.
|
||||
\
|
||||
‣ **Add Documentation 💎 ([`/add_docs`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/documentation/))**: Generates documentation to methods/functions/classes that changed in the PR.
|
||||
‣ **Add Documentation 💎 ([`/add_docs`](https://pr-agent-docs.codium.ai/tools/documentation/))**: Generates documentation to methods/functions/classes that changed in the PR.
|
||||
\
|
||||
‣ **Generate Custom Labels 💎 ([`/generate_labels`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/custom_labels/))**: Generates custom labels for the PR, based on specific guidelines defined by the user.
|
||||
‣ **Generate Custom Labels 💎 ([`/generate_labels`](https://pr-agent-docs.codium.ai/tools/custom_labels/))**: Generates custom labels for the PR, based on specific guidelines defined by the user.
|
||||
\
|
||||
‣ **Analyze 💎 ([`/analyze`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/analyze/))**: Identify code components that changed in the PR, and enables to interactively generate tests, docs, and code suggestions for each component.
|
||||
‣ **Analyze 💎 ([`/analyze`](https://pr-agent-docs.codium.ai/tools/analyze/))**: Identify code components that changed in the PR, and enables to interactively generate tests, docs, and code suggestions for each component.
|
||||
\
|
||||
‣ **Test 💎 ([`/test`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/test/))**: Generate tests for a selected component, based on the PR code changes.
|
||||
‣ **Custom Prompt 💎 ([`/custom_prompt`](https://pr-agent-docs.codium.ai/tools/custom_prompt/))**: Automatically generates custom suggestions for improving the PR code, based on specific guidelines defined by the user.
|
||||
\
|
||||
‣ **Custom Prompt 💎 ([`/custom_prompt`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/custom_prompt/))**: Automatically generates custom suggestions for improving the PR code, based on specific guidelines defined by the user.
|
||||
‣ **Generate Tests 💎 ([`/test component_name`](https://pr-agent-docs.codium.ai/tools/test/))**: Generates unit tests for a selected component, based on the PR code changes.
|
||||
\
|
||||
‣ **Generate Tests 💎 ([`/test component_name`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/test/))**: Generates unit tests for a selected component, based on the PR code changes.
|
||||
‣ **CI Feedback 💎 ([`/checks ci_job`](https://pr-agent-docs.codium.ai/tools/ci_feedback/))**: Automatically generates feedback and analysis for a failed CI job.
|
||||
\
|
||||
‣ **CI Feedback 💎 ([`/checks ci_job`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/ci_feedback/))**: Automatically generates feedback and analysis for a failed CI job.
|
||||
\
|
||||
‣ **Similar Code 💎 ([`/find_similar_component`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/similar_code/))**: Retrieves the most similar code components from inside the organization's codebase, or from open-source code.
|
||||
\
|
||||
‣ **Implement 💎 ([`/implement`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/implement/))**: Generates implementation code from review suggestions.
|
||||
‣ **Similar Code 💎 ([`/find_similar_component`](https://pr-agent-docs.codium.ai/tools/similar_code/))**: Retrieves the most similar code components from inside the organization's codebase, or from open-source code.
|
||||
___
|
||||
|
||||
## Example results
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<h4><a href="https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/530">/describe</a></h4>
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
@ -177,45 +180,96 @@ ___
|
||||
</kbd>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<hr>
|
||||
|
||||
<h4><a href="https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/530">/generate_labels</a></h4>
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<p float="center">
|
||||
<kbd><img src="https://www.codium.ai/images/pr_agent/geneare_custom_labels_main_short.png" width="300"></kbd>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (<h4><a href="https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/78#issuecomment-1639739496">/reflect_and_review:</a></h4>)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (<div align="center">)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (<p float="center">)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (<img src="https://www.codium.ai/images/reflect_and_review.gif" width="800">)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (</p>)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (</div>)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (<h4><a href="https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/229#issuecomment-1695020538">/ask:</a></h4>)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (<div align="center">)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (<p float="center">)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (<img src="https://www.codium.ai/images/ask-2.gif" width="800">)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (</p>)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (</div>)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (<h4><a href="https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/229#issuecomment-1695024952">/improve:</a></h4>)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (<div align="center">)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (<p float="center">)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (<img src="https://www.codium.ai/images/improve-2.gif" width="800">)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (</p>)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (</div>)
|
||||
<div align="left">
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<hr>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Try it now
|
||||
|
||||
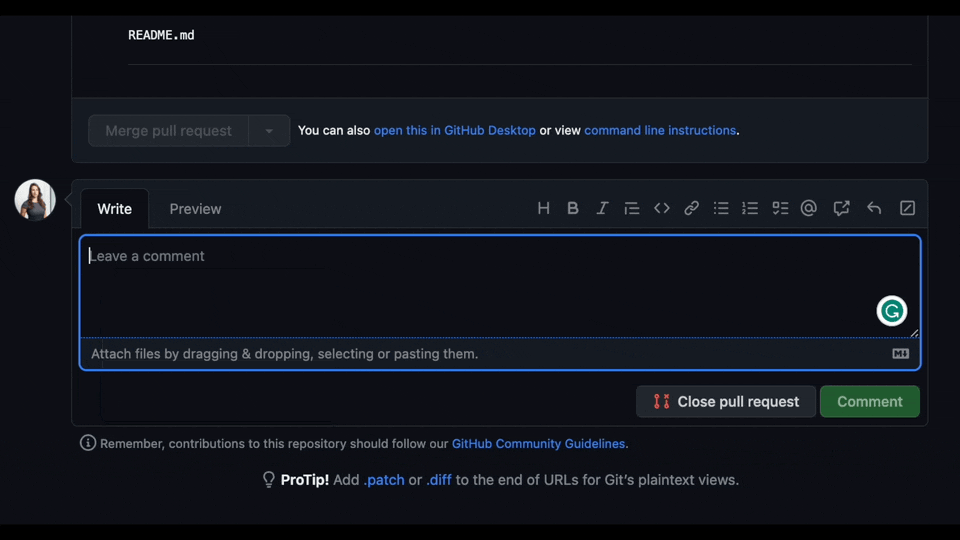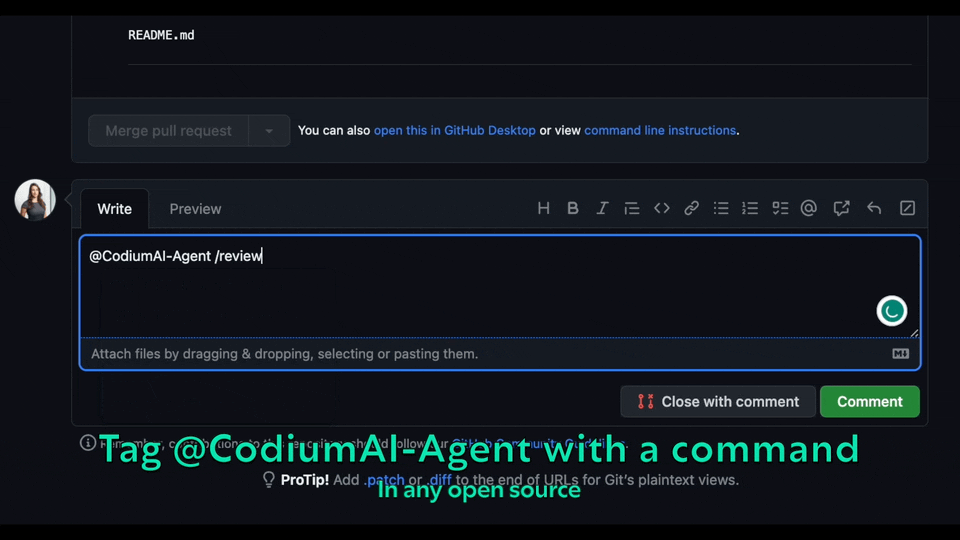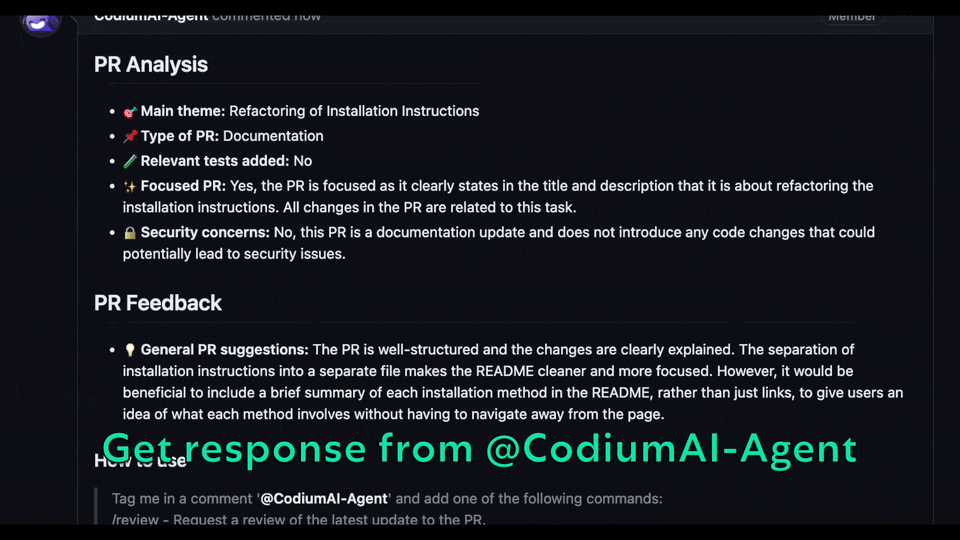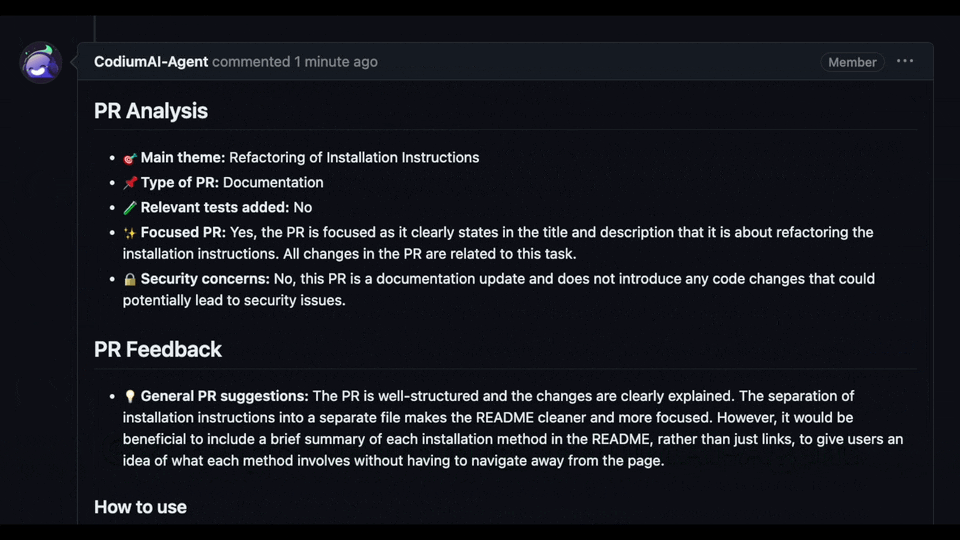
Try the Claude Sonnet powered PR-Agent instantly on _your public GitHub repository_. Just mention `@CodiumAI-Agent` and add the desired command in any PR comment. The agent will generate a response based on your command.
|
||||
Try the GPT-4 powered PR-Agent instantly on _your public GitHub repository_. Just mention `@CodiumAI-Agent` and add the desired command in any PR comment. The agent will generate a response based on your command.
|
||||
For example, add a comment to any pull request with the following text:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
@CodiumAI-Agent /review
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and the agent will respond with a review of your PR.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that this is a promotional bot, suitable only for initial experimentation.
|
||||
It does not have 'edit' access to your repo, for example, so it cannot update the PR description or add labels (`@CodiumAI-Agent /describe` will publish PR description as a comment). In addition, the bot cannot be used on private repositories, as it does not have access to the files there.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
To set up your own PR-Agent, see the [Installation](https://pr-agent-docs.codium.ai/installation/) section below.
|
||||
Note that when you set your own PR-Agent or use CodiumAI hosted PR-Agent, there is no need to mention `@CodiumAI-Agent ...`. Instead, directly start with the command, e.g., `/ask ...`.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Qodo Merge 💎
|
||||
|
||||
[Qodo Merge](https://www.qodo.ai/pricing/) is a hosted version of PR-Agent, provided by Qodo. It is available for a monthly fee, and provides the following benefits:
|
||||
## PR-Agent Pro 💎
|
||||
[PR-Agent Pro](https://www.codium.ai/pricing/) is a hosted version of PR-Agent, provided by CodiumAI. It is available for a monthly fee, and provides the following benefits:
|
||||
1. **Fully managed** - We take care of everything for you - hosting, models, regular updates, and more. Installation is as simple as signing up and adding the PR-Agent app to your GitHub\GitLab\BitBucket repo.
|
||||
2. **Improved privacy** - No data will be stored or used to train models. PR-Agent Pro will employ zero data retention, and will use an OpenAI account with zero data retention.
|
||||
3. **Improved support** - PR-Agent Pro users will receive priority support, and will be able to request new features and capabilities.
|
||||
4. **Extra features** -In addition to the benefits listed above, PR-Agent Pro will emphasize more customization, and the usage of static code analysis, in addition to LLM logic, to improve results.
|
||||
See [here](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/overview/pr_agent_pro/) for a list of features available in PR-Agent Pro.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Fully managed** - We take care of everything for you - hosting, models, regular updates, and more. Installation is as simple as signing up and adding the Qodo Merge app to your GitHub/GitLab/BitBucket repo.
|
||||
2. **Improved privacy** - No data will be stored or used to train models. Qodo Merge will employ zero data retention, and will use an OpenAI account with zero data retention.
|
||||
3. **Improved support** - Qodo Merge users will receive priority support, and will be able to request new features and capabilities.
|
||||
4. **Extra features** - In addition to the benefits listed above, Qodo Merge will emphasize more customization, and the usage of static code analysis, in addition to LLM logic, to improve results.
|
||||
See [here](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/overview/pr_agent_pro/) for a list of features available in Qodo Merge.
|
||||
|
||||
## How it works
|
||||
|
||||
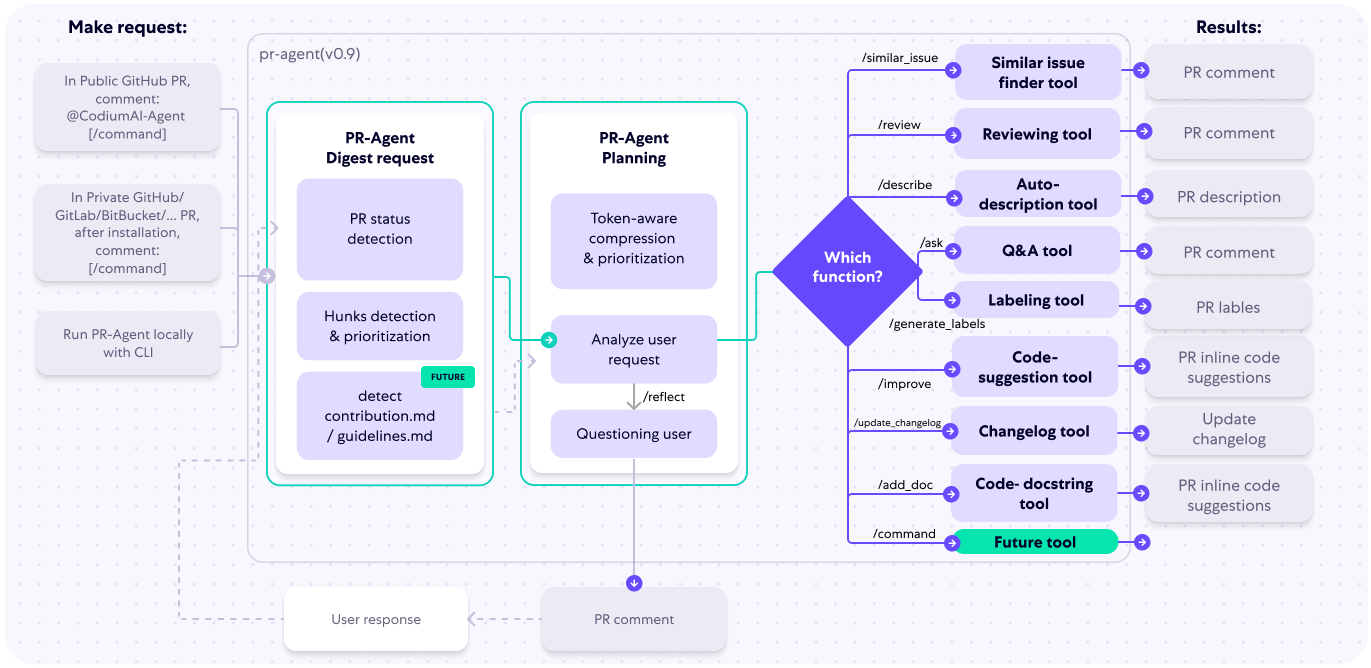
The following diagram illustrates PR-Agent tools and their flow:
|
||||
|
||||
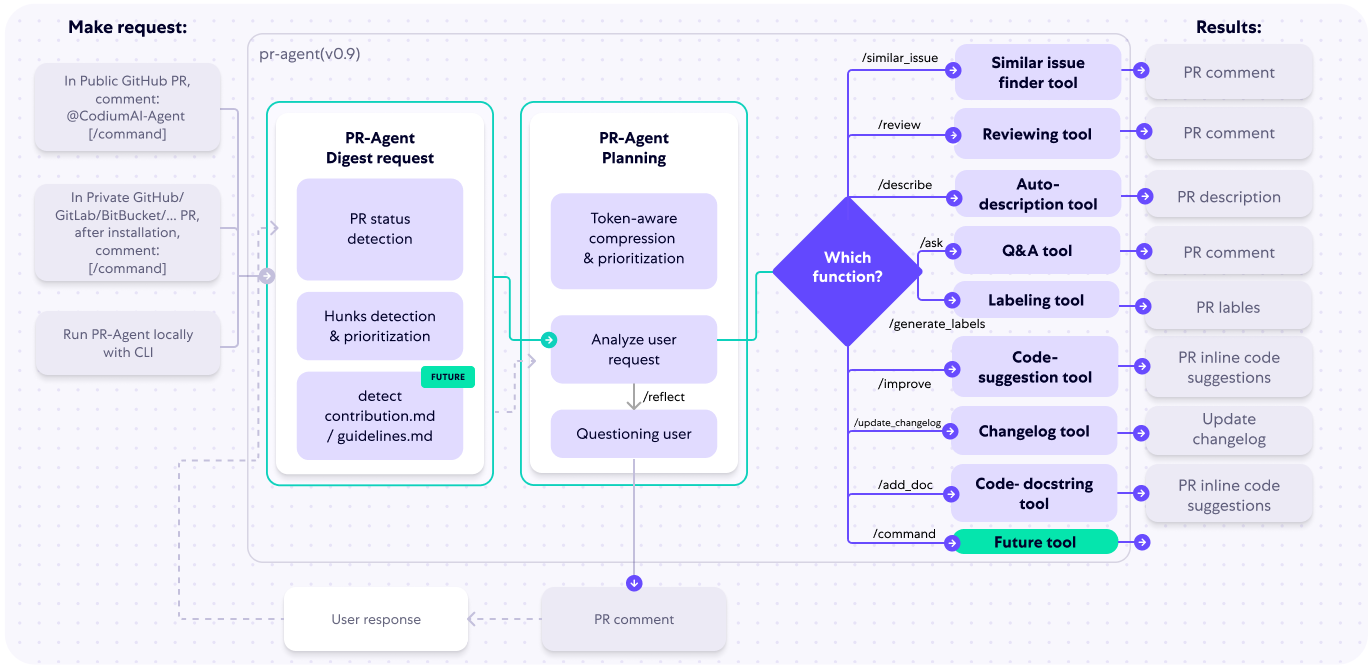
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Check out the [PR Compression strategy](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/#pr-compression-strategy) page for more details on how we convert a code diff to a manageable LLM prompt
|
||||
Check out the [PR Compression strategy](https://pr-agent-docs.codium.ai/core-abilities/#pr-compression-strategy) page for more details on how we convert a code diff to a manageable LLM prompt
|
||||
|
||||
## Why use PR-Agent?
|
||||
|
||||
@ -223,10 +277,11 @@ A reasonable question that can be asked is: `"Why use PR-Agent? What makes it st
|
||||
|
||||
Here are some advantages of PR-Agent:
|
||||
|
||||
- We emphasize **real-life practical usage**. Each tool (review, improve, ask, ...) has a single LLM call, no more. We feel that this is critical for realistic team usage - obtaining an answer quickly (~30 seconds) and affordably.
|
||||
- Our [PR Compression strategy](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/#pr-compression-strategy) is a core ability that enables to effectively tackle both short and long PRs.
|
||||
- We emphasize **real-life practical usage**. Each tool (review, improve, ask, ...) has a single GPT-4 call, no more. We feel that this is critical for realistic team usage - obtaining an answer quickly (~30 seconds) and affordably.
|
||||
- Our [PR Compression strategy](https://pr-agent-docs.codium.ai/core-abilities/#pr-compression-strategy) is a core ability that enables to effectively tackle both short and long PRs.
|
||||
- Our JSON prompting strategy enables to have **modular, customizable tools**. For example, the '/review' tool categories can be controlled via the [configuration](pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml) file. Adding additional categories is easy and accessible.
|
||||
- We support **multiple git providers** (GitHub, GitLab, BitBucket), **multiple ways** to use the tool (CLI, GitHub Action, GitHub App, Docker, ...), and **multiple models** (GPT, Claude, Deepseek, ...)
|
||||
- We support **multiple git providers** (GitHub, Gitlab, Bitbucket), **multiple ways** to use the tool (CLI, GitHub Action, GitHub App, Docker, ...), and **multiple models** (GPT-4, GPT-3.5, Anthropic, Cohere, Llama2).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Data privacy
|
||||
|
||||
@ -235,26 +290,24 @@ Here are some advantages of PR-Agent:
|
||||
- If you host PR-Agent with your OpenAI API key, it is between you and OpenAI. You can read their API data privacy policy here:
|
||||
https://openai.com/enterprise-privacy
|
||||
|
||||
### Qodo-hosted Qodo Merge 💎
|
||||
### CodiumAI-hosted PR-Agent Pro 💎
|
||||
|
||||
- When using Qodo Merge 💎, hosted by Qodo, we will not store any of your data, nor will we use it for training. You will also benefit from an OpenAI account with zero data retention.
|
||||
- When using PR-Agent Pro 💎, hosted by CodiumAI, we will not store any of your data, nor will we use it for training. You will also benefit from an OpenAI account with zero data retention.
|
||||
|
||||
- For certain clients, Qodo-hosted Qodo Merge will use Qodo’s proprietary models — if this is the case, you will be notified.
|
||||
- For certain clients, CodiumAI-hosted PR-Agent Pro will use CodiumAI’s proprietary models — if this is the case, you will be notified.
|
||||
|
||||
- No passive collection of Code and Pull Requests’ data — Qodo Merge will be active only when you invoke it, and it will then extract and analyze only data relevant to the executed command and queried pull request.
|
||||
- No passive collection of Code and Pull Requests’ data — PR-Agent will be active only when you invoke it, and it will then extract and analyze only data relevant to the executed command and queried pull request.
|
||||
|
||||
### Qodo Merge Chrome extension
|
||||
### PR-Agent Chrome extension
|
||||
|
||||
- The [Qodo Merge Chrome extension](https://chromewebstore.google.com/detail/qodo-merge-ai-powered-cod/ephlnjeghhogofkifjloamocljapahnl) serves solely to modify the visual appearance of a GitHub PR screen. It does not transmit any user's repo or pull request code. Code is only sent for processing when a user submits a GitHub comment that activates a PR-Agent tool, in accordance with the standard privacy policy of Qodo-Merge.
|
||||
|
||||
## Contributing
|
||||
|
||||
To contribute to the project, get started by reading our [Contributing Guide](https://github.com/qodo-ai/pr-agent/blob/b09eec265ef7d36c232063f76553efb6b53979ff/CONTRIBUTING.md).
|
||||
- The [PR-Agent Chrome extension](https://chromewebstore.google.com/detail/pr-agent-chrome-extension/ephlnjeghhogofkifjloamocljapahnl) serves solely to modify the visual appearance of a GitHub PR screen. It does not transmit any user's repo or pull request code. Code is only sent for processing when a user submits a GitHub comment that activates a PR-Agent tool, in accordance with the standard privacy policy of PR-Agent.
|
||||
|
||||
## Links
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://discord.gg/kG35uSHDBc)
|
||||
|
||||
- Discord community: https://discord.gg/kG35uSHDBc
|
||||
- Qodo site: https://www.qodo.ai/
|
||||
- Blog: https://www.qodo.ai/blog/
|
||||
- Troubleshooting: https://www.qodo.ai/blog/technical-faq-and-troubleshooting/
|
||||
- Support: support@qodo.ai
|
||||
- CodiumAI site: https://codium.ai
|
||||
- Blog: https://www.codium.ai/blog/
|
||||
- Troubleshooting: https://www.codium.ai/blog/technical-faq-and-troubleshooting/
|
||||
- Support: support@codium.ai
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,4 @@
|
||||
## [Version 0.11] - 2023-12-07
|
||||
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.11
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.11-github_app
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.11-bitbucket-app
|
||||
@ -8,18 +7,16 @@
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.11-github_action
|
||||
|
||||
### Added::Algo
|
||||
|
||||
- New section in `/describe` tool - [PR changes walkthrough](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/509)
|
||||
- Improving PR Agent [prompts](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/501)
|
||||
- Persistent tools (`/review`, `/describe`) now send an [update message](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/499) after finishing
|
||||
- Add Amazon Bedrock [support](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/483)
|
||||
|
||||
### Fixed
|
||||
|
||||
- Update [dependencies](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/503) in requirements.txt for Python 3.12
|
||||
|
||||
## [Version 0.10] - 2023-11-15
|
||||
|
||||
## [Version 0.10] - 2023-11-15
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.10
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.10-github_app
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.10-bitbucket-app
|
||||
@ -28,7 +25,6 @@
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.10-github_action
|
||||
|
||||
### Added::Algo
|
||||
|
||||
- Review tool now works with [persistent comments](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/451) by default
|
||||
- Bitbucket now publishes review suggestions with [code links](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/428)
|
||||
- Enabling to limit [max number of tokens](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/437/files)
|
||||
@ -38,13 +34,11 @@
|
||||
- Decoupled custom labels from [PR type](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/431)
|
||||
|
||||
### Fixed
|
||||
|
||||
- Fixed bug in [parsing quotes](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/446) in CLI
|
||||
- Preserve [user-added labels](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/433) in pull requests
|
||||
- Bug fixes in GitLab and BitBucket
|
||||
|
||||
## [Version 0.9] - 2023-10-29
|
||||
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.9
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.9-github_app
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.9-bitbucket-app
|
||||
@ -53,7 +47,6 @@
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.9-github_action
|
||||
|
||||
### Added::Algo
|
||||
|
||||
- New tool - [generate_labels](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/docs/GENERATE_CUSTOM_LABELS.md)
|
||||
- New ability to use [customize labels](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/docs/GENERATE_CUSTOM_LABELS.md#how-to-enable-custom-labels) on the `review` and `describe` tools.
|
||||
- New tool - [add_docs](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/docs/ADD_DOCUMENTATION.md)
|
||||
@ -63,17 +56,14 @@
|
||||
- PR Description default mode is now in [bullet points](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml#L35).
|
||||
|
||||
### Added::Documentation
|
||||
|
||||
Significant documentation updates (see [Installation Guide](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/INSTALL.md), [Usage Guide](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/Usage.md), and [Tools Guide](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/docs/TOOLS_GUIDE.md))
|
||||
|
||||
### Fixed
|
||||
|
||||
- Fixed support for BitBucket pipeline (see [link](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/386))
|
||||
- Fixed a bug in `review -i` tool
|
||||
- Added blacklist for specific file extensions in `add_docs` tool (see [link](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/385/))
|
||||
|
||||
## [Version 0.8] - 2023-09-27
|
||||
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.8
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.8-github_app
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.8-bitbucket-app
|
||||
@ -82,37 +72,32 @@ Significant documentation updates (see [Installation Guide](https://github.com/C
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.8-github_action
|
||||
|
||||
### Added::Algo
|
||||
|
||||
- GitHub Action: Can control which tools will run automatically when a new PR is created. (see usage guide: https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/Usage.md#working-with-github-action)
|
||||
- Code suggestion tool: Will try to avoid an 'add comments' suggestion (see https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/327)
|
||||
|
||||
### Fixed
|
||||
|
||||
- Gitlab: Fixed a bug of improper usage of pr_id
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## [Version 0.7] - 2023-09-20
|
||||
|
||||
### Docker Tags
|
||||
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.7
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.7-github_app
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.7-bitbucket-app
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.7-gitlab_webhook
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.7-github_polling
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.7-github_action
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Added::Algo
|
||||
|
||||
- New tool /similar_issue - Currently on GitHub app and CLI: indexes the issues in the repo, find the most similar issues to the target issue.
|
||||
- Describe markers: Empower the /describe tool with a templating capability (see more details in https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/273).
|
||||
- New feature in the /review tool - added an estimated effort estimation to the review (https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/306).
|
||||
|
||||
### Added::Infrastructure
|
||||
|
||||
- Implementation of a GitLab webhook.
|
||||
- Implementation of a BitBucket app.
|
||||
|
||||
### Fixed
|
||||
|
||||
- Protection against no code suggestions generated.
|
||||
- Resilience to repositories where the languages cannot be automatically detected.
|
||||
|
||||
64
SECURITY.md
@ -1,64 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Security Policy
|
||||
|
||||
PR-Agent is an open-source tool to help efficiently review and handle pull requests. Qodo Merge is a paid version of PR-Agent, designed for companies and teams that require additional features and capabilities.
|
||||
|
||||
This document describes the security policy of PR-Agent. For Qodo Merge's security policy, see [here](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/overview/data_privacy/#qodo-merge).
|
||||
|
||||
## PR-Agent Self-Hosted Solutions
|
||||
|
||||
When using PR-Agent with your OpenAI (or other LLM provider) API key, the security relationship is directly between you and the provider. We do not send your code to Qodo servers.
|
||||
|
||||
Types of [self-hosted solutions](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation):
|
||||
|
||||
- Locally
|
||||
- GitHub integration
|
||||
- GitLab integration
|
||||
- BitBucket integration
|
||||
- Azure DevOps integration
|
||||
|
||||
## PR-Agent Supported Versions
|
||||
|
||||
This section outlines which versions of PR-Agent are currently supported with security updates.
|
||||
|
||||
### Docker Deployment Options
|
||||
|
||||
#### Latest Version
|
||||
|
||||
For the most recent updates, use our latest Docker image which is automatically built nightly:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
uses: qodo-ai/pr-agent@main
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Specific Release Version
|
||||
|
||||
For a fixed version, you can pin your action to a specific release version. Browse available releases at:
|
||||
[PR-Agent Releases](https://github.com/qodo-ai/pr-agent/releases)
|
||||
|
||||
For example, to github action:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: PR Agent action step
|
||||
id: pragent
|
||||
uses: docker://codiumai/pr-agent:0.26-github_action
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Enhanced Security with Docker Digest
|
||||
|
||||
For maximum security, you can specify the Docker image using its digest:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: PR Agent action step
|
||||
id: pragent
|
||||
uses: docker://codiumai/pr-agent@sha256:14165e525678ace7d9b51cda8652c2d74abb4e1d76b57c4a6ccaeba84663cc64
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Reporting a Vulnerability
|
||||
|
||||
We take the security of PR-Agent seriously. If you discover a security vulnerability, please report it immediately to:
|
||||
|
||||
Email: tal.r@qodo.ai
|
||||
|
||||
Please include a description of the vulnerability, steps to reproduce, and the affected PR-Agent version.
|
||||
@ -1,12 +1,10 @@
|
||||
FROM python:3.12.10-slim AS base
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt update && apt install --no-install-recommends -y git curl && apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
|
||||
FROM python:3.12.3 AS base
|
||||
|
||||
WORKDIR /app
|
||||
ADD pyproject.toml .
|
||||
ADD requirements.txt .
|
||||
ADD docs docs
|
||||
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir . && rm pyproject.toml requirements.txt
|
||||
RUN pip install . && rm pyproject.toml requirements.txt
|
||||
ENV PYTHONPATH=/app
|
||||
|
||||
FROM base AS github_app
|
||||
@ -35,7 +33,7 @@ CMD ["python", "pr_agent/servers/azuredevops_server_webhook.py"]
|
||||
|
||||
FROM base AS test
|
||||
ADD requirements-dev.txt .
|
||||
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir -r requirements-dev.txt && rm requirements-dev.txt
|
||||
RUN pip install -r requirements-dev.txt && rm requirements-dev.txt
|
||||
ADD pr_agent pr_agent
|
||||
ADD tests tests
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,12 +1,12 @@
|
||||
FROM public.ecr.aws/lambda/python:3.12
|
||||
FROM public.ecr.aws/lambda/python:3.10
|
||||
|
||||
RUN dnf update -y && \
|
||||
dnf install -y gcc python3-devel git && \
|
||||
dnf clean all
|
||||
RUN yum update -y && \
|
||||
yum install -y gcc python3-devel git && \
|
||||
yum clean all
|
||||
|
||||
ADD pyproject.toml requirements.txt ./
|
||||
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir . && rm pyproject.toml
|
||||
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir mangum==0.17.0
|
||||
ADD pyproject.toml requirements.txt .
|
||||
RUN pip install . && rm pyproject.toml
|
||||
RUN pip install mangum==0.17.0
|
||||
COPY pr_agent/ ${LAMBDA_TASK_ROOT}/pr_agent/
|
||||
|
||||
CMD ["pr_agent.servers.serverless.serverless"]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,315 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<div class="search-section">
|
||||
<h1>AI Docs Search</h1>
|
||||
<p class="search-description">
|
||||
Search through our documentation using AI-powered natural language queries.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
<div class="search-container">
|
||||
<input
|
||||
type="text"
|
||||
id="searchInput"
|
||||
class="search-input"
|
||||
placeholder="Enter your search term..."
|
||||
>
|
||||
<button id="searchButton" class="search-button">Search</button>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div id="spinner" class="spinner-container" style="display: none;">
|
||||
<div class="spinner"></div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div id="results" class="results-container"></div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<style>
|
||||
Untitled
|
||||
.search-section {
|
||||
max-width: 800px;
|
||||
margin: 0 auto;
|
||||
padding: 0 1rem 2rem;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
h1 {
|
||||
color: #666;
|
||||
font-size: 2.125rem;
|
||||
font-weight: normal;
|
||||
margin-bottom: 1rem;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.search-description {
|
||||
color: #666;
|
||||
font-size: 1rem;
|
||||
line-height: 1.5;
|
||||
margin-bottom: 2rem;
|
||||
max-width: 800px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.search-container {
|
||||
display: flex;
|
||||
gap: 1rem;
|
||||
max-width: 800px;
|
||||
margin: 0; /* Changed from auto to 0 to align left */
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.search-input {
|
||||
flex: 1;
|
||||
padding: 0 0.875rem;
|
||||
border: 1px solid #ddd;
|
||||
border-radius: 4px;
|
||||
font-size: 0.9375rem;
|
||||
outline: none;
|
||||
height: 40px; /* Explicit height */
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.search-input:focus {
|
||||
border-color: #6c63ff;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.search-button {
|
||||
padding: 0 1.25rem;
|
||||
background-color: #2196F3;
|
||||
color: white;
|
||||
border: none;
|
||||
border-radius: 4px;
|
||||
cursor: pointer;
|
||||
font-size: 0.875rem;
|
||||
transition: background-color 0.2s;
|
||||
height: 40px; /* Match the height of search input */
|
||||
display: flex;
|
||||
align-items: center;
|
||||
justify-content: center;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.search-button:hover {
|
||||
background-color: #1976D2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.spinner-container {
|
||||
display: flex;
|
||||
justify-content: center;
|
||||
margin-top: 2rem;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.spinner {
|
||||
width: 40px;
|
||||
height: 40px;
|
||||
border: 4px solid #f3f3f3;
|
||||
border-top: 4px solid #2196F3;
|
||||
border-radius: 50%;
|
||||
animation: spin 1s linear infinite;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@keyframes spin {
|
||||
0% { transform: rotate(0deg); }
|
||||
100% { transform: rotate(360deg); }
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.results-container {
|
||||
margin-top: 2rem;
|
||||
max-width: 800px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.result-item {
|
||||
padding: 1rem;
|
||||
border: 1px solid #ddd;
|
||||
border-radius: 4px;
|
||||
margin-bottom: 1rem;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.result-title {
|
||||
font-size: 1.2rem;
|
||||
color: #2196F3;
|
||||
margin-bottom: 0.5rem;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.result-description {
|
||||
color: #666;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.error-message {
|
||||
color: #dc3545;
|
||||
padding: 1rem;
|
||||
border: 1px solid #dc3545;
|
||||
border-radius: 4px;
|
||||
margin-top: 1rem;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.markdown-content {
|
||||
line-height: 1.6;
|
||||
color: var(--md-typeset-color);
|
||||
background: var(--md-default-bg-color);
|
||||
border: 1px solid var(--md-default-fg-color--lightest);
|
||||
border-radius: 12px;
|
||||
padding: 1.5rem;
|
||||
box-shadow: 0 2px 4px rgba(0,0,0,0.05);
|
||||
position: relative;
|
||||
margin-top: 2rem;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.markdown-content::before {
|
||||
content: '';
|
||||
position: absolute;
|
||||
top: -8px;
|
||||
left: 24px;
|
||||
width: 16px;
|
||||
height: 16px;
|
||||
background: var(--md-default-bg-color);
|
||||
border-left: 1px solid var(--md-default-fg-color--lightest);
|
||||
border-top: 1px solid var(--md-default-fg-color--lightest);
|
||||
transform: rotate(45deg);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.markdown-content > *:first-child {
|
||||
margin-top: 0;
|
||||
padding-top: 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.markdown-content p {
|
||||
margin-bottom: 1rem;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.markdown-content p:last-child {
|
||||
margin-bottom: 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.markdown-content code {
|
||||
background: var(--md-code-bg-color);
|
||||
color: var(--md-code-fg-color);
|
||||
padding: 0.2em 0.4em;
|
||||
border-radius: 3px;
|
||||
font-size: 0.9em;
|
||||
font-family: ui-monospace, SFMono-Regular, SF Mono, Menlo, Consolas, Liberation Mono, monospace;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.markdown-content pre {
|
||||
background: var(--md-code-bg-color);
|
||||
padding: 1rem;
|
||||
border-radius: 6px;
|
||||
overflow-x: auto;
|
||||
margin: 1rem 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.markdown-content pre code {
|
||||
background: none;
|
||||
padding: 0;
|
||||
font-size: 0.9em;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
[data-md-color-scheme="slate"] .markdown-content {
|
||||
box-shadow: 0 2px 4px rgba(0,0,0,0.1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</style>
|
||||
|
||||
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/marked/9.1.6/marked.min.js"></script>
|
||||
|
||||
<script>
|
||||
window.addEventListener('load', function() {
|
||||
function displayResults(responseText) {
|
||||
const resultsContainer = document.getElementById('results');
|
||||
const spinner = document.getElementById('spinner');
|
||||
const searchContainer = document.querySelector('.search-container');
|
||||
|
||||
// Hide spinner
|
||||
spinner.style.display = 'none';
|
||||
|
||||
// Scroll to search bar
|
||||
searchContainer.scrollIntoView({ behavior: 'smooth', block: 'start' });
|
||||
|
||||
try {
|
||||
const results = JSON.parse(responseText);
|
||||
|
||||
marked.setOptions({
|
||||
breaks: true,
|
||||
gfm: true,
|
||||
headerIds: false,
|
||||
sanitize: false
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
const htmlContent = marked.parse(results.message);
|
||||
|
||||
resultsContainer.className = 'markdown-content';
|
||||
resultsContainer.innerHTML = htmlContent;
|
||||
|
||||
// Scroll after content is rendered
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
const searchContainer = document.querySelector('.search-container');
|
||||
const offset = 55; // Offset from top in pixels
|
||||
const elementPosition = searchContainer.getBoundingClientRect().top;
|
||||
const offsetPosition = elementPosition + window.pageYOffset - offset;
|
||||
|
||||
window.scrollTo({
|
||||
top: offsetPosition,
|
||||
behavior: 'smooth'
|
||||
});
|
||||
}, 100);
|
||||
} catch (error) {
|
||||
console.error('Error parsing results:', error);
|
||||
resultsContainer.innerHTML = '<div class="error-message">Error processing results</div>';
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
async function performSearch() {
|
||||
const searchInput = document.getElementById('searchInput');
|
||||
const resultsContainer = document.getElementById('results');
|
||||
const spinner = document.getElementById('spinner');
|
||||
const searchTerm = searchInput.value.trim();
|
||||
|
||||
if (!searchTerm) {
|
||||
resultsContainer.innerHTML = '<div class="error-message">Please enter a search term</div>';
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Show spinner, clear results
|
||||
spinner.style.display = 'flex';
|
||||
resultsContainer.innerHTML = '';
|
||||
|
||||
try {
|
||||
const data = {
|
||||
"query": searchTerm
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
const options = {
|
||||
method: 'POST',
|
||||
headers: {
|
||||
'accept': 'text/plain',
|
||||
'content-type': 'application/json',
|
||||
},
|
||||
body: JSON.stringify(data)
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// const API_ENDPOINT = 'http://0.0.0.0:3000/api/v1/docs_help';
|
||||
const API_ENDPOINT = 'https://help.merge.qodo.ai/api/v1/docs_help';
|
||||
|
||||
const response = await fetch(API_ENDPOINT, options);
|
||||
|
||||
if (!response.ok) {
|
||||
throw new Error(`HTTP error! status: ${response.status}`);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const responseText = await response.text();
|
||||
displayResults(responseText);
|
||||
} catch (error) {
|
||||
spinner.style.display = 'none';
|
||||
resultsContainer.innerHTML = `
|
||||
<div class="error-message">
|
||||
An error occurred while searching. Please try again later.
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
`;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add event listeners
|
||||
const searchButton = document.getElementById('searchButton');
|
||||
const searchInput = document.getElementById('searchInput');
|
||||
|
||||
if (searchButton) {
|
||||
searchButton.addEventListener('click', performSearch);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (searchInput) {
|
||||
searchInput.addEventListener('keypress', function(e) {
|
||||
if (e.key === 'Enter') {
|
||||
performSearch();
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
</script>
|
||||
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 15 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 4.2 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 57 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 263 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 24 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 1.2 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 17 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 8.7 KiB |
@ -1,4 +1,5 @@
|
||||
We take your code's security and privacy seriously:
|
||||
|
||||
- The Chrome extension will not send your code to any external servers.
|
||||
- For private repositories, we will first validate the user's identity and permissions. After authentication, we generate responses using the existing Qodo Merge integration.
|
||||
- For private repositories, we will first validate the user's identity and permissions. After authentication, we generate responses using the existing Qodo Merge Pro integration.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -8,7 +8,7 @@ To enable private chat, simply install the Qodo Merge Chrome extension. After in
|
||||
This chat session is **private**, and won't be visible to other users.
|
||||
|
||||
All open-source repositories are supported.
|
||||
For private repositories, you will also need to install Qodo Merge. After installation, make sure to open at least one new PR to fully register your organization. Once done, you can chat with both new and existing PRs across all installed repositories.
|
||||
For private repositories, you will also need to install Qodo Merge Pro, After installation, make sure to open at least one new PR to fully register your organization. Once done, you can chat with both new and existing PRs across all installed repositories.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Context-aware PR chat
|
||||
|
||||
@ -17,8 +17,8 @@ Qodo Merge constructs a comprehensive context for each pull request, incorporati
|
||||
<img src="https://codium.ai/images/pr_agent/pr_chat_1.png" width="768">
|
||||
<img src="https://codium.ai/images/pr_agent/pr_chat_2.png" width="768">
|
||||
|
||||
### Toolbar extension
|
||||
|
||||
### Toolbar extension
|
||||
With Qodo Merge Chrome extension, it's [easier than ever](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gT5tli7X4H4) to interactively configure and experiment with the different tools and configuration options.
|
||||
|
||||
For private repositories, after you found the setup that works for you, you can also easily export it as a persistent configuration file, and use it for automatic commands.
|
||||
@ -37,6 +37,7 @@ For example, you can choose to present only message from Qodo Merge, or filter t
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://codium.ai/images/pr_agent/pr_agent_filters2.png" width="256">
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Enhanced code suggestions
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge Chrome extension adds the following capabilities to code suggestions tool's comments:
|
||||
@ -44,6 +45,7 @@ Qodo Merge Chrome extension adds the following capabilities to code suggestions
|
||||
- Auto-expand the table when you are viewing a code block, to avoid clipping.
|
||||
- Adding a "quote-and-reply" button, that enables to address and comment on a specific suggestion (for example, asking the author to fix the issue)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://codium.ai/images/pr_agent/chrome_extension_code_suggestion1.png" width="512">
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://codium.ai/images/pr_agent/chrome_extension_code_suggestion2.png" width="512">
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,11 +1,11 @@
|
||||
[Qodo Merge Chrome extension](https://chromewebstore.google.com/detail/pr-agent-chrome-extension/ephlnjeghhogofkifjloamocljapahnl){:target="_blank"} is a collection of tools that integrates seamlessly with your GitHub environment, aiming to enhance your Git usage experience, and providing AI-powered capabilities to your PRs.
|
||||
[Qodo Merge Chrome extension](https://chromewebstore.google.com/detail/pr-agent-chrome-extension/ephlnjeghhogofkifjloamocljapahnl) is a collection of tools that integrates seamlessly with your GitHub environment, aiming to enhance your Git usage experience, and providing AI-powered capabilities to your PRs.
|
||||
|
||||
With a single-click installation you will gain access to a context-aware chat on your pull requests code, a toolbar extension with multiple AI feedbacks, Qodo Merge filters, and additional abilities.
|
||||
|
||||
The extension is powered by top code models like Claude 3.7 Sonnet and o4-mini. All the extension's features are free to use on public repositories.
|
||||
The extension is powered by top code models like Claude 3.5 Sonnet and GPT4. All the extension's features are free to use on public repositories.
|
||||
|
||||
For private repositories, you will need to install [Qodo Merge](https://github.com/apps/qodo-merge-pro){:target="_blank"} in addition to the extension (Quick GitHub app setup with a 14-day free trial. No credit card needed).
|
||||
For a demonstration of how to install Qodo Merge and use it with the Chrome extension, please refer to the tutorial video at the provided [link](https://codium.ai/images/pr_agent/private_repos.mp4){:target="_blank"}.
|
||||
For private repositories, you will need to install [Qodo Merge Pro](https://github.com/apps/codiumai-pr-agent-pro) in addition to the extension (Quick GitHub app setup with a 14-day free trial. No credit card needed).
|
||||
For a demonstration of how to install Qodo Merge Pro and use it with the Chrome extension, please refer to the tutorial video at the provided [link](https://codium.ai/images/pr_agent/private_repos.mp4).
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://codium.ai/images/pr_agent/PR-AgentChat.gif" width="768">
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,39 +0,0 @@
|
||||
## Options and Configurations
|
||||
|
||||
### Accessing the Options Page
|
||||
|
||||
To access the options page for the Qodo Merge Chrome extension:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Find the extension icon in your Chrome toolbar (usually in the top-right corner of your browser)
|
||||
2. Right-click on the extension icon
|
||||
3. Select "Options" from the context menu that appears
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively, you can access the options page directly using this URL:
|
||||
|
||||
[chrome-extension://ephlnjeghhogofkifjloamocljapahnl/options.html](chrome-extension://ephlnjeghhogofkifjloamocljapahnl/options.html)
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://codium.ai/images/pr_agent/chrome_ext_options.png" width="256">
|
||||
|
||||
### Configuration Options
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://codium.ai/images/pr_agent/chrome_ext_settings_page.png" width="512">
|
||||
|
||||
#### API Base Host
|
||||
|
||||
For single-tenant customers, you can configure the extension to communicate directly with your company's Qodo Merge server instance.
|
||||
|
||||
To set this up:
|
||||
|
||||
- Enter your organization's Qodo Merge API endpoint in the "API Base Host" field
|
||||
- This endpoint should be provided by your Qodo DevOps Team
|
||||
|
||||
*Note: The extension does not send your code to the server, but only triggers your previously installed Qodo Merge application.*
|
||||
|
||||
#### Interface Options
|
||||
|
||||
You can customize the extension's interface by:
|
||||
|
||||
- Toggling the "Show Qodo Merge Toolbar" option
|
||||
- When disabled, the toolbar will not appear in your Github comment bar
|
||||
|
||||
Remember to click "Save Settings" after making any changes.
|
||||
@ -1,67 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Auto Best Practices 💎
|
||||
|
||||
`Supported Git Platforms: GitHub`
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
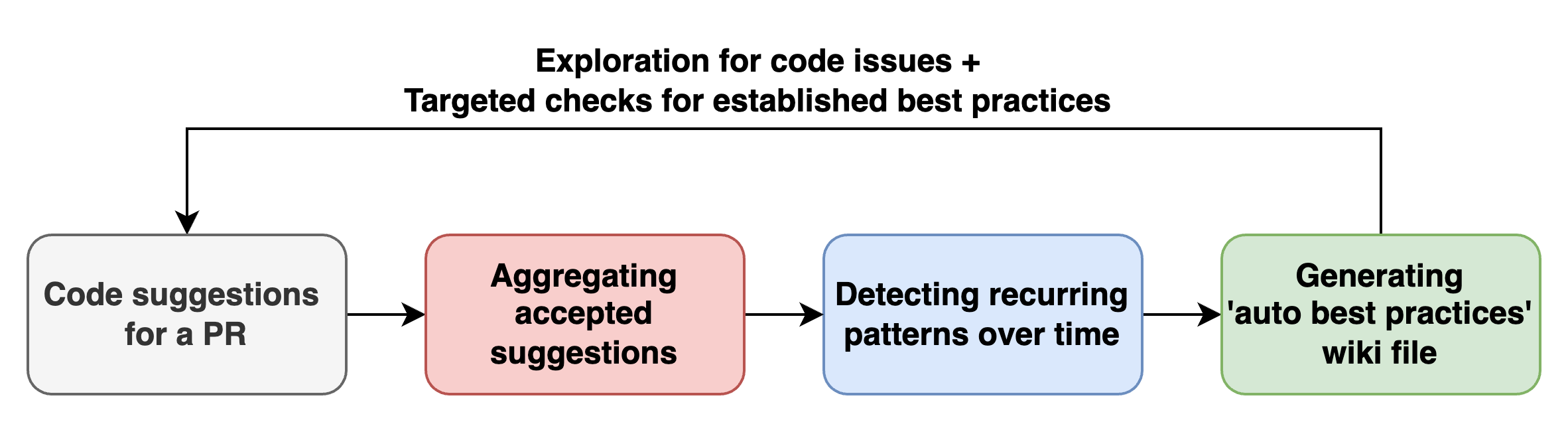{width=684}
|
||||
|
||||
> Note - enabling a [Wiki](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/enabling_a_wiki/) is required for this feature.
|
||||
|
||||
### Finding Code Problems - Exploration Phase
|
||||
|
||||
The `improve` tool identifies potential issues, problems and bugs in Pull Request (PR) code changes.
|
||||
Rather than focusing on minor issues like code style or formatting, the tool intelligently analyzes code to detect meaningful problems.
|
||||
|
||||
The analysis intentionally takes a flexible, _exploratory_ approach to identify meaningful potential issues, allowing the tool to surface relevant code suggestions without being constrained by predefined categories.
|
||||
|
||||
### Tracking Implemented Suggestions
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge features a novel [tracking system](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#suggestion-tracking) that automatically detects when PR authors implement AI-generated code suggestions.
|
||||
All accepted suggestions are aggregated in a repository-specific wiki page called [`.pr_agent_accepted_suggestions`](https://github.com/qodo-ai/pr-agent/wiki/.pr_agent_accepted_suggestions)
|
||||
|
||||
### Learning and Applying Auto Best Practices
|
||||
|
||||
Monthly, Qodo Merge analyzes the collection of accepted suggestions to generate repository-specific best practices, stored in [`.pr_agent_auto_best_practices`](https://github.com/qodo-ai/pr-agent/wiki/.pr_agent_auto_best_practices) wiki file.
|
||||
These best practices reflect recurring patterns in accepted code improvements.
|
||||
|
||||
The `improve` tool will incorporate these best practices as an additional analysis layer, checking PR code changes against known patterns of previously accepted improvements.
|
||||
This creates a two-phase analysis:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Open exploration for general code issues
|
||||
2. Targeted checking against established best practices - exploiting the knowledge gained from past suggestions
|
||||
|
||||
By keeping these phases decoupled, the tool remains free to discover new or unseen issues and problems, while also learning from past experiences.
|
||||
|
||||
When presenting the suggestions generated by the `improve` tool, Qodo Merge will add a dedicated label for each suggestion generated from the auto best practices - 'Learned best practice':
|
||||
|
||||
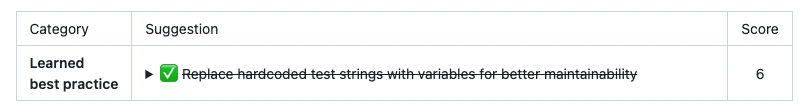{width=684}
|
||||
|
||||
## Auto Best Practices vs Custom Best Practices
|
||||
|
||||
Teams and companies can also manually define their own [custom best practices](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#best-practices) in Qodo Merge.
|
||||
|
||||
When custom best practices exist, Qodo Merge will still generate an 'auto best practices' wiki file, though it won't be used by the `improve` tool.
|
||||
However, this auto-generated file can still serve two valuable purposes:
|
||||
|
||||
1. It can help enhance your custom best practices with additional insights derived from suggestions your team found valuable enough to implement
|
||||
2. It demonstrates effective patterns for writing AI-friendly best practices
|
||||
|
||||
Even when using custom best practices, we recommend regularly reviewing the auto best practices file to refine your custom rules.
|
||||
|
||||
## Relevant configurations
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[auto_best_practices]
|
||||
# Disable all auto best practices usage or generation
|
||||
enable_auto_best_practices = true
|
||||
|
||||
# Disable usage of auto best practices file in the 'improve' tool
|
||||
utilize_auto_best_practices = true
|
||||
|
||||
# Extra instructions to the auto best practices generation prompt
|
||||
extra_instructions = ""
|
||||
|
||||
# Max number of patterns to be detected
|
||||
max_patterns = 5
|
||||
```
|
||||
2
docs/docs/core-abilities/code_oriented_yaml.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
TBD
|
||||
@ -1,40 +0,0 @@
|
||||
## Introduction
|
||||
|
||||
The Git environment usually represents the final stage before code enters production. Hence, Detecting bugs and issues during the review process is critical.
|
||||
|
||||
The [`improve`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/) tool provides actionable code suggestions for your pull requests, aiming to help detect and fix bugs and problems.
|
||||
By default, suggestions appear as a comment in a table format:
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
## Validation of Code Suggestions
|
||||
|
||||
Each suggestion in the table can be "applied" by clicking on the `Apply this suggestion` checkbox, converting it to a committable Git code change that can be committed directly to the PR.
|
||||
This approach allows to fix issues without returning to your IDE for manual edits — significantly faster and more convenient.
|
||||
|
||||
However, committing a suggestion in a Git environment carries more risk than in a local IDE, as you don't have the opportunity to fully run and test the code before committing.
|
||||
|
||||
To balance convenience with safety, Qodo Merge implements a dual validation system for each generated code suggestion:
|
||||
|
||||
1) **Localization** - Qodo Merge confirms that the suggestion's line numbers and surrounding code, as predicted by the model, actually match the repo code. This means that the model correctly identified the context and location of the code to be changed.
|
||||
|
||||
2) **"Compilation"** - Using static code analysis, Qodo Merge verifies that after applying the suggestion, the modified file will still be valid, meaning tree-sitter syntax processing will not throw an error. This process is relevant for multiple programming languages, see [here](https://pypi.org/project/tree-sitter-languages/) for the full list of supported languages.
|
||||
|
||||
When a suggestion fails to meet these validation criteria, it may still provide valuable feedback, but isn't suitable for direct application to the PR.
|
||||
In such cases, Qodo Merge will omit the 'apply' checkbox and instead display:
|
||||
|
||||
`[To ensure code accuracy, apply this suggestion manually]`
|
||||
|
||||
All suggestions that pass these validations undergo a final stage of **self-reflection**, where the AI model evaluates, scores, and re-ranks its own suggestions, eliminating any that are irrelevant or incorrect.
|
||||
Read more about this process in the [self-reflection](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/self_reflection/) page.
|
||||
|
||||
## Conclusion
|
||||
|
||||
The validation methods described above enhance the reliability of code suggestions and help PR authors determine which suggestions are safer to apply in the Git environment.
|
||||
Of course, additional factors should be considered, such as suggestion complexity and potential code impact.
|
||||
|
||||
Human judgment remains essential. After clicking 'apply', Qodo Merge still presents the 'before' and 'after' code snippets for review, allowing you to assess the changes before finalizing the commit.
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,5 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview - PR Compression Strategy
|
||||
|
||||
There are two scenarios:
|
||||
|
||||
1. The PR is small enough to fit in a single prompt (including system and user prompt)
|
||||
@ -9,41 +8,35 @@ There are two scenarios:
|
||||
For both scenarios, we first use the following strategy
|
||||
|
||||
#### Repo language prioritization strategy
|
||||
|
||||
We prioritize the languages of the repo based on the following criteria:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Exclude binary files and non code files (e.g. images, pdfs, etc)
|
||||
2. Given the main languages used in the repo
|
||||
3. We sort the PR files by the most common languages in the repo (in descending order):
|
||||
3. We sort the PR files by the most common languages in the repo (in descending order):
|
||||
* ```[[file.py, file2.py],[file3.js, file4.jsx],[readme.md]]```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Small PR
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, we can fit the entire PR in a single prompt:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Exclude binary files and non code files (e.g. images, pdfs, etc)
|
||||
2. We Expand the surrounding context of each patch to 3 lines above and below the patch
|
||||
|
||||
### Large PR
|
||||
|
||||
#### Motivation
|
||||
|
||||
Pull Requests can be very long and contain a lot of information with varying degree of relevance to the pr-agent.
|
||||
We want to be able to pack as much information as possible in a single LMM prompt, while keeping the information relevant to the pr-agent.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Compression strategy
|
||||
|
||||
We prioritize additions over deletions:
|
||||
- Combine all deleted files into a single list (`deleted files`)
|
||||
- File patches are a list of hunks, remove all hunks of type deletion-only from the hunks in the file patch
|
||||
|
||||
* Combine all deleted files into a single list (`deleted files`)
|
||||
* File patches are a list of hunks, remove all hunks of type deletion-only from the hunks in the file patch
|
||||
|
||||
#### Adaptive and token-aware file patch fitting
|
||||
|
||||
#### Adaptive and token-aware file patch fitting
|
||||
We use [tiktoken](https://github.com/openai/tiktoken) to tokenize the patches after the modifications described above, and we use the following strategy to fit the patches into the prompt:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Within each language we sort the files by the number of tokens in the file (in descending order):
|
||||
* ```[[file2.py, file.py],[file4.jsx, file3.js],[readme.md]]```
|
||||
- ```[[file2.py, file.py],[file4.jsx, file3.js],[readme.md]]```
|
||||
2. Iterate through the patches in the order described above
|
||||
3. Add the patches to the prompt until the prompt reaches a certain buffer from the max token length
|
||||
4. If there are still patches left, add the remaining patches as a list called `other modified files` to the prompt until the prompt reaches the max token length (hard stop), skip the rest of the patches.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,14 +1,13 @@
|
||||
## TL;DR
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge uses an **asymmetric and dynamic context strategy** to improve AI analysis of code changes in pull requests.
|
||||
It provides more context before changes than after, and dynamically adjusts the context based on code structure (e.g., enclosing functions or classes).
|
||||
Qodo Merge uses an **asymmetric and dynamic context strategy** to improve AI analysis of code changes in pull requests.
|
||||
It provides more context before changes than after, and dynamically adjusts the context based on code structure (e.g., enclosing functions or classes).
|
||||
This approach balances providing sufficient context for accurate analysis, while avoiding needle-in-the-haystack information overload that could degrade AI performance or exceed token limits.
|
||||
|
||||
## Introduction
|
||||
|
||||
Pull request code changes are retrieved in a unified diff format, showing three lines of context before and after each modified section, with additions marked by '+' and deletions by '-'.
|
||||
|
||||
```diff
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -12,5 +12,5 @@ def func1():
|
||||
code line that already existed in the file...
|
||||
code line that already existed in the file...
|
||||
@ -18,14 +17,15 @@ Pull request code changes are retrieved in a unified diff format, showing three
|
||||
code line that already existed in the file...
|
||||
code line that already existed in the file...
|
||||
code line that already existed in the file...
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -26,2 +26,4 @@ def func2():
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This unified diff format can be challenging for AI models to interpret accurately, as it provides limited context for understanding the full scope of code changes.
|
||||
This unified diff format can be challenging for AI models to interpret accurately, as it provides limited context for understanding the full scope of code changes.
|
||||
The presentation of code using '+', '-', and ' ' symbols to indicate additions, deletions, and unchanged lines respectively also differs from the standard code formatting typically used to train AI models.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Challenges of expanding the context window
|
||||
|
||||
While expanding the context window is technically feasible, it presents a more fundamental trade-off:
|
||||
@ -37,38 +37,36 @@ Pros:
|
||||
Cons:
|
||||
|
||||
- Excessive context may overwhelm the model with extraneous information, creating a "needle in a haystack" scenario where focusing on the relevant details (the code that actually changed) becomes challenging.
|
||||
LLM quality is known to degrade when the context gets larger.
|
||||
LLM quality is known to degrade when the context gets larger.
|
||||
Pull requests often encompass multiple changes across many files, potentially spanning hundreds of lines of modified code. This complexity presents a genuine risk of overwhelming the model with excessive context.
|
||||
|
||||
- Increased context expands the token count, increasing processing time and cost, and may prevent the model from processing the entire pull request in a single pass.
|
||||
|
||||
## Asymmetric and dynamic context
|
||||
|
||||
To address these challenges, Qodo Merge employs an **asymmetric** and **dynamic** context strategy, providing the model with more focused and relevant context information for each code change.
|
||||
|
||||
**Asymmetric:**
|
||||
|
||||
We start by recognizing that the context preceding a code change is typically more crucial for understanding the modification than the context following it.
|
||||
We start by recognizing that the context preceding a code change is typically more crucial for understanding the modification than the context following it.
|
||||
Consequently, Qodo Merge implements an asymmetric context policy, decoupling the context window into two distinct segments: one for the code before the change and another for the code after.
|
||||
|
||||
By independently adjusting each context window, Qodo Merge can supply the model with a more tailored and pertinent context for individual code changes.
|
||||
By independently adjusting each context window, Qodo Merge can supply the model with a more tailored and pertinent context for individual code changes.
|
||||
|
||||
**Dynamic:**
|
||||
|
||||
We also employ a "dynamic" context strategy.
|
||||
We start by recognizing that the optimal context for a code change often corresponds to its enclosing code component (e.g., function, class), rather than a fixed number of lines.
|
||||
We start by recognizing that the optimal context for a code change often corresponds to its enclosing code component (e.g., function, class), rather than a fixed number of lines.
|
||||
Consequently, we dynamically adjust the context window based on the code's structure, ensuring the model receives the most pertinent information for each modification.
|
||||
|
||||
To prevent overwhelming the model with excessive context, we impose a limit on the number of lines searched when identifying the enclosing component.
|
||||
To prevent overwhelming the model with excessive context, we impose a limit on the number of lines searched when identifying the enclosing component.
|
||||
This balance allows for comprehensive understanding while maintaining efficiency and limiting context token usage.
|
||||
|
||||
## Appendix - relevant configuration options
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
patch_extension_skip_types =[".md",".txt"] # Skip files with these extensions when trying to extend the context
|
||||
allow_dynamic_context=true # Allow dynamic context extension
|
||||
max_extra_lines_before_dynamic_context = 8 # will try to include up to X extra lines before the hunk in the patch, until we reach an enclosing function or class
|
||||
patch_extra_lines_before = 3 # Number of extra lines (+3 default ones) to include before each hunk in the patch
|
||||
patch_extra_lines_after = 1 # Number of extra lines (+3 default ones) to include after each hunk in the patch
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -1,302 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Fetching Ticket Context for PRs
|
||||
|
||||
`Supported Git Platforms: GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket`
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge streamlines code review workflows by seamlessly connecting with multiple ticket management systems.
|
||||
This integration enriches the review process by automatically surfacing relevant ticket information and context alongside code changes.
|
||||
|
||||
**Ticket systems supported**:
|
||||
|
||||
- GitHub
|
||||
- Jira (💎)
|
||||
|
||||
**Ticket data fetched:**
|
||||
|
||||
1. Ticket Title
|
||||
2. Ticket Description
|
||||
3. Custom Fields (Acceptance criteria)
|
||||
4. Subtasks (linked tasks)
|
||||
5. Labels
|
||||
6. Attached Images/Screenshots
|
||||
|
||||
## Affected Tools
|
||||
|
||||
Ticket Recognition Requirements:
|
||||
|
||||
- The PR description should contain a link to the ticket or if the branch name starts with the ticket id / number.
|
||||
- For Jira tickets, you should follow the instructions in [Jira Integration](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/fetching_ticket_context/#jira-integration) in order to authenticate with Jira.
|
||||
|
||||
### Describe tool
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge will recognize the ticket and use the ticket content (title, description, labels) to provide additional context for the code changes.
|
||||
By understanding the reasoning and intent behind modifications, the LLM can offer more insightful and relevant code analysis.
|
||||
|
||||
### Review tool
|
||||
|
||||
Similarly to the `describe` tool, the `review` tool will use the ticket content to provide additional context for the code changes.
|
||||
|
||||
In addition, this feature will evaluate how well a Pull Request (PR) adheres to its original purpose/intent as defined by the associated ticket or issue mentioned in the PR description.
|
||||
Each ticket will be assigned a label (Compliance/Alignment level), Indicates the degree to which the PR fulfills its original purpose, Options: Fully compliant, Partially compliant or Not compliant.
|
||||
|
||||
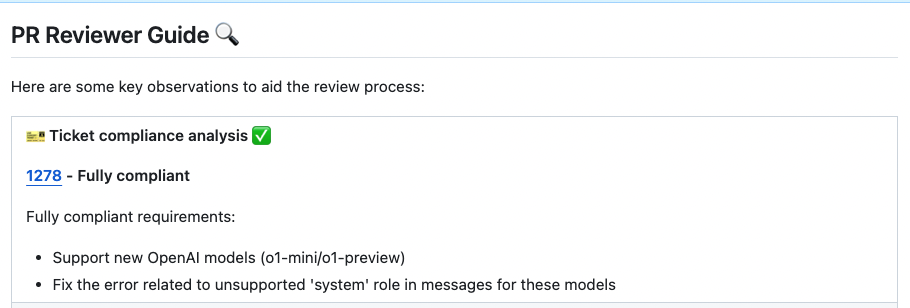{width=768}
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the tool will automatically validate if the PR complies with the referenced ticket.
|
||||
If you want to disable this feedback, add the following line to your configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[pr_reviewer]
|
||||
require_ticket_analysis_review=false
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## GitHub Issues Integration
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge will automatically recognize GitHub issues mentioned in the PR description and fetch the issue content.
|
||||
Examples of valid GitHub issue references:
|
||||
|
||||
- `https://github.com/<ORG_NAME>/<REPO_NAME>/issues/<ISSUE_NUMBER>`
|
||||
- `#<ISSUE_NUMBER>`
|
||||
- `<ORG_NAME>/<REPO_NAME>#<ISSUE_NUMBER>`
|
||||
|
||||
Since Qodo Merge is integrated with GitHub, it doesn't require any additional configuration to fetch GitHub issues.
|
||||
|
||||
## Jira Integration 💎
|
||||
|
||||
We support both Jira Cloud and Jira Server/Data Center.
|
||||
|
||||
### Jira Cloud
|
||||
|
||||
There are two ways to authenticate with Jira Cloud:
|
||||
|
||||
**1) Jira App Authentication**
|
||||
|
||||
The recommended way to authenticate with Jira Cloud is to install the Qodo Merge app in your Jira Cloud instance. This will allow Qodo Merge to access Jira data on your behalf.
|
||||
|
||||
Installation steps:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Click [here](https://auth.atlassian.com/authorize?audience=api.atlassian.com&client_id=8krKmA4gMD8mM8z24aRCgPCSepZNP1xf&scope=read%3Ajira-work%20offline_access&redirect_uri=https%3A%2F%2Fregister.jira.pr-agent.codium.ai&state=qodomerge&response_type=code&prompt=consent) to install the Qodo Merge app in your Jira Cloud instance, click the `accept` button.<br>
|
||||
{width=384}
|
||||
|
||||
2. After installing the app, you will be redirected to the Qodo Merge registration page. and you will see a success message.<br>
|
||||
{width=384}
|
||||
|
||||
3. Now Qodo Merge will be able to fetch Jira ticket context for your PRs.
|
||||
|
||||
**2) Email/Token Authentication**
|
||||
|
||||
You can create an API token from your Atlassian account:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Log in to https://id.atlassian.com/manage-profile/security/api-tokens.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Click Create API token.
|
||||
|
||||
3. From the dialog that appears, enter a name for your new token and click Create.
|
||||
|
||||
4. Click Copy to clipboard.
|
||||
|
||||
{width=384}
|
||||
|
||||
5. In your [configuration file](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/) add the following lines:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[jira]
|
||||
jira_api_token = "YOUR_API_TOKEN"
|
||||
jira_api_email = "YOUR_EMAIL"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Jira Data Center/Server
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ()
|
||||
[//]: # (##### Local App Authentication (For Qodo Merge On-Premise Customers))
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ()
|
||||
[//]: # (##### 1. Step 1: Set up an application link in Jira Data Center/Server)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (* Go to Jira Administration > Applications > Application Links > Click on `Create link`)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ()
|
||||
[//]: # ({width=384})
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (* Choose `External application` and set the direction to `Incoming` and then click `Continue`)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ()
|
||||
[//]: # (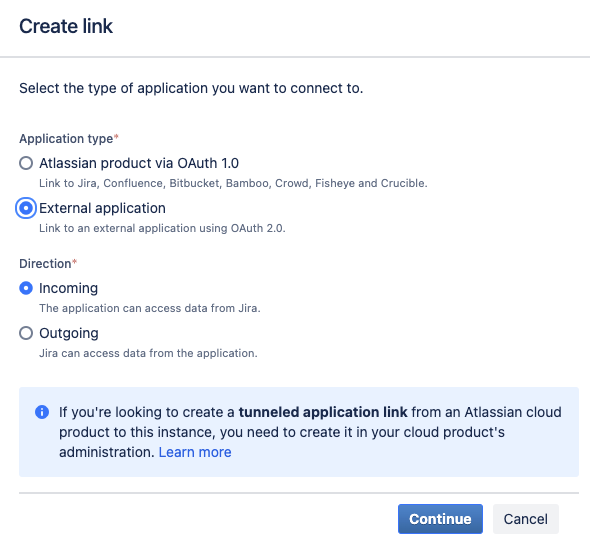{width=256})
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (* In the following screen, enter the following details:)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ( * Name: `Qodo Merge`)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ( * Redirect URL: Enter your Qodo Merge URL followed `https://{QODO_MERGE_ENDPOINT}/register_ticket_provider`)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ( * Permission: Select `Read`)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ( * Click `Save`)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ()
|
||||
[//]: # (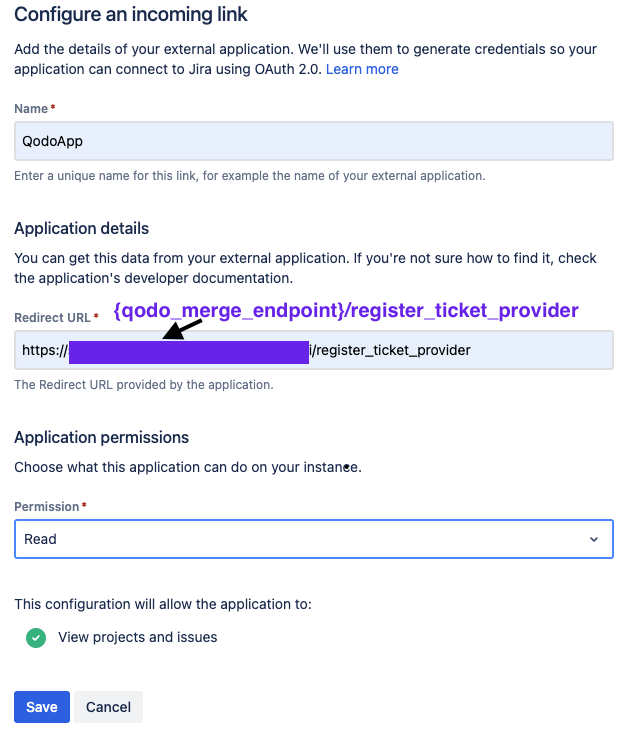{width=384})
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (* Copy the `Client ID` and `Client secret` and set them in your `.secrets` file:)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ()
|
||||
[//]: # (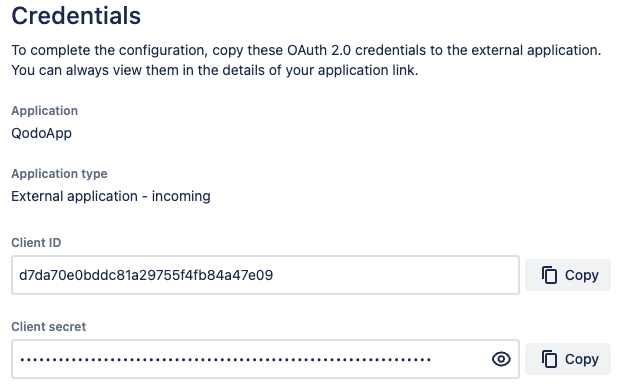{width=256})
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (```toml)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ([jira])
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (jira_app_secret = "...")
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (jira_client_id = "...")
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (```)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ()
|
||||
[//]: # (##### 2. Step 2: Authenticate with Jira Data Center/Server)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (* Open this URL in your browser: `https://{QODO_MERGE_ENDPOINT}/jira_auth`)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (* Click on link)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ()
|
||||
[//]: # ({width=384})
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ()
|
||||
[//]: # (* You will be redirected to Jira Data Center/Server, click `Allow`)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (* You will be redirected back to Qodo Merge and you will see a success message.)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (Personal Access Token (PAT) Authentication)
|
||||
|
||||
#### Using Basic Authentication for Jira Data Center/Server
|
||||
|
||||
You can use your Jira username and password to authenticate with Jira Data Center/Server.
|
||||
|
||||
In your Configuration file/Environment variables/Secrets file, add the following lines:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
jira_api_email = "your_username"
|
||||
jira_api_token = "your_password"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
(Note that indeed the 'jira_api_email' field is used for the username, and the 'jira_api_token' field is used for the user password.)
|
||||
|
||||
##### Validating Basic authentication via Python script
|
||||
|
||||
If you are facing issues retrieving tickets in Qodo Merge with Basic auth, you can validate the flow using a Python script.
|
||||
This following steps will help you check if the basic auth is working correctly, and if you can access the Jira ticket details:
|
||||
|
||||
1. run `pip install jira==3.8.0`
|
||||
|
||||
2. run the following Python script (after replacing the placeholders with your actual values):
|
||||
|
||||
??? example "Script to validate basic auth"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from jira import JIRA
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
try:
|
||||
# Jira server URL
|
||||
server = "https://..."
|
||||
# Basic auth
|
||||
username = "..."
|
||||
password = "..."
|
||||
# Jira ticket code (e.g. "PROJ-123")
|
||||
ticket_id = "..."
|
||||
|
||||
print("Initializing JiraServerTicketProvider with JIRA server")
|
||||
# Initialize JIRA client
|
||||
jira = JIRA(
|
||||
server=server,
|
||||
basic_auth=(username, password),
|
||||
timeout=30
|
||||
)
|
||||
if jira:
|
||||
print(f"JIRA client initialized successfully")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print("Error initializing JIRA client")
|
||||
|
||||
# Fetch ticket details
|
||||
ticket = jira.issue(ticket_id)
|
||||
print(f"Ticket title: {ticket.fields.summary}")
|
||||
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
print(f"Error fetching JIRA ticket details: {e}")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Using a Personal Access Token (PAT) for Jira Data Center/Server
|
||||
|
||||
1. Create a [Personal Access Token (PAT)](https://confluence.atlassian.com/enterprise/using-personal-access-tokens-1026032365.html) in your Jira account
|
||||
2. In your Configuration file/Environment variables/Secrets file, add the following lines:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[jira]
|
||||
jira_base_url = "YOUR_JIRA_BASE_URL" # e.g. https://jira.example.com
|
||||
jira_api_token = "YOUR_API_TOKEN"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
##### Validating PAT token via Python script
|
||||
|
||||
If you are facing issues retrieving tickets in Qodo Merge with PAT token, you can validate the flow using a Python script.
|
||||
This following steps will help you check if the token is working correctly, and if you can access the Jira ticket details:
|
||||
|
||||
1. run `pip install jira==3.8.0`
|
||||
|
||||
2. run the following Python script (after replacing the placeholders with your actual values):
|
||||
|
||||
??? example "Script to validate PAT token"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from jira import JIRA
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
try:
|
||||
# Jira server URL
|
||||
server = "https://..."
|
||||
# Jira PAT token
|
||||
token_auth = "..."
|
||||
# Jira ticket code (e.g. "PROJ-123")
|
||||
ticket_id = "..."
|
||||
|
||||
print("Initializing JiraServerTicketProvider with JIRA server")
|
||||
# Initialize JIRA client
|
||||
jira = JIRA(
|
||||
server=server,
|
||||
token_auth=token_auth,
|
||||
timeout=30
|
||||
)
|
||||
if jira:
|
||||
print(f"JIRA client initialized successfully")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print("Error initializing JIRA client")
|
||||
|
||||
# Fetch ticket details
|
||||
ticket = jira.issue(ticket_id)
|
||||
print(f"Ticket title: {ticket.fields.summary}")
|
||||
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
print(f"Error fetching JIRA ticket details: {e}")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### How to link a PR to a Jira ticket
|
||||
|
||||
To integrate with Jira, you can link your PR to a ticket using either of these methods:
|
||||
|
||||
**Method 1: Description Reference:**
|
||||
|
||||
Include a ticket reference in your PR description using either the complete URL format https://<JIRA_ORG>.atlassian.net/browse/ISSUE-123 or the shortened ticket ID ISSUE-123.
|
||||
|
||||
**Method 2: Branch Name Detection:**
|
||||
|
||||
Name your branch with the ticket ID as a prefix (e.g., `ISSUE-123-feature-description` or `ISSUE-123/feature-description`).
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Jira Base URL"
|
||||
For shortened ticket IDs or branch detection (method 2 for JIRA cloud), you must configure the Jira base URL in your configuration file under the [jira] section:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[jira]
|
||||
jira_base_url = "https://<JIRA_ORG>.atlassian.net"
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -3,24 +3,22 @@
|
||||
Demonstrating the return on investment (ROI) of AI-powered initiatives is crucial for modern organizations.
|
||||
To address this need, Qodo Merge has developed an AI impact measurement tools and metrics, providing advanced analytics to help businesses quantify the tangible benefits of AI adoption in their PR review process.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Auto Impact Validator - Real-Time Tracking of Implemented Qodo Merge Suggestions
|
||||
|
||||
### How It Works
|
||||
|
||||
When a user pushes a new commit to the pull request, Qodo Merge automatically compares the updated code against the previous suggestions, marking them as implemented if the changes address these recommendations, whether directly or indirectly:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Direct Implementation:** The user directly addresses the suggestion as-is in the PR, either by clicking on the "apply code suggestion" checkbox or by making the changes manually.
|
||||
2. **Indirect Implementation:** Qodo Merge recognizes when a suggestion's intent is fulfilled, even if the exact code changes differ from the original recommendation. It marks these suggestions as implemented, acknowledging that users may achieve the same goal through alternative solutions.
|
||||
|
||||
### Real-Time Visual Feedback
|
||||
|
||||
Upon confirming that a suggestion was implemented, Qodo Merge automatically adds a ✅ (check mark) to the relevant suggestion, enabling transparent tracking of Qodo Merge's impact analysis.
|
||||
Qodo Merge will also add, inside the relevant suggestions, an explanation of how the new code was impacted by each suggestion.
|
||||
|
||||
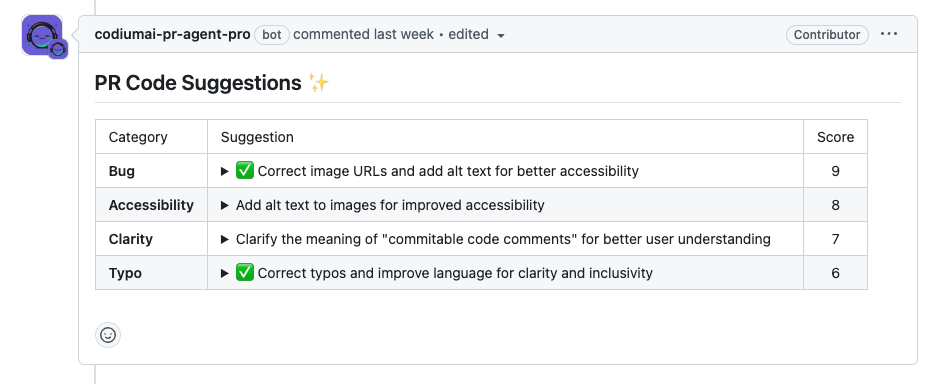{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
### Dashboard Metrics
|
||||
|
||||
The dashboard provides macro-level insights into the overall impact of Qodo Merge on the pull-request process with key productivity metrics.
|
||||
|
||||
By offering clear, data-driven evidence of Qodo Merge's impact, it empowers leadership teams to make informed decisions about the tool's effectiveness and ROI.
|
||||
@ -28,7 +26,6 @@ By offering clear, data-driven evidence of Qodo Merge's impact, it empowers lead
|
||||
Here are key metrics that the dashboard tracks:
|
||||
|
||||
#### Qodo Merge Impacts per 1K Lines
|
||||
|
||||
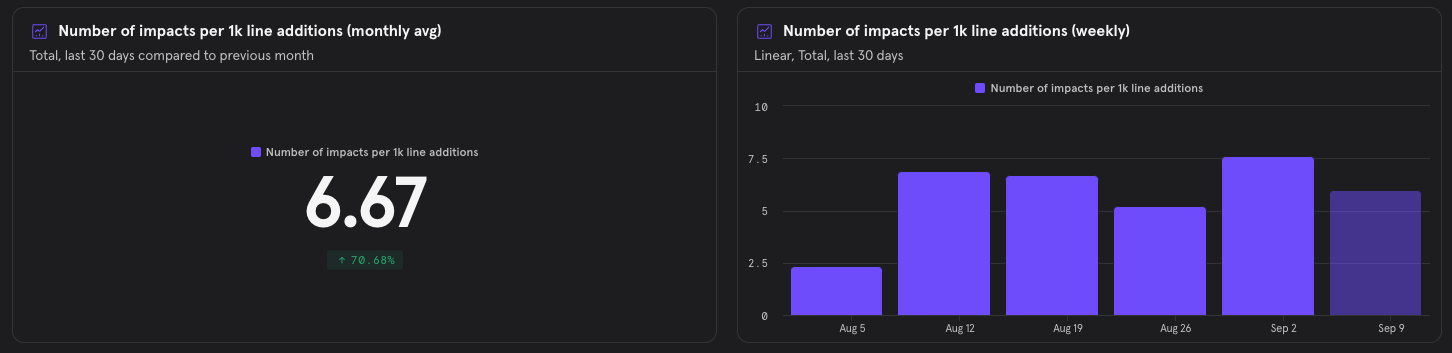{width=512}
|
||||
> Explanation: for every 1K lines of code (additions/edits), Qodo Merge had on average ~X suggestions implemented.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -39,11 +36,9 @@ Here are key metrics that the dashboard tracks:
|
||||
3. **Quantifies Value and ROI:** The metric directly correlates with the value Qodo Merge is providing, showing how frequently it offers improvements relative to the amount of new code being written. This provides a clear, quantifiable way to demonstrate Qodo Merge's return on investment to stakeholders.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Suggestion Effectiveness Across Categories
|
||||
|
||||
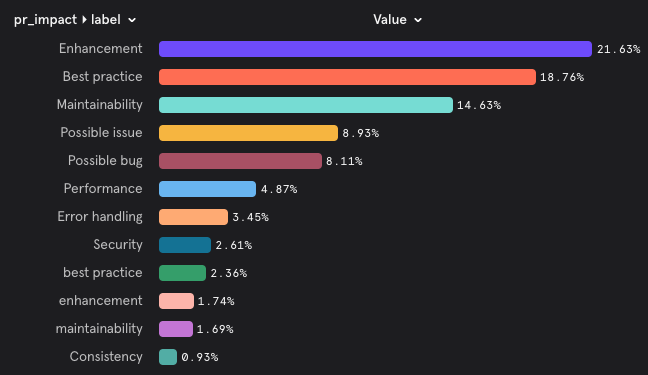{width=512}
|
||||
> Explanation: This chart illustrates the distribution of implemented suggestions across different categories, enabling teams to better understand Qodo Merge's impact on various aspects of code quality and development practices.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Suggestion Score Distribution
|
||||
|
||||
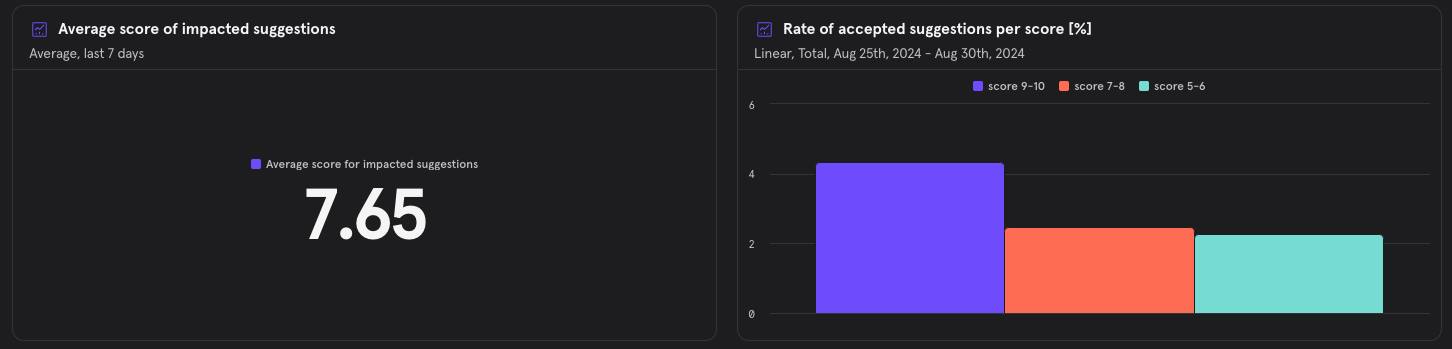{width=512}
|
||||
> Explanation: The distribution of the suggestion score for the implemented suggestions, ensuring that higher-scored suggestions truly represent more significant improvements.
|
||||
> Explanation: The distribution of the suggestion score for the implemented suggestions, ensuring that higher-scored suggestions truly represent more significant improvements.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,35 +1,28 @@
|
||||
# Core Abilities
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge utilizes a variety of core abilities to provide a comprehensive and efficient code review experience. These abilities include:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Auto best practices](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/auto_best_practices/)
|
||||
- [Code validation](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/code_validation/)
|
||||
- [Compression strategy](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/compression_strategy/)
|
||||
- [Local and global metadata](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/metadata/)
|
||||
- [Dynamic context](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/dynamic_context/)
|
||||
- [Fetching ticket context](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/fetching_ticket_context/)
|
||||
- [Self-reflection](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/self_reflection/)
|
||||
- [Impact evaluation](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/impact_evaluation/)
|
||||
- [Interactivity](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/interactivity/)
|
||||
- [Local and global metadata](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/metadata/)
|
||||
- [RAG context enrichment](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/rag_context_enrichment/)
|
||||
- [Self-reflection](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/self_reflection/)
|
||||
- [Compression strategy](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/compression_strategy/)
|
||||
- [Code-oriented YAML](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/code_oriented_yaml/)
|
||||
- [Static code analysis](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/static_code_analysis/)
|
||||
- [Code fine-tuning benchmark](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/finetuning_benchmark/)
|
||||
|
||||
## Blogs
|
||||
|
||||
Here are some additional technical blogs from Qodo, that delve deeper into the core capabilities and features of Large Language Models (LLMs) when applied to coding tasks.
|
||||
Here are some additional technical blogs from Qodo, that delve deeper into the core capabilities and features of Large Language Models (LLMs) when applied to coding tasks.
|
||||
These resources provide more comprehensive insights into leveraging LLMs for software development.
|
||||
|
||||
### Code Generation and LLMs
|
||||
|
||||
- [Effective AI code suggestions: less is more](https://www.qodo.ai/blog/effective-code-suggestions-llms-less-is-more/)
|
||||
- [State-of-the-art Code Generation with AlphaCodium – From Prompt Engineering to Flow Engineering](https://www.qodo.ai/blog/qodoflow-state-of-the-art-code-generation-for-code-contests/)
|
||||
- [RAG for a Codebase with 10k Repos](https://www.qodo.ai/blog/rag-for-large-scale-code-repos/)
|
||||
|
||||
### Development Processes
|
||||
|
||||
- [Understanding the Challenges and Pain Points of the Pull Request Cycle](https://www.qodo.ai/blog/understanding-the-challenges-and-pain-points-of-the-pull-request-cycle/)
|
||||
- [Introduction to Code Coverage Testing](https://www.qodo.ai/blog/introduction-to-code-coverage-testing/)
|
||||
|
||||
### Cost Optimization
|
||||
|
||||
- [Reduce Your Costs by 30% When Using GPT for Python Code](https://www.qodo.ai/blog/reduce-your-costs-by-30-when-using-gpt-3-for-python-code/)
|
||||
- [Reduce Your Costs by 30% When Using GPT for Python Code](https://www.qodo.ai/blog/reduce-your-costs-by-30-when-using-gpt-3-for-python-code/)
|
||||
@ -1,41 +1,2 @@
|
||||
# Interactivity
|
||||
|
||||
`Supported Git Platforms: GitHub, GitLab`
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge transforms static code reviews into interactive experiences by enabling direct actions from pull request (PR) comments.
|
||||
Developers can immediately trigger actions and apply changes with simple checkbox clicks.
|
||||
|
||||
This focused workflow maintains context while dramatically reducing the time between PR creation and final merge.
|
||||
The approach eliminates manual steps, provides clear visual indicators, and creates immediate feedback loops all within the same interface.
|
||||
|
||||
## Key Interactive Features
|
||||
|
||||
### 1\. Interactive `/improve` Tool
|
||||
|
||||
The [`/improve`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/) command delivers a comprehensive interactive experience:
|
||||
|
||||
- _**Apply this suggestion**_: Clicking this checkbox instantly converts a suggestion into a committable code change. When committed to the PR, changes made to code that was flagged for improvement will be marked with a check mark, allowing developers to easily track and review implemented recommendations.
|
||||
|
||||
- _**More**_: Triggers additional suggestions generation while keeping each suggestion focused and relevant as the original set
|
||||
|
||||
- _**Update**_: Triggers a re-analysis of the code, providing updated suggestions based on the latest changes
|
||||
|
||||
- _**Author self-review**_: Interactive acknowledgment that developers have opened and reviewed collapsed suggestions
|
||||
|
||||
### 2\. Interactive `/analyze` Tool
|
||||
|
||||
The [`/analyze`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/analyze/) command provides component-level analysis with interactive options for each identified code component:
|
||||
|
||||
- Interactive checkboxes to generate tests, documentation, and code suggestions for specific components
|
||||
|
||||
- On-demand similar code search that activates when a checkbox is clicked
|
||||
|
||||
- Component-specific actions that trigger only for the selected elements, providing focused assistance
|
||||
|
||||
### 3\. Interactive `/help` Tool
|
||||
|
||||
The [`/help`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/help/) command not only lists available tools and their descriptions but also enables immediate tool invocation through interactive checkboxes.
|
||||
When a user checks a tool's checkbox, Qodo Merge instantly triggers that tool without requiring additional commands.
|
||||
This transforms the standard help menu into an interactive launch pad for all Qodo Merge capabilities, eliminating context switching by keeping developers within their PR workflow.
|
||||
## Interactive invocation 💎
|
||||
TBD
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,5 @@
|
||||
## Local and global metadata injection with multi-stage analysis
|
||||
|
||||
1\.
|
||||
(1)
|
||||
Qodo Merge initially retrieves for each PR the following data:
|
||||
|
||||
- PR title and branch name
|
||||
@ -12,7 +11,7 @@ Qodo Merge initially retrieves for each PR the following data:
|
||||
!!! tip "Tip: Organization-level metadata"
|
||||
In addition to the inputs above, Qodo Merge can incorporate supplementary preferences provided by the user, like [`extra_instructions` and `organization best practices`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#extra-instructions-and-best-practices). This information can be used to enhance the PR analysis.
|
||||
|
||||
2\.
|
||||
(2)
|
||||
By default, the first command that Qodo Merge executes is [`describe`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/describe/), which generates three types of outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
- PR Type (e.g. bug fix, feature, refactor, etc)
|
||||
@ -24,7 +23,7 @@ This effectively enables multi-stage chain-of-thought analysis, without doing an
|
||||
|
||||
For example, when generating code suggestions for different files, Qodo Merge can inject the AI-generated ["Changes walkthrough"](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/1202#issue-2511546839) file summary in the prompt:
|
||||
|
||||
```diff
|
||||
```
|
||||
## File: 'src/file1.py'
|
||||
### AI-generated file summary:
|
||||
- edited function `func1` that does X
|
||||
@ -33,14 +32,14 @@ For example, when generating code suggestions for different files, Qodo Merge ca
|
||||
|
||||
@@ ... @@ def func1():
|
||||
__new hunk__
|
||||
11 unchanged code line0
|
||||
12 unchanged code line1
|
||||
13 +new code line2 added
|
||||
14 unchanged code line3
|
||||
11 unchanged code line0 in the PR
|
||||
12 unchanged code line1 in the PR
|
||||
13 +new code line2 added in the PR
|
||||
14 unchanged code line3 in the PR
|
||||
__old hunk__
|
||||
unchanged code line0
|
||||
unchanged code line1
|
||||
-old code line2 removed
|
||||
-old code line2 removed in the PR
|
||||
unchanged code line3
|
||||
|
||||
@@ ... @@ def func2():
|
||||
@ -50,7 +49,8 @@ __old hunk__
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3\. The entire PR files that were retrieved are also used to expand and enhance the PR context (see [Dynamic Context](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/dynamic_context/)).
|
||||
(3) The entire PR files that were retrieved are also used to expand and enhance the PR context (see [Dynamic Context](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/dynamic_context/)).
|
||||
|
||||
4\. All the metadata described above represents several level of cumulative analysis - ranging from hunk level, to file level, to PR level, to organization level.
|
||||
This comprehensive approach enables Qodo Merge AI models to generate more precise and contextually relevant suggestions and feedback.
|
||||
|
||||
(4) All the metadata described above represents several level of cumulative analysis - ranging from hunk level, to file level, to PR level, to organization level.
|
||||
This comprehensive approach enables Qodo Merge AI models to generate more precise and contextually relevant suggestions and feedback.
|
||||
@ -1,77 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# RAG Context Enrichment 💎
|
||||
|
||||
`Supported Git Platforms: GitHub, Bitbucket Data Center`
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info "Prerequisites"
|
||||
- RAG is available only for Qodo enterprise plan users, with single tenant or on-premises setup.
|
||||
- Database setup and codebase indexing must be completed before proceeding. [Contact support](https://www.qodo.ai/contact/) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
### What is RAG Context Enrichment?
|
||||
|
||||
A feature that enhances AI analysis by retrieving and referencing relevant code patterns from your project, enabling context-aware insights during code reviews.
|
||||
|
||||
### How does RAG Context Enrichment work?
|
||||
|
||||
Using Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), it searches your configured repositories for contextually relevant code segments, enriching pull request (PR) insights and accelerating review accuracy.
|
||||
|
||||
## Getting started
|
||||
|
||||
### Configuration options
|
||||
|
||||
In order to enable the RAG feature, add the following lines to your configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[rag_arguments]
|
||||
enable_rag=true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! example "RAG Arguments Options"
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>enable_rag</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, repository enrichment using RAG will be enabled. Default is false.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>rag_repo_list</b></td>
|
||||
<td>A list of repositories that will be used by the semantic search for RAG. Use `['all']` to consider the entire codebase or a select list of repositories, for example: ['my-org/my-repo', ...]. Default: the repository from which the PR was opened.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
### Applications
|
||||
|
||||
RAG capability is exclusively available in the following tools:
|
||||
|
||||
=== "`/review`"
|
||||
The [`/review`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/review/) tool offers the _Focus area from RAG data_ which contains feedback based on the RAG references analysis.
|
||||
The complete list of references found relevant to the PR will be shown in the _References_ section, helping developers understand the broader context by exploring the provided references.
|
||||
|
||||
{width=640}
|
||||
|
||||
=== "`/implement`"
|
||||
The [`/implement`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/implement/) tool utilizes the RAG feature to provide comprehensive context of the repository codebase, allowing it to generate more refined code output.
|
||||
The _References_ section contains links to the content used to support the code generation.
|
||||
|
||||
{width=640}
|
||||
|
||||
=== "`/ask`"
|
||||
The [`/ask`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/ask/) tool can access broader repository context through the RAG feature when answering questions that go beyond the PR scope alone.
|
||||
The _References_ section displays the additional repository content consulted to formulate the answer.
|
||||
|
||||
{width=640}
|
||||
|
||||
## Limitations
|
||||
|
||||
### Querying the codebase presents significant challenges
|
||||
|
||||
- **Search Method**: RAG uses natural language queries to find semantically relevant code sections
|
||||
- **Result Quality**: No guarantee that RAG results will be useful for all queries
|
||||
- **Scope Recommendation**: To reduce noise, focus on the PR repository rather than searching across multiple repositories
|
||||
|
||||
### This feature has several requirements and restrictions
|
||||
|
||||
- **Codebase**: Must be properly indexed for search functionality
|
||||
- **Security**: Requires secure and private indexed codebase implementation
|
||||
- **Deployment**: Only available for Qodo Merge Enterprise plan using single tenant or on-premises setup
|
||||
@ -1,11 +1,12 @@
|
||||
## TL;DR
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge implements a **self-reflection** process where the AI model reflects, scores, and re-ranks its own suggestions, eliminating irrelevant or incorrect ones.
|
||||
This approach improves the quality and relevance of suggestions, saving users time and enhancing their experience.
|
||||
Qodo Merge implements a **self-reflection** process where the AI model reflects, scores, and re-ranks its own suggestions, eliminating irrelevant or incorrect ones.
|
||||
This approach improves the quality and relevance of suggestions, saving users time and enhancing their experience.
|
||||
Configuration options allow users to set a score threshold for further filtering out suggestions.
|
||||
|
||||
## Introduction - Efficient Review with Hierarchical Presentation
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Given that not all generated code suggestions will be relevant, it is crucial to enable users to review them in a fast and efficient way, allowing quick identification and filtering of non-applicable ones.
|
||||
|
||||
To achieve this goal, Qodo Merge offers a dedicated hierarchical structure when presenting suggestions to users:
|
||||
@ -23,7 +24,7 @@ The AI model is initially tasked with generating suggestions, and outputting the
|
||||
However, in practice we observe that models often struggle to simultaneously generate high-quality code suggestions and rank them well in a single pass.
|
||||
Furthermore, the initial set of generated suggestions sometimes contains easily identifiable errors.
|
||||
|
||||
To address these issues, we implemented a "self-reflection" process that refines suggestion ranking and eliminates irrelevant or incorrect proposals.
|
||||
To address these issues, we implemented a "self-reflection" process that refines suggestion ranking and eliminates irrelevant or incorrect proposals.
|
||||
This process consists of the following steps:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Presenting the generated suggestions to the model in a follow-up call.
|
||||
@ -41,9 +42,10 @@ This results in a more refined and valuable set of suggestions for the user, sav
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
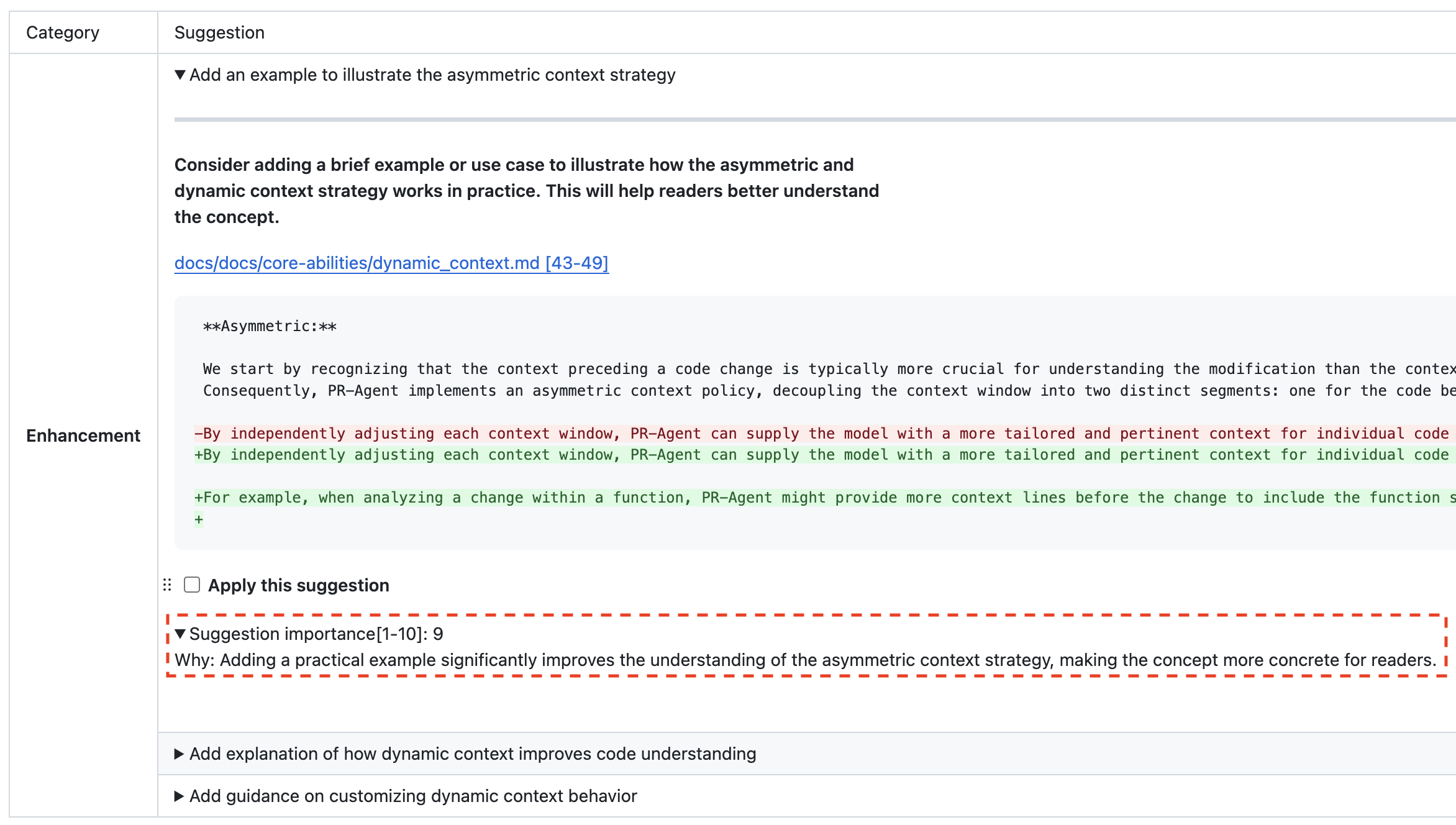{width=768}
|
||||
|
||||
## Appendix - Relevant Configuration Options
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[pr_code_suggestions]
|
||||
suggestions_score_threshold = 0 # Filter out suggestions with a score below this threshold (0-10)
|
||||
## Appendix - Relevant Configuration Options
|
||||
```
|
||||
[pr_code_suggestions]
|
||||
self_reflect_on_suggestions = true # Enable self-reflection on code suggestions
|
||||
suggestions_score_threshold = 0 # Filter out suggestions with a score below this threshold (0-10)
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -7,13 +7,14 @@ It scans the PR code changes, finds all the code components (methods, functions,
|
||||
!!! note "Language that are currently supported:"
|
||||
Python, Java, C++, JavaScript, TypeScript, C#.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Capabilities
|
||||
|
||||
### Analyze PR
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The [`analyze`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/analyze/) tool enables to interactively generate tests, docs, code suggestions and similar code search for each component that changed in the PR.
|
||||
It can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/analyze
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -28,11 +29,9 @@ Clicking on each checkbox will trigger the relevant tool for the selected compon
|
||||
|
||||
The [`test`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/test/) tool generate tests for a selected component, based on the PR code changes.
|
||||
It can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/test component_name
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
where 'component_name' is the name of a specific component in the PR, Or be triggered interactively by using the `analyze` tool.
|
||||
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
@ -41,7 +40,6 @@ where 'component_name' is the name of a specific component in the PR, Or be tri
|
||||
|
||||
The [`add_docs`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/documentation/) tool scans the PR code changes, and automatically generate docstrings for any code components that changed in the PR.
|
||||
It can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/add_docs component_name
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -51,10 +49,8 @@ Or be triggered interactively by using the `analyze` tool.
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
|
||||
### Generate Code Suggestions for a Component
|
||||
|
||||
The [`improve_component`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve_component/) tool generates code suggestions for a specific code component that changed in the PR.
|
||||
It can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/improve_component component_name
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -65,7 +61,7 @@ Or be triggered interactively by using the `analyze` tool.
|
||||
|
||||
### Find Similar Code
|
||||
|
||||
The [`similar code`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/similar_code/) tool retrieves the most similar code components from inside the organization's codebase or from open-source code, including details about the license associated with each repository.
|
||||
The [`similar code`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/similar_code/) tool retrieves the most similar code components from inside the organization's codebase, or from open-source code.
|
||||
|
||||
For example:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
# FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
??? note "Q: Can Qodo Merge serve as a substitute for a human reviewer?"
|
||||
??? note "Question: Can Qodo Merge serve as a substitute for a human reviewer?"
|
||||
#### Answer:<span style="display:none;">1</span>
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge is designed to assist, not replace, human reviewers.
|
||||
@ -12,7 +12,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
1. Preserves user's original PR header
|
||||
2. Places user's description above the AI-generated PR description
|
||||
3. Won't approve PRs; approval remains reviewer's responsibility
|
||||
3. Cannot approve PRs; approval remains reviewer's responsibility
|
||||
4. The code suggestions are optional, and aim to:
|
||||
- Encourage self-review and self-reflection
|
||||
- Highlight potential bugs or oversights
|
||||
@ -22,69 +22,46 @@
|
||||
|
||||
___
|
||||
|
||||
??? note "Q: I received an incorrect or irrelevant suggestion. Why?"
|
||||
??? note "Question: I received an incorrect or irrelevant suggestion. Why?"
|
||||
|
||||
#### Answer:<span style="display:none;">2</span>
|
||||
|
||||
- Modern AI models, like Claude Sonnet and GPT-4, are improving rapidly but remain imperfect. Users should critically evaluate all suggestions rather than accepting them automatically.
|
||||
- AI errors are rare, but possible. A main value from reviewing the code suggestions lies in their high probability of catching **mistakes or bugs made by the PR author**. We believe it's worth spending 30-60 seconds reviewing suggestions, even if some aren't relevant, as this practice can enhance code quality and prevent bugs in production.
|
||||
- Modern AI models, like Claude 3.5 Sonnet and GPT-4, are improving rapidly but remain imperfect. Users should critically evaluate all suggestions rather than accepting them automatically.
|
||||
- AI errors are rare, but possible. A main value from reviewing the code suggestions lies in their high probability of catching **mistakes or bugs made by the PR author**. We believe it's worth spending 30-60 seconds reviewing suggestions, even if some aren't relevant, as this practice can enhances code quality and prevent bugs in production.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- The hierarchical structure of the suggestions is designed to help the user _quickly_ understand them, and to decide which ones are relevant and which are not:
|
||||
|
||||
- The hierarchical structure of the suggestions is designed to help the user to _quickly_ understand them, and to decide which ones are relevant and which are not:
|
||||
|
||||
- Only if the `Category` header is relevant, the user should move to the summarized suggestion description.
|
||||
- Only if the summarized suggestion description is relevant, the user should click on the collapsible, to read the full suggestion description with a code preview example.
|
||||
|
||||
- In addition, we recommend to use the [`extra_instructions`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#extra-instructions-and-best-practices) field to guide the model to suggestions that are more relevant to the specific needs of the project.
|
||||
- In addition, we recommend to use the [`extra_instructions`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#extra-instructions-and-best-practices) field to guide the model to suggestions that are more relevant to the specific needs of the project.
|
||||
- The interactive [PR chat](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/chrome-extension/) also provides an easy way to get more tailored suggestions and feedback from the AI model.
|
||||
|
||||
___
|
||||
|
||||
??? note "Q: How can I get more tailored suggestions?"
|
||||
??? note "Question: How can I get more tailored suggestions?"
|
||||
#### Answer:<span style="display:none;">3</span>
|
||||
|
||||
See [here](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#extra-instructions-and-best-practices) for more information on how to use the `extra_instructions` and `best_practices` configuration options, to guide the model to more tailored suggestions.
|
||||
|
||||
___
|
||||
|
||||
??? note "Q: Will you store my code? Are you using my code to train models?"
|
||||
??? note "Question: Will you store my code ? Are you using my code to train models?"
|
||||
#### Answer:<span style="display:none;">4</span>
|
||||
|
||||
No. Qodo Merge strict privacy policy ensures that your code is not stored or used for training purposes.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
For a detailed overview of our data privacy policy, please refer to [this link](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/overview/data_privacy/)
|
||||
|
||||
___
|
||||
|
||||
??? note "Q: Can I use my own LLM keys with Qodo Merge?"
|
||||
??? note "Question: Can I use my own LLM keys with Qodo Merge?"
|
||||
#### Answer:<span style="display:none;">5</span>
|
||||
|
||||
When you self-host the [open-source](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent) version, you use your own keys.
|
||||
When you self-host, you use your own keys.
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge with SaaS deployment is a hosted version of Qodo Merge, where Qodo manages the infrastructure and the keys.
|
||||
Qodo Merge Pro with SaaS deployment is a hosted version of Qodo Merge, where Qodo manages the infrastructure and the keys.
|
||||
For enterprise customers, on-prem deployment is also available. [Contact us](https://www.codium.ai/contact/#pricing) for more information.
|
||||
___
|
||||
|
||||
??? note "Q: Can Qodo Merge review draft/offline PRs?"
|
||||
#### Answer:<span style="display:none;">5</span>
|
||||
|
||||
Yes. While Qodo Merge won't automatically review draft PRs, you can still get feedback by manually requesting it through [online commenting](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/automations_and_usage/#online-usage).
|
||||
|
||||
For active PRs, you can customize the automatic feedback settings [here](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/automations_and_usage/#qodo-merge-automatic-feedback) to match your team's workflow.
|
||||
___
|
||||
|
||||
??? note "Q: Can the 'Review effort' feedback be calibrated or customized?"
|
||||
#### Answer:<span style="display:none;">5</span>
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, you can customize review effort estimates using the `extra_instructions` configuration option (see [documentation](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/review/#configuration-options)).
|
||||
|
||||
Example mapping:
|
||||
|
||||
- Effort 1: < 30 minutes review time
|
||||
- Effort 2: 30-60 minutes review time
|
||||
- Effort 3: 60-90 minutes review time
|
||||
- ...
|
||||
|
||||
Note: The effort levels (1-5) are primarily meant for _comparative_ purposes, helping teams prioritize reviewing smaller PRs first. The actual review duration may vary, as the focus is on providing consistent relative effort estimates.
|
||||
|
||||
___
|
||||
___
|
||||
93
docs/docs/finetuning_benchmark/index.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,93 @@
|
||||
# Qodo Merge Code Fine-tuning Benchmark
|
||||
|
||||
On coding tasks, the gap between open-source models and top closed-source models such as GPT4 is significant.
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
In practice, open-source models are unsuitable for most real-world code tasks, and require further fine-tuning to produce acceptable results.
|
||||
|
||||
_Qodo Merge fine-tuning benchmark_ aims to benchmark open-source models on their ability to be fine-tuned for a coding task.
|
||||
Specifically, we chose to fine-tune open-source models on the task of analyzing a pull request, and providing useful feedback and code suggestions.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are the results:
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
|
||||
**Model performance:**
|
||||
|
||||
| Model name | Model size [B] | Better than gpt-4 rate, after fine-tuning [%] |
|
||||
|-----------------------------|----------------|----------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| **DeepSeek 34B-instruct** | **34** | **40.7** |
|
||||
| DeepSeek 34B-base | 34 | 38.2 |
|
||||
| Phind-34b | 34 | 38 |
|
||||
| Granite-34B | 34 | 37.6 |
|
||||
| Codestral-22B-v0.1 | 22 | 32.7 |
|
||||
| QWEN-1.5-32B | 32 | 29 |
|
||||
| | | |
|
||||
| **CodeQwen1.5-7B** | **7** | **35.4** |
|
||||
| Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct | 8 | 35.2 |
|
||||
| Granite-8b-code-instruct | 8 | 34.2 |
|
||||
| CodeLlama-7b-hf | 7 | 31.8 |
|
||||
| Gemma-7B | 7 | 27.2 |
|
||||
| DeepSeek coder-7b-instruct | 7 | 26.8 |
|
||||
| Llama-3-8B-Instruct | 8 | 26.8 |
|
||||
| Mistral-7B-v0.1 | 7 | 16.1 |
|
||||
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
|
||||
**Fine-tuning impact:**
|
||||
|
||||
| Model name | Model size [B] | Fine-tuned | Better than gpt-4 rate [%] |
|
||||
|---------------------------|----------------|------------|----------------------------|
|
||||
| DeepSeek 34B-instruct | 34 | yes | 40.7 |
|
||||
| DeepSeek 34B-instruct | 34 | no | 3.6 |
|
||||
|
||||
## Results analysis
|
||||
|
||||
- **Fine-tuning is a must** - without fine-tuning, open-source models provide poor results on most real-world code tasks, which include complicated prompt and lengthy context. We clearly see that without fine-tuning, deepseek model was 96.4% of the time inferior to GPT-4, while after fine-tuning, it is better 40.7% of the time.
|
||||
- **Always start from a code-dedicated model** — When fine-tuning, always start from a code-dedicated model, and not from a general-usage model. The gaps in downstream results are very big.
|
||||
- **Don't believe the hype** —newer models, or models from big-tech companies (Llama3, Gemma, Mistral), are not always better for fine-tuning.
|
||||
- **The best large model** - For large 34B code-dedicated models, the gaps when doing proper fine-tuning are small. The current top model is **DeepSeek 34B-instruct**
|
||||
- **The best small model** - For small 7B code-dedicated models, the gaps when fine-tuning are much larger. **CodeQWEN 1.5-7B** is by far the best model for fine-tuning.
|
||||
- **Base vs. instruct** - For the top model (deepseek), we saw small advantage when starting from the instruct version. However, we recommend testing both versions on each specific task, as the base model is generally considered more suitable for fine-tuning.
|
||||
|
||||
## The dataset
|
||||
|
||||
### Training dataset
|
||||
|
||||
Our training dataset comprises 25,000 pull requests, aggregated from permissive license repos. For each pull request, we generated responses for the three main tools of Qodo Merge:
|
||||
[Describe](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/describe/), [Review](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/) and [Improve](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/).
|
||||
|
||||
On the raw data collected, we employed various automatic and manual cleaning techniques to ensure the outputs were of the highest quality, and suitable for instruct-tuning.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are the prompts, and example outputs, used as input-output pairs to fine-tune the models:
|
||||
|
||||
| Tool | Prompt | Example output |
|
||||
|----------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------|
|
||||
| Describe | [link](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/pr_description_prompts.toml) | [link](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/910#issue-2303989601) |
|
||||
| Review | [link](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/pr_reviewer_prompts.toml) | [link](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/910#issuecomment-2118761219) |
|
||||
| Improve | [link](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/pr_code_suggestions_prompts.toml) | [link](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/910#issuecomment-2118761309) |
|
||||
|
||||
### Evaluation dataset
|
||||
|
||||
- For each tool, we aggregated 100 additional examples to be used for evaluation. These examples were not used in the training dataset, and were manually selected to represent diverse real-world use-cases.
|
||||
- For each test example, we generated two responses: one from the fine-tuned model, and one from the best code model in the world, `gpt-4-turbo-2024-04-09`.
|
||||
|
||||
- We used a third LLM to judge which response better answers the prompt, and will likely be perceived by a human as better response.
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
|
||||
We experimented with three model as judges: `gpt-4-turbo-2024-04-09`, `gpt-4o`, and `claude-3-opus-20240229`. All three produced similar results, with the same ranking order. This strengthens the validity of our testing protocol.
|
||||
The evaluation prompt can be found [here](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/pr_evaluate_prompt_response.toml)
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example of a judge model feedback:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
command: improve
|
||||
model1_score: 9,
|
||||
model2_score: 6,
|
||||
why: |
|
||||
Response 1 is better because it provides more actionable and specific suggestions that directly
|
||||
enhance the code's maintainability, performance, and best practices. For example, it suggests
|
||||
using a variable for reusable widget instances and using named routes for navigation, which
|
||||
are practical improvements. In contrast, Response 2 focuses more on general advice and less
|
||||
actionable suggestions, such as changing variable names and adding comments, which are less
|
||||
critical for immediate code improvement."
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -1,17 +1,15 @@
|
||||
# Overview
|
||||
|
||||
[PR-Agent](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent) is an open-source tool to help efficiently review and handle pull requests.
|
||||
Qodo Merge is a hosted version of PR-Agent, designed for companies and teams that require additional features and capabilities
|
||||
Qodo Merge is an open-source tool to help efficiently review and handle pull requests.
|
||||
|
||||
- See the [Installation Guide](./installation/index.md) for instructions on installing and running the tool on different git platforms.
|
||||
|
||||
- See the [Usage Guide](./usage-guide/index.md) for instructions on running commands via different interfaces, including _CLI_, _online usage_, or by _automatically triggering_ them when a new PR is opened.
|
||||
- See the [Usage Guide](./usage-guide/index.md) for instructions on running the Qodo Merge commands via different interfaces, including _CLI_, _online usage_, or by _automatically triggering_ them when a new PR is opened.
|
||||
|
||||
- See the [Tools Guide](./tools/index.md) for a detailed description of the different tools.
|
||||
|
||||
- See the [Video Tutorials](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLRTpyDOSgbwFMA_VBeKMnPLaaZKwjGBFT) for practical demonstrations on how to use the tools.
|
||||
|
||||
## Docs Smart Search
|
||||
## Qodo Merge Docs Smart Search
|
||||
|
||||
To search the documentation site using natural language:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -20,84 +18,67 @@ To search the documentation site using natural language:
|
||||
- A pull request where Qodo Merge is installed
|
||||
- A [PR Chat](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/chrome-extension/features/#pr-chat)
|
||||
|
||||
2) The bot will respond with an [answer](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/1241#issuecomment-2365259334) that includes relevant documentation links.
|
||||
2) Qodo Merge will respond with an [answer](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/1241#issuecomment-2365259334) that includes relevant documentation links.
|
||||
|
||||
## Features
|
||||
|
||||
PR-Agent and Qodo Merge offers extensive pull request functionalities across various git providers:
|
||||
## Qodo Merge Features
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge offers extensive pull request functionalities across various git providers.
|
||||
|
||||
| | | GitHub | Gitlab | Bitbucket | Azure DevOps |
|
||||
|-------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|:------:|:------:|:---------:|:------------:|
|
||||
| TOOLS | Review | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | ⮑ Incremental | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | Ask | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | Describe | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | ⮑ [Inline file summary](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/describe/#inline-file-summary){:target="_blank"} 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | Improve | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | ⮑ Extended | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Custom Prompt](./tools/custom_prompt.md){:target="_blank"} 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | Reflect and Review | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | Update CHANGELOG.md | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ️ |
|
||||
| | Find Similar Issue | ✅ | | | ️ |
|
||||
| | [Add PR Documentation](./tools/documentation.md){:target="_blank"} 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Generate Custom Labels](./tools/describe.md#handle-custom-labels-from-the-repos-labels-page-💎){:target="_blank"} 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Analyze PR Components](./tools/analyze.md){:target="_blank"} 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | | | | | ️ |
|
||||
| USAGE | CLI | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | App / webhook | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | Actions | ✅ | | | ️ |
|
||||
| | | | | |
|
||||
| CORE | PR compression | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | Repo language prioritization | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | Adaptive and token-aware file patch fitting | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | Multiple models support | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | Incremental PR review | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | [Static code analysis](./tools/analyze.md/){:target="_blank"} 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | [Multiple configuration options](./usage-guide/configuration_options.md){:target="_blank"} 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
|
||||
💎 marks a feature available only in [Qodo Merge Pro](https://www.codium.ai/pricing/){:target="_blank"}
|
||||
|
||||
| | | GitHub | GitLab | Bitbucket | Azure DevOps |
|
||||
| ----- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |:------:|:------:|:---------:|:------------:|
|
||||
| TOOLS | [Review](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/review/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Describe](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/describe/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Improve](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Ask](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/ask/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | ⮑ [Ask on code lines](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/ask/#ask-lines) | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Update CHANGELOG](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/update_changelog/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Help Docs](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/help_docs/?h=auto#auto-approval) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | [Ticket Context](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/fetching_ticket_context/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | [Utilizing Best Practices](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#best-practices) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | [PR Chat](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/chrome-extension/features/#pr-chat) 💎 | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | [Suggestion Tracking](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#suggestion-tracking) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [CI Feedback](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/ci_feedback/) 💎 | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | [PR Documentation](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/documentation/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Custom Labels](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/custom_labels/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Analyze](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/analyze/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Similar Code](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/similar_code/) 💎 | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | [Custom Prompt](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/custom_prompt/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | [Test](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/test/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Implement](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/implement/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | [Scan Repo Discussions](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/scan_repo_discussions/) 💎 | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | [Repo Statistics](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/repo_statistics/) 💎 | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | [Auto-Approve](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/?h=auto#auto-approval) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | | | | | |
|
||||
| USAGE | [CLI](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/automations_and_usage/#local-repo-cli) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [App / webhook](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/automations_and_usage/#github-app) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Tagging bot](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent#try-it-now) | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | [Actions](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/github/#run-as-a-github-action) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | | | | | |
|
||||
| CORE | [PR compression](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/compression_strategy/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | Adaptive and token-aware file patch fitting | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Multiple models support](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/changing_a_model/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Local and global metadata](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/metadata/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Dynamic context](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/dynamic_context/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Self reflection](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/self_reflection/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Static code analysis](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/static_code_analysis/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Global and wiki configurations](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | [PR interactive actions](https://www.qodo.ai/images/pr_agent/pr-actions.mp4) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Impact Evaluation](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/impact_evaluation/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Code Validation 💎](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/code_validation/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Auto Best Practices 💎](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/auto_best_practices/) | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
!!! note "💎 means Qodo Merge only"
|
||||
All along the documentation, 💎 marks a feature available only in [Qodo Merge](https://www.codium.ai/pricing/){:target="_blank"}, and not in the open-source version.
|
||||
|
||||
## Example Results
|
||||
|
||||
<hr>
|
||||
|
||||
#### [/describe](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/530)
|
||||
|
||||
<figure markdown="1">
|
||||
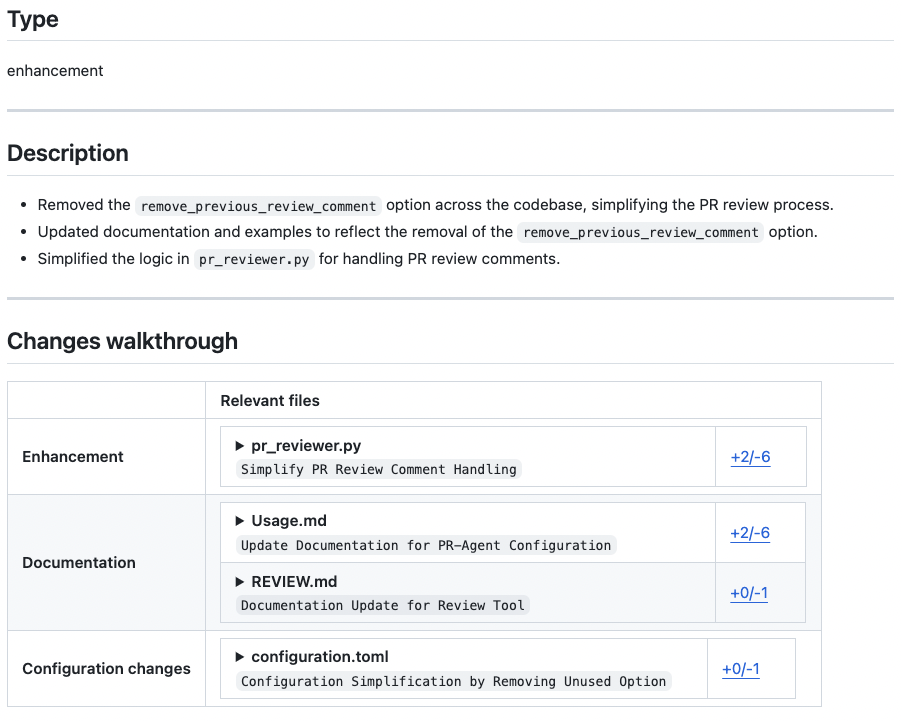{width=512}
|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
<hr>
|
||||
|
||||
#### [/review](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/732#issuecomment-1975099151)
|
||||
|
||||
<figure markdown="1">
|
||||
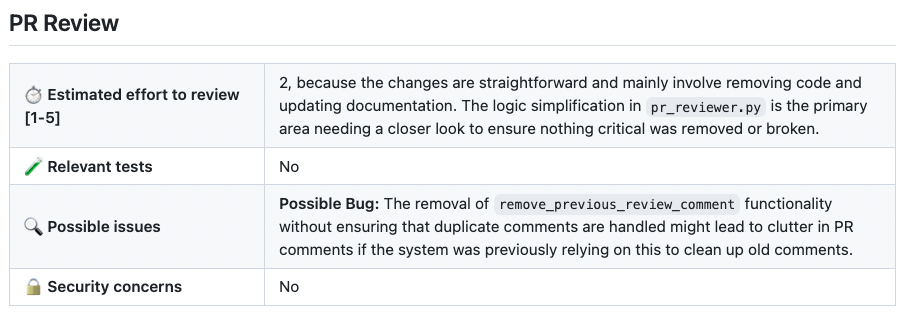{width=512}
|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
<hr>
|
||||
|
||||
#### [/improve](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/732#issuecomment-1975099159)
|
||||
|
||||
<figure markdown="1">
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
<hr>
|
||||
|
||||
#### [/generate_labels](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/530)
|
||||
|
||||
<figure markdown="1">
|
||||
{width=300}
|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
@ -109,4 +90,4 @@ The following diagram illustrates Qodo Merge tools and their flow:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Check out the [PR Compression strategy](core-abilities/index.md) page for more details on how we convert a code diff to a manageable LLM prompt
|
||||
Check out the [core abilities](core-abilities/index.md) page for a comprehensive overview of the variety of core abilities used by Qodo Merge.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
|
||||
## Azure DevOps Pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
You can use a pre-built Action Docker image to run PR-Agent as an Azure devops pipeline.
|
||||
You can use a pre-built Action Docker image to run Qodo Merge as an Azure devops pipeline.
|
||||
add the following file to your repository under `azure-pipelines.yml`:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
# Opt out of CI triggers
|
||||
trigger: none
|
||||
@ -42,7 +40,7 @@ stages:
|
||||
|
||||
export azure_devops__org="$ORG_URL"
|
||||
export config__git_provider="azure"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
pr-agent --pr_url="$PR_URL" describe
|
||||
pr-agent --pr_url="$PR_URL" review
|
||||
pr-agent --pr_url="$PR_URL" improve
|
||||
@ -51,51 +49,45 @@ stages:
|
||||
openai__key: $(OPENAI_KEY)
|
||||
displayName: 'Run Qodo Merge'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This script will run Qodo Merge on every new merge request, with the `improve`, `review`, and `describe` commands.
|
||||
Note that you need to export the `azure_devops__pat` and `OPENAI_KEY` variables in the Azure DevOps pipeline settings (Pipelines -> Library -> + Variable group):
|
||||
|
||||
{width=468}
|
||||
{width=468}
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to give pipeline permissions to the `pr_agent` variable group.
|
||||
|
||||
> Note that Azure Pipelines lacks support for triggering workflows from PR comments. If you find a viable solution, please contribute it to our [issue tracker](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/issues)
|
||||
|
||||
## Azure DevOps from CLI
|
||||
|
||||
To use Azure DevOps provider use the following settings in configuration.toml:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
git_provider="azure"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Azure DevOps provider supports [PAT token](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/devops/organizations/accounts/use-personal-access-tokens-to-authenticate?view=azure-devops&tabs=Windows) or [DefaultAzureCredential](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/developer/python/sdk/authentication-overview#authentication-in-server-environments) authentication.
|
||||
PAT is faster to create, but has build in expiration date, and will use the user identity for API calls.
|
||||
PAT is faster to create, but has build in expiration date, and will use the user identity for API calls.
|
||||
Using DefaultAzureCredential you can use managed identity or Service principle, which are more secure and will create separate ADO user identity (via AAD) to the agent.
|
||||
|
||||
If PAT was chosen, you can assign the value in .secrets.toml.
|
||||
If DefaultAzureCredential was chosen, you can assigned the additional env vars like AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET directly,
|
||||
If PAT was chosen, you can assign the value in .secrets.toml.
|
||||
If DefaultAzureCredential was chosen, you can assigned the additional env vars like AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET directly,
|
||||
or use managed identity/az cli (for local development) without any additional configuration.
|
||||
in any case, 'org' value must be assigned in .secrets.toml:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[azure_devops]
|
||||
org = "https://dev.azure.com/YOUR_ORGANIZATION/"
|
||||
# pat = "YOUR_PAT_TOKEN" needed only if using PAT for authentication
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Azure DevOps Webhook
|
||||
### Azure DevOps Webhook
|
||||
|
||||
To trigger from an Azure webhook, you need to manually [add a webhook](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/devops/service-hooks/services/webhooks?view=azure-devops).
|
||||
To trigger from an Azure webhook, you need to manually [add a webhook](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/devops/service-hooks/services/webhooks?view=azure-devops).
|
||||
Use the "Pull request created" type to trigger a review, or "Pull request commented on" to trigger any supported comment with /<command> <args> comment on the relevant PR. Note that for the "Pull request commented on" trigger, only API v2.0 is supported.
|
||||
|
||||
For webhook security, create a sporadic username/password pair and configure the webhook username and password on both the server and Azure DevOps webhook. These will be sent as basic Auth data by the webhook with each request:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
For webhook security, create a sporadic username/password pair and configure the webhook username and password on both the server and Azure DevOps webhook. These will be sent as basic Auth data by the webhook with each request:
|
||||
```
|
||||
[azure_devops_server]
|
||||
webhook_username = "<basic auth user>"
|
||||
webhook_password = "<basic auth password>"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> :warning: **Ensure that the webhook endpoint is only accessible over HTTPS** to mitigate the risk of credential interception when using basic authentication.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,8 +1,9 @@
|
||||
## Run as a Bitbucket Pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
You can use the Bitbucket Pipeline system to run PR-Agent on every pull request open or update.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Add the following file in your repository bitbucket-pipelines.yml
|
||||
You can use the Bitbucket Pipeline system to run Qodo Merge on every pull request open or update.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Add the following file in your repository bitbucket_pipelines.yml
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
pipelines:
|
||||
@ -10,24 +11,27 @@ pipelines:
|
||||
'**':
|
||||
- step:
|
||||
name: PR Agent Review
|
||||
image: codiumai/pr-agent:latest
|
||||
image: python:3.10
|
||||
services:
|
||||
- docker
|
||||
script:
|
||||
- pr-agent --pr_url=https://bitbucket.org/$BITBUCKET_WORKSPACE/$BITBUCKET_REPO_SLUG/pull-requests/$BITBUCKET_PR_ID review
|
||||
- docker run -e CONFIG.GIT_PROVIDER=bitbucket -e OPENAI.KEY=$OPENAI_API_KEY -e BITBUCKET.BEARER_TOKEN=$BITBUCKET_BEARER_TOKEN codiumai/pr-agent:latest --pr_url=https://bitbucket.org/$BITBUCKET_WORKSPACE/$BITBUCKET_REPO_SLUG/pull-requests/$BITBUCKET_PR_ID review
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Add the following secure variables to your repository under Repository settings > Pipelines > Repository variables.
|
||||
|
||||
- CONFIG__GIT_PROVIDER: `bitbucket`
|
||||
- OPENAI__KEY: `<your key>`
|
||||
- BITBUCKET__AUTH_TYPE: `basic` or `bearer` (default is `bearer`)
|
||||
- BITBUCKET__BEARER_TOKEN: `<your token>` (required when auth_type is bearer)
|
||||
- BITBUCKET__BASIC_TOKEN: `<your token>` (required when auth_type is basic)
|
||||
OPENAI_API_KEY: `<your key>`
|
||||
BITBUCKET_BEARER_TOKEN: `<your token>`
|
||||
|
||||
You can get a Bitbucket token for your repository by following Repository Settings -> Security -> Access Tokens.
|
||||
For basic auth, you can generate a base64 encoded token from your username:password combination.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that comments on a PR are not supported in Bitbucket Pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Run using CodiumAI-hosted Bitbucket app 💎
|
||||
|
||||
Please contact visit [Qodo Merge Pro](https://www.codium.ai/pricing/) if you're interested in a hosted BitBucket app solution that provides full functionality including PR reviews and comment handling. It's based on the [bitbucket_app.py](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/git_providers/bitbucket_provider.py) implementation.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Bitbucket Server and Data Center
|
||||
|
||||
Login into your on-prem instance of Bitbucket with your service account username and password.
|
||||
@ -48,16 +52,14 @@ git_provider="bitbucket_server"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and pass the Pull request URL:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
python cli.py --pr_url https://git.onpreminstanceofbitbucket.com/projects/PROJECT/repos/REPO/pull-requests/1 review
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Run it as service
|
||||
|
||||
To run PR-Agent as webhook, build the docker image:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
To run Qodo Merge as webhook, build the docker image:
|
||||
```
|
||||
docker build . -t codiumai/pr-agent:bitbucket_server_webhook --target bitbucket_server_webhook -f docker/Dockerfile
|
||||
docker push codiumai/pr-agent:bitbucket_server_webhook # Push to your Docker repository
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
## Run as a GitHub Action
|
||||
|
||||
You can use our pre-built Github Action Docker image to run PR-Agent as a Github Action.
|
||||
You can use our pre-built Github Action Docker image to run Qodo Merge as a Github Action.
|
||||
|
||||
1) Add the following file to your repository under `.github/workflows/pr_agent.yml`:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -21,7 +21,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: PR Agent action step
|
||||
id: pragent
|
||||
uses: qodo-ai/pr-agent@main
|
||||
uses: Codium-ai/pr-agent@main
|
||||
env:
|
||||
OPENAI_KEY: ${{ secrets.OPENAI_KEY }}
|
||||
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
@ -40,7 +40,6 @@ The GITHUB_TOKEN secret is automatically created by GitHub.
|
||||
When you open your next PR, you should see a comment from `github-actions` bot with a review of your PR, and instructions on how to use the rest of the tools.
|
||||
|
||||
4) You may configure Qodo Merge by adding environment variables under the env section corresponding to any configurable property in the [configuration](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml) file. Some examples:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
env:
|
||||
# ... previous environment values
|
||||
@ -48,11 +47,9 @@ When you open your next PR, you should see a comment from `github-actions` bot w
|
||||
PR_REVIEWER.REQUIRE_TESTS_REVIEW: "false" # Disable tests review
|
||||
PR_CODE_SUGGESTIONS.NUM_CODE_SUGGESTIONS: 6 # Increase number of code suggestions
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
See detailed usage instructions in the [USAGE GUIDE](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/automations_and_usage/#github-action)
|
||||
|
||||
### Using a specific release
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip ""
|
||||
if you want to pin your action to a specific release (v0.23 for example) for stability reasons, use:
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
@ -63,7 +60,7 @@ See detailed usage instructions in the [USAGE GUIDE](https://qodo-merge-docs.qod
|
||||
uses: docker://codiumai/pr-agent:0.23-github_action
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
For enhanced security, you can also specify the Docker image by its [digest](https://hub.docker.com/repository/docker/codiumai/pr-agent/tags):
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
...
|
||||
@ -74,22 +71,21 @@ See detailed usage instructions in the [USAGE GUIDE](https://qodo-merge-docs.qod
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Action for GitHub enterprise server
|
||||
|
||||
### Action for GitHub enterprise server
|
||||
!!! tip ""
|
||||
To use the action with a GitHub enterprise server, add an environment variable `GITHUB.BASE_URL` with the API URL of your GitHub server.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
For example, if your GitHub server is at `https://github.mycompany.com`, add the following to your workflow file:
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
env:
|
||||
# ... previous environment values
|
||||
GITHUB.BASE_URL: "https://github.mycompany.com/api/v3"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Run as a GitHub App
|
||||
|
||||
Allowing you to automate the review process on your private or public repositories.
|
||||
|
||||
1) Create a GitHub App from the [Github Developer Portal](https://docs.github.com/en/developers/apps/creating-a-github-app).
|
||||
@ -106,7 +102,7 @@ Allowing you to automate the review process on your private or public repositori
|
||||
|
||||
2) Generate a random secret for your app, and save it for later. For example, you can use:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
```
|
||||
WEBHOOK_SECRET=$(python -c "import secrets; print(secrets.token_hex(10))")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@ -117,29 +113,28 @@ WEBHOOK_SECRET=$(python -c "import secrets; print(secrets.token_hex(10))")
|
||||
|
||||
4) Clone this repository:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
```
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
5) Copy the secrets template file and fill in the following:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
cp pr_agent/settings/.secrets_template.toml pr_agent/settings/.secrets.toml
|
||||
# Edit .secrets.toml file
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- Your OpenAI key.
|
||||
- Copy your app's private key to the private_key field.
|
||||
- Copy your app's ID to the app_id field.
|
||||
- Copy your app's webhook secret to the webhook_secret field.
|
||||
- Set deployment_type to 'app' in [configuration.toml](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml)
|
||||
- Your OpenAI key.
|
||||
- Copy your app's private key to the private_key field.
|
||||
- Copy your app's ID to the app_id field.
|
||||
- Copy your app's webhook secret to the webhook_secret field.
|
||||
- Set deployment_type to 'app' in [configuration.toml](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml)
|
||||
|
||||
> The .secrets.toml file is not copied to the Docker image by default, and is only used for local development.
|
||||
> If you want to use the .secrets.toml file in your Docker image, you can add remove it from the .dockerignore file.
|
||||
> In most production environments, you would inject the secrets file as environment variables or as mounted volumes.
|
||||
> For example, in order to inject a secrets file as a volume in a Kubernetes environment you can update your pod spec to include the following,
|
||||
> assuming you have a secret named `pr-agent-settings` with a key named `.secrets.toml`:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
volumes:
|
||||
- name: settings-volume
|
||||
@ -152,12 +147,12 @@ cp pr_agent/settings/.secrets_template.toml pr_agent/settings/.secrets.toml
|
||||
- mountPath: /app/pr_agent/settings_prod
|
||||
name: settings-volume
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
> Another option is to set the secrets as environment variables in your deployment environment, for example `OPENAI.KEY` and `GITHUB.USER_TOKEN`.
|
||||
|
||||
6) Build a Docker image for the app and optionally push it to a Docker repository. We'll use Dockerhub as an example:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
```
|
||||
docker build . -t codiumai/pr-agent:github_app --target github_app -f docker/Dockerfile
|
||||
docker push codiumai/pr-agent:github_app # Push to your Docker repository
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -185,19 +180,14 @@ For example: `GITHUB.WEBHOOK_SECRET` --> `GITHUB__WEBHOOK_SECRET`
|
||||
|
||||
1. Follow steps 1-5 from [here](#run-as-a-github-app).
|
||||
2. Build a docker image that can be used as a lambda function
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
docker buildx build --platform=linux/amd64 . -t codiumai/pr-agent:serverless -f docker/Dockerfile.lambda
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Push image to ECR
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
|
||||
docker tag codiumai/pr-agent:serverless <AWS_ACCOUNT>.dkr.ecr.<AWS_REGION>.amazonaws.com/codiumai/pr-agent:serverless
|
||||
docker push <AWS_ACCOUNT>.dkr.ecr.<AWS_REGION>.amazonaws.com/codiumai/pr-agent:serverless
|
||||
docker tag codiumai/pr-agent:serverless <AWS_ACCOUNT>.dkr.ecr.<AWS_REGION>.amazonaws.com/codiumai/pr-agent:serverless
|
||||
docker push <AWS_ACCOUNT>.dkr.ecr.<AWS_REGION>.amazonaws.com/codiumai/pr-agent:serverless
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4. Create a lambda function that uses the uploaded image. Set the lambda timeout to be at least 3m.
|
||||
5. Configure the lambda function to have a Function URL.
|
||||
6. In the environment variables of the Lambda function, specify `AZURE_DEVOPS_CACHE_DIR` to a writable location such as /tmp. (see [link](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/450#issuecomment-1840242269))
|
||||
@ -211,27 +201,28 @@ For example: `GITHUB.WEBHOOK_SECRET` --> `GITHUB__WEBHOOK_SECRET`
|
||||
Not all features have been added to CodeCommit yet. As of right now, CodeCommit has been implemented to run the Qodo Merge CLI on the command line, using AWS credentials stored in environment variables. (More features will be added in the future.) The following is a set of instructions to have Qodo Merge do a review of your CodeCommit pull request from the command line:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Create an IAM user that you will use to read CodeCommit pull requests and post comments
|
||||
- Note: That user should have CLI access only, not Console access
|
||||
* Note: That user should have CLI access only, not Console access
|
||||
2. Add IAM permissions to that user, to allow access to CodeCommit (see IAM Role example below)
|
||||
3. Generate an Access Key for your IAM user
|
||||
4. Set the Access Key and Secret using environment variables (see Access Key example below)
|
||||
5. Set the `git_provider` value to `codecommit` in the `pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml` settings file
|
||||
6. Set the `PYTHONPATH` to include your `pr-agent` project directory
|
||||
- Option A: Add `PYTHONPATH="/PATH/TO/PROJECTS/pr-agent` to your `.env` file
|
||||
- Option B: Set `PYTHONPATH` and run the CLI in one command, for example:
|
||||
- `PYTHONPATH="/PATH/TO/PROJECTS/pr-agent python pr_agent/cli.py [--ARGS]`
|
||||
* Option A: Add `PYTHONPATH="/PATH/TO/PROJECTS/pr-agent` to your `.env` file
|
||||
* Option B: Set `PYTHONPATH` and run the CLI in one command, for example:
|
||||
* `PYTHONPATH="/PATH/TO/PROJECTS/pr-agent python pr_agent/cli.py [--ARGS]`
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### AWS CodeCommit IAM Role Example
|
||||
|
||||
Example IAM permissions to that user to allow access to CodeCommit:
|
||||
|
||||
- Note: The following is a working example of IAM permissions that has read access to the repositories and write access to allow posting comments
|
||||
- Note: If you only want pr-agent to review your pull requests, you can tighten the IAM permissions further, however this IAM example will work, and allow the pr-agent to post comments to the PR
|
||||
- Note: You may want to replace the `"Resource": "*"` with your list of repos, to limit access to only those repos
|
||||
* Note: The following is a working example of IAM permissions that has read access to the repositories and write access to allow posting comments
|
||||
* Note: If you only want pr-agent to review your pull requests, you can tighten the IAM permissions further, however this IAM example will work, and allow the pr-agent to post comments to the PR
|
||||
* Note: You may want to replace the `"Resource": "*"` with your list of repos, to limit access to only those repos
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
```
|
||||
{
|
||||
"Version": "2012-10-17",
|
||||
"Statement": [
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
|
||||
## Run as a GitLab Pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
You can use a pre-built Action Docker image to run PR-Agent as a GitLab pipeline. This is a simple way to get started with Qodo Merge without setting up your own server.
|
||||
You can use a pre-built Action Docker image to run Qodo Merge as a GitLab pipeline. This is a simple way to get started with Qodo Merge without setting up your own server.
|
||||
|
||||
(1) Add the following file to your repository under `.gitlab-ci.yml`:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
stages:
|
||||
- pr_agent
|
||||
@ -28,10 +26,10 @@ pr_agent_job:
|
||||
rules:
|
||||
- if: '$CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == "merge_request_event"'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This script will run Qodo Merge on every new merge request. You can modify the `rules` section to run Qodo Merge on different events.
|
||||
You can also modify the `script` section to run different Qodo Merge commands, or with different parameters by exporting different environment variables.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
(2) Add the following masked variables to your GitLab repository (CI/CD -> Variables):
|
||||
|
||||
- `GITLAB_PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN`: Your GitLab personal access token.
|
||||
@ -40,51 +38,25 @@ You can also modify the `script` section to run different Qodo Merge commands, o
|
||||
|
||||
Note that if your base branches are not protected, don't set the variables as `protected`, since the pipeline will not have access to them.
|
||||
|
||||
> **Note**: The `$CI_SERVER_FQDN` variable is available starting from GitLab version 16.10. If you're using an earlier version, this variable will not be available. However, you can combine `$CI_SERVER_HOST` and `$CI_SERVER_PORT` to achieve the same result. Please ensure you're using a compatible version or adjust your configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Run a GitLab webhook server
|
||||
|
||||
1. In GitLab create a new user and give it "Reporter" role ("Developer" if using Pro version of the agent) for the intended group or project.
|
||||
1. From the GitLab workspace or group, create an access token. Enable the "api" scope only.
|
||||
|
||||
2. For the user from step 1. generate a `personal_access_token` with `api` access.
|
||||
2. Generate a random secret for your app, and save it for later. For example, you can use:
|
||||
|
||||
3. Generate a random secret for your app, and save it for later (`shared_secret`). For example, you can use:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
SHARED_SECRET=$(python -c "import secrets; print(secrets.token_hex(10))")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4. Clone this repository:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/qodo-ai/pr-agent.git
|
||||
WEBHOOK_SECRET=$(python -c "import secrets; print(secrets.token_hex(10))")
|
||||
```
|
||||
3. Follow the instructions to build the Docker image, setup a secrets file and deploy on your own server from [here](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/github/#run-as-a-github-app) steps 4-7.
|
||||
|
||||
5. Prepare variables and secrets. Skip this step if you plan on setting these as environment variables when running the agent:
|
||||
1. In the configuration file/variables:
|
||||
- Set `config.git_provider` to "gitlab"
|
||||
4. In the secrets file, fill in the following:
|
||||
- Your OpenAI key.
|
||||
- In the [gitlab] section, fill in personal_access_token and shared_secret. The access token can be a personal access token, or a group or project access token.
|
||||
- Set deployment_type to 'gitlab' in [configuration.toml](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml)
|
||||
|
||||
2. In the secrets file/variables:
|
||||
- Set your AI model key in the respective section
|
||||
- In the [gitlab] section, set `personal_access_token` (with token from step 2) and `shared_secret` (with secret from step 3)
|
||||
5. Create a webhook in GitLab. Set the URL to ```http[s]://<PR_AGENT_HOSTNAME>/webhook```. Set the secret token to the generated secret from step 2.
|
||||
In the "Trigger" section, check the ‘comments’ and ‘merge request events’ boxes.
|
||||
|
||||
6. Build a Docker image for the app and optionally push it to a Docker repository. We'll use Dockerhub as an example:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
docker build . -t gitlab_pr_agent --target gitlab_webhook -f docker/Dockerfile
|
||||
docker push codiumai/pr-agent:gitlab_webhook # Push to your Docker repository
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
7. Set the environmental variables, the method depends on your docker runtime. Skip this step if you included your secrets/configuration directly in the Docker image.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
CONFIG__GIT_PROVIDER=gitlab
|
||||
GITLAB__PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN=<personal_access_token>
|
||||
GITLAB__SHARED_SECRET=<shared_secret>
|
||||
GITLAB__URL=https://gitlab.com
|
||||
OPENAI__KEY=<your_openai_api_key>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
8. Create a webhook in your GitLab project. Set the URL to `http[s]://<PR_AGENT_HOSTNAME>/webhook`, the secret token to the generated secret from step 3, and enable the triggers `push`, `comments` and `merge request events`.
|
||||
|
||||
9. Test your installation by opening a merge request or commenting on a merge request using one of PR Agent's commands.
|
||||
6. Test your installation by opening a merge request or commenting or a merge request using one of CodiumAI's commands.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,18 +1,21 @@
|
||||
# Installation
|
||||
|
||||
## Self-hosted PR-Agent
|
||||
## Self-hosted Qodo Merge
|
||||
If you choose to host your own Qodo Merge, you first need to acquire two tokens:
|
||||
|
||||
There are several ways to use self-hosted PR-Agent:
|
||||
1. An OpenAI key from [here](https://platform.openai.com/api-keys), with access to GPT-4 (or a key for other [language models](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/changing_a_model/), if you prefer).
|
||||
2. A GitHub\GitLab\BitBucket personal access token (classic), with the repo scope. [GitHub from [here](https://github.com/settings/tokens)]
|
||||
|
||||
There are several ways to use self-hosted Qodo Merge:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Locally](./locally.md)
|
||||
- [GitHub integration](./github.md)
|
||||
- [GitLab integration](./gitlab.md)
|
||||
- [BitBucket integration](./bitbucket.md)
|
||||
- [Azure DevOps integration](./azure.md)
|
||||
- [GitHub](./github.md)
|
||||
- [GitLab](./gitlab.md)
|
||||
- [BitBucket](./bitbucket.md)
|
||||
- [Azure DevOps](./azure.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## Qodo Merge 💎
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge, an app hosted by QodoAI for GitHub\GitLab\BitBucket, is also available.
|
||||
## Qodo Merge Pro 💎
|
||||
Qodo Merge Pro, an app hosted by CodiumAI for GitHub\GitLab\BitBucket, is also available.
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
With Qodo Merge, installation is as simple as adding the Qodo Merge app to your relevant repositories.
|
||||
See [here](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/qodo_merge/) for more details.
|
||||
With Qodo Merge Pro, installation is as simple as signing up and adding the Qodo Merge app to your relevant repo.
|
||||
See [here](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/pr_agent_pro/) for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,87 +1,8 @@
|
||||
To run PR-Agent locally, you first need to acquire two keys:
|
||||
|
||||
1. An OpenAI key from [here](https://platform.openai.com/api-keys){:target="_blank"}, with access to GPT-4 and o4-mini (or a key for other [language models](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/changing_a_model/), if you prefer).
|
||||
2. A personal access token from your Git platform (GitHub, GitLab, BitBucket) with repo scope. GitHub token, for example, can be issued from [here](https://github.com/settings/tokens){:target="_blank"}
|
||||
|
||||
## Using Docker image
|
||||
|
||||
A list of the relevant tools can be found in the [tools guide](../tools/).
|
||||
|
||||
To invoke a tool (for example `review`), you can run PR-Agent directly from the Docker image. Here's how:
|
||||
|
||||
- For GitHub:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
docker run --rm -it -e OPENAI.KEY=<your key> -e GITHUB.USER_TOKEN=<your token> codiumai/pr-agent:latest --pr_url <pr_url> review
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you are using GitHub enterprise server, you need to specify the custom url as variable.
|
||||
For example, if your GitHub server is at `https://github.mycompany.com`, add the following to the command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
-e GITHUB.BASE_URL=https://github.mycompany.com/api/v3
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- For GitLab:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
docker run --rm -it -e OPENAI.KEY=<your key> -e CONFIG.GIT_PROVIDER=gitlab -e GITLAB.PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN=<your token> codiumai/pr-agent:latest --pr_url <pr_url> review
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you have a dedicated GitLab instance, you need to specify the custom url as variable:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
-e GITLAB.URL=<your gitlab instance url>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- For BitBucket:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
docker run --rm -it -e CONFIG.GIT_PROVIDER=bitbucket -e OPENAI.KEY=$OPENAI_API_KEY -e BITBUCKET.BEARER_TOKEN=$BITBUCKET_BEARER_TOKEN codiumai/pr-agent:latest --pr_url=<pr_url> review
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For other git providers, update `CONFIG.GIT_PROVIDER` accordingly and check the [`pr_agent/settings/.secrets_template.toml`](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/.secrets_template.toml) file for environment variables expected names and values.
|
||||
|
||||
### Utilizing environment variables
|
||||
|
||||
It is also possible to provide or override the configuration by setting the corresponding environment variables.
|
||||
You can define the corresponding environment variables by following this convention: `<TABLE>__<KEY>=<VALUE>` or `<TABLE>.<KEY>=<VALUE>`.
|
||||
The `<TABLE>` refers to a table/section in a configuration file and `<KEY>=<VALUE>` refers to the key/value pair of a setting in the configuration file.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, suppose you want to run `pr_agent` that connects to a self-hosted GitLab instance similar to an example above.
|
||||
You can define the environment variables in a plain text file named `.env` with the following content:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
CONFIG__GIT_PROVIDER="gitlab"
|
||||
GITLAB__URL="<your url>"
|
||||
GITLAB__PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN="<your token>"
|
||||
OPENAI__KEY="<your key>"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then, you can run `pr_agent` using Docker with the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
docker run --rm -it --env-file .env codiumai/pr-agent:latest <tool> <tool parameter>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
### I get an error when running the Docker image. What should I do?
|
||||
|
||||
If you encounter an error when running the Docker image, it is almost always due to a misconfiguration of api keys or tokens.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that litellm, which is used by pr-agent, sometimes returns non-informative error messages such as `APIError: OpenAIException - Connection error.`
|
||||
Carefully check the api keys and tokens you provided and make sure they are correct.
|
||||
Adjustments may be needed depending on your llm provider.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, for Azure OpenAI, additional keys are [needed](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/changing_a_model/#azure).
|
||||
Same goes for other providers, make sure to check the [documentation](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/changing_a_model/#changing-a-model)
|
||||
|
||||
## Using pip package
|
||||
|
||||
Install the package:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
```
|
||||
pip install pr-agent
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@ -114,17 +35,52 @@ if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
main()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Using Docker image
|
||||
|
||||
A list of the relevant tools can be found in the [tools guide](../tools/ask.md).
|
||||
|
||||
To invoke a tool (for example `review`), you can run directly from the Docker image. Here's how:
|
||||
|
||||
- For GitHub:
|
||||
```
|
||||
docker run --rm -it -e OPENAI.KEY=<your key> -e GITHUB.USER_TOKEN=<your token> codiumai/pr-agent:latest --pr_url <pr_url> review
|
||||
```
|
||||
If you are using GitHub enterprise server, you need to specify the custom url as variable.
|
||||
For example, if your GitHub server is at `https://github.mycompany.com`, add the following to the command:
|
||||
```
|
||||
-e GITHUB.BASE_URL=https://github.mycompany.com/api/v3
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- For GitLab:
|
||||
```
|
||||
docker run --rm -it -e OPENAI.KEY=<your key> -e CONFIG.GIT_PROVIDER=gitlab -e GITLAB.PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN=<your token> codiumai/pr-agent:latest --pr_url <pr_url> review
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you have a dedicated GitLab instance, you need to specify the custom url as variable:
|
||||
```
|
||||
-e GITLAB.URL=<your gitlab instance url>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- For BitBucket:
|
||||
```
|
||||
docker run --rm -it -e CONFIG.GIT_PROVIDER=bitbucket -e OPENAI.KEY=$OPENAI_API_KEY -e BITBUCKET.BEARER_TOKEN=$BITBUCKET_BEARER_TOKEN codiumai/pr-agent:latest --pr_url=<pr_url> review
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For other git providers, update CONFIG.GIT_PROVIDER accordingly, and check the `pr_agent/settings/.secrets_template.toml` file for the environment variables expected names and values.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Run from source
|
||||
|
||||
1. Clone this repository:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
```
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Navigate to the `/pr-agent` folder and install the requirements in your favorite virtual environment:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
```
|
||||
pip install -e .
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@ -132,7 +88,7 @@ pip install -e .
|
||||
|
||||
3. Copy the secrets template file and fill in your OpenAI key and your GitHub user token:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
```
|
||||
cp pr_agent/settings/.secrets_template.toml pr_agent/settings/.secrets.toml
|
||||
chmod 600 pr_agent/settings/.secrets.toml
|
||||
# Edit .secrets.toml file
|
||||
@ -140,7 +96,7 @@ chmod 600 pr_agent/settings/.secrets.toml
|
||||
|
||||
4. Run the cli.py script:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
```
|
||||
python3 -m pr_agent.cli --pr_url <pr_url> review
|
||||
python3 -m pr_agent.cli --pr_url <pr_url> ask <your question>
|
||||
python3 -m pr_agent.cli --pr_url <pr_url> describe
|
||||
@ -152,7 +108,6 @@ python3 -m pr_agent.cli --issue_url <issue_url> similar_issue
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[Optional] Add the pr_agent folder to your PYTHONPATH
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export PYTHONPATH=$PYTHONPATH:<PATH to pr_agent folder>
|
||||
```
|
||||
export PYTHONPATH=$PYTHONPATH:<PATH to pr_agent folder>
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -1,49 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# PR-Agent Installation Guide
|
||||
|
||||
PR-Agent can be deployed in various environments and platforms. Choose the installation method that best suits your needs:
|
||||
|
||||
## 🖥️ Local Installation
|
||||
|
||||
Learn how to run PR-Agent locally using:
|
||||
|
||||
- Docker image
|
||||
- pip package
|
||||
- CLI from source code
|
||||
|
||||
[View Local Installation Guide →](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/locally/)
|
||||
|
||||
## 🐙 GitHub Integration
|
||||
|
||||
Set up PR-Agent with GitHub as:
|
||||
|
||||
- GitHub Action
|
||||
- Local GitHub App
|
||||
|
||||
[View GitHub Integration Guide →](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/github/)
|
||||
|
||||
## 🦊 GitLab Integration
|
||||
|
||||
Deploy PR-Agent on GitLab as:
|
||||
|
||||
- GitLab pipeline job
|
||||
- Local GitLab webhook server
|
||||
|
||||
[View GitLab Integration Guide →](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/gitlab/)
|
||||
|
||||
## 🟦 BitBucket Integration
|
||||
|
||||
Implement PR-Agent in BitBucket as:
|
||||
|
||||
- BitBucket pipeline job
|
||||
- Local BitBucket server
|
||||
|
||||
[View BitBucket Integration Guide →](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/bitbucket/)
|
||||
|
||||
## 🔷 Azure DevOps Integration
|
||||
|
||||
Configure PR-Agent with Azure DevOps as:
|
||||
|
||||
- Azure DevOps pipeline job
|
||||
- Local Azure DevOps webhook
|
||||
|
||||
[View Azure DevOps Integration Guide →](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/azure/)
|
||||
68
docs/docs/installation/pr_agent_pro.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## Getting Started with Qodo Merge Pro
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge Pro is a versatile application compatible with GitHub, GitLab, and BitBucket, hosted by CodiumAI.
|
||||
See [here](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/overview/pr_agent_pro/) for more details about the benefits of using Qodo Merge Pro.
|
||||
|
||||
Interested parties can subscribe to Qodo Merge Pro through the following [link](https://www.codium.ai/pricing/).
|
||||
After subscribing, you are granted the ability to easily install the application across any of your repositories.
|
||||
|
||||
{width=468}
|
||||
|
||||
Each user who wants to use Qodo Merge pro needs to buy a seat.
|
||||
Initially, CodiumAI offers a two-week trial period at no cost, after which continued access requires each user to secure a personal seat.
|
||||
Once a user acquires a seat, they gain the flexibility to use Qodo Merge Pro across any repository where it was enabled.
|
||||
|
||||
Users without a purchased seat who interact with a repository featuring Qodo Merge Pro are entitled to receive up to five complimentary feedbacks.
|
||||
Beyond this limit, Qodo Merge Pro will cease to respond to their inquiries unless a seat is purchased.
|
||||
|
||||
## Install Qodo Merge Pro for GitHub Enterprise Server
|
||||
|
||||
To use Qodo Merge Pro application on your private GitHub Enterprise Server, you will need to contact us for starting an [Enterprise](https://www.codium.ai/pricing/) trial.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Install Qodo Merge Pro for GitLab (Teams & Enterprise)
|
||||
|
||||
Since GitLab platform does not support apps, installing Qodo Merge Pro for GitLab is a bit more involved, and requires the following steps:
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1
|
||||
|
||||
Acquire a personal, project or group level access token. Enable the “api” scope in order to allow Qodo Merge to read pull requests, comment and respond to requests.
|
||||
|
||||
<figure markdown="1">
|
||||
{width=750}
|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
|
||||
Store the token in a safe place, you won’t be able to access it again after it was generated.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 2
|
||||
|
||||
Generate a shared secret and link it to the access token. Browse to [https://register.gitlab.pr-agent.codium.ai](https://register.gitlab.pr-agent.codium.ai).
|
||||
Fill in your generated GitLab token and your company or personal name in the appropriate fields and click "Submit".
|
||||
|
||||
You should see "Success!" displayed above the Submit button, and a shared secret will be generated. Store it in a safe place, you won’t be able to access it again after it was generated.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 3
|
||||
|
||||
Install a webhook for your repository or groups, by clicking “webhooks” on the settings menu. Click the “Add new webhook” button.
|
||||
|
||||
<figure markdown="1">
|
||||

|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
|
||||
In the webhook definition form, fill in the following fields:
|
||||
URL: https://pro.gitlab.pr-agent.codium.ai/webhook
|
||||
|
||||
Secret token: Your CodiumAI key
|
||||
Trigger: Check the ‘comments’ and ‘merge request events’ boxes.
|
||||
Enable SSL verification: Check the box.
|
||||
|
||||
<figure markdown="1">
|
||||
{width=750}
|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 4
|
||||
|
||||
You’re all set!
|
||||
|
||||
Open a new merge request or add a MR comment with one of Qodo Merge’s commands such as /review, /describe or /improve.
|
||||
@ -1,98 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Qodo Merge is a versatile application compatible with GitHub, GitLab, and BitBucket, hosted by QodoAI.
|
||||
See [here](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/overview/pr_agent_pro/) for more details about the benefits of using Qodo Merge.
|
||||
|
||||
## Trial Period and Licensing
|
||||
|
||||
### Cloud Users with Teams Account
|
||||
|
||||
A complimentary two-week trial is provided to all new users (with three additional grace usages). When the trial period ends, users will stop receiving feedback from Qodo Merge.
|
||||
|
||||
Following the trial period, user licenses (seats) are required for continued access. Each user requires an individual seat license.
|
||||
After purchasing seats, the team owner can assign them to specific users through the management portal.
|
||||
|
||||
With an assigned seat, users can seamlessly deploy the application across any of their code repositories.
|
||||
|
||||
### Enterprise Account
|
||||
|
||||
For organizations who require an Enterprise account, please [contact](https://www.qodo.ai/contact/#pricing) us to initiate a trial period, and to discuss pricing and licensing options.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Install Qodo Merge for GitHub
|
||||
|
||||
### GitHub Cloud
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge for GitHub cloud is available for installation through the [GitHub Marketplace](https://github.com/apps/qodo-merge-pro).
|
||||
|
||||
{width=468}
|
||||
|
||||
### GitHub Enterprise Server
|
||||
|
||||
To use Qodo Merge application on your private GitHub Enterprise Server, you will need to [contact](https://www.qodo.ai/contact/#pricing) Qodo for starting an Enterprise trial.
|
||||
|
||||
### GitHub Open Source Projects
|
||||
|
||||
For open-source projects, Qodo Merge is available for free usage. To install Qodo Merge for your open-source repositories, use the following marketplace [link](https://github.com/apps/qodo-merge-pro-for-open-source).
|
||||
|
||||
## Install Qodo Merge for Bitbucket
|
||||
|
||||
### Bitbucket Cloud
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge for Bitbucket Cloud is available for installation through the following [link](https://bitbucket.org/site/addons/authorize?addon_key=d6df813252c37258)
|
||||
|
||||
{width=468}
|
||||
|
||||
### Bitbucket Server
|
||||
|
||||
To use Qodo Merge application on your private Bitbucket Server, you will need to contact us for starting an [Enterprise](https://www.qodo.ai/pricing/) trial.
|
||||
|
||||
## Install Qodo Merge for GitLab
|
||||
|
||||
### GitLab Cloud
|
||||
|
||||
Since GitLab platform does not support apps, installing Qodo Merge for GitLab is a bit more involved, and requires the following steps:
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 1
|
||||
|
||||
Acquire a personal, project or group level access token. Enable the “api” scope in order to allow Qodo Merge to read pull requests, comment and respond to requests.
|
||||
|
||||
<figure markdown="1">
|
||||
{width=750}
|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
|
||||
Store the token in a safe place, you won’t be able to access it again after it was generated.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 2
|
||||
|
||||
Generate a shared secret and link it to the access token. Browse to [https://register.gitlab.pr-agent.codium.ai](https://register.gitlab.pr-agent.codium.ai).
|
||||
Fill in your generated GitLab token and your company or personal name in the appropriate fields and click "Submit".
|
||||
|
||||
You should see "Success!" displayed above the Submit button, and a shared secret will be generated. Store it in a safe place, you won’t be able to access it again after it was generated.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 3
|
||||
|
||||
Install a webhook for your repository or groups, by clicking “webhooks” on the settings menu. Click the “Add new webhook” button.
|
||||
|
||||
<figure markdown="1">
|
||||

|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
|
||||
In the webhook definition form, fill in the following fields:
|
||||
URL: https://pro.gitlab.pr-agent.codium.ai/webhook
|
||||
|
||||
Secret token: Your QodoAI key
|
||||
Trigger: Check the ‘comments’ and ‘merge request events’ boxes.
|
||||
Enable SSL verification: Check the box.
|
||||
|
||||
<figure markdown="1">
|
||||
{width=750}
|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 4
|
||||
|
||||
You’re all set!
|
||||
|
||||
Open a new merge request or add a MR comment with one of Qodo Merge’s commands such as /review, /describe or /improve.
|
||||
|
||||
### GitLab Server
|
||||
|
||||
For a trial period of two weeks on your private GitLab Server, the same [installation steps](#gitlab-cloud) as for GitLab Cloud apply. After the trial period, you will need to [contact](https://www.qodo.ai/contact/#pricing) Qodo for moving to an Enterprise account.
|
||||
@ -1,15 +1,16 @@
|
||||
## Self-hosted PR-Agent
|
||||
## Self-hosted Qodo Merge
|
||||
|
||||
- If you self-host PR-Agent with your OpenAI (or other LLM provider) API key, it is between you and the provider. We don't send your code data to Qodo servers.
|
||||
- If you self-host Qodo Merge with your OpenAI (or other LLM provider) API key, it is between you and the provider. We don't send your code data to Qodo Merge servers.
|
||||
|
||||
## Qodo Merge 💎
|
||||
## Qodo Merge Pro 💎
|
||||
|
||||
- When using Qodo Merge💎, hosted by Qodo, we will not store any of your data, nor will we use it for training. You will also benefit from an OpenAI account with zero data retention.
|
||||
- When using Qodo Merge Pro 💎, hosted by CodiumAI, we will not store any of your data, nor will we use it for training. You will also benefit from an OpenAI account with zero data retention.
|
||||
|
||||
- For certain clients, Qodo Merge will use Qodo’s proprietary models. If this is the case, you will be notified.
|
||||
- For certain clients, CodiumAI-hosted Qodo Merge Pro will use CodiumAI’s proprietary models. If this is the case, you will be notified.
|
||||
|
||||
- No passive collection of Code and Pull Requests’ data — Qodo Merge will be active only when you invoke it, and it will then extract and analyze only data relevant to the executed command and queried pull request.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Qodo Merge Chrome extension
|
||||
|
||||
- The [Qodo Merge Chrome extension](https://chromewebstore.google.com/detail/pr-agent-chrome-extension/ephlnjeghhogofkifjloamocljapahnl) will not send your code to any external servers.
|
||||
|
||||
93
docs/docs/overview/index.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,93 @@
|
||||
# Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge is an open-source tool to help efficiently review and handle pull requests.
|
||||
|
||||
- See the [Installation Guide](./installation/index.md) for instructions on installing and running the tool on different git platforms.
|
||||
|
||||
- See the [Usage Guide](./usage-guide/index.md) for instructions on running the Qodo Merge commands via different interfaces, including _CLI_, _online usage_, or by _automatically triggering_ them when a new PR is opened.
|
||||
|
||||
- See the [Tools Guide](./tools/index.md) for a detailed description of the different tools.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Qodo Merge Docs Smart Search
|
||||
|
||||
To search the documentation site using natural language:
|
||||
|
||||
1) Comment `/help "your question"` in either:
|
||||
|
||||
- A pull request where Qodo Merge is installed
|
||||
- A [PR Chat](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/chrome-extension/features/#pr-chat)
|
||||
|
||||
2) Qodo Merge will respond with an [answer](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/1241#issuecomment-2365259334) that includes relevant documentation links.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Qodo Merge Features
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge offers extensive pull request functionalities across various git providers.
|
||||
|
||||
| | | GitHub | Gitlab | Bitbucket | Azure DevOps |
|
||||
|-------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|:------:|:------:|:---------:|:------------:|
|
||||
| TOOLS | Review | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | ⮑ Incremental | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | Ask | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | Describe | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | ⮑ [Inline file summary](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/describe/#inline-file-summary){:target="_blank"} 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | ✅ |
|
||||
| | Improve | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | ⮑ Extended | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Custom Prompt](./tools/custom_prompt.md){:target="_blank"} 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | Reflect and Review | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | Update CHANGELOG.md | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ️ |
|
||||
| | Find Similar Issue | ✅ | | | ️ |
|
||||
| | [Add PR Documentation](./tools/documentation.md){:target="_blank"} 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Generate Custom Labels](./tools/describe.md#handle-custom-labels-from-the-repos-labels-page-💎){:target="_blank"} 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Analyze PR Components](./tools/analyze.md){:target="_blank"} 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | ✅ |
|
||||
| | | | | | ️ |
|
||||
| USAGE | CLI | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | App / webhook | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | Actions | ✅ | | | ️ |
|
||||
| | | | | |
|
||||
| CORE | PR compression | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | Repo language prioritization | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | Adaptive and token-aware file patch fitting | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | Multiple models support | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | Incremental PR review | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | [Static code analysis](./tools/analyze.md/){:target="_blank"} 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Multiple configuration options](./usage-guide/configuration_options.md){:target="_blank"} 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
|
||||
💎 marks a feature available only in [Qodo Merge Pro](https://www.codium.ai/pricing/){:target="_blank"}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Example Results
|
||||
<hr>
|
||||
|
||||
#### [/describe](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/530)
|
||||
<figure markdown="1">
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
<hr>
|
||||
|
||||
#### [/review](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/732#issuecomment-1975099151)
|
||||
<figure markdown="1">
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
<hr>
|
||||
|
||||
#### [/improve](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/732#issuecomment-1975099159)
|
||||
<figure markdown="1">
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
<hr>
|
||||
|
||||
#### [/generate_labels](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/530)
|
||||
<figure markdown="1">
|
||||
{width=300}
|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
<hr>
|
||||
|
||||
## How it Works
|
||||
|
||||
The following diagram illustrates Qodo Merge tools and their flow:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Check out the [PR Compression strategy](core-abilities/index.md) page for more details on how we convert a code diff to a manageable LLM prompt
|
||||
@ -1,51 +1,51 @@
|
||||
### Overview
|
||||
|
||||
[Qodo Merge](https://www.codium.ai/pricing/){:target="_blank"} is a paid, hosted version of open-source [PR-Agent](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent){:target="_blank"}. A complimentary two-week trial is offered, followed by a monthly subscription fee.
|
||||
Qodo Merge is designed for companies and teams that require additional features and capabilities. It provides the following benefits:
|
||||
[Qodo Merge Pro](https://www.codium.ai/pricing/) is a hosted version of Qodo Merge, provided by Qodo. A complimentary two-week trial is offered, followed by a monthly subscription fee.
|
||||
Qodo Merge Pro is designed for companies and teams that require additional features and capabilities. It provides the following benefits:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Fully managed** - We take care of everything for you - hosting, models, regular updates, and more. Installation is as simple as signing up and adding the Qodo Merge app to your GitHub\GitLab\BitBucket repo.
|
||||
|
||||
2. **Improved privacy** - No data will be stored or used to train models. Qodo Merge will employ zero data retention, and will use an OpenAI and Claude accounts with zero data retention.
|
||||
2. **Improved privacy** - No data will be stored or used to train models. Qodo Merge Pro will employ zero data retention, and will use an OpenAI and Claude accounts with zero data retention.
|
||||
|
||||
3. **Improved support** - Qodo Merge users will receive priority support, and will be able to request new features and capabilities.
|
||||
3. **Improved support** - Qodo Merge Pro users will receive priority support, and will be able to request new features and capabilities.
|
||||
|
||||
4. **Supporting self-hosted git servers** - Qodo Merge can be installed on GitHub Enterprise Server, GitLab, and BitBucket. For more information, see the [installation guide](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/pr_agent_pro/).
|
||||
4. **Supporting self-hosted git servers** - Qodo Merge Pro can be installed on GitHub Enterprise Server, GitLab, and BitBucket. For more information, see the [installation guide](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/pr_agent_pro/).
|
||||
|
||||
5. **PR Chat** - Qodo Merge allows you to engage in [private chat](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/chrome-extension/features/#pr-chat) about your pull requests on private repositories.
|
||||
5. **PR Chat** - Qodo Merge Pro allows you to engage in [private chat](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/chrome-extension/features/#pr-chat) about your pull requests on private repositories.
|
||||
|
||||
### Additional features
|
||||
|
||||
Here are some of the additional features and capabilities that Qodo Merge offers, and are not available in the open-source version of PR-Agent:
|
||||
Here are some of the additional features and capabilities that Qodo Merge Pro offers:
|
||||
|
||||
| Feature | Description |
|
||||
| -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| [**Model selection**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/PR_agent_pro_models/) | Choose the model that best fits your needs, among top models like `Claude Sonnet`, `o4-mini` |
|
||||
| [**Global and wiki configuration**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/) | Control configurations for many repositories from a single location; <br>Edit configuration of a single repo without committing code |
|
||||
| [**Apply suggestions**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#overview) | Generate committable code from the relevant suggestions interactively by clicking on a checkbox |
|
||||
| [**Suggestions impact**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#assessing-impact) | Automatically mark suggestions that were implemented by the user (either directly in GitHub, or indirectly in the IDE) to enable tracking of the impact of the suggestions |
|
||||
| [**CI feedback**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/ci_feedback/) | Automatically analyze failed CI checks on GitHub and provide actionable feedback in the PR conversation, helping to resolve issues quickly |
|
||||
| [**Advanced usage statistics**](https://www.codium.ai/contact/#/) | Qodo Merge offers detailed statistics at user, repository, and company levels, including metrics about Qodo Merge usage, and also general statistics and insights |
|
||||
| [**Incorporating companies' best practices**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#best-practices) | Use the companies' best practices as reference to increase the effectiveness and the relevance of the code suggestions |
|
||||
| [**Interactive triggering**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/analyze/#example-usage) | Interactively apply different tools via the `analyze` command |
|
||||
| [**Custom labels**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/describe/#handle-custom-labels-from-the-repos-labels-page) | Define custom labels for Qodo Merge to assign to the PR |
|
||||
| Feature | Description |
|
||||
|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| [**Model selection**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/PR_agent_pro_models/) | Choose the model that best fits your needs, among top models like `GPT4` and `Claude-Sonnet-3.5`
|
||||
| [**Global and wiki configuration**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/) | Control configurations for many repositories from a single location; <br>Edit configuration of a single repo without committing code |
|
||||
| [**Apply suggestions**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#overview) | Generate committable code from the relevant suggestions interactively by clicking on a checkbox |
|
||||
| [**Suggestions impact**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#assessing-impact) | Automatically mark suggestions that were implemented by the user (either directly in GitHub, or indirectly in the IDE) to enable tracking of the impact of the suggestions |
|
||||
| [**CI feedback**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/ci_feedback/) | Automatically analyze failed CI checks on GitHub and provide actionable feedback in the PR conversation, helping to resolve issues quickly |
|
||||
| [**Advanced usage statistics**](https://www.codium.ai/contact/#/) | Qodo Merge Pro offers detailed statistics at user, repository, and company levels, including metrics about Qodo Merge usage, and also general statistics and insights |
|
||||
| [**Incorporating companies' best practices**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#best-practices) | Use the companies' best practices as reference to increase the effectiveness and the relevance of the code suggestions |
|
||||
| [**Interactive triggering**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/analyze/#example-usage) | Interactively apply different tools via the `analyze` command |
|
||||
| [**Custom labels**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/describe/#handle-custom-labels-from-the-repos-labels-page) | Define custom labels for Qodo Merge to assign to the PR |
|
||||
|
||||
### Additional tools
|
||||
|
||||
Here are additional tools that are available only for Qodo Merge users:
|
||||
Here are additional tools that are available only for Qodo Merge Pro users:
|
||||
|
||||
| Feature | Description |
|
||||
|---------|-------------|
|
||||
| [**Custom Prompt Suggestions**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/custom_prompt/) | Generate code suggestions based on custom prompts from the user |
|
||||
| [**Analyze PR components**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/analyze/) | Identify the components that changed in the PR, and enable to interactively apply different tools to them |
|
||||
| [**Tests**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/test/) | Generate tests for code components that changed in the PR |
|
||||
| [**PR documentation**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/documentation/) | Generate docstring for code components that changed in the PR |
|
||||
| [**Improve Component**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve_component/) | Generate code suggestions for code components that changed in the PR |
|
||||
| [**Similar code search**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/similar_code/) | Search for similar code in the repository, organization, or entire GitHub |
|
||||
|
||||
| Feature | Description |
|
||||
| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
| [**Custom Prompt Suggestions**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/custom_prompt/) | Generate code suggestions based on custom prompts from the user |
|
||||
| [**Analyze PR components**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/analyze/) | Identify the components that changed in the PR, and enable to interactively apply different tools to them |
|
||||
| [**Tests**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/test/) | Generate tests for code components that changed in the PR |
|
||||
| [**PR documentation**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/documentation/) | Generate docstring for code components that changed in the PR |
|
||||
| [**Improve Component**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve_component/) | Generate code suggestions for code components that changed in the PR |
|
||||
| [**Similar code search**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/similar_code/) | Search for similar code in the repository, organization, or entire GitHub |
|
||||
| [**Code implementation**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/implement/) | Generates implementation code from review suggestions |
|
||||
|
||||
### Supported languages
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge leverages the world's leading code models, such as Claude 3.7 Sonnet and o3-mini.
|
||||
Qodo Merge Pro leverages the world's leading code models - Claude 3.5 Sonnet and GPT-4.
|
||||
As a result, its primary tools such as `describe`, `review`, and `improve`, as well as the PR-chat feature, support virtually all programming languages.
|
||||
|
||||
For specialized commands that require static code analysis, Qodo Merge offers support for specific languages. For more details about features that require static code analysis, please refer to the [documentation](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/analyze/#overview).
|
||||
For specialized commands that require static code analysis, Qodo Merge Pro offers support for specific languages. For more details about features that require static code analysis, please refer to the [documentation](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/analyze/#overview).
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,201 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Qodo Merge Pull Request Benchmark
|
||||
|
||||
## Methodology
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge PR Benchmark evaluates and compares the performance of two Large Language Models (LLMs) in analyzing pull request code and providing meaningful code suggestions.
|
||||
Our diverse dataset comprises of 400 pull requests from over 100 repositories, spanning various programming languages and frameworks to reflect real-world scenarios.
|
||||
|
||||
- For each pull request, two distinct LLMs process the same prompt using the Qodo Merge `improve` tool, each generating two sets of responses. The prompt for response generation can be found [here](https://github.com/qodo-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/code_suggestions/pr_code_suggestions_prompts_not_decoupled.toml).
|
||||
|
||||
- Subsequently, a high-performing third model (an AI judge) evaluates the responses from the initial two models to determine the superior one. We utilize OpenAI's `o3` model as the judge, though other models have yielded consistent results. The prompt for this comparative judgment is available [here](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent-settings/tree/main/benchmark).
|
||||
|
||||
- We aggregate comparison outcomes across all the pull requests, calculating the win rate for each model. We also analyze the qualitative feedback (the "why" explanations from the judge) to identify each model's comparative strengths and weaknesses.
|
||||
This approach provides not just a quantitative score but also a detailed analysis of each model's strengths and weaknesses.
|
||||
|
||||
- For each model we build a "Model Card", comparing it against others. To ensure full transparency and enable community scrutiny, we also share the raw code suggestions generated by each model, and the judge's specific feedback. See example for the full output [here](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent-settings/blob/main/benchmark/sonnet_37_vs_gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Note that this benchmark focuses on quality: the ability of an LLM to process complex pull request with multiple files and nuanced task to produce high-quality code suggestions.
|
||||
Other factors like speed, cost, and availability, while also relevant for model selection, are outside this benchmark's scope.
|
||||
|
||||
## TL;DR
|
||||
|
||||
Here's a summary of the win rates based on the benchmark:
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (| Model A | Model B | Model A Win Rate | Model B Win Rate |)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (|:-------------------------------|:-------------------------------|:----------------:|:----------------:|)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (| Gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06 | GPT-4.1 | 70.4% | 29.6% |)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (| Gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06 | Sonnet 3.7 | 78.1% | 21.9% |)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (| GPT-4.1 | Sonnet 3.7 | 61.0% | 39.0% |)
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<thead>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<th style="text-align:left;">Model A</th>
|
||||
<th style="text-align:left;">Model B</th>
|
||||
<th style="text-align:center;">Model A Win Rate</th> <th style="text-align:center;">Model B Win Rate</th> </tr>
|
||||
</thead>
|
||||
<tbody>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style="text-align:left;">Gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06</td>
|
||||
<td style="text-align:left;">GPT-4.1</td>
|
||||
<td style="text-align:center; color: #1E8449;"><b>70.4%</b></td> <td style="text-align:center; color: #D8000C;"><b>29.6%</b></td> </tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style="text-align:left;">Gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06</td>
|
||||
<td style="text-align:left;">Sonnet 3.7</td>
|
||||
<td style="text-align:center; color: #1E8449;"><b>78.1%</b></td> <td style="text-align:center; color: #D8000C;"><b>21.9%</b></td> </tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style="text-align:left;">Gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06</td>
|
||||
<td style="text-align:left;">Gemini-2.5-flash-preview-04-17</td>
|
||||
<td style="text-align:center; color: #1E8449;"><b>73.0%</b></td> <td style="text-align:center; color: #D8000C;"><b>27.0%</b></td> </tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style="text-align:left;">Gemini-2.5-flash-preview-04-17</td>
|
||||
<td style="text-align:left;">GPT-4.1</td>
|
||||
<td style="text-align:center; color: #1E8449;"><b>54.6%</b></td> <td style="text-align:center; color: #D8000C;"><b>45.4%</b></td> </tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style="text-align:left;">Gemini-2.5-flash-preview-04-17</td>
|
||||
<td style="text-align:left;">Sonnet 3.7</td>
|
||||
<td style="text-align:center; color: #1E8449;"><b>60.6%</b></td> <td style="text-align:center; color: #D8000C;"><b>39.4%</b></td> </tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style="text-align:left;">GPT-4.1</td>
|
||||
<td style="text-align:left;">Sonnet 3.7</td>
|
||||
<td style="text-align:center; color: #1E8449;"><b>61.0%</b></td> <td style="text-align:center; color: #D8000C;"><b>39.0%</b></td> </tr>
|
||||
</tbody>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06 - Model Card
|
||||
|
||||
### Comparison against GPT-4.1
|
||||
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
|
||||
#### Analysis Summary
|
||||
|
||||
Model 'Gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06' is generally more useful thanks to wider and more accurate bug detection and concrete patches, but it sacrifices compliance discipline and sometimes oversteps the task rules. Model 'GPT-4.1' is safer and highly rule-abiding, yet often too timid—missing many genuine issues and providing limited insight. An ideal reviewer would combine 'GPT-4.1’ restraint with 'Gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06' thoroughness.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Detailed Analysis
|
||||
|
||||
Gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06 strengths:
|
||||
|
||||
- better_bug_coverage: Detects and explains more critical issues, winning in ~70 % of comparisons and achieving a higher average score.
|
||||
- actionable_fixes: Supplies clear code snippets, correct language labels, and often multiple coherent suggestions per diff.
|
||||
- deeper_reasoning: Shows stronger grasp of logic, edge cases, and cross-file implications, leading to broader, high-impact reviews.
|
||||
|
||||
Gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06 weaknesses:
|
||||
|
||||
- guideline_violations: More prone to over-eager advice—non-critical tweaks, touching unchanged code, suggesting new imports, or minor format errors.
|
||||
- occasional_overreach: Some fixes are speculative or risky, potentially introducing new bugs.
|
||||
- redundant_or_duplicate: At times repeats the same point or exceeds the required brevity.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Comparison against Sonnet 3.7
|
||||
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
|
||||
#### Analysis Summary
|
||||
|
||||
Model 'Gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06' is the stronger reviewer—more frequently identifies genuine, high-impact bugs and provides well-formed, actionable fixes. Model 'Sonnet 3.7' is safer against false positives and tends to be concise but often misses important defects or offers low-value or incorrect suggestions.
|
||||
|
||||
See raw results [here](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent-settings/blob/main/benchmark/sonnet_37_vs_gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06.md)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Detailed Analysis
|
||||
|
||||
Gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06 strengths:
|
||||
|
||||
- higher_accuracy_and_coverage: finds real critical bugs and supplies actionable patches in most examples (better in 78 % of cases).
|
||||
- guideline_awareness: usually respects new-lines-only scope, ≤3 suggestions, proper YAML, and stays silent when no issues exist.
|
||||
- detailed_reasoning_and_patches: explanations tie directly to the diff and fixes are concrete, often catching multiple related defects that 'Sonnet 3.7' overlooks.
|
||||
|
||||
Gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06 weaknesses:
|
||||
|
||||
- occasional_rule_violations: sometimes proposes new imports, package-version changes, or edits outside the added lines.
|
||||
- overzealous_suggestions: may add speculative or stylistic fixes that exceed the “critical” scope, or mis-label severity.
|
||||
- sporadic_technical_slips: a few patches contain minor coding errors, oversized snippets, or duplicate/contradicting advice.
|
||||
|
||||
## GPT-4.1 - Model Card
|
||||
|
||||
### Comparison against Sonnet 3.7
|
||||
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
|
||||
#### Analysis Summary
|
||||
|
||||
Model 'GPT-4.1' is safer and more compliant, preferring silence over speculation, which yields fewer rule breaches and false positives but misses some real bugs.
|
||||
Model 'Sonnet 3.7' is more adventurous and often uncovers important issues that 'GPT-4.1' ignores, yet its aggressive style leads to frequent guideline violations and a higher proportion of incorrect or non-critical advice.
|
||||
|
||||
See raw results [here](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent-settings/blob/main/benchmark/gpt-4.1_vs_sonnet_3.7_judge_o3.md)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Detailed Analysis
|
||||
|
||||
GPT-4.1 strengths:
|
||||
- Strong guideline adherence: usually stays strictly on `+` lines, avoids non-critical or stylistic advice, and rarely suggests forbidden imports; often outputs an empty list when no real bug exists.
|
||||
- Lower false-positive rate: suggestions are more accurate and seldom introduce new bugs; fixes compile more reliably.
|
||||
- Good schema discipline: YAML is almost always well-formed and fields are populated correctly.
|
||||
|
||||
GPT-4.1 weaknesses:
|
||||
- Misses bugs: often returns an empty list even when a clear critical issue is present, so coverage is narrower.
|
||||
- Sparse feedback: when it does comment, it tends to give fewer suggestions and sometimes lacks depth or completeness.
|
||||
- Occasional metadata/slip-ups (wrong language tags, overly broad code spans), though less harmful than Sonnet 3.7 errors.
|
||||
|
||||
### Comparison against Gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06
|
||||
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
|
||||
#### Analysis Summary
|
||||
|
||||
Model 'Gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06' is generally more useful thanks to wider and more accurate bug detection and concrete patches, but it sacrifices compliance discipline and sometimes oversteps the task rules. Model 'GPT-4.1' is safer and highly rule-abiding, yet often too timid—missing many genuine issues and providing limited insight. An ideal reviewer would combine 'GPT-4.1’ restraint with 'Gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06' thoroughness.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Detailed Analysis
|
||||
|
||||
GPT-4.1 strengths:
|
||||
- strict_compliance: Usually sticks to the “critical bugs only / new ‘+’ lines only” rule, so outputs rarely violate task constraints.
|
||||
- low_risk: Conservative behaviour avoids harmful or speculative fixes; safer when no obvious issue exists.
|
||||
- concise_formatting: Tends to produce minimal, correctly-structured YAML without extra noise.
|
||||
|
||||
GPT-4.1 weaknesses:
|
||||
- under_detection: Frequently returns an empty list even when real bugs are present, missing ~70 % of the time.
|
||||
- shallow_analysis: When it does suggest fixes, coverage is narrow and technical depth is limited, sometimes with wrong language tags or minor format slips.
|
||||
- occasional_inaccuracy: A few suggestions are unfounded or duplicate, and rare guideline breaches (e.g., import advice) still occur.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Sonnet 3.7 - Model Card
|
||||
|
||||
### Comparison against GPT-4.1
|
||||
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
|
||||
#### Analysis Summary
|
||||
|
||||
Model 'GPT-4.1' is safer and more compliant, preferring silence over speculation, which yields fewer rule breaches and false positives but misses some real bugs.
|
||||
Model 'Sonnet 3.7' is more adventurous and often uncovers important issues that 'GPT-4.1' ignores, yet its aggressive style leads to frequent guideline violations and a higher proportion of incorrect or non-critical advice.
|
||||
|
||||
See raw results [here](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent-settings/blob/main/benchmark/gpt-4.1_vs_sonnet_3.7_judge_o3.md)
|
||||
|
||||
#### Detailed Analysis
|
||||
|
||||
'Sonnet 3.7' strengths:
|
||||
- Better bug discovery breadth: more willing to dive into logic and spot critical problems that 'GPT-4.1' overlooks; often supplies multiple, detailed fixes.
|
||||
- Richer explanations & patches: gives fuller context and, when correct, proposes more functional or user-friendly solutions.
|
||||
- Generally correct language/context tagging and targeted code snippets.
|
||||
|
||||
'Sonnet 3.7' weaknesses:
|
||||
- Guideline violations: frequently flags non-critical issues, edits untouched code, or recommends adding imports, breaching task rules.
|
||||
- Higher error rate: suggestions are more speculative and sometimes introduce new defects or duplicate work already done.
|
||||
- Occasional schema or formatting mistakes (missing list value, duplicated suggestions), reducing reliability.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Comparison against Gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06
|
||||
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
|
||||
#### Analysis Summary
|
||||
|
||||
Model 'Gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06' is the stronger reviewer—more frequently identifies genuine, high-impact bugs and provides well-formed, actionable fixes. Model 'Sonnet 3.7' is safer against false positives and tends to be concise but often misses important defects or offers low-value or incorrect suggestions.
|
||||
|
||||
See raw results [here](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent-settings/blob/main/benchmark/sonnet_37_vs_gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06.md)
|
||||
@ -1,22 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Recent Updates and Future Roadmap
|
||||
|
||||
`Page last updated: 2025-05-11`
|
||||
|
||||
This page summarizes recent enhancements to Qodo Merge (last three months).
|
||||
|
||||
It also outlines our development roadmap for the upcoming three months. Please note that the roadmap is subject to change, and features may be adjusted, added, or reprioritized.
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Recent Updates"
|
||||
- **Qodo Merge Pull Request Benchmark** - evaluating the performance of LLMs in analyzing pull request code ([Learn more](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/pr_benchmark/))
|
||||
- **Chat on Suggestions**: Users can now chat with Qodo Merge code suggestions ([Learn more](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#chat-on-code-suggestions))
|
||||
- **Scan Repo Discussions Tool**: A new tool that analyzes past code discussions to generate a `best_practices.md` file, distilling key insights and recommendations. ([Learn more](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/scan_repo_discussions/))
|
||||
- **Enhanced Models**: Qodo Merge now defaults to a combination of top models (Claude Sonnet 3.7 and Gemini 2.5 Pro) and incorporates dedicated code validation logic for improved results. ([Details 1](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/qodo_merge_models/), [Details 2](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/code_validation/))
|
||||
- **Chrome Extension Update**: Qodo Merge Chrome extension now supports single-tenant users. ([Learn more](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/chrome-extension/options/#configuration-options/))
|
||||
- **Repo Statistics Tool**: A new tool that provides repository statistics on time to merge and time to first comment. ([Learn more](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/repo_statistics/))
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Future Roadmap"
|
||||
- **Smart Update**: Upon PR updates, Qodo Merge will offer tailored code suggestions, addressing both the entire PR and the specific incremental changes since the last feedback.
|
||||
- **CLI Endpoint**: A new Qodo Merge endpoint will accept lists of before/after code changes, execute Qodo Merge commands, and return the results.
|
||||
- **Simplified Free Tier**: We plan to transition from a two-week free trial to a free tier offering a limited number of suggestions per month per organization.
|
||||
- **Best Practices Hierarchy**: Introducing support for structured best practices, such as for folders in monorepos or a unified best practice file for a group of repositories.
|
||||
- **Installation Metrics**: Upon installation, Qodo Merge will analyze past PRs for key metrics (e.g., time to merge, time to first reviewer feedback), enabling pre/post-installation comparison to calculate ROI.
|
||||
@ -1,11 +1,9 @@
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The `analyze` tool combines advanced static code analysis with LLM capabilities to provide a comprehensive analysis of the PR code changes.
|
||||
|
||||
The tool scans the PR code changes, finds the code components (methods, functions, classes) that changed, and enables to interactively generate tests, docs, code suggestions and similar code search for each component.
|
||||
|
||||
It can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/analyze
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -16,5 +14,6 @@ An example result:
|
||||
|
||||
{width=750}
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Language that are currently supported:"
|
||||
Python, Java, C++, JavaScript, TypeScript, C#.
|
||||
**Notes**
|
||||
|
||||
- Language that are currently supported: Python, Java, C++, JavaScript, TypeScript, C#.
|
||||
@ -2,7 +2,6 @@
|
||||
|
||||
The `ask` tool answers questions about the PR, based on the PR code changes. Make sure to be specific and clear in your questions.
|
||||
It can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/ask "..."
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -16,9 +15,8 @@ It can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
## Ask lines
|
||||
|
||||
You can run `/ask` on specific lines of code in the PR from the PR's diff view. The tool will answer questions based on the code changes in the selected lines.
|
||||
|
||||
- Click on the '+' sign next to the line number to select the line.
|
||||
- To select multiple lines, click on the '+' sign of the first line and then hold and drag to select the rest of the lines.
|
||||
- To select multiple lines, click on the '+' sign of the first line and then hold and drag to select the rest of the lines.
|
||||
- write `/ask "..."` in the comment box and press `Add single comment` button.
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
@ -30,33 +28,32 @@ Note that the tool does not have "memory" of previous questions, and answers eac
|
||||
You can also ask questions about images that appear in the comment, where the entire PR code will be used as context.
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
The basic syntax is:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/ask "..."
|
||||
|
||||
[Image](https://real_link_to_image)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
where `https://real_link_to_image` is the direct link to the image.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that GitHub has a built-in mechanism of pasting images in comments. However, pasted image does not provide a direct link.
|
||||
To get a direct link to an image, we recommend using the following scheme:
|
||||
|
||||
1\. First, post a comment that contains **only** the image:
|
||||
1) First, post a comment that contains **only** the image:
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
2\. Quote reply to that comment:
|
||||
2) Quote reply to that comment:
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
3\. In the screen opened, type the question below the image:
|
||||
3) In the screen opened, type the question below the image:
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
4\. Post the comment, and receive the answer:
|
||||
4) Post the comment, and receive the answer:
|
||||
|
||||
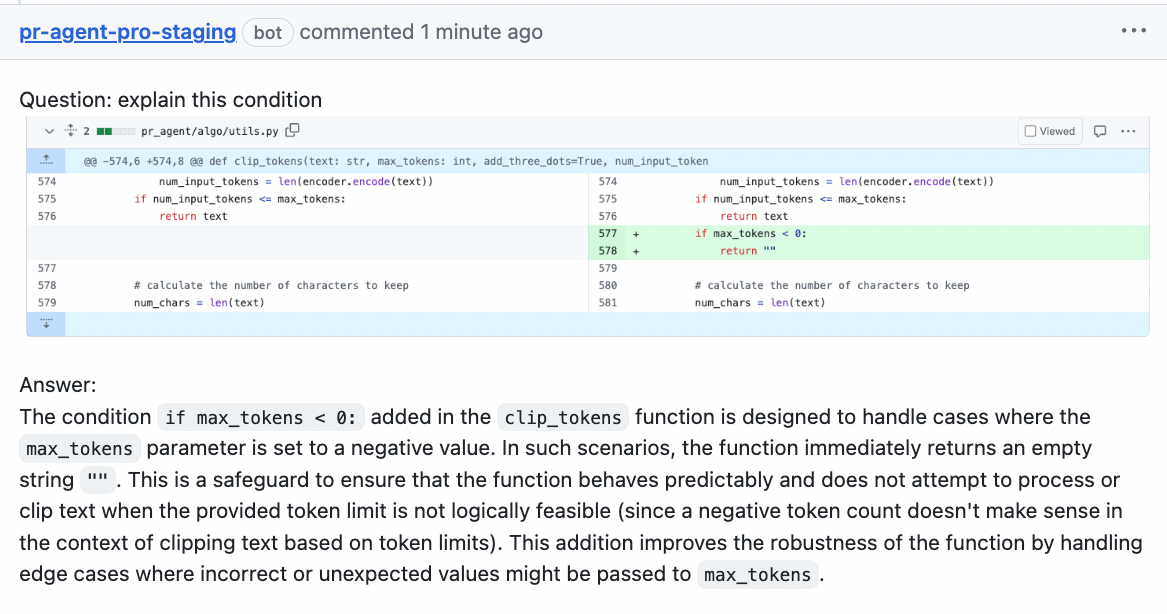{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
See a full video tutorial [here](https://codium.ai/images/pr_agent/ask_image_video.mov)
|
||||
|
||||
See a full video tutorial [here](https://codium.ai/images/pr_agent/ask_image_video.mov)
|
||||
@ -18,24 +18,20 @@ The tool analyzes the failed checks and provides several feedbacks:
|
||||
___
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to being automatically triggered, the tool can also be invoked manually by commenting on a PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/checks "https://github.com/{repo_name}/actions/runs/{run_number}/job/{job_number}"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
where `{repo_name}` is the name of the repository, `{run_number}` is the run number of the failed check, and `{job_number}` is the job number of the failed check.
|
||||
|
||||
## Disabling the tool from running automatically
|
||||
|
||||
If you wish to disable the tool from running automatically, you can do so by adding the following configuration to the configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[checks]
|
||||
enable_auto_checks_feedback = false
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuration options
|
||||
|
||||
- `enable_auto_checks_feedback` - if set to true, the tool will automatically provide feedback when a check is failed. Default is true.
|
||||
- `excluded_checks_list` - a list of checks to exclude from the feedback, for example: ["check1", "check2"]. Default is an empty list.
|
||||
- `persistent_comment` - if set to true, the tool will overwrite a previous checks comment with the new feedback. Default is true.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The `generate_labels` tool scans the PR code changes, and given a list of labels and their descriptions, it automatically suggests labels that match the PR code changes.
|
||||
|
||||
It can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/generate_labels
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -21,26 +19,21 @@ When running the `generate_labels` tool on a PR that includes changes in SQL que
|
||||
Note that in addition to the dedicated tool `generate_labels`, the custom labels will also be used by the `describe` tool.
|
||||
|
||||
### How to enable custom labels
|
||||
|
||||
There are 3 ways to enable custom labels:
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1. CLI (local configuration file)
|
||||
|
||||
When working from CLI, you need to apply the [configuration changes](#configuration-options) to the [custom_labels file](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/custom_labels.toml):
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. Repo configuration file
|
||||
|
||||
To enable custom labels, you need to apply the [configuration changes](#configuration-options) to the local `.pr_agent.toml` file in your repository.
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3. Handle custom labels from the Repo's labels page 💎
|
||||
|
||||
> This feature is available only in Qodo Merge
|
||||
> This feature is available only in Qodo Merge Pro
|
||||
|
||||
* GitHub : `https://github.com/{owner}/{repo}/labels`, or click on the "Labels" tab in the issues or PRs page.
|
||||
* GitLab : `https://gitlab.com/{owner}/{repo}/-/labels`, or click on "Manage" -> "Labels" on the left menu.
|
||||
|
||||
b. Add/edit the custom labels. It should be formatted as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
* Label name: The name of the custom label.
|
||||
* Description: Start the description of with prefix `pr_agent:`, for example: `pr_agent: Description of when AI should suggest this label`.<br>
|
||||
The description should be comprehensive and detailed, indicating when to add the desired label.
|
||||
@ -52,9 +45,8 @@ c. Now the custom labels will be included in the `generate_labels` tool.
|
||||
> This feature is supported in GitHub and GitLab.
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuration options
|
||||
|
||||
* Change `enable_custom_labels` to True: This will turn off the default labels and enable the custom labels provided in the custom_labels.toml file.
|
||||
* Add the custom labels. It should be formatted as follows:
|
||||
- Change `enable_custom_labels` to True: This will turn off the default labels and enable the custom labels provided in the custom_labels.toml file.
|
||||
- Add the custom labels. It should be formatted as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,4 @@
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The `custom_prompt` tool scans the PR code changes, and automatically generates suggestions for improving the PR code.
|
||||
It shares similarities with the `improve` tool, but with one main difference: the `custom_prompt` tool will **only propose suggestions that follow specific guidelines defined by the prompt** in: `pr_custom_prompt.prompt` configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -18,7 +17,7 @@ The code suggestions should focus only on the following:
|
||||
|
||||
With a [configuration file](../usage-guide/automations_and_usage.md#github-app), use the following template:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[pr_custom_prompt]
|
||||
prompt="""\
|
||||
The suggestions should focus only on the following:
|
||||
@ -34,8 +33,7 @@ You might benefit from several trial-and-error iterations, until you get the cor
|
||||
## Example usage
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example of a possible prompt, defined in the configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[pr_custom_prompt]
|
||||
prompt="""\
|
||||
The code suggestions should focus only on the following:
|
||||
@ -43,7 +41,7 @@ The code suggestions should focus only on the following:
|
||||
- make sure every variable has a meaningful name
|
||||
- make sure the code is efficient
|
||||
"""
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
(The instructions above are just an example. We want to emphasize that the prompt should be specific and clear, and be tailored to the needs of your project)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -53,8 +51,8 @@ Results obtained with the prompt above:
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuration options
|
||||
|
||||
- `prompt`: the prompt for the tool. It should be a multi-line string.
|
||||
`prompt`: the prompt for the tool. It should be a multi-line string.
|
||||
|
||||
- `num_code_suggestions_per_chunk`: number of code suggestions provided by the 'custom_prompt' tool, per chunk. Default is 3.
|
||||
`num_code_suggestions`: number of code suggestions provided by the 'custom_prompt' tool. Default is 4.
|
||||
|
||||
- `enable_help_text`: if set to true, the tool will display a help text in the comment. Default is true.
|
||||
`enable_help_text`: if set to true, the tool will display a help text in the comment. Default is true.
|
||||
@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The `describe` tool scans the PR code changes, and generates a description for the PR - title, type, summary, walkthrough and labels.
|
||||
|
||||
The tool can be triggered automatically every time a new PR is [opened](../usage-guide/automations_and_usage.md#github-app-automatic-tools-when-a-new-pr-is-opened), or it can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/describe
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -21,7 +19,6 @@ After ~30 seconds, the tool will generate a description for the PR:
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to edit [configurations](#configuration-options), add the relevant ones to the command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/describe --pr_description.some_config1=... --pr_description.some_config2=...
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -29,7 +26,6 @@ If you want to edit [configurations](#configuration-options), add the relevant o
|
||||
### Automatic triggering
|
||||
|
||||
To run the `describe` automatically when a PR is opened, define in a [configuration file](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/#wiki-configuration-file):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[github_app]
|
||||
pr_commands = [
|
||||
@ -45,71 +41,62 @@ publish_labels = true
|
||||
- The `pr_commands` lists commands that will be executed automatically when a PR is opened.
|
||||
- The `[pr_description]` section contains the configurations for the `describe` tool you want to edit (if any).
|
||||
|
||||
## Preserving the original user description
|
||||
|
||||
By default, Qodo Merge preserves your original PR description by placing it above the generated content.
|
||||
This requires including your description during the initial PR creation.
|
||||
Be aware that if you edit the description while the automated tool is running, a race condition may occur, potentially causing your original description to be lost.
|
||||
|
||||
When updating PR descriptions, the `/describe` tool considers everything above the "PR Type" field as user content and will preserve it.
|
||||
Everything below this marker is treated as previously auto-generated content and will be replaced.
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuration options
|
||||
|
||||
!!! example "Possible configurations"
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>publish_labels</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will publish labels to the PR. Default is false.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>publish_description_as_comment</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will publish the description as a comment to the PR. If false, it will overwrite the original description. Default is false.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>publish_description_as_comment_persistent</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true and `publish_description_as_comment` is true, the tool will publish the description as a persistent comment to the PR. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>add_original_user_description</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will add the original user description to the generated description. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>generate_ai_title</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will also generate an AI title for the PR. Default is false.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>extra_instructions</b></td>
|
||||
<td>Optional extra instructions to the tool. For example: "focus on the changes in the file X. Ignore change in ..."</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>enable_pr_type</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to false, it will not show the `PR type` as a text value in the description content. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>final_update_message</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, it will add a comment message [`PR Description updated to latest commit...`](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/499#issuecomment-1837412176) after finishing calling `/describe`. Default is false.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>enable_semantic_files_types</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, "Changes walkthrough" section will be generated. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>collapsible_file_list</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the file list in the "Changes walkthrough" section will be collapsible. If set to "adaptive", the file list will be collapsible only if there are more than 8 files. Default is "adaptive".</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>enable_large_pr_handling</b></td>
|
||||
<td>Pro feature. If set to true, in case of a large PR the tool will make several calls to the AI and combine them to be able to cover more files. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>enable_help_text</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will display a help text in the comment. Default is false.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>publish_labels</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will publish labels to the PR. Default is false.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>publish_description_as_comment</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will publish the description as a comment to the PR. If false, it will overwrite the original description. Default is false.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>publish_description_as_comment_persistent</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true and `publish_description_as_comment` is true, the tool will publish the description as a persistent comment to the PR. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>add_original_user_description</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will add the original user description to the generated description. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>generate_ai_title</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will also generate an AI title for the PR. Default is false.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>extra_instructions</b></td>
|
||||
<td>Optional extra instructions to the tool. For example: "focus on the changes in the file X. Ignore change in ..."</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>enable_pr_type</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to false, it will not show the `PR type` as a text value in the description content. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>final_update_message</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, it will add a comment message [`PR Description updated to latest commit...`](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/499#issuecomment-1837412176) after finishing calling `/describe`. Default is false.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>enable_semantic_files_types</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, "Changes walkthrough" section will be generated. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>collapsible_file_list</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the file list in the "Changes walkthrough" section will be collapsible. If set to "adaptive", the file list will be collapsible only if there are more than 8 files. Default is "adaptive".</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>enable_large_pr_handling</b></td>
|
||||
<td>Pro feature. If set to true, in case of a large PR the tool will make several calls to the AI and combine them to be able to cover more files. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>enable_help_text</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will display a help text in the comment. Default is false.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Inline file summary 💎
|
||||
|
||||
@ -133,13 +120,13 @@ If you prefer to have the file summaries appear in the "Files changed" tab on ev
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: that this feature is currently available only for GitHub.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Markers template
|
||||
|
||||
To enable markers, set `pr_description.use_description_markers=true`.
|
||||
Markers enable to easily integrate user's content and auto-generated content, with a template-like mechanism.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, if the PR original description was:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
User content...
|
||||
|
||||
@ -152,22 +139,21 @@ pr_agent:summary
|
||||
## PR Walkthrough:
|
||||
pr_agent:walkthrough
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The marker `pr_agent:type` will be replaced with the PR type, `pr_agent:summary` will be replaced with the PR summary, and `pr_agent:walkthrough` will be replaced with the PR walkthrough.
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
becomes
|
||||
→
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Configuration params**:
|
||||
|
||||
- `use_description_markers`: if set to true, the tool will use markers template. It replaces every marker of the form `pr_agent:marker_name` with the relevant content. Default is false.
|
||||
- `include_generated_by_header`: if set to true, the tool will add a dedicated header: 'Generated by PR Agent at ...' to any automatic content. Default is true.
|
||||
|
||||
## Custom labels
|
||||
|
||||
The default labels of the describe tool are quite generic, since they are meant to be used in any repo: [`Bug fix`, `Tests`, `Enhancement`, `Documentation`, `Other`].
|
||||
|
||||
You can define custom labels that are relevant for your repo and use cases.
|
||||
@ -177,9 +163,7 @@ Make sure to provide proper title, and a detailed and well-phrased description f
|
||||
Each label description should be a **conditional statement**, that indicates if to add the label to the PR or not, according to the PR content.
|
||||
|
||||
### Handle custom labels from a configuration file
|
||||
|
||||
Example for a custom labels configuration setup in a configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
enable_custom_labels=true
|
||||
@ -198,25 +182,26 @@ description = "use when a PR primarily contains new tests"
|
||||
|
||||
You can also control the custom labels that will be suggested by the `describe` tool from the repo's labels page:
|
||||
|
||||
- GitHub : go to `https://github.com/{owner}/{repo}/labels` (or click on the "Labels" tab in the issues or PRs page)
|
||||
- GitLab : go to `https://gitlab.com/{owner}/{repo}/-/labels` (or click on "Manage" -> "Labels" on the left menu)
|
||||
* GitHub : go to `https://github.com/{owner}/{repo}/labels` (or click on the "Labels" tab in the issues or PRs page)
|
||||
* GitLab : go to `https://gitlab.com/{owner}/{repo}/-/labels` (or click on "Manage" -> "Labels" on the left menu)
|
||||
|
||||
Now add/edit the custom labels. they should be formatted as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
- Label name: The name of the custom label.
|
||||
- Description: Start the description of with prefix `pr_agent:`, for example: `pr_agent: Description of when AI should suggest this label`.<br>
|
||||
* Label name: The name of the custom label.
|
||||
* Description: Start the description of with prefix `pr_agent:`, for example: `pr_agent: Description of when AI should suggest this label`.<br>
|
||||
|
||||
Examples for custom labels:
|
||||
|
||||
- `Main topic:performance` - pr_agent:The main topic of this PR is performance
|
||||
- `New endpoint` - pr_agent:A new endpoint was added in this PR
|
||||
- `SQL query` - pr_agent:A new SQL query was added in this PR
|
||||
- `Dockerfile changes` - pr_agent:The PR contains changes in the Dockerfile
|
||||
- ...
|
||||
- `Main topic:performance` - pr_agent:The main topic of this PR is performance
|
||||
- `New endpoint` - pr_agent:A new endpoint was added in this PR
|
||||
- `SQL query` - pr_agent:A new SQL query was added in this PR
|
||||
- `Dockerfile changes` - pr_agent:The PR contains changes in the Dockerfile
|
||||
- ...
|
||||
|
||||
The description should be comprehensive and detailed, indicating when to add the desired label. For example:
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage Tips
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip "Automation"
|
||||
@ -226,15 +211,14 @@ The description should be comprehensive and detailed, indicating when to add the
|
||||
```
|
||||
meaning the `describe` tool will run automatically on every PR, with the default configurations.
|
||||
|
||||
- Markers are an alternative way to control the generated description, to give maximal control to the user. If you set:
|
||||
|
||||
- Markers are an alternative way to control the generated description, to give maximal control to the user. If you set:
|
||||
```
|
||||
pr_commands = ["/describe --pr_description.use_description_markers=true", ...]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
the tool will replace every marker of the form `pr_agent:marker_name` in the PR description with the relevant content, where `marker_name` is one of the following:
|
||||
*`type`: the PR type.
|
||||
* `type`: the PR type.
|
||||
* `summary`: the PR summary.
|
||||
* `walkthrough`: the PR walkthrough.
|
||||
|
||||
- Note that when markers are enabled, if the original PR description does not contain any markers, the tool will not alter the description at all.
|
||||
- Note that when markers are enabled, if the original PR description does not contain any markers, the tool will not alter the description at all.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The `add_docs` tool scans the PR code changes, and automatically suggests documentation for any code components that changed in the PR (functions, classes, etc.).
|
||||
|
||||
It can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/add_docs
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -21,16 +19,15 @@ The tool will generate documentation for all the components that changed in the
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
|
||||
You can state a name of a specific component in the PR to get documentation only for that component:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/add_docs component_name
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuration options
|
||||
- `docs_style`: The exact style of the documentation (for python docstring). you can choose between: `google`, `numpy`, `sphinx`, `restructuredtext`, `plain`. Default is `sphinx`.
|
||||
- `extra_instructions`: Optional extra instructions to the tool. For example: "focus on the changes in the file X. Ignore change in ...".
|
||||
|
||||
- `docs_style`: The exact style of the documentation (for python docstring). you can choose between: `google`, `numpy`, `sphinx`, `restructuredtext`, `plain`. Default is `sphinx`.
|
||||
- `extra_instructions`: Optional extra instructions to the tool. For example: "focus on the changes in the file X. Ignore change in ...".
|
||||
**Notes**
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Notes"
|
||||
- The following languages are currently supported: Python, Java, C++, JavaScript, TypeScript, C#.
|
||||
- This tool can also be triggered interactively by using the [`analyze`](./analyze.md) tool.
|
||||
- Language that are currently fully supported: Python, Java, C++, JavaScript, TypeScript, C#.
|
||||
- This tool can also be triggered interactively by using the [`analyze`](./analyze.md) tool.
|
||||
@ -1,16 +1,13 @@
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The `help` tool provides a list of all the available tools and their descriptions.
|
||||
For Qodo Merge users, it also enables to trigger each tool by checking the relevant box.
|
||||
For Qodo Merge Pro users, it also enables to trigger each tool by checking the relevant box.
|
||||
|
||||
It can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/help
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Example usage
|
||||
|
||||
An example [result](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/546#issuecomment-1868524805):
|
||||
|
||||
{width=750}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,110 +0,0 @@
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The `help_docs` tool can answer a free-text question based on a git documentation folder.
|
||||
|
||||
It can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR or Issue:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/help_docs "..."
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Or configured to be triggered automatically when a [new issue is opened](#run-as-a-github-action).
|
||||
|
||||
The tool assumes by default that the documentation is located in the root of the repository, at `/docs` folder.
|
||||
However, this can be customized by setting the `docs_path` configuration option:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[pr_help_docs]
|
||||
repo_url = "" # The repository to use as context
|
||||
docs_path = "docs" # The documentation folder
|
||||
repo_default_branch = "main" # The branch to use in case repo_url overwritten
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
See more configuration options in the [Configuration options](#configuration-options) section.
|
||||
|
||||
## Example usage
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (#### Asking a question about this repository:)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ({width=512})
|
||||
|
||||
**Asking a question about another repository**
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
**Response**:
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
## Run automatically when a new issue is opened
|
||||
|
||||
You can configure PR-Agent to run `help_docs` automatically on any newly created issue.
|
||||
This can be useful, for example, for providing immediate feedback to users who open issues with questions on open-source projects with extensive documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
Here's how:
|
||||
|
||||
1) Follow the steps depicted under [Run as a Github Action](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/github/#run-as-a-github-action) to create a new workflow, such as:`.github/workflows/help_docs.yml`:
|
||||
|
||||
2) Edit your yaml file to the following:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
name: Run pr agent on every opened issue, respond to user comments on an issue
|
||||
|
||||
#When the action is triggered
|
||||
on:
|
||||
issues:
|
||||
types: [opened] #New issue
|
||||
|
||||
# Read env. variables
|
||||
env:
|
||||
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
GITHUB_API_URL: ${{ github.api_url }}
|
||||
GIT_REPO_URL: ${{ github.event.repository.clone_url }}
|
||||
ISSUE_URL: ${{ github.event.issue.html_url || github.event.comment.html_url }}
|
||||
ISSUE_BODY: ${{ github.event.issue.body || github.event.comment.body }}
|
||||
OPENAI_KEY: ${{ secrets.OPENAI_KEY }}
|
||||
|
||||
# The actual set of actions
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
issue_agent:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
if: ${{ github.event.sender.type != 'Bot' }} #Do not respond to bots
|
||||
|
||||
# Set required permissions
|
||||
permissions:
|
||||
contents: read # For reading repository contents
|
||||
issues: write # For commenting on issues
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Run PR Agent on Issues
|
||||
if: ${{ env.ISSUE_URL != '' }}
|
||||
uses: docker://codiumai/pr-agent:latest
|
||||
with:
|
||||
entrypoint: /bin/bash #Replace invoking cli.py directly with a shell
|
||||
args: |
|
||||
-c "cd /app && \
|
||||
echo 'Running Issue Agent action step on ISSUE_URL=$ISSUE_URL' && \
|
||||
export config__git_provider='github' && \
|
||||
export github__user_token=$GITHUB_TOKEN && \
|
||||
export github__base_url=$GITHUB_API_URL && \
|
||||
export openai__key=$OPENAI_KEY && \
|
||||
python -m pr_agent.cli --issue_url=$ISSUE_URL --pr_help_docs.repo_url="..." --pr_help_docs.docs_path="..." --pr_help_docs.openai_key=$OPENAI_KEY && \help_docs \"$ISSUE_BODY\""
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3) Following completion of the remaining steps (such as adding secrets and relevant configurations, such as `repo_url` and `docs_path`) merge this change to your main branch.
|
||||
When a new issue is opened, you should see a comment from `github-actions` bot with an auto response, assuming the question is related to the documentation of the repository.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuration options
|
||||
|
||||
Under the section `pr_help_docs`, the [configuration file](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml#L50) contains options to customize the 'help docs' tool:
|
||||
|
||||
- `repo_url`: If not overwritten, will use the repo from where the context came from (issue or PR), otherwise - use the given repo as context.
|
||||
- `repo_default_branch`: The branch to use in case repo_url overwritten, otherwise - has no effect.
|
||||
- `docs_path`: Relative path from root of repository (either the one this PR has been issued for, or above repo url).
|
||||
- `exclude_root_readme`: Whether or not to exclude the root README file for querying the model.
|
||||
- `supported_doc_exts` : Which file extensions should be included for the purpose of querying the model.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
@ -1,57 +0,0 @@
|
||||
`Platforms supported: GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket`
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The `implement` tool converts human code review discussions and feedback into ready-to-commit code changes.
|
||||
It leverages LLM technology to transform PR comments and review suggestions into concrete implementation code, helping developers quickly turn feedback into working solutions.
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage Scenarios
|
||||
|
||||
### For Reviewers
|
||||
|
||||
Reviewers can request code changes by:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Selecting the code block to be modified.
|
||||
2. Adding a comment with the syntax:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/implement <code-change-description>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
{width=640}
|
||||
|
||||
### For PR Authors
|
||||
|
||||
PR authors can implement suggested changes by replying to a review comment using either: <br>
|
||||
|
||||
1. Add specific implementation details as described above
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/implement <code-change-description>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Use the original review comment as instructions
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/implement
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
{width=640}
|
||||
|
||||
### For Referencing Comments
|
||||
|
||||
You can reference and implement changes from any comment by:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/implement <link-to-review-comment>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
{width=640}
|
||||
|
||||
Note that the implementation will occur within the review discussion thread.
|
||||
|
||||
**Configuration options**
|
||||
|
||||
- Use `/implement` to implement code change within and based on the review discussion.
|
||||
- Use `/implement <code-change-description>` inside a review discussion to implement specific instructions.
|
||||
- Use `/implement <link-to-review-comment>` to indirectly call the tool from any comment.
|
||||
@ -1,26 +1,16 @@
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The `improve` tool scans the PR code changes, and automatically generates meaningful suggestions for improving the PR code.
|
||||
The `improve` tool scans the PR code changes, and automatically generates [meaningful](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/pr_code_suggestions_prompts.toml#L41) suggestions for improving the PR code.
|
||||
The tool can be triggered automatically every time a new PR is [opened](../usage-guide/automations_and_usage.md#github-app-automatic-tools-when-a-new-pr-is-opened), or it can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
/improve
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## How it looks
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Suggestions Overview"
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Selecting a specific suggestion"
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
Note that the `Apply this suggestion` checkbox, which interactively converts a suggestion into a commitable code comment, is available only for Qodo Merge Pro 💎 users.
|
||||
|
||||
___
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "The following features are available only for Qodo Merge 💎 users:"
|
||||
- The `Apply / Chat` checkbox, which interactively converts a suggestion into a committable code comment
|
||||
- The `More` checkbox to generate additional suggestions
|
||||
- On Bitbucket (Cloud & Data Center) and GitLab Server (v16 and earlier), you can invoke [More Suggestions manually](#manual-more-suggestions)
|
||||
|
||||
## Example usage
|
||||
|
||||
@ -28,34 +18,25 @@ ___
|
||||
|
||||
Invoke the tool manually by commenting `/improve` on any PR. The code suggestions by default are presented as a single comment:
|
||||
|
||||
To edit [configurations](#configuration-options) related to the `improve` tool, use the following template:
|
||||
|
||||
To edit [configurations](#configuration-options) related to the improve tool, use the following template:
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
/improve --pr_code_suggestions.some_config1=... --pr_code_suggestions.some_config2=...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For example, you can choose to present all the suggestions as committable code comments, by running the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
For example, you can choose to present all the suggestions as commitable code comments, by running the following command:
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
/improve --pr_code_suggestions.commitable_code_suggestions=true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
As can be seen, a single table comment has a significantly smaller PR footprint. We recommend this mode for most cases.
|
||||
Also note that collapsible are not supported in _Bitbucket_. Hence, the suggestions can only be presented in Bitbucket as code comments.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Manual more suggestions
|
||||
To generate more suggestions (distinct from the ones already generated), for git-providers that don't support interactive checkbox option, you can manually run:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/improve --more_suggestions=true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Automatic triggering
|
||||
|
||||
To run the `improve` automatically when a PR is opened, define in a [configuration file](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/#wiki-configuration-file):
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[github_app]
|
||||
pr_commands = [
|
||||
@ -71,28 +52,25 @@ num_code_suggestions_per_chunk = ...
|
||||
- The `pr_commands` lists commands that will be executed automatically when a PR is opened.
|
||||
- The `[pr_code_suggestions]` section contains the configurations for the `improve` tool you want to edit (if any)
|
||||
|
||||
### Assessing Impact
|
||||
### Assessing Impact 💎
|
||||
|
||||
>`💎 feature`
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge tracks two types of implementations for tracking implemented suggestions:
|
||||
Note that Qodo Merge pro tracks two types of implementations:
|
||||
|
||||
- Direct implementation - when the user directly applies the suggestion by clicking the `Apply` checkbox.
|
||||
- Indirect implementation - when the user implements the suggestion in their IDE environment. In this case, Qodo Merge will utilize, after each commit, a dedicated logic to identify if a suggestion was implemented, and will mark it as implemented.
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
In post-process, Qodo Merge counts the number of suggestions that were implemented, and provides general statistics and insights about the suggestions' impact on the PR process.
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
## Suggestion tracking
|
||||
## Suggestion tracking 💎
|
||||
`Platforms supported: GitHub, GitLab`
|
||||
|
||||
>`💎 feature. Platforms supported: GitHub, GitLab`
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge employs a novel detection system to automatically [identify](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/impact_evaluation/) AI code suggestions that PR authors have accepted and implemented.
|
||||
Qodo Merge employs an novel detection system to automatically [identify](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/impact_evaluation/) AI code suggestions that PR authors have accepted and implemented.
|
||||
|
||||
Accepted suggestions are also automatically documented in a dedicated wiki page called `.pr_agent_accepted_suggestions`, allowing users to track historical changes, assess the tool's effectiveness, and learn from previously implemented recommendations in the repository.
|
||||
An example [result](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/wiki/.pr_agent_accepted_suggestions):
|
||||
@ -105,179 +83,21 @@ This feature is controlled by a boolean configuration parameter: `pr_code_sugges
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Wiki must be enabled"
|
||||
While the aggregation process is automatic, GitHub repositories require a one-time manual wiki setup.
|
||||
|
||||
To initialize the wiki: navigate to `Wiki`, select `Create the first page`, then click `Save page`.
|
||||
|
||||
To initialize the wiki: navigate to `Wiki`, select `Create the first page`, then click `Save page`.
|
||||
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
|
||||
Once a wiki repo is created, the tool will automatically use this wiki for tracking suggestions.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Why a wiki page?"
|
||||
Your code belongs to you, and we respect your privacy. Hence, we won't store any code suggestions in an external database.
|
||||
Your code belongs to you, and we respect your privacy. Hence, we won't store any code suggestions in an external database.
|
||||
|
||||
Instead, we leverage a dedicated private page, within your repository wiki, to track suggestions. This approach offers convenient secure suggestion tracking while avoiding pull requests or any noise to the main repository.
|
||||
|
||||
## `Extra instructions` and `best practices`
|
||||
|
||||
The `improve` tool can be further customized by providing additional instructions and best practices to the AI model.
|
||||
|
||||
### Extra instructions
|
||||
|
||||
You can use the `extra_instructions` configuration option to give the AI model additional instructions for the `improve` tool.
|
||||
Be specific, clear, and concise in the instructions. With extra instructions, you are the prompter.
|
||||
|
||||
Examples for possible instructions:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[pr_code_suggestions]
|
||||
extra_instructions="""\
|
||||
(1) Answer in Japanese
|
||||
(2) Don't suggest to add try-except block
|
||||
(3) Ignore changes in toml files
|
||||
...
|
||||
"""
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Use triple quotes to write multi-line instructions. Use bullet points or numbers to make the instructions more readable.
|
||||
|
||||
### Best practices
|
||||
|
||||
> `💎 feature. Platforms supported: GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket`
|
||||
|
||||
Another option to give additional guidance to the AI model is by creating a `best_practices.md` file in your repository's root directory.
|
||||
This page can contain a list of best practices, coding standards, and guidelines that are specific to your repo/organization.
|
||||
|
||||
The AI model will use this `best_practices.md` file as a reference, and in case the PR code violates any of the guidelines, it will create additional suggestions, with a dedicated label: `Organization
|
||||
best practice`.
|
||||
|
||||
Example for a Python `best_practices.md` content:
|
||||
|
||||
```markdown
|
||||
## Project best practices
|
||||
- Make sure that I/O operations are encapsulated in a try-except block
|
||||
- Use the `logging` module for logging instead of `print` statements
|
||||
- Use `is` and `is not` to compare with `None`
|
||||
- Use `if __name__ == '__main__':` to run the code only when the script is executed
|
||||
- Use `with` statement to open files
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Tips for writing an effective `best_practices.md` file:
|
||||
|
||||
- Write clearly and concisely
|
||||
- Include brief code examples when helpful
|
||||
- Focus on project-specific guidelines, that will result in relevant suggestions you actually want to get
|
||||
- Keep the file relatively short, under 800 lines, since:
|
||||
- AI models may not process effectively very long documents
|
||||
- Long files tend to contain generic guidelines already known to AI
|
||||
|
||||
To control the number of best practices suggestions generated by the `improve` tool, give the following configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[best_practices]
|
||||
num_best_practice_suggestions = 2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Local and global best practices
|
||||
|
||||
By default, Qodo Merge will look for a local `best_practices.md` in the root of the relevant local repo.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to enable also a global `best_practices.md` file, set first in the global configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[best_practices]
|
||||
enable_global_best_practices = true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then, create a `best_practices.md` file in the root of [global](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/#global-configuration-file) configuration repository, `pr-agent-settings`.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Best practices for multiple languages
|
||||
|
||||
For a git organization working with multiple programming languages, you can maintain a centralized global `best_practices.md` file containing language-specific guidelines.
|
||||
When reviewing pull requests, Qodo Merge automatically identifies the programming language and applies the relevant best practices from this file.
|
||||
|
||||
To do this, structure your `best_practices.md` file using the following format:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# [Python]
|
||||
...
|
||||
# [Java]
|
||||
...
|
||||
# [JavaScript]
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Dedicated label for best practices suggestions
|
||||
|
||||
Best practice suggestions are labeled as `Organization best practice` by default.
|
||||
To customize this label, modify it in your configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[best_practices]
|
||||
organization_name = "..."
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And the label will be: `{organization_name} best practice`.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example results
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
### Auto best practices
|
||||
|
||||
>`💎 feature. Platforms supported: GitHub.`
|
||||
|
||||
`Auto best practices` is a novel Qodo Merge capability that:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Identifies recurring patterns from accepted suggestions
|
||||
2. **Automatically** generates [best practices page](https://github.com/qodo-ai/pr-agent/wiki/.pr_agent_auto_best_practices) based on what your team consistently values
|
||||
3. Applies these learned patterns to future code reviews
|
||||
|
||||
This creates an automatic feedback loop where the system continuously learns from your team's choices to provide increasingly relevant suggestions.
|
||||
The system maintains two analysis phases:
|
||||
|
||||
- Open exploration for new issues
|
||||
- Targeted checking against established best practices
|
||||
|
||||
Note that when a [custom best practices](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#best-practices) exist, Qodo Merge will still generate an 'auto best practices' wiki file, though it won't use it in the `improve` tool.
|
||||
Learn more about utilizing 'auto best practices' in our [detailed guide](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/auto_best_practices/).
|
||||
|
||||
#### Relevant configurations
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[auto_best_practices]
|
||||
# Disable all auto best practices usage or generation
|
||||
enable_auto_best_practices = true
|
||||
|
||||
# Disable usage of auto best practices file in the 'improve' tool
|
||||
utilize_auto_best_practices = true
|
||||
|
||||
# Extra instructions to the auto best practices generation prompt
|
||||
extra_instructions = ""
|
||||
|
||||
# Max number of patterns to be detected
|
||||
max_patterns = 5
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Multiple best practices sources
|
||||
|
||||
The `improve` tool will combine best practices from all available sources - global configuration, local configuration, and auto-generated files - to provide you with comprehensive recommendations.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Combining 'extra instructions' and 'best practices'
|
||||
|
||||
> `💎 feature`
|
||||
|
||||
The `extra instructions` configuration is more related to the `improve` tool prompt. It can be used, for example, to avoid specific suggestions ("Don't suggest to add try-except block", "Ignore changes in toml files", ...) or to emphasize specific aspects or formats ("Answer in Japanese", "Give only short suggestions", ...)
|
||||
|
||||
In contrast, the `best_practices.md` file is a general guideline for the way code should be written in the repo.
|
||||
|
||||
Using a combination of both can help the AI model to provide relevant and tailored suggestions.
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage Tips
|
||||
|
||||
### Implementing the proposed code suggestions
|
||||
|
||||
Each generated suggestion consists of three key elements:
|
||||
|
||||
1. A single-line summary of the proposed change
|
||||
@ -285,54 +105,14 @@ Each generated suggestion consists of three key elements:
|
||||
3. A diff snippet showing the recommended code modification (before and after)
|
||||
|
||||
We advise users to apply critical analysis and judgment when implementing the proposed suggestions.
|
||||
In addition to mistakes (which may happen, but are rare), sometimes the presented code modification may serve more as an _illustrative example_ than a directly applicable solution.
|
||||
In addition to mistakes (which may happen, but are rare), sometimes the presented code modification may serve more as an _illustrative example_ than a direct applicable solution.
|
||||
In such cases, we recommend prioritizing the suggestion's detailed description, using the diff snippet primarily as a supporting reference.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Chat on code suggestions
|
||||
|
||||
> `💎 feature` Platforms supported: GitHub, GitLab
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge implements an orchestrator agent that enables interactive code discussions, listening and responding to comments without requiring explicit tool calls.
|
||||
The orchestrator intelligently analyzes your responses to determine if you want to implement a suggestion, ask a question, or request help, then delegates to the appropriate specialized tool.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Setup and Activation
|
||||
|
||||
Enable interactive code discussions by adding the following to your configuration file (default is `True`):
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[pr_code_suggestions]
|
||||
enable_chat_in_code_suggestions = true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info "Activating Dynamic Responses"
|
||||
To obtain dynamic responses, the following steps are required:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Run the `/improve` command (mostly automatic)
|
||||
2. Tick the `/improve` recommendation checkboxes (_Apply this suggestion_) to have Qodo Merge generate a new inline code suggestion discussion
|
||||
3. The orchestrator agent will then automatically listen and reply to comments within the discussion without requiring additional commands
|
||||
|
||||
#### Explore the available interaction patterns:
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip "Tip: Direct the agent with keywords"
|
||||
Use "implement" or "apply" for code generation. Use "explain", "why", or "how" for information and help.
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Asking for Details"
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Implementing Suggestions"
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Providing Additional Help"
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Dual publishing mode
|
||||
|
||||
Our recommended approach for presenting code suggestions is through a [table](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#overview) (`--pr_code_suggestions.commitable_code_suggestions=false`).
|
||||
Our recommended approach for presenting code suggestions is through a [table](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#overview) (`--pr_code_suggestions.commitable_code_suggestions=false`).
|
||||
This method significantly reduces the PR footprint and allows for quick and easy digestion of multiple suggestions.
|
||||
|
||||
We also offer a complementary **dual publishing mode**. When enabled, suggestions exceeding a certain score threshold are not only displayed in the table, but also presented as committable PR comments.
|
||||
We also offer a complementary **dual publishing mode**. When enabled, suggestions exceeding a certain score threshold are not only displayed in the table, but also presented as commitable PR comments.
|
||||
This mode helps highlight suggestions deemed more critical.
|
||||
|
||||
To activate dual publishing mode, use the following setting:
|
||||
@ -342,14 +122,10 @@ To activate dual publishing mode, use the following setting:
|
||||
dual_publishing_score_threshold = x
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Where x represents the minimum score threshold (>=) for suggestions to be presented as committable PR comments in addition to the table. Default is -1 (disabled).
|
||||
Where x represents the minimum score threshold (>=) for suggestions to be presented as commitable PR comments in addition to the table. Default is -1 (disabled).
|
||||
|
||||
### Self-review
|
||||
|
||||
> `💎 feature` Platforms supported: GitHub, GitLab
|
||||
|
||||
If you set in a configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[pr_code_suggestions]
|
||||
demand_code_suggestions_self_review = true
|
||||
@ -357,7 +133,6 @@ demand_code_suggestions_self_review = true
|
||||
|
||||
The `improve` tool will add a checkbox below the suggestions, prompting user to acknowledge that they have reviewed the suggestions.
|
||||
You can set the content of the checkbox text via:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[pr_code_suggestions]
|
||||
code_suggestions_self_review_text = "... (your text here) ..."
|
||||
@ -365,6 +140,7 @@ code_suggestions_self_review_text = "... (your text here) ..."
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip "Tip - Reducing visual footprint after self-review 💎"
|
||||
|
||||
The configuration parameter `pr_code_suggestions.fold_suggestions_on_self_review` (default is True)
|
||||
@ -372,6 +148,8 @@ code_suggestions_self_review_text = "... (your text here) ..."
|
||||
|
||||
This reduces the visual footprint of the suggestions, and also indicates to the PR reviewer that the suggestions have been reviewed by the PR author, and don't require further attention.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip "Tip - Demanding self-review from the PR author 💎"
|
||||
|
||||
By setting:
|
||||
@ -387,102 +165,103 @@ code_suggestions_self_review_text = "... (your text here) ..."
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
- If you keep the number of required reviewers for a PR to 1 and enable this configuration, this effectively means that the PR author can approve the PR by actively clicking the self-review checkbox.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
To prevent unauthorized approvals, this configuration defaults to false, and cannot be altered through online comments; enabling requires a direct update to the configuration file and a commit to the repository. This ensures that utilizing the feature demands a deliberate documented decision by the repository owner.
|
||||
|
||||
### Auto-approval
|
||||
|
||||
> `💎 feature. Platforms supported: GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket`
|
||||
|
||||
Under specific conditions, Qodo Merge can auto-approve a PR when a specific comment is invoked, or when the PR meets certain criteria.
|
||||
|
||||
**To ensure safety, the auto-approval feature is disabled by default.**
|
||||
To enable auto-approval features, you need to actively set one or both of the following options in a pre-defined _configuration file_:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
enable_comment_approval = true # For approval via comments
|
||||
enable_auto_approval = true # For criteria-based auto-approval
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Notes"
|
||||
- Note that this specific flag cannot be set with a command line argument, only in the configuration file, committed to the repository.
|
||||
- Enabling auto-approval must be a deliberate decision by the repository owner.
|
||||
|
||||
1\. **Auto-approval by commenting**
|
||||
|
||||
To enable auto-approval by commenting, set in the configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
enable_comment_approval = true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
After enabling, by commenting on a PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/review auto_approve
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge will automatically approve the PR, and add a comment with the approval.
|
||||
|
||||
2\. **Auto-approval when the PR meets certain criteria**
|
||||
|
||||
To enable auto-approval based on specific criteria, first, you need to enable the top-level flag:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
enable_auto_approval = true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
There are two criteria that can be set for auto-approval:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Review effort score**
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
enable_auto_approval = true
|
||||
auto_approve_for_low_review_effort = X # X is a number between 1 to 5
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
When the [review effort score](https://www.qodo.ai/images/pr_agent/review3.png) is lower or equal to X, the PR will be auto-approved.
|
||||
|
||||
___
|
||||
|
||||
- **No code suggestions**
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
enable_auto_approval = true
|
||||
auto_approve_for_no_suggestions = true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
When no [code suggestion](https://www.qodo.ai/images/pr_agent/code_suggestions_as_comment_closed.png) were found for the PR, the PR will be auto-approved.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### How many code suggestions are generated?
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge uses a dynamic strategy to generate code suggestions based on the size of the pull request (PR). Here's how it works:
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1. Chunking large PRs
|
||||
1) Chunking large PRs:
|
||||
|
||||
- Qodo Merge divides large PRs into 'chunks'.
|
||||
- Each chunk contains up to `pr_code_suggestions.max_context_tokens` tokens (default: 24,000).
|
||||
- Each chunk contains up to `pr_code_suggestions.max_context_tokens` tokens (default: 14,000).
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. Generating suggestions
|
||||
|
||||
2) Generating suggestions:
|
||||
|
||||
- For each chunk, Qodo Merge generates up to `pr_code_suggestions.num_code_suggestions_per_chunk` suggestions (default: 4).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
This approach has two main benefits:
|
||||
|
||||
- Scalability: The number of suggestions scales with the PR size, rather than being fixed.
|
||||
- Quality: By processing smaller chunks, the AI can maintain higher quality suggestions, as larger contexts tend to decrease AI performance.
|
||||
|
||||
Note: Chunking is primarily relevant for large PRs. For most PRs (up to 600 lines of code), Qodo Merge will be able to process the entire code in a single call.
|
||||
Note: Chunking is primarily relevant for large PRs. For most PRs (up to 500 lines of code), Qodo Merge will be able to process the entire code in a single call.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 'Extra instructions' and 'best practices'
|
||||
|
||||
#### Extra instructions
|
||||
|
||||
>`Platforms supported: GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket`
|
||||
|
||||
You can use the `extra_instructions` configuration option to give the AI model additional instructions for the `improve` tool.
|
||||
Be specific, clear, and concise in the instructions. With extra instructions, you are the prompter. Specify relevant aspects that you want the model to focus on.
|
||||
|
||||
Examples for possible instructions:
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[pr_code_suggestions]
|
||||
extra_instructions="""\
|
||||
(1) Answer in japanese
|
||||
(2) Don't suggest to add try-excpet block
|
||||
(3) Ignore changes in toml files
|
||||
...
|
||||
"""
|
||||
```
|
||||
Use triple quotes to write multi-line instructions. Use bullet points or numbers to make the instructions more readable.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Best practices 💎
|
||||
|
||||
>`Platforms supported: GitHub, GitLab`
|
||||
|
||||
Another option to give additional guidance to the AI model is by creating a dedicated [**wiki page**](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/wiki) called `best_practices.md`.
|
||||
This page can contain a list of best practices, coding standards, and guidelines that are specific to your repo/organization.
|
||||
|
||||
The AI model will use this wiki page as a reference, and in case the PR code violates any of the guidelines, it will suggest improvements accordingly, with a dedicated label: `Organization
|
||||
best practice`.
|
||||
|
||||
Example for a `best_practices.md` content can be found [here](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/docs/docs/usage-guide/EXAMPLE_BEST_PRACTICE.md) (adapted from Google's [pyguide](https://google.github.io/styleguide/pyguide.html)).
|
||||
This file is only an example. Since it is used as a prompt for an AI model, we want to emphasize the following:
|
||||
|
||||
- It should be written in a clear and concise manner
|
||||
- If needed, it should give short relevant code snippets as examples
|
||||
- Recommended to limit the text to 800 lines or fewer. Here’s why:
|
||||
|
||||
1) Extremely long best practices documents may not be fully processed by the AI model.
|
||||
|
||||
2) A lengthy file probably represent a more "**generic**" set of guidelines, which the AI model is already familiar with. The objective is to focus on a more targeted set of guidelines tailored to the specific needs of this project.
|
||||
|
||||
##### Local and global best practices
|
||||
By default, Qodo Merge will look for a local `best_practices.md` wiki file in the root of the relevant local repo.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to enable also a global `best_practices.md` wiki file, set first in the global configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[best_practices]
|
||||
enable_global_best_practices = true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then, create a `best_practices.md` wiki file in the root of [global](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/#global-configuration-file) configuration repository, `pr-agent-settings`.
|
||||
|
||||
##### Example results
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### How to combine `extra instructions` and `best practices`
|
||||
|
||||
The `extra instructions` configuration is more related to the `improve` tool prompt. It can be used, for example, to avoid specific suggestions ("Don't suggest to add try-except block", "Ignore changes in toml files", ...) or to emphasize specific aspects or formats ("Answer in Japanese", "Give only short suggestions", ...)
|
||||
|
||||
In contrast, the `best_practices.md` file is a general guideline for the way code should be written in the repo.
|
||||
|
||||
Using a combination of both can help the AI model to provide relevant and tailored suggestions.
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuration options
|
||||
|
||||
??? example "General options"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>extra_instructions</b></td>
|
||||
@ -490,23 +269,19 @@ Note: Chunking is primarily relevant for large PRs. For most PRs (up to 600 line
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>commitable_code_suggestions</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will display the suggestions as committable code comments. Default is false.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>enable_chat_in_code_suggestions</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, QM bot will interact with comments made on code changes it has proposed. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will display the suggestions as commitable code comments. Default is false.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>dual_publishing_score_threshold</b></td>
|
||||
<td>Minimum score threshold for suggestions to be presented as committable PR comments in addition to the table. Default is -1 (disabled).</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>focus_only_on_problems</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, suggestions will focus primarily on identifying and fixing code problems, and less on style considerations like best practices, maintainability, or readability. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
<td>Minimum score threshold for suggestions to be presented as commitable PR comments in addition to the table. Default is -1 (disabled).</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>persistent_comment</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the improve comment will be persistent, meaning that every new improve request will edit the previous one. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the improve comment will be persistent, meaning that every new improve request will edit the previous one. Default is false.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>self_reflect_on_suggestions</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the improve tool will calculate an importance score for each suggestion [1-10], and sort the suggestion labels group based on this score. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>suggestions_score_threshold</b></td>
|
||||
@ -516,10 +291,6 @@ Note: Chunking is primarily relevant for large PRs. For most PRs (up to 600 line
|
||||
<td><b>apply_suggestions_checkbox</b></td>
|
||||
<td> Enable the checkbox to create a committable suggestion. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>enable_more_suggestions_checkbox</b></td>
|
||||
<td> Enable the checkbox to generate more suggestions. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>enable_help_text</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will display a help text in the comment. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
@ -528,17 +299,10 @@ Note: Chunking is primarily relevant for large PRs. For most PRs (up to 600 line
|
||||
<td><b>enable_chat_text</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will display a reference to the PR chat in the comment. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>publish_output_no_suggestions</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will publish a comment even if no suggestions were found. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>wiki_page_accepted_suggestions</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will automatically track accepted suggestions in a dedicated wiki page called `.pr_agent_accepted_suggestions`. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>allow_thumbs_up_down</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, all code suggestions will have thumbs up and thumbs down buttons, to encourage users to provide feedback on the suggestions. Default is false. Note that this feature is for statistics tracking. It will not affect future feedback from the AI model.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
??? example "Params for number of suggestions and AI calls"
|
||||
@ -550,21 +314,26 @@ Note: Chunking is primarily relevant for large PRs. For most PRs (up to 600 line
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>num_code_suggestions_per_chunk</b></td>
|
||||
<td>Number of code suggestions provided by the 'improve' tool, per chunk. Default is 3.</td>
|
||||
<td>Number of code suggestions provided by the 'improve' tool, per chunk. Default is 4.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>max_number_of_calls</b></td>
|
||||
<td>Maximum number of chunks. Default is 3.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>rank_extended_suggestions</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will rank the suggestions, based on importance. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
## Understanding AI Code Suggestions
|
||||
## A note on code suggestions quality
|
||||
|
||||
- **AI Limitations:** AI models for code are getting better and better, but they are not flawless. Not all the suggestions will be perfect, and a user should not accept all of them automatically. Critical reading and judgment are required. Mistakes of the AI are rare but can happen, and it is usually quite easy for a human to spot them.
|
||||
- **Purpose of Suggestions:**
|
||||
- **Self-reflection:** The suggestions aim to enable developers to _self-reflect_ and improve their pull requests. This process can help to identify blind spots, uncover missed edge cases, and enhance code readability and coherency. Even when a specific code suggestion isn't suitable, the underlying issue it highlights often reveals something important that might deserve attention.
|
||||
- **Bug detection:** The suggestions also alert on any _critical bugs_ that may have been identified during the analysis. This provides an additional safety net to catch potential issues before they make it into production. It's perfectly acceptable to implement only the suggestions you find valuable for your specific context.
|
||||
- **Hierarchy:** Presenting the suggestions in a structured hierarchical table enables the user to _quickly_ understand them, and to decide which ones are relevant and which are not.
|
||||
- **Customization:** To guide the model to suggestions that are more relevant to the specific needs of your project, we recommend using the [`extra_instructions`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#extra-instructions-and-best-practices) and [`best practices`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#best-practices) fields.
|
||||
- **Model Selection:** SaaS users can also [choose](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/qodo_merge_models/) between different models. For specific programming languages or use cases, some models may perform better than others.
|
||||
- **Interactive usage:** The interactive [PR chat](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/chrome-extension/) also provides an easy way to get more tailored suggestions and feedback from the AI model.
|
||||
- AI models for code are getting better and better (Sonnet-3.5 and GPT-4), but they are not flawless. Not all the suggestions will be perfect, and a user should not accept all of them automatically. Critical reading and judgment are required.
|
||||
- While mistakes of the AI are rare but can happen, a real benefit from the suggestions of the `improve` (and [`review`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/review/)) tool is to catch, with high probability, **mistakes or bugs done by the PR author**, when they happen. So, it's a good practice to spend the needed ~30-60 seconds to review the suggestions, even if not all of them are always relevant.
|
||||
- The hierarchical structure of the suggestions is designed to help the user to _quickly_ understand them, and to decide which ones are relevant and which are not:
|
||||
|
||||
- Only if the `Category` header is relevant, the user should move to the summarized suggestion description
|
||||
- Only if the summarized suggestion description is relevant, the user should click on the collapsible, to read the full suggestion description with a code preview example.
|
||||
|
||||
- In addition, we recommend to use the [`extra_instructions`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#extra-instructions-and-best-practices) field to guide the model to suggestions that are more relevant to the specific needs of the project.
|
||||
- The interactive [PR chat](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/chrome-extension/) also provides an easy way to get more tailored suggestions and feedback from the AI model.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,14 +1,13 @@
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The `improve_component` tool generates code suggestions for a specific code component that changed in the PR.
|
||||
it can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/improve_component component_name
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To get a list of the components that changed in the PR and choose the relevant component interactively, use the [`analyze`](./analyze.md) tool.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Example usage
|
||||
|
||||
Invoke the tool manually by commenting `/improve_component` on any PR:
|
||||
@ -19,13 +18,12 @@ The tool will generate code suggestions for the selected component (if no compon
|
||||
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Notes"
|
||||
- Language that are currently supported by the tool: Python, Java, C++, JavaScript, TypeScript, C#.
|
||||
- This tool can also be triggered interactively by using the [`analyze`](./analyze.md) tool.
|
||||
**Notes**
|
||||
- Language that are currently supported by the tool: Python, Java, C++, JavaScript, TypeScript, C#.
|
||||
- This tool can also be triggered interactively by using the [`analyze`](./analyze.md) tool.
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuration options
|
||||
|
||||
- `num_code_suggestions`: number of code suggestions to provide. Default is 4
|
||||
- `extra_instructions`: Optional extra instructions to the tool. For example: "focus on ...".
|
||||
- `file`: in case there are several components with the same name, you can specify the relevant file.
|
||||
- `class_name`: in case there are several methods with the same name in the same file, you can specify the relevant class name.
|
||||
- `class_name`: in case there are several methods with the same name in the same file, you can specify the relevant class name.
|
||||
@ -9,17 +9,14 @@ Here is a list of Qodo Merge tools, each with a dedicated page that explains how
|
||||
| **[Code Suggestions (`/improve`](./improve.md))** | Code suggestions for improving the PR |
|
||||
| **[Question Answering (`/ask ...`](./ask.md))** | Answering free-text questions about the PR, or on specific code lines |
|
||||
| **[Update Changelog (`/update_changelog`](./update_changelog.md))** | Automatically updating the CHANGELOG.md file with the PR changes |
|
||||
| **[Find Similar Issue (`/similar_issue`](./similar_issues.md))** | Automatically retrieves and presents similar issues |
|
||||
| **[Help (`/help`](./help.md))** | Provides a list of all the available tools. Also enables to trigger them interactively (💎) |
|
||||
| **💎 [Add Documentation (`/add_docs`](./documentation.md))** | Generates documentation to methods/functions/classes that changed in the PR |
|
||||
| **💎 [Generate Custom Labels (`/generate_labels`](./custom_labels.md))** | Generates custom labels for the PR, based on specific guidelines defined by the user |
|
||||
| **💎 [Analyze (`/analyze`](./analyze.md))** | Identify code components that changed in the PR, and enables to interactively generate tests, docs, and code suggestions for each component |
|
||||
| **💎 [Test (`/test`](./test.md))** | generate tests for a selected component, based on the PR code changes |
|
||||
| **💎 [Custom Prompt (`/custom_prompt`](./custom_prompt.md))** | Automatically generates custom suggestions for improving the PR code, based on specific guidelines defined by the user |
|
||||
| **💎 [Generate Tests (`/test component_name`](./test.md))** | Automatically generates unit tests for a selected component, based on the PR code changes |
|
||||
| **💎 [Improve Component (`/improve_component component_name`](./improve_component.md))** | Generates code suggestions for a specific code component that changed in the PR |
|
||||
| **💎 [CI Feedback (`/checks ci_job`](./ci_feedback.md))** | Automatically generates feedback and analysis for a failed CI job |
|
||||
| **💎 [Implement (`/implement`](./implement.md))** | Generates implementation code from review suggestions |
|
||||
| **💎 [Scan Repo Discussions (`/scan_repo_discussions`](./scan_repo_discussions.md))** | Generates `best_practices.md` file based on previous discussions in the repository |
|
||||
| **💎 [Repo Statistics (`/repo_statistics`](./repo_statistics.md))** | Provides repository statistics on time to merge and time to first comment |
|
||||
|
||||
Note that the tools marked with 💎 are available only for Qodo Merge users.
|
||||
Note that the tools marked with 💎 are available only for Qodo Merge Pro users.
|
||||
@ -1,44 +0,0 @@
|
||||
`Platforms supported: GitHub`
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The `repo_statistics` tool analyzes statistics from merged pull requests over the past 12 months prior to Qodo Merge installation.
|
||||
It calculates key metrics that help teams establish a baseline of their PR workflow efficiency.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Active repositories are needed"
|
||||
The tool is designed to work with real-life repositories, as it relies on actual discussions to generate meaningful insights.
|
||||
At least 30 merged PRs are required to generate meaningful statistical data.
|
||||
|
||||
### Metrics Analyzed
|
||||
|
||||
- **Time to merge:** The median and average time it takes for PRs to be merged after opening
|
||||
- **Time to first comment:** The median and average time it takes to get the first comment on a PR
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Usage
|
||||
|
||||
The tool can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/repo_statistics
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In response, the bot will comment with the statistical data.
|
||||
Note that the scan can take several minutes to complete, since up to 100 PRs are scanned.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info "Automatic trigger"
|
||||
Upon adding the Qodo Merge bot to a repository, the tool will automatically scan the last 365 days of PRs and send them to MixPanel, if enabled.
|
||||
|
||||
## Example usage
|
||||
|
||||
{width=640}
|
||||
|
||||
MixPanel optional presentation:
|
||||
|
||||
{width=640}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Configuration options
|
||||
|
||||
- Use `/repo_statistics --repo_statistics.days_back=X` to specify the number of days back to scan for discussions. The default is 365 days.
|
||||
- Use `/repo_statistics --repo_statistics.minimal_number_of_prs=X` to specify the minimum number of merged PRs needed to generate the statistics. The default is 30 PRs.
|
||||
@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The `review` tool scans the PR code changes, and generates a list of feedbacks about the PR, aiming to aid the reviewing process.
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
The tool can be triggered automatically every time a new PR is [opened](../usage-guide/automations_and_usage.md#github-app-automatic-tools-when-a-new-pr-is-opened), or can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/review
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -12,6 +10,7 @@ Note that the main purpose of the `review` tool is to provide the **PR reviewer*
|
||||
|
||||
(Read more about the different personas in the PR process and how Qodo Merge aims to assist them in our [blog](https://www.codium.ai/blog/understanding-the-challenges-and-pain-points-of-the-pull-request-cycle/))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Example usage
|
||||
|
||||
### Manual triggering
|
||||
@ -25,7 +24,6 @@ After ~30 seconds, the tool will generate a review for the PR:
|
||||
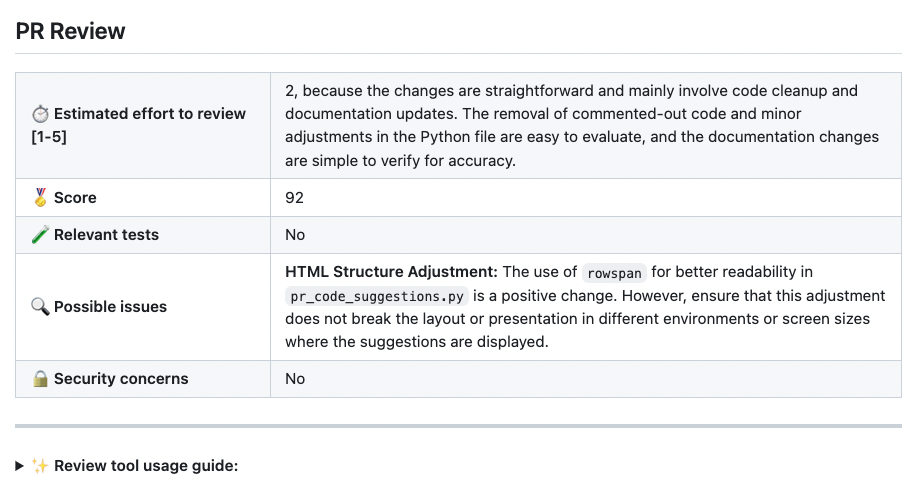{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to edit [configurations](#configuration-options), add the relevant ones to the command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/review --pr_reviewer.some_config1=... --pr_reviewer.some_config2=...
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -33,7 +31,6 @@ If you want to edit [configurations](#configuration-options), add the relevant o
|
||||
### Automatic triggering
|
||||
|
||||
To run the `review` automatically when a PR is opened, define in a [configuration file](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/#wiki-configuration-file):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[github_app]
|
||||
pr_commands = [
|
||||
@ -42,79 +39,140 @@ pr_commands = [
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
[pr_reviewer]
|
||||
extra_instructions = "..."
|
||||
num_code_suggestions = ...
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- The `pr_commands` lists commands that will be executed automatically when a PR is opened.
|
||||
- The `[pr_reviewer]` section contains the configurations for the `review` tool you want to edit (if any).
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ()
|
||||
[//]: # (### Incremental Mode)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (Incremental review only considers changes since the last Qodo Merge review. This can be useful when working on the PR in an iterative manner, and you want to focus on the changes since the last review instead of reviewing the entire PR again.)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (For invoking the incremental mode, the following command can be used:)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (```)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (/review -i)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (```)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (Note that the incremental mode is only available for GitHub.)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ()
|
||||
[//]: # (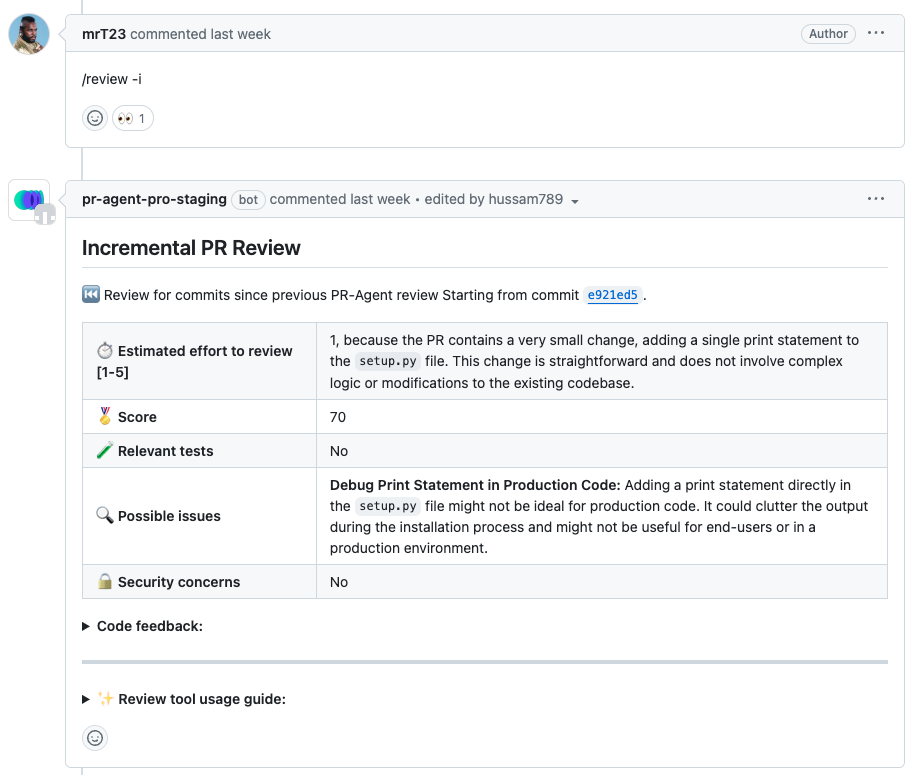{width=512})
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (### PR Reflection)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ()
|
||||
[//]: # (By invoking:)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (```)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (/reflect_and_review)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (```)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (The tool will first ask the author questions about the PR, and will guide the review based on their answers.)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ()
|
||||
[//]: # (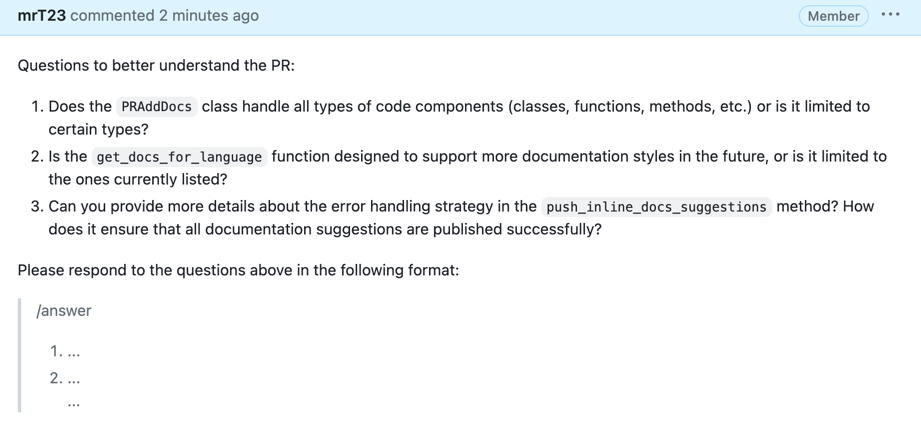{width=512})
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ()
|
||||
[//]: # (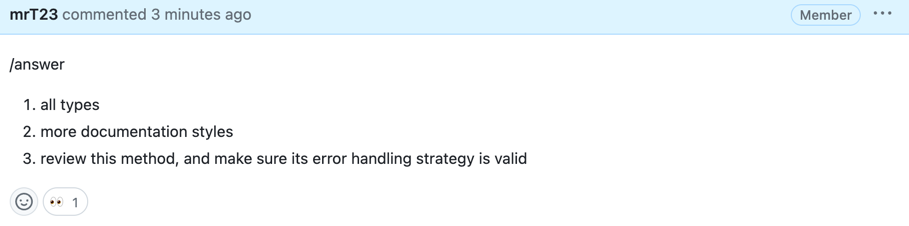{width=512})
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ()
|
||||
[//]: # (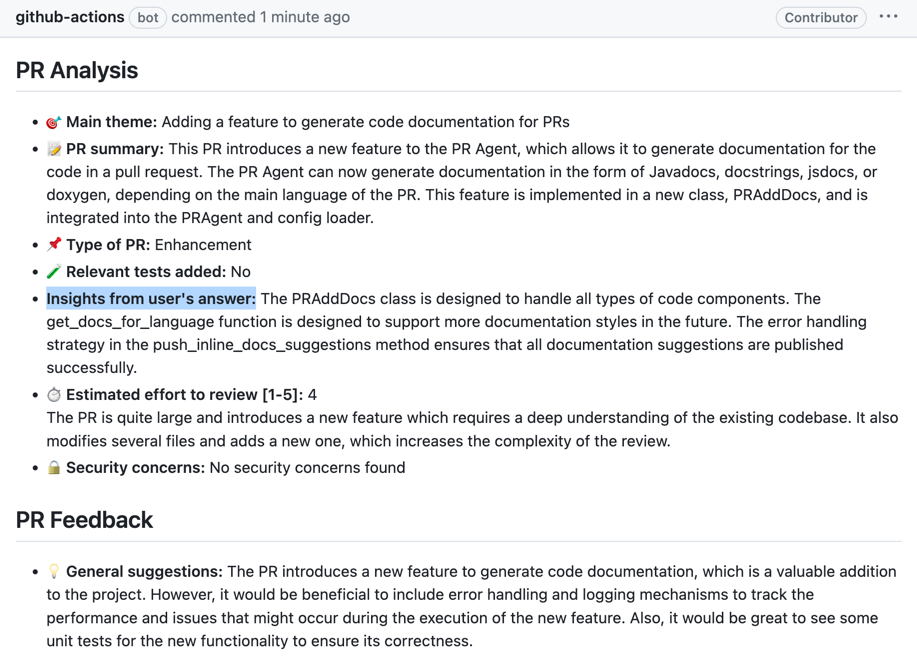{width=512})
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuration options
|
||||
|
||||
!!! example "General options"
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>persistent_comment</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the review comment will be persistent, meaning that every new review request will edit the previous one. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>final_update_message</b></td>
|
||||
<td>When set to true, updating a persistent review comment during online commenting will automatically add a short comment with a link to the updated review in the pull request .Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>extra_instructions</b></td>
|
||||
<td>Optional extra instructions to the tool. For example: "focus on the changes in the file X. Ignore change in ...".</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>enable_help_text</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will display a help text in the comment. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>num_code_suggestions</b></td>
|
||||
<td>Number of code suggestions provided by the 'review' tool. Default is 0, meaning no code suggestions will be provided by the `review` tool.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>inline_code_comments</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will publish the code suggestions as comments on the code diff. Default is false. Note that you need to set `num_code_suggestions`>0 to get code suggestions </td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>persistent_comment</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the review comment will be persistent, meaning that every new review request will edit the previous one. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>extra_instructions</b></td>
|
||||
<td>Optional extra instructions to the tool. For example: "focus on the changes in the file X. Ignore change in ...".</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>enable_help_text</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will display a help text in the comment. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
!!! example "Enable\\disable specific sub-sections"
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>require_score_review</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will add a section that scores the PR. Default is false.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>require_tests_review</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will add a section that checks if the PR contains tests. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>require_estimate_effort_to_review</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will add a section that estimates the effort needed to review the PR. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>require_can_be_split_review</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will add a section that checks if the PR contains several themes, and can be split into smaller PRs. Default is false.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>require_security_review</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will add a section that checks if the PR contains a possible security or vulnerability issue. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>require_ticket_analysis_review</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, and the PR contains a GitHub or Jira ticket link, the tool will add a section that checks if the PR in fact fulfilled the ticket requirements. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>require_score_review</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will add a section that scores the PR. Default is false.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>require_tests_review</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will add a section that checks if the PR contains tests. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>require_estimate_effort_to_review</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will add a section that estimates the effort needed to review the PR. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>require_can_be_split_review</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will add a section that checks if the PR contains several themes, and can be split into smaller PRs. Default is false.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>require_security_review</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will add a section that checks if the PR contains a possible security or vulnerability issue. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>require_ticket_analysis_review</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, and the PR contains a GitHub ticket number, the tool will add a section that checks if the PR in fact fulfilled the ticket requirements. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
!!! example "Adding PR labels"
|
||||
|
||||
You can enable\disable the `review` tool to add specific labels to the PR:
|
||||
You can enable\disable the `review` tool to add specific labels to the PR:
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>enable_review_labels_security</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will publish a 'possible security issue' label if it detects a security issue. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>enable_review_labels_effort</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will publish a 'Review effort [1-5]: x' label. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>enable_review_labels_security</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will publish a 'possible security issue' label if it detects a security issue. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>enable_review_labels_effort</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will publish a 'Review effort [1-5]: x' label. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
!!! example "Auto-approval"
|
||||
|
||||
If enabled, the `review` tool can approve a PR when a specific comment, `/review auto_approve`, is invoked.
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>enable_auto_approval</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will approve the PR when invoked with the 'auto_approve' command. Default is false. This flag can be changed only from a configuration file.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>maximal_review_effort</b></td>
|
||||
<td>Maximal effort level for auto-approval. If the PR's estimated review effort is above this threshold, the auto-approval will not run. Default is 5.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage Tips
|
||||
|
||||
@ -122,36 +180,36 @@ extra_instructions = "..."
|
||||
|
||||
The `review` tool provides a collection of configurable feedbacks about a PR.
|
||||
It is recommended to review the [Configuration options](#configuration-options) section, and choose the relevant options for your use case.
|
||||
|
||||
Some of the features that are disabled by default are quite useful, and should be considered for enabling. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
Some of the features that are disabled by default are quite useful, and should be considered for enabling. For example:
|
||||
`require_score_review`, and more.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
On the other hand, if you find one of the enabled features to be irrelevant for your use case, disable it. No default configuration can fit all use cases.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip "Automation"
|
||||
When you first install Qodo Merge app, the [default mode](../usage-guide/automations_and_usage.md#github-app-automatic-tools-when-a-new-pr-is-opened) for the `review` tool is:
|
||||
```
|
||||
pr_commands = ["/review", ...]
|
||||
pr_commands = ["/review --pr_reviewer.num_code_suggestions=0", ...]
|
||||
```
|
||||
Meaning the `review` tool will run automatically on every PR, without any additional configurations.
|
||||
Meaning the `review` tool will run automatically on every PR, without providing code suggestions.
|
||||
Edit this field to enable/disable the tool, or to change the configurations used.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip "Possible labels from the review tool"
|
||||
|
||||
The `review` tool can auto-generate two specific types of labels for a PR:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- a `possible security issue` label that detects if a possible [security issue](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/tr/user_description/pr_agent/settings/pr_reviewer_prompts.toml#L136) exists in the PR code (`enable_review_labels_security` flag)
|
||||
- a `Review effort [1-5]: x` label, where x is the estimated effort to review the PR (`enable_review_labels_effort` flag)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Both modes are useful, and we recommended to enable them.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip "Extra instructions"
|
||||
|
||||
Extra instructions are important.
|
||||
The `review` tool can be configured with extra instructions, which can be used to guide the model to a feedback tailored to the needs of your project.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Be specific, clear, and concise in the instructions. With extra instructions, you are the prompter. Specify the relevant sub-tool, and the relevant aspects of the PR that you want to emphasize.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Examples of extra instructions:
|
||||
```
|
||||
[pr_reviewer]
|
||||
@ -165,6 +223,39 @@ extra_instructions = "..."
|
||||
```
|
||||
Use triple quotes to write multi-line instructions. Use bullet points to make the instructions more readable.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip "Code suggestions"
|
||||
|
||||
The `review` tool previously included a legacy feature for providing code suggestions (controlled by `--pr_reviewer.num_code_suggestion`). This functionality has been deprecated and replaced by the [`improve`](./improve.md) tool, which offers higher quality and more actionable code suggestions.
|
||||
!!! tip "Auto-approval"
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge can approve a PR when a specific comment is invoked.
|
||||
|
||||
To ensure safety, the auto-approval feature is disabled by default. To enable auto-approval, you need to actively set in a pre-defined configuration file the following:
|
||||
```
|
||||
[pr_reviewer]
|
||||
enable_auto_approval = true
|
||||
```
|
||||
(this specific flag cannot be set with a command line argument, only in the configuration file, committed to the repository)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
After enabling, by commenting on a PR:
|
||||
```
|
||||
/review auto_approve
|
||||
```
|
||||
Qodo Merge will automatically approve the PR, and add a comment with the approval.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
You can also enable auto-approval only if the PR meets certain requirements, such as that the `estimated_review_effort` label is equal or below a certain threshold, by adjusting the flag:
|
||||
```
|
||||
[pr_reviewer]
|
||||
maximal_review_effort = 5
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (!!! tip "Code suggestions")
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ()
|
||||
[//]: # ( If you set `num_code_suggestions`>0 , the `review` tool will also provide code suggestions.)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ( )
|
||||
[//]: # ( Notice If you are interested **only** in the code suggestions, it is recommended to use the [`improve`](./improve.md) feature instead, since it is a dedicated only to code suggestions, and usually gives better results.)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ( Use the `review` tool if you want to get more comprehensive feedback, which includes code suggestions as well.)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,44 +0,0 @@
|
||||
`Platforms supported: GitHub`
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The `scan_repo_discussions` tool analyzes code discussions (meaning review comments over code lines) from merged pull requests over the past 12 months.
|
||||
It processes these discussions alongside other PR metadata to identify recurring patterns related to best practices in team feedback and code reviews, generating a comprehensive [`best_practices.md`](https://github.com/qodo-ai/pr-agent/blob/qodo-merge-best-practices_2025-04-16_1018/best_practices.md) document that distills key insights and recommendations.
|
||||
|
||||
This file captures repository-specific patterns derived from your team's actual workflow and discussions, rather than more generic best practices.
|
||||
It will be utilized by Qodo Merge to provide tailored suggestions for improving code quality in future pull requests.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Active repositories are needed"
|
||||
The tool is designed to work with real-life repositories, as it relies on actual discussions to generate meaningful insights.
|
||||
At least 50 merged PRs are required to generate the `best_practices.md` file.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Additional customization"
|
||||
Teams are encouraged to further customize and refine these insights to better align with their specific development priorities and contexts.
|
||||
This can be done by editing the `best_practices.md` file directly when the PR is created, or iteratively over time to enhance the 'best practices' suggestions provided by Qodo Merge.
|
||||
|
||||
The tool can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/scan_repo_discussions
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
As a response, the bot will create a new PR that contains an auto-generated `best_practices.md` file.
|
||||
Note that the scan can take several minutes to complete, since up to 250 PRs are scanned.
|
||||
|
||||
## Example usage
|
||||
|
||||
{width=640}
|
||||
|
||||
The PR created by the bot:
|
||||
|
||||
{width=640}
|
||||
|
||||
The `best_practices.md` file in the PR:
|
||||
|
||||
{width=640}
|
||||
|
||||
### Configuration options
|
||||
|
||||
- Use `/scan_repo_discussions --scan_repo_discussions.force_scan=true` to force generating a PR with a new `best_practices.md` file, even if it already exists (by default, the bot will not generate a new file if it already exists).
|
||||
- Use `/scan_repo_discussions --scan_repo_discussions.days_back=X` to specify the number of days back to scan for discussions. The default is 365 days.
|
||||
- Use `/scan_repo_discussions --scan_repo_discussions.minimal_number_of_prs=X` to specify the minimum number of merged PRs needed to generate the `best_practices.md` file. The default is 50 PRs.
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,4 @@
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The similar code tool retrieves the most similar code components from inside the organization's codebase, or from open-source code.
|
||||
|
||||
For example:
|
||||
@ -8,6 +7,7 @@ For example:
|
||||
|
||||
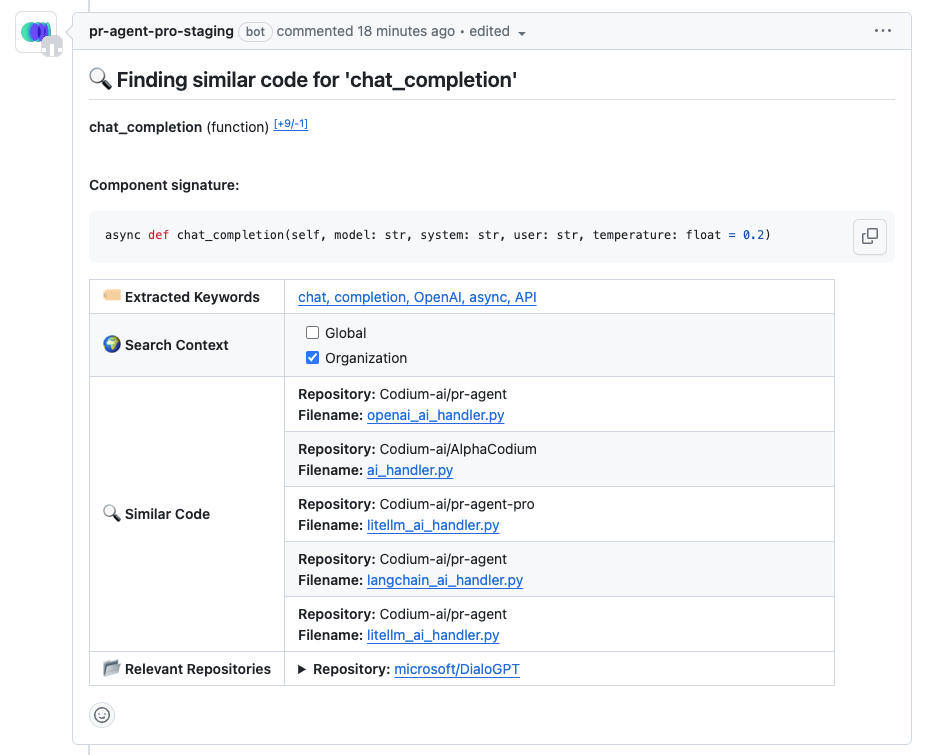{width=768}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge will examine the code component and will extract the most relevant keywords to search for similar code:
|
||||
|
||||
- `extracted keywords`: the keywords that were extracted from the code by Qodo Merge. the link will open a search page with the extracted keywords, to allow the user to modify the search if needed.
|
||||
@ -19,20 +19,18 @@ Search result link example:
|
||||
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
`Organization Search`:
|
||||
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## How to use
|
||||
|
||||
### Manually
|
||||
|
||||
To invoke the `similar code` tool manually, comment on the PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/find_similar_component COMPONENT_NAME
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Where `COMPONENT_NAME` should be the name of a code component in the PR (class, method, function).
|
||||
|
||||
If there is a name ambiguity, there are two configurations that will help the tool to find the correct component:
|
||||
@ -41,27 +39,23 @@ If there is a name ambiguity, there are two configurations that will help the to
|
||||
- `--pr_find_similar_component.class_name`: in case there are several methods with the same name in the same file, you can specify the relevant class name.
|
||||
|
||||
example:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/find_similar_component COMPONENT_NAME --pr_find_similar_component.file=FILE_NAME
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Automatically (via Analyze table)
|
||||
|
||||
It can be invoked automatically from the analyze table, can be accessed by:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/analyze
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Choose the components you want to find similar code for, and click on the `similar` checkbox.
|
||||
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
|
||||
You can search for similar code either within the organization's codebase or globally, which includes open-source repositories. Each result will include the relevant code components along with their associated license details.
|
||||
If you are looking to search for similar code in the organization's codebase, you can click on the `Organization` checkbox, and it will invoke a new search command just for the organization's codebase.
|
||||
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuration options
|
||||
|
||||
- `search_from_org`: if set to true, the tool will search for similar code in the organization's codebase. Default is false.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,12 +1,11 @@
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The similar issue tool retrieves the most similar issues to the current issue.
|
||||
It can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/similar_issue
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Example usage
|
||||
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
@ -17,35 +16,28 @@ It can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
Note that to perform retrieval, the `similar_issue` tool indexes all the repo previous issues (once).
|
||||
|
||||
### Selecting a Vector Database
|
||||
|
||||
Configure your preferred database by changing the `pr_similar_issue` parameter in `configuration.toml` file.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Available Options
|
||||
|
||||
Choose from the following Vector Databases:
|
||||
**Select VectorDBs** by changing `pr_similar_issue` parameter in `configuration.toml` file
|
||||
|
||||
2 VectorDBs are available to switch in
|
||||
1. LanceDB
|
||||
2. Pinecone
|
||||
|
||||
#### Pinecone Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
To use Pinecone with the `similar issue` tool, add these credentials to `.secrets.toml` (or set as environment variables):
|
||||
To enable usage of the '**similar issue**' tool for Pinecone, you need to set the following keys in `.secrets.toml` (or in the relevant environment variables):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[pinecone]
|
||||
api_key = "..."
|
||||
environment = "..."
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
These parameters can be obtained by registering to [Pinecone](https://app.pinecone.io/?sessionType=signup/).
|
||||
|
||||
## How to use
|
||||
|
||||
## How to use
|
||||
- To invoke the 'similar issue' tool from **CLI**, run:
|
||||
`python3 cli.py --issue_url=... similar_issue`
|
||||
|
||||
- To invoke the 'similar' issue tool via online usage, [comment](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/issues/178#issuecomment-1716934893) on a PR:
|
||||
`/similar_issue`
|
||||
|
||||
- You can also enable the 'similar issue' tool to run automatically when a new issue is opened, by adding it to the [pr_commands list in the github_app section](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml#L66)
|
||||
- You can also enable the 'similar issue' tool to run automatically when a new issue is opened, by adding it to the [pr_commands list in the github_app section](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml#L66)
|
||||
@ -1,12 +1,9 @@
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
By combining LLM abilities with static code analysis, the `test` tool generate tests for a selected component, based on the PR code changes.
|
||||
It can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/test component_name
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
where 'component_name' is the name of a specific component in the PR.
|
||||
To get a list of the components that changed in the PR and choose the relevant component interactively, use the [`analyze`](./analyze.md) tool.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -17,18 +14,19 @@ The tool will generate tests for the selected component (if no component is stat
|
||||
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
(Example taken from [here](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/598#issuecomment-1913679429)):
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Notes"
|
||||
- The following languages are currently supported: Python, Java, C++, JavaScript, TypeScript, C#.
|
||||
- This tool can also be triggered interactively by using the [`analyze`](./analyze.md) tool.
|
||||
**Notes**
|
||||
- Language that are currently supported by the tool: Python, Java, C++, JavaScript, TypeScript, C#.
|
||||
- This tool can also be triggered interactively by using the [`analyze`](./analyze.md) tool.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuration options
|
||||
|
||||
- `num_tests`: number of tests to generate. Default is 3.
|
||||
- `testing_framework`: the testing framework to use. If not set, for Python it will use `pytest`, for Java it will use `JUnit`, for C++ it will use `Catch2`, and for JavaScript and TypeScript it will use `jest`.
|
||||
- `avoid_mocks`: if set to true, the tool will try to avoid using mocks in the generated tests. Note that even if this option is set to true, the tool might still use mocks if it cannot generate a test without them. Default is true.
|
||||
- `extra_instructions`: Optional extra instructions to the tool. For example: "use the following mock injection scheme: ...".
|
||||
- `file`: in case there are several components with the same name, you can specify the relevant file.
|
||||
- `class_name`: in case there are several methods with the same name in the same file, you can specify the relevant class name.
|
||||
- `enable_help_text`: if set to true, the tool will add a help text to the PR comment. Default is true.
|
||||
- `enable_help_text`: if set to true, the tool will add a help text to the PR comment. Default is true.
|
||||
@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The `update_changelog` tool automatically updates the CHANGELOG.md file with the PR changes.
|
||||
It can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/update_changelog
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -17,7 +15,5 @@ It can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
Under the section `pr_update_changelog`, the [configuration file](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml#L50) contains options to customize the 'update changelog' tool:
|
||||
|
||||
- `push_changelog_changes`: whether to push the changes to CHANGELOG.md, or just publish them as a comment. Default is false (publish as comment).
|
||||
- `extra_instructions`: Optional extra instructions to the tool. For example: "Use the following structure: ..."
|
||||
- `add_pr_link`: whether the model should try to add a link to the PR in the changelog. Default is true.
|
||||
- `skip_ci_on_push`: whether the commit message (when `push_changelog_changes` is true) will include the term "[skip ci]", preventing CI tests to be triggered on the changelog commit. Default is true.
|
||||
- `push_changelog_changes`: whether to push the changes to CHANGELOG.md, or just print them. Default is false (print only).
|
||||
- `extra_instructions`: Optional extra instructions to the tool. For example: "focus on the changes in the file X. Ignore change in ...
|
||||
@ -1,8 +1,7 @@
|
||||
## Recommend Python Best Practices
|
||||
|
||||
This document outlines a series of recommended best practices for Python development. These guidelines aim to improve code quality, maintainability, and readability.
|
||||
|
||||
### Imports
|
||||
### Imports
|
||||
|
||||
Use `import` statements for packages and modules only, not for individual types, classes, or functions.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -10,16 +9,16 @@ Use `import` statements for packages and modules only, not for individual type
|
||||
|
||||
Reusability mechanism for sharing code from one module to another.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Decision
|
||||
#### Decision
|
||||
|
||||
- Use `import x` for importing packages and modules.
|
||||
- Use `from x import y` where `x` is the package prefix and `y` is the module name with no prefix.
|
||||
- Use `from x import y as z` in any of the following circumstances:
|
||||
- Two modules named `y` are to be imported.
|
||||
- `y` conflicts with a top-level name defined in the current module.
|
||||
- `y` conflicts with a common parameter name that is part of the public API (e.g., `features`).
|
||||
- `y` is an inconveniently long name, or too generic in the context of your code
|
||||
- Use `import y as z` only when `z` is a standard abbreviation (e.g., `import numpy as np`).
|
||||
- Use `import x` for importing packages and modules.
|
||||
- Use `from x import y` where `x` is the package prefix and `y` is the module name with no prefix.
|
||||
- Use `from x import y as z` in any of the following circumstances:
|
||||
- Two modules named `y` are to be imported.
|
||||
- `y` conflicts with a top-level name defined in the current module.
|
||||
- `y` conflicts with a common parameter name that is part of the public API (e.g., `features`).
|
||||
- `y` is an inconveniently long name, or too generic in the context of your code
|
||||
- Use `import y as z` only when `z` is a standard abbreviation (e.g., `import numpy as np`).
|
||||
|
||||
For example the module `sound.effects.echo` may be imported as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -36,13 +35,13 @@ Do not use relative names in imports. Even if the module is in the same package,
|
||||
|
||||
Exemptions from this rule:
|
||||
|
||||
- Symbols from the following modules are used to support static analysis and type checking:
|
||||
- [`typing` module](https://google.github.io/styleguide/pyguide.html#typing-imports)
|
||||
- [`collections.abc` module](https://google.github.io/styleguide/pyguide.html#typing-imports)
|
||||
- [`typing_extensions` module](https://github.com/python/typing_extensions/blob/main/README.md)
|
||||
- Redirects from the [six.moves module](https://six.readthedocs.io/#module-six.moves).
|
||||
- Symbols from the following modules are used to support static analysis and type checking:
|
||||
- [`typing` module](https://google.github.io/styleguide/pyguide.html#typing-imports)
|
||||
- [`collections.abc` module](https://google.github.io/styleguide/pyguide.html#typing-imports)
|
||||
- [`typing_extensions` module](https://github.com/python/typing_extensions/blob/main/README.md)
|
||||
- Redirects from the [six.moves module](https://six.readthedocs.io/#module-six.moves).
|
||||
|
||||
### Packages
|
||||
### Packages
|
||||
|
||||
Import each module using the full pathname location of the module.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -86,7 +85,6 @@ No:
|
||||
The directory the main binary is located in should not be assumed to be in `sys.path` despite that happening in some environments. This being the case, code should assume that `import jodie` refers to a third-party or top-level package named `jodie`, not a local `jodie.py`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Default Iterators and Operators
|
||||
|
||||
Use default iterators and operators for types that support them, like lists, dictionaries, and files.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Definition
|
||||
@ -127,7 +125,7 @@ Okay in most cases.
|
||||
|
||||
You can specify values for variables at the end of a function’s parameter list, e.g., `def foo(a, b=0):`. If `foo` is called with only one argument, `b` is set to 0. If it is called with two arguments, `b` has the value of the second argument.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Decision
|
||||
#### Decision
|
||||
|
||||
Okay to use with the following caveat:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -160,6 +158,7 @@ No: def foo(a, b: Mapping = {}): # Could still get passed to unchecked code.
|
||||
|
||||
### True/False Evaluations
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Use the “implicit” false if possible, e.g., `if foo:` rather than `if foo != []:`
|
||||
|
||||
### Lexical Scoping
|
||||
@ -176,15 +175,15 @@ def get_adder(summand1: float) -> Callable[[float], float]:
|
||||
|
||||
return adder
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Decision
|
||||
|
||||
Okay to use.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Threading
|
||||
|
||||
Do not rely on the atomicity of built-in types.
|
||||
|
||||
While Python’s built-in data types such as dictionaries appear to have atomic operations, there are corner cases where they aren’t atomic (e.g. if `__hash__` or `__eq__` are implemented as Python methods) and their atomicity should not be relied upon. Neither should you rely on atomic variable assignment (since this in turn depends on dictionaries).
|
||||
|
||||
Use the `queue` module’s `Queue` data type as the preferred way to communicate data between threads. Otherwise, use the `threading` module and its locking primitives. Prefer condition variables and `threading.Condition` instead of using lower-level locks.
|
||||
Use the `queue` module’s `Queue` data type as the preferred way to communicate data between threads. Otherwise, use the `threading` module and its locking primitives. Prefer condition variables and `threading.Condition` instead of using lower-level locks.
|
||||
18
docs/docs/usage-guide/PR_agent_pro_models.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
|
||||
## Qodo Merge Pro Models
|
||||
|
||||
The default models used by Qodo Merge Pro are a combination of Claude-3.5-sonnet and OpenAI's GPT-4 models.
|
||||
|
||||
Users can configure Qodo Merge Pro to use solely a specific model by editing the [configuration](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/) file.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, to restrict Qodo Merge Pro to using only `Claude-3.5-sonnet`, add this setting:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
model="claude-3-5-sonnet"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Or to restrict Qodo Merge Pro to using only `GPT-4o`, add this setting:
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
model="gpt-4o"
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -1,35 +1,32 @@
|
||||
## Show possible configurations
|
||||
|
||||
The possible configurations of Qodo Merge are stored in [here](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml){:target="_blank"}.
|
||||
The possible configurations of Qodo Merge are stored in [here](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml).
|
||||
In the [tools](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/) page you can find explanations on how to use these configurations for each tool.
|
||||
|
||||
To print all the available configurations as a comment on your PR, you can use the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/config
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
To view the **actual** configurations used for a specific tool, after all the user settings are applied, you can add for each tool a `--config.output_relevant_configurations=true` suffix.
|
||||
For example:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/improve --config.output_relevant_configurations=true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Will output an additional field showing the actual configurations used for the `improve` tool.
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Ignoring files from analysis
|
||||
|
||||
In some cases, you may want to exclude specific files or directories from the analysis performed by Qodo Merge. This can be useful, for example, when you have files that are generated automatically or files that shouldn't be reviewed, like vendor code.
|
||||
|
||||
You can ignore files or folders using the following methods:
|
||||
|
||||
- `IGNORE.GLOB`
|
||||
- `IGNORE.REGEX`
|
||||
- `IGNORE.GLOB`
|
||||
- `IGNORE.REGEX`
|
||||
|
||||
which you can edit to ignore files or folders based on glob or regex patterns.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -40,15 +37,14 @@ Let's look at an example where we want to ignore all files with `.py` extension
|
||||
To ignore Python files in a PR with online usage, comment on a PR:
|
||||
`/review --ignore.glob="['*.py']"`
|
||||
|
||||
To ignore Python files in all PRs using `glob` pattern, set in a configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
To ignore Python files in all PRs using `glob` pattern, set in a configuration file:
|
||||
```
|
||||
[ignore]
|
||||
glob = ['*.py']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And to ignore Python files in all PRs using `regex` pattern, set in a configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[regex]
|
||||
regex = ['.*\.py$']
|
||||
@ -57,50 +53,26 @@ regex = ['.*\.py$']
|
||||
## Extra instructions
|
||||
|
||||
All Qodo Merge tools have a parameter called `extra_instructions`, that enables to add free-text extra instructions. Example usage:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/update_changelog --pr_update_changelog.extra_instructions="Make sure to update also the version ..."
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Language Settings
|
||||
## Working with large PRs
|
||||
|
||||
The default response language for Qodo Merge is **U.S. English**. However, some development teams may prefer to display information in a different language. For example, your team's workflow might improve if PR descriptions and code suggestions are set to your country's native language.
|
||||
The default mode of CodiumAI is to have a single call per tool, using GPT-4, which has a token limit of 8000 tokens.
|
||||
This mode provides a very good speed-quality-cost tradeoff, and can handle most PRs successfully.
|
||||
When the PR is above the token limit, it employs a [PR Compression strategy](../core-abilities/index.md).
|
||||
|
||||
To configure this, set the `response_language` parameter in the configuration file. This will prompt the model to respond in the specified language. Use a **standard locale code** based on [ISO 3166](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ISO_3166) (country codes) and [ISO 639](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ISO_639) (language codes) to define a language-country pair. See this [comprehensive list of locale codes](https://simplelocalize.io/data/locales/).
|
||||
However, for very large PRs, or in case you want to emphasize quality over speed and cost, there are two possible solutions:
|
||||
1) [Use a model](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/changing_a_model/) with larger context, like GPT-32K, or claude-100K. This solution will be applicable for all the tools.
|
||||
2) For the `/improve` tool, there is an ['extended' mode](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/) (`/improve --extended`),
|
||||
which divides the PR into chunks, and processes each chunk separately. With this mode, regardless of the model, no compression will be done (but for large PRs, multiple model calls may occur)
|
||||
|
||||
Example:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
response_language = "it-IT"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will set the response language globally for all the commands to Italian.
|
||||
|
||||
> **Important:** Note that only dynamic text generated by the AI model is translated to the configured language. Static text such as labels and table headers that are not part of the AI models response will remain in US English. In addition, the model you are using must have good support for the specified language.
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (## Working with large PRs)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ()
|
||||
[//]: # (The default mode of CodiumAI is to have a single call per tool, using GPT-4, which has a token limit of 8000 tokens.)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (This mode provides a very good speed-quality-cost tradeoff, and can handle most PRs successfully.)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (When the PR is above the token limit, it employs a [PR Compression strategy](../core-abilities/index.md).)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ()
|
||||
[//]: # (However, for very large PRs, or in case you want to emphasize quality over speed and cost, there are two possible solutions:)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (1) [Use a model](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/changing_a_model/) with larger context, like GPT-32K, or claude-100K. This solution will be applicable for all the tools.)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (2) For the `/improve` tool, there is an ['extended' mode](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/) (`/improve --extended`),)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (which divides the PR into chunks, and processes each chunk separately. With this mode, regardless of the model, no compression will be done (but for large PRs, multiple model calls may occur))
|
||||
|
||||
## Patch Extra Lines
|
||||
|
||||
By default, around any change in your PR, git patch provides three lines of context above and below the change.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -12,5 +12,5 @@ def func1():
|
||||
code line that already existed in the file...
|
||||
@ -114,7 +86,6 @@ By default, around any change in your PR, git patch provides three lines of cont
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge will try to increase the number of lines of context, via the parameter:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
patch_extra_lines_before=3
|
||||
@ -125,23 +96,30 @@ Increasing this number provides more context to the model, but will also increas
|
||||
|
||||
If the PR is too large (see [PR Compression strategy](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/PR_COMPRESSION.md)), Qodo Merge may automatically set this number to 0, and will use the original git patch.
|
||||
|
||||
## Log Level
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge allows you to control the verbosity of logging by using the `log_level` configuration parameter. This is particularly useful for troubleshooting and debugging issues with your PR workflows.
|
||||
## Editing the prompts
|
||||
|
||||
The prompts for the various Qodo Merge tools are defined in the `pr_agent/settings` folder.
|
||||
In practice, the prompts are loaded and stored as a standard setting object.
|
||||
Hence, editing them is similar to editing any other configuration value - just place the relevant key in `.pr_agent.toml`file, and override the default value.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, if you want to edit the prompts of the [describe](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/pr_description_prompts.toml) tool, you can add the following to your `.pr_agent.toml` file:
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
log_level = "DEBUG" # Options: "DEBUG", "INFO", "WARNING", "ERROR", "CRITICAL"
|
||||
[pr_description_prompt]
|
||||
system="""
|
||||
...
|
||||
"""
|
||||
user="""
|
||||
...
|
||||
"""
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The default log level is "DEBUG", which provides detailed output of all operations. If you prefer less verbose logs, you can set higher log levels like "INFO" or "WARNING".
|
||||
Note that the new prompt will need to generate an output compatible with the relevant [post-process function](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/tools/pr_description.py#L137).
|
||||
|
||||
## Integrating with Logging Observability Platforms
|
||||
|
||||
Various logging observability tools can be used out-of-the box when using the default LiteLLM AI Handler. Simply configure the LiteLLM callback settings in `configuration.toml` and set environment variables according to the LiteLLM [documentation](https://docs.litellm.ai/docs/).
|
||||
|
||||
For example, to use [LangSmith](https://www.langchain.com/langsmith) you can add the following to your `configuration.toml` file:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[litellm]
|
||||
enable_callbacks = true
|
||||
@ -160,31 +138,21 @@ LANGSMITH_BASE_URL=<url>
|
||||
|
||||
## Ignoring automatic commands in PRs
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge allows you to automatically ignore certain PRs based on various criteria:
|
||||
|
||||
- PRs with specific titles (using regex matching)
|
||||
- PRs between specific branches (using regex matching)
|
||||
- PRs from specific repositories (using regex matching)
|
||||
- PRs not from specific folders
|
||||
- PRs containing specific labels
|
||||
- PRs opened by specific users
|
||||
|
||||
### Ignoring PRs with specific titles
|
||||
In some cases, you may want to automatically ignore specific PRs . Qodo Merge enables you to ignore PR with a specific title, or from/to specific branches (regex matching).
|
||||
|
||||
To ignore PRs with a specific title such as "[Bump]: ...", you can add the following to your `configuration.toml` file:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
ignore_pr_title = ["\\[Bump\\]"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Where the `ignore_pr_title` is a list of regex patterns to match the PR title you want to ignore. Default is `ignore_pr_title = ["^\\[Auto\\]", "^Auto"]`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Ignoring PRs between specific branches
|
||||
|
||||
To ignore PRs from specific source or target branches, you can add the following to your `configuration.toml` file:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
ignore_pr_source_branches = ['develop', 'main', 'master', 'stage']
|
||||
ignore_pr_target_branches = ["qa"]
|
||||
@ -192,61 +160,3 @@ ignore_pr_target_branches = ["qa"]
|
||||
|
||||
Where the `ignore_pr_source_branches` and `ignore_pr_target_branches` are lists of regex patterns to match the source and target branches you want to ignore.
|
||||
They are not mutually exclusive, you can use them together or separately.
|
||||
|
||||
### Ignoring PRs from specific repositories
|
||||
|
||||
To ignore PRs from specific repositories, you can add the following to your `configuration.toml` file:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
ignore_repositories = ["my-org/my-repo1", "my-org/my-repo2"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Where the `ignore_repositories` is a list of regex patterns to match the repositories you want to ignore. This is useful when you have multiple repositories and want to exclude certain ones from analysis.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Ignoring PRs not from specific folders
|
||||
|
||||
To allow only specific folders (often needed in large monorepos), set:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
allow_only_specific_folders=['folder1','folder2']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For the configuration above, automatic feedback will only be triggered when the PR changes include files where 'folder1' or 'folder2' is in the file path
|
||||
|
||||
### Ignoring PRs containing specific labels
|
||||
|
||||
To ignore PRs containing specific labels, you can add the following to your `configuration.toml` file:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
ignore_pr_labels = ["do-not-merge"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Where the `ignore_pr_labels` is a list of labels that when present in the PR, the PR will be ignored.
|
||||
|
||||
### Ignoring PRs from specific users
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge tries to automatically identify and ignore pull requests created by bots using:
|
||||
|
||||
- GitHub's native bot detection system
|
||||
- Name-based pattern matching
|
||||
|
||||
While this detection is robust, it may not catch all cases, particularly when:
|
||||
|
||||
- Bots are registered as regular user accounts
|
||||
- Bot names don't match common patterns
|
||||
|
||||
To supplement the automatic bot detection, you can manually specify users to ignore. Add the following to your `configuration.toml` file to ignore PRs from specific users:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
ignore_pr_authors = ["my-special-bot-user", ...]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Where the `ignore_pr_authors` is a list of usernames that you want to ignore.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note
|
||||
There is one specific case where bots will receive an automatic response - when they generated a PR with a _failed test_. In that case, the [`ci_feedback`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/ci_feedback/) tool will be invoked.
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,4 @@
|
||||
## Local repo (CLI)
|
||||
|
||||
When running from your locally cloned Qodo Merge repo (CLI), your local configuration file will be used.
|
||||
Examples of invoking the different tools via the CLI:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -7,55 +6,38 @@ Examples of invoking the different tools via the CLI:
|
||||
- **Describe**: `python -m pr_agent.cli --pr_url=<pr_url> describe`
|
||||
- **Improve**: `python -m pr_agent.cli --pr_url=<pr_url> improve`
|
||||
- **Ask**: `python -m pr_agent.cli --pr_url=<pr_url> ask "Write me a poem about this PR"`
|
||||
- **Reflect**: `python -m pr_agent.cli --pr_url=<pr_url> reflect`
|
||||
- **Update Changelog**: `python -m pr_agent.cli --pr_url=<pr_url> update_changelog`
|
||||
|
||||
`<pr_url>` is the url of the relevant PR (for example: [#50](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/50)).
|
||||
|
||||
**Notes:**
|
||||
|
||||
1. in addition to editing your local configuration file, you can also change any configuration value by adding it to the command line:
|
||||
|
||||
(1) in addition to editing your local configuration file, you can also change any configuration value by adding it to the command line:
|
||||
```
|
||||
python -m pr_agent.cli --pr_url=<pr_url> /review --pr_reviewer.extra_instructions="focus on the file: ..."
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. You can print results locally, without publishing them, by setting in `configuration.toml`:
|
||||
|
||||
(2) You can print results locally, without publishing them, by setting in `configuration.toml`:
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
publish_output=false
|
||||
verbosity_level=2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This is useful for debugging or experimenting with different tools.
|
||||
|
||||
3. **git provider**: The [git_provider](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml#L5) field in a configuration file determines the GIT provider that will be used by Qodo Merge. Currently, the following providers are supported:
|
||||
`github` **(default)**, `gitlab`, `bitbucket`, `azure`, `codecommit`, `local`, and `gerrit`.
|
||||
(3)
|
||||
|
||||
### CLI Health Check
|
||||
**git provider**: The [git_provider](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml#L5) field in a configuration file determines the GIT provider that will be used by Qodo Merge. Currently, the following providers are supported:
|
||||
`
|
||||
"github", "gitlab", "bitbucket", "azure", "codecommit", "local", "gerrit"
|
||||
`
|
||||
|
||||
To verify that Qodo Merge has been configured correctly, you can run this health check command from the repository root:
|
||||
Default is "github".
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -m tests.health_test.main
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If the health check passes, you will see the following output:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
========
|
||||
Health test passed successfully
|
||||
========
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
At the end of the run.
|
||||
|
||||
Before running the health check, ensure you have:
|
||||
|
||||
- Configured your [LLM provider](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/changing_a_model/)
|
||||
- Added a valid GitHub token to your configuration file
|
||||
|
||||
## Online usage
|
||||
### Online usage
|
||||
|
||||
Online usage means invoking Qodo Merge tools by [comments](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/229#issuecomment-1695021901) on a PR.
|
||||
Commands for invoking the different tools via comments:
|
||||
@ -64,113 +46,74 @@ Commands for invoking the different tools via comments:
|
||||
- **Describe**: `/describe`
|
||||
- **Improve**: `/improve` (or `/improve_code` for bitbucket, since `/improve` is sometimes reserved)
|
||||
- **Ask**: `/ask "..."`
|
||||
- **Reflect**: `/reflect`
|
||||
- **Update Changelog**: `/update_changelog`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
To edit a specific configuration value, just add `--config_path=<value>` to any command.
|
||||
For example, if you want to edit the `review` tool configurations, you can run:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/review --pr_reviewer.extra_instructions="..." --pr_reviewer.require_score_review=false
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Any configuration value in [configuration file](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml) file can be similarly edited. Comment `/config` to see the list of available configurations.
|
||||
|
||||
## Qodo Merge Automatic Feedback
|
||||
|
||||
### Disabling all automatic feedback
|
||||
## GitHub App
|
||||
|
||||
To easily disable all automatic feedback from Qodo Merge (GitHub App, GitLab Webhook, BitBucket App, Azure DevOps Webhook), set in a configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
disable_auto_feedback = true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
When this parameter is set to `true`, Qodo Merge will not run any automatic tools (like `describe`, `review`, `improve`) when a new PR is opened, or when new code is pushed to an open PR.
|
||||
|
||||
### GitHub App
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Configurations for Qodo Merge"
|
||||
Qodo Merge for GitHub is an App, hosted by Qodo. So all the instructions below are relevant also for Qodo Merge users.
|
||||
!!! note "Configurations for Qodo Merge Pro"
|
||||
Qodo Merge Pro for GitHub is an App, hosted by CodiumAI. So all the instructions below are relevant also for Qodo Merge Pro users.
|
||||
Same goes for [GitLab webhook](#gitlab-webhook) and [BitBucket App](#bitbucket-app) sections.
|
||||
|
||||
#### GitHub app automatic tools when a new PR is opened
|
||||
### GitHub app automatic tools when a new PR is opened
|
||||
|
||||
The [github_app](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml#L220) section defines GitHub app specific configurations.
|
||||
The [github_app](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml#L108) section defines GitHub app specific configurations.
|
||||
|
||||
The configuration parameter `pr_commands` defines the list of tools that will be **run automatically** when a new PR is opened:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
The configuration parameter `pr_commands` defines the list of tools that will be **run automatically** when a new PR is opened.
|
||||
```
|
||||
[github_app]
|
||||
pr_commands = [
|
||||
"/describe",
|
||||
"/review",
|
||||
"/describe --pr_description.final_update_message=false",
|
||||
"/review --pr_reviewer.num_code_suggestions=0",
|
||||
"/improve",
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This means that when a new PR is opened/reopened or marked as ready for review, Qodo Merge will run the `describe`, `review` and `improve` tools.
|
||||
For the `review` tool, for example, the `num_code_suggestions` parameter will be set to 0.
|
||||
|
||||
**Draft PRs:**
|
||||
|
||||
By default, draft PRs are not considered for automatic tools, but you can change this by setting the `feedback_on_draft_pr` parameter to `true` in the configuration file.
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[github_app]
|
||||
feedback_on_draft_pr = true
|
||||
You can override the default tool parameters by using one the three options for a [configuration file](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/): **wiki**, **local**, or **global**.
|
||||
For example, if your local `.pr_agent.toml` file contains:
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Changing default tool parameters:**
|
||||
|
||||
You can override the default tool parameters by using one the three options for a [configuration file](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/): **wiki**, **local**, or **global**.
|
||||
For example, if your configuration file contains:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[pr_description]
|
||||
generate_ai_title = true
|
||||
```
|
||||
Every time you run the `describe` tool, including automatic runs, the PR title will be generated by the AI.
|
||||
|
||||
Every time you run the `describe` tool (including automatic runs) the PR title will be generated by the AI.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters for automated runs:**
|
||||
|
||||
You can customize configurations specifically for automated runs by using the `--config_path=<value>` parameter.
|
||||
For instance, to modify the `review` tool settings only for newly opened PRs, use:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
To cancel the automatic run of all the tools, set:
|
||||
```
|
||||
[github_app]
|
||||
pr_commands = [
|
||||
"/describe",
|
||||
"/review --pr_reviewer.extra_instructions='focus on the file: ...'",
|
||||
"/improve",
|
||||
]
|
||||
pr_commands = []
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### GitHub app automatic tools for push actions (commits to an open PR)
|
||||
### GitHub app automatic tools for push actions (commits to an open PR)
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to running automatic tools when a PR is opened, the GitHub app can also respond to new code that is pushed to an open PR.
|
||||
|
||||
The configuration toggle `handle_push_trigger` can be used to enable this feature.
|
||||
The configuration toggle `handle_push_trigger` can be used to enable this feature.
|
||||
The configuration parameter `push_commands` defines the list of tools that will be **run automatically** when new code is pushed to the PR.
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[github_app]
|
||||
handle_push_trigger = true
|
||||
push_commands = [
|
||||
"/describe",
|
||||
"/review",
|
||||
"/review --pr_reviewer.num_code_suggestions=0 --pr_reviewer.final_update_message=false",
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This means that when new code is pushed to the PR, the Qodo Merge will run the `describe` and `review` tools, with the specified parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
### GitHub Action
|
||||
|
||||
## GitHub Action
|
||||
`GitHub Action` is a different way to trigger Qodo Merge tools, and uses a different configuration mechanism than `GitHub App`.<br>
|
||||
You can configure settings for `GitHub Action` by adding environment variables under the env section in `.github/workflows/pr_agent.yml` file.
|
||||
You can configure settings for `GitHub Action` by adding environment variables under the env section in `.github/workflows/pr_agent.yml` file.
|
||||
Specifically, start by setting the following environment variables:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
env:
|
||||
OPENAI_KEY: ${{ secrets.OPENAI_KEY }} # Make sure to add your OpenAI key to your repo secrets
|
||||
@ -178,137 +121,116 @@ Specifically, start by setting the following environment variables:
|
||||
github_action_config.auto_review: "true" # enable\disable auto review
|
||||
github_action_config.auto_describe: "true" # enable\disable auto describe
|
||||
github_action_config.auto_improve: "true" # enable\disable auto improve
|
||||
github_action_config.pr_actions: '["opened", "reopened", "ready_for_review", "review_requested"]'
|
||||
github_action_config.pr_actions: ["opened", "reopened", "ready_for_review", "review_requested"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`github_action_config.auto_review`, `github_action_config.auto_describe` and `github_action_config.auto_improve` are used to enable/disable automatic tools that run when a new PR is opened.
|
||||
If not set, the default configuration is for all three tools to run automatically when a new PR is opened.
|
||||
|
||||
`github_action_config.pr_actions` is used to configure which `pull_requests` events will trigger the enabled auto flags
|
||||
If not set, the default configuration is `["opened", "reopened", "ready_for_review", "review_requested"]`
|
||||
|
||||
`github_action_config.enable_output` are used to enable/disable github actions [output parameter](https://docs.github.com/en/actions/creating-actions/metadata-syntax-for-github-actions#outputs-for-docker-container-and-javascript-actions) (default is `true`).
|
||||
`github_action_config.enable_output` are used to enable/disable github actions [output parameter](https://docs.github.com/en/actions/creating-actions/metadata-syntax-for-github-actions#outputs-for-docker-container-and-javascript-actions) (default is `true`).
|
||||
Review result is output as JSON to `steps.{step-id}.outputs.review` property.
|
||||
The JSON structure is equivalent to the yaml data structure defined in [pr_reviewer_prompts.toml](https://github.com/qodo-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/pr_reviewer_prompts.toml).
|
||||
The JSON structure is equivalent to the yaml data structure defined in [pr_reviewer_prompts.toml](https://github.com/idubnori/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/pr_reviewer_prompts.toml).
|
||||
|
||||
Note that you can give additional config parameters by adding environment variables to `.github/workflows/pr_agent.yml`, or by using a `.pr_agent.toml` [configuration file](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/#global-configuration-file) in the root of your repo
|
||||
|
||||
For example, you can set an environment variable: `pr_description.publish_labels=false`, or add a `.pr_agent.toml` file with the following content:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[pr_description]
|
||||
publish_labels = false
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
to prevent Qodo Merge from publishing labels when running the `describe` tool.
|
||||
|
||||
### GitLab Webhook
|
||||
|
||||
## GitLab Webhook
|
||||
After setting up a GitLab webhook, to control which commands will run automatically when a new MR is opened, you can set the `pr_commands` parameter in the configuration file, similar to the GitHub App:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[gitlab]
|
||||
pr_commands = [
|
||||
"/describe",
|
||||
"/review",
|
||||
"/review --pr_reviewer.num_code_suggestions=0",
|
||||
"/improve",
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
the GitLab webhook can also respond to new code that is pushed to an open MR.
|
||||
The configuration toggle `handle_push_trigger` can be used to enable this feature.
|
||||
The configuration toggle `handle_push_trigger` can be used to enable this feature.
|
||||
The configuration parameter `push_commands` defines the list of tools that will be **run automatically** when new code is pushed to the MR.
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[gitlab]
|
||||
handle_push_trigger = true
|
||||
push_commands = [
|
||||
"/describe",
|
||||
"/review",
|
||||
"/review --pr_reviewer.num_code_suggestions=0 --pr_reviewer.final_update_message=false",
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note that to use the 'handle_push_trigger' feature, you need to give the gitlab webhook also the "Push events" scope.
|
||||
|
||||
### BitBucket App
|
||||
## BitBucket App
|
||||
Similar to GitHub app, when running Qodo Merge from BitBucket App, the default [configuration file](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml) from a pre-built docker will be initially loaded.
|
||||
|
||||
Similar to GitHub app, when running Qodo Merge from BitBucket App, the default [configuration file](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml) will be initially loaded.
|
||||
|
||||
By uploading a local `.pr_agent.toml` file to the root of the repo's default branch, you can edit and customize any configuration parameter. Note that you need to upload `.pr_agent.toml` prior to creating a PR, in order for the configuration to take effect.
|
||||
By uploading a local `.pr_agent.toml` file to the root of the repo's main branch, you can edit and customize any configuration parameter. Note that you need to upload `.pr_agent.toml` prior to creating a PR, in order for the configuration to take effect.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, if your local `.pr_agent.toml` file contains:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[pr_reviewer]
|
||||
extra_instructions = "Answer in japanese"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Each time you invoke a `/review` tool, it will use the extra instructions you set in the local configuration file.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Note that among other limitations, BitBucket provides relatively low rate-limits for applications (up to 1000 requests per hour), and does not provide an API to track the actual rate-limit usage.
|
||||
If you experience a lack of responses from Qodo Merge, you might want to set: `bitbucket_app.avoid_full_files=true` in your configuration file.
|
||||
If you experience lack of responses from Qodo Merge, you might want to set: `bitbucket_app.avoid_full_files=true` in your configuration file.
|
||||
This will prevent Qodo Merge from acquiring the full file content, and will only use the diff content. This will reduce the number of requests made to BitBucket, at the cost of small decrease in accuracy, as dynamic context will not be applicable.
|
||||
|
||||
#### BitBucket Self-Hosted App automatic tools
|
||||
|
||||
### BitBucket Self-Hosted App automatic tools
|
||||
|
||||
To control which commands will run automatically when a new PR is opened, you can set the `pr_commands` parameter in the configuration file:
|
||||
Specifically, set the following values:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[bitbucket_app]
|
||||
pr_commands = [
|
||||
"/review",
|
||||
"/review --pr_reviewer.num_code_suggestions=0",
|
||||
"/improve --pr_code_suggestions.commitable_code_suggestions=true --pr_code_suggestions.suggestions_score_threshold=7",
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note that we set specifically for bitbucket, we recommend using: `--pr_code_suggestions.suggestions_score_threshold=7` and that is the default value we set for bitbucket.
|
||||
Since this platform only supports inline code suggestions, we want to limit the number of suggestions, and only present a limited number.
|
||||
|
||||
To enable BitBucket app to respond to each **push** to the PR, set (for example):
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[bitbucket_app]
|
||||
handle_push_trigger = true
|
||||
push_commands = [
|
||||
"/describe",
|
||||
"/review",
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Azure DevOps provider
|
||||
## Azure DevOps provider
|
||||
|
||||
To use Azure DevOps provider use the following settings in configuration.toml:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
git_provider="azure"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Azure DevOps provider supports [PAT token](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/devops/organizations/accounts/use-personal-access-tokens-to-authenticate?view=azure-devops&tabs=Windows) or [DefaultAzureCredential](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/developer/python/sdk/authentication-overview#authentication-in-server-environments) authentication.
|
||||
PAT is faster to create, but has build in expiration date, and will use the user identity for API calls.
|
||||
PAT is faster to create, but has build in expiration date, and will use the user identity for API calls.
|
||||
Using DefaultAzureCredential you can use managed identity or Service principle, which are more secure and will create separate ADO user identity (via AAD) to the agent.
|
||||
|
||||
If PAT was chosen, you can assign the value in .secrets.toml.
|
||||
If DefaultAzureCredential was chosen, you can assigned the additional env vars like AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET directly,
|
||||
If PAT was chosen, you can assign the value in .secrets.toml.
|
||||
If DefaultAzureCredential was chosen, you can assigned the additional env vars like AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET directly,
|
||||
or use managed identity/az cli (for local development) without any additional configuration.
|
||||
in any case, 'org' value must be assigned in .secrets.toml:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[azure_devops]
|
||||
org = "https://dev.azure.com/YOUR_ORGANIZATION/"
|
||||
# pat = "YOUR_PAT_TOKEN" needed only if using PAT for authentication
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Azure DevOps Webhook
|
||||
### Azure DevOps Webhook
|
||||
|
||||
To control which commands will run automatically when a new PR is opened, you can set the `pr_commands` parameter in the configuration file, similar to the GitHub App:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[azure_devops_server]
|
||||
pr_commands = [
|
||||
"/describe",
|
||||
"/review",
|
||||
"/review --pr_reviewer.num_code_suggestions=0",
|
||||
"/improve",
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,43 +1,21 @@
|
||||
## Changing a model in PR-Agent
|
||||
## Changing a model
|
||||
|
||||
See [here](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/algo/__init__.py) for a list of available models.
|
||||
To use a different model than the default (o4-mini), you need to edit in the [configuration file](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml#L2) the fields:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
To use a different model than the default (GPT-4), you need to edit in the [configuration file](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml#L2) the fields:
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
model = "..."
|
||||
model_turbo = "..."
|
||||
fallback_models = ["..."]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For models and environments not from OpenAI, you might need to provide additional keys and other parameters.
|
||||
You can give parameters via a configuration file, or from environment variables.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Model-specific environment variables"
|
||||
See [litellm documentation](https://litellm.vercel.app/docs/proxy/quick_start#supported-llms) for the environment variables needed per model, as they may vary and change over time. Our documentation per-model may not always be up-to-date with the latest changes.
|
||||
Failing to set the needed keys of a specific model will usually result in litellm not identifying the model type, and failing to utilize it.
|
||||
|
||||
### OpenAI like API
|
||||
To use an OpenAI like API, set the following in your `.secrets.toml` file:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[openai]
|
||||
api_base = "https://api.openai.com/v1"
|
||||
api_key = "sk-..."
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
or use the environment variables (make sure to use double underscores `__`):
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
OPENAI__API_BASE=https://api.openai.com/v1
|
||||
OPENAI__KEY=sk-...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For models and environments not from OpenAI, you might need to provide additional keys and other parameters.
|
||||
You can give parameters via a configuration file (see below for instructions), or from environment variables. See [litellm documentation](https://litellm.vercel.app/docs/proxy/quick_start#supported-llms) for the environment variables relevant per model.
|
||||
|
||||
### Azure
|
||||
|
||||
To use Azure, set in your `.secrets.toml` (working from CLI), or in the GitHub `Settings > Secrets and variables` (working from GitHub App or GitHub Action):
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[openai]
|
||||
key = "" # your azure api key
|
||||
api_type = "azure"
|
||||
@ -47,131 +25,103 @@ deployment_id = "" # The deployment name you chose when you deployed the engine
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and set in your configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
model="" # the OpenAI model you've deployed on Azure (e.g. gpt-4o)
|
||||
fallback_models=["..."]
|
||||
model="" # the OpenAI model you've deployed on Azure (e.g. gpt-3.5-turbo)
|
||||
model_turbo="" # the OpenAI model you've deployed on Azure (e.g. gpt-3.5-turbo)
|
||||
fallback_models=["..."] # the OpenAI model you've deployed on Azure (e.g. gpt-3.5-turbo)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To use Azure AD (Entra id) based authentication set in your `.secrets.toml` (working from CLI), or in the GitHub `Settings > Secrets and variables` (working from GitHub App or GitHub Action):
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[azure_ad]
|
||||
client_id = "" # Your Azure AD application client ID
|
||||
client_secret = "" # Your Azure AD application client secret
|
||||
tenant_id = "" # Your Azure AD tenant ID
|
||||
api_base = "" # Your Azure OpenAI service base URL (e.g., https://openai.xyz.com/)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Passing custom headers to the underlying LLM Model API can be done by setting extra_headers parameter to litellm.
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[litellm]
|
||||
extra_headers='{"projectId": "<authorized projectId >", ...}') #The value of this setting should be a JSON string representing the desired headers, a ValueError is thrown otherwise.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This enables users to pass authorization tokens or API keys, when routing requests through an API management gateway.
|
||||
|
||||
### Ollama
|
||||
|
||||
You can run models locally through either [VLLM](https://docs.litellm.ai/docs/providers/vllm) or [Ollama](https://docs.litellm.ai/docs/providers/ollama)
|
||||
|
||||
E.g. to use a new model locally via Ollama, set in `.secrets.toml` or in a configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
model = "ollama/qwen2.5-coder:32b"
|
||||
fallback_models=["ollama/qwen2.5-coder:32b"]
|
||||
custom_model_max_tokens=128000 # set the maximal input tokens for the model
|
||||
duplicate_examples=true # will duplicate the examples in the prompt, to help the model to generate structured output
|
||||
|
||||
[ollama]
|
||||
api_base = "http://localhost:11434" # or whatever port you're running Ollama on
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
By default, Ollama uses a context window size of 2048 tokens. In most cases this is not enough to cover pr-agent promt and pull-request diff. Context window size can be overridden with the `OLLAMA_CONTEXT_LENGTH` environment variable. For example, to set the default context length to 8K, use: `OLLAMA_CONTEXT_LENGTH=8192 ollama serve`. More information you can find on the [official ollama faq](https://github.com/ollama/ollama/blob/main/docs/faq.md#how-can-i-specify-the-context-window-size).
|
||||
|
||||
Please note that the `custom_model_max_tokens` setting should be configured in accordance with the `OLLAMA_CONTEXT_LENGTH`. Failure to do so may result in unexpected model output.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Local models vs commercial models"
|
||||
Qodo Merge is compatible with almost any AI model, but analyzing complex code repositories and pull requests requires a model specifically optimized for code analysis.
|
||||
|
||||
Commercial models such as GPT-4, Claude Sonnet, and Gemini have demonstrated robust capabilities in generating structured output for code analysis tasks with large input. In contrast, most open-source models currently available (as of January 2025) face challenges with these complex tasks.
|
||||
|
||||
Based on our testing, local open-source models are suitable for experimentation and learning purposes (mainly for the `ask` command), but they are not suitable for production-level code analysis tasks.
|
||||
|
||||
Hence, for production workflows and real-world usage, we recommend using commercial models.
|
||||
|
||||
### Hugging Face
|
||||
|
||||
To use a new model with Hugging Face Inference Endpoints, for example, set:
|
||||
**Local**
|
||||
You can run Hugging Face models locally through either [VLLM](https://docs.litellm.ai/docs/providers/vllm) or [Ollama](https://docs.litellm.ai/docs/providers/ollama)
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
E.g. to use a new Hugging Face model locally via Ollama, set:
|
||||
```
|
||||
[__init__.py]
|
||||
MAX_TOKENS = {
|
||||
"model-name-on-ollama": <max_tokens>
|
||||
}
|
||||
e.g.
|
||||
MAX_TOKENS={
|
||||
...,
|
||||
"ollama/llama2": 4096
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[config] # in configuration.toml
|
||||
model = "ollama/llama2"
|
||||
model_turbo = "ollama/llama2"
|
||||
fallback_models=["ollama/llama2"]
|
||||
|
||||
[ollama] # in .secrets.toml
|
||||
api_base = ... # the base url for your Hugging Face inference endpoint
|
||||
# e.g. if running Ollama locally, you may use:
|
||||
api_base = "http://localhost:11434/"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Inference Endpoints
|
||||
|
||||
To use a new model with Hugging Face Inference Endpoints, for example, set:
|
||||
```
|
||||
[__init__.py]
|
||||
MAX_TOKENS = {
|
||||
"model-name-on-huggingface": <max_tokens>
|
||||
}
|
||||
e.g.
|
||||
MAX_TOKENS={
|
||||
...,
|
||||
"meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-chat-hf": 4096
|
||||
}
|
||||
[config] # in configuration.toml
|
||||
model = "huggingface/meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-chat-hf"
|
||||
model_turbo = "huggingface/meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-chat-hf"
|
||||
fallback_models=["huggingface/meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-chat-hf"]
|
||||
custom_model_max_tokens=... # set the maximal input tokens for the model
|
||||
|
||||
[huggingface] # in .secrets.toml
|
||||
key = ... # your Hugging Face api key
|
||||
api_base = ... # the base url for your Hugging Face inference endpoint
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
(you can obtain a Llama2 key from [here](https://replicate.com/replicate/llama-2-70b-chat/api))
|
||||
|
||||
### Replicate
|
||||
|
||||
To use Llama2 model with Replicate, for example, set:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config] # in configuration.toml
|
||||
model = "replicate/llama-2-70b-chat:2c1608e18606fad2812020dc541930f2d0495ce32eee50074220b87300bc16e1"
|
||||
model_turbo = "replicate/llama-2-70b-chat:2c1608e18606fad2812020dc541930f2d0495ce32eee50074220b87300bc16e1"
|
||||
fallback_models=["replicate/llama-2-70b-chat:2c1608e18606fad2812020dc541930f2d0495ce32eee50074220b87300bc16e1"]
|
||||
[replicate] # in .secrets.toml
|
||||
key = ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
(you can obtain a Llama2 key from [here](https://replicate.com/replicate/llama-2-70b-chat/api))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Also, review the [AiHandler](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/algo/ai_handler.py) file for instructions on how to set keys for other models.
|
||||
|
||||
### Groq
|
||||
|
||||
To use Llama3 model with Groq, for example, set:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config] # in configuration.toml
|
||||
model = "llama3-70b-8192"
|
||||
fallback_models = ["groq/llama3-70b-8192"]
|
||||
model_turbo = "llama3-70b-8192"
|
||||
fallback_models = ["groq/llama3-70b-8192"]
|
||||
[groq] # in .secrets.toml
|
||||
key = ... # your Groq api key
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
(you can obtain a Groq key from [here](https://console.groq.com/keys))
|
||||
|
||||
### xAI
|
||||
|
||||
To use xAI's models with PR-Agent, set:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config] # in configuration.toml
|
||||
model = "xai/grok-2-latest"
|
||||
fallback_models = ["xai/grok-2-latest"] # or any other model as fallback
|
||||
|
||||
[xai] # in .secrets.toml
|
||||
key = "..." # your xAI API key
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can obtain an xAI API key from [xAI's console](https://console.x.ai/) by creating an account and navigating to the developer settings page.
|
||||
|
||||
### Vertex AI
|
||||
|
||||
To use Google's Vertex AI platform and its associated models (chat-bison/codechat-bison) set:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config] # in configuration.toml
|
||||
model = "vertex_ai/codechat-bison"
|
||||
model_turbo = "vertex_ai/codechat-bison"
|
||||
fallback_models="vertex_ai/codechat-bison"
|
||||
|
||||
[vertexai] # in .secrets.toml
|
||||
@ -183,174 +133,57 @@ Your [application default credentials](https://cloud.google.com/docs/authenticat
|
||||
|
||||
If you do want to set explicit credentials, then you can use the `GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS` environment variable set to a path to a json credentials file.
|
||||
|
||||
### Google AI Studio
|
||||
|
||||
To use [Google AI Studio](https://aistudio.google.com/) models, set the relevant models in the configuration section of the configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config] # in configuration.toml
|
||||
model="gemini/gemini-1.5-flash"
|
||||
fallback_models=["gemini/gemini-1.5-flash"]
|
||||
|
||||
[google_ai_studio] # in .secrets.toml
|
||||
gemini_api_key = "..."
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you don't want to set the API key in the .secrets.toml file, you can set the `GOOGLE_AI_STUDIO.GEMINI_API_KEY` environment variable.
|
||||
|
||||
### Anthropic
|
||||
|
||||
To use Anthropic models, set the relevant models in the configuration section of the configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
model="anthropic/claude-3-opus-20240229"
|
||||
model_turbo="anthropic/claude-3-opus-20240229"
|
||||
fallback_models=["anthropic/claude-3-opus-20240229"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And also set the api key in the .secrets.toml file:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[anthropic]
|
||||
KEY = "..."
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
See [litellm](https://docs.litellm.ai/docs/providers/anthropic#usage) documentation for more information about the environment variables required for Anthropic.
|
||||
|
||||
### Amazon Bedrock
|
||||
|
||||
To use Amazon Bedrock and its foundational models, add the below configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config] # in configuration.toml
|
||||
model="bedrock/anthropic.claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620-v1:0"
|
||||
fallback_models=["bedrock/anthropic.claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620-v1:0"]
|
||||
|
||||
[aws]
|
||||
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID="..."
|
||||
AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY="..."
|
||||
AWS_REGION_NAME="..."
|
||||
model="bedrock/anthropic.claude-3-sonnet-20240229-v1:0"
|
||||
model_turbo="bedrock/anthropic.claude-3-sonnet-20240229-v1:0"
|
||||
fallback_models=["bedrock/anthropic.claude-v2:1"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
See [litellm](https://docs.litellm.ai/docs/providers/bedrock#usage) documentation for more information about the environment variables required for Amazon Bedrock.
|
||||
Note that you have to add access to foundational models before using them. Please refer to [this document](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/bedrock/latest/userguide/setting-up.html) for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
### DeepSeek
|
||||
|
||||
To use deepseek-chat model with DeepSeek, for example, set:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config] # in configuration.toml
|
||||
model = "deepseek/deepseek-chat"
|
||||
fallback_models=["deepseek/deepseek-chat"]
|
||||
If you are using the claude-3 model, please configure the following settings as there are parameters incompatible with claude-3.
|
||||
```
|
||||
[litellm]
|
||||
drop_params = true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and fill up your key
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[deepseek] # in .secrets.toml
|
||||
key = ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
(you can obtain a deepseek-chat key from [here](https://platform.deepseek.com))
|
||||
|
||||
### DeepInfra
|
||||
|
||||
To use DeepSeek model with DeepInfra, for example, set:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config] # in configuration.toml
|
||||
model = "deepinfra/deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama-70B"
|
||||
fallback_models = ["deepinfra/deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B"]
|
||||
[deepinfra] # in .secrets.toml
|
||||
key = ... # your DeepInfra api key
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
(you can obtain a DeepInfra key from [here](https://deepinfra.com/dash/api_keys))
|
||||
|
||||
### Mistral
|
||||
|
||||
To use models like Mistral or Codestral with Mistral, for example, set:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config] # in configuration.toml
|
||||
model = "mistral/mistral-small-latest"
|
||||
fallback_models = ["mistral/mistral-medium-latest"]
|
||||
[mistral] # in .secrets.toml
|
||||
key = "..." # your Mistral api key
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
(you can obtain a Mistral key from [here](https://console.mistral.ai/api-keys))
|
||||
|
||||
### Codestral
|
||||
|
||||
To use Codestral model with Codestral, for example, set:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config] # in configuration.toml
|
||||
model = "codestral/codestral-latest"
|
||||
fallback_models = ["codestral/codestral-2405"]
|
||||
[codestral] # in .secrets.toml
|
||||
key = "..." # your Codestral api key
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
(you can obtain a Codestral key from [here](https://console.mistral.ai/codestral))
|
||||
|
||||
### Openrouter
|
||||
|
||||
To use model from Openrouter, for example, set:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config] # in configuration.toml
|
||||
model="openrouter/anthropic/claude-3.7-sonnet"
|
||||
fallback_models=["openrouter/deepseek/deepseek-chat"]
|
||||
custom_model_max_tokens=20000
|
||||
|
||||
[openrouter] # in .secrets.toml or passed an environment variable openrouter__key
|
||||
key = "..." # your openrouter api key
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
(you can obtain an Openrouter API key from [here](https://openrouter.ai/settings/keys))
|
||||
AWS session is automatically authenticated from your environment, but you can also explicitly set `AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID`, `AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY` and `AWS_REGION_NAME` environment variables. Please refer to [this document](https://litellm.vercel.app/docs/providers/bedrock) for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
### Custom models
|
||||
|
||||
If the relevant model doesn't appear [here](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/algo/__init__.py), you can still use it as a custom model:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Set the model name in the configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
(1) Set the model name in the configuration file:
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
model="custom_model_name"
|
||||
model_turbo="custom_model_name"
|
||||
fallback_models=["custom_model_name"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Set the maximal tokens for the model:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
(2) Set the maximal tokens for the model:
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
custom_model_max_tokens= ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Go to [litellm documentation](https://litellm.vercel.app/docs/proxy/quick_start#supported-llms), find the model you want to use, and set the relevant environment variables.
|
||||
|
||||
4. Most reasoning models do not support chat-style inputs (`system` and `user` messages) or temperature settings.
|
||||
To bypass chat templates and temperature controls, set `config.custom_reasoning_model = true` in your configuration file.
|
||||
|
||||
## Dedicated parameters
|
||||
|
||||
### OpenAI models
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
reasoning_efffort= = "medium" # "low", "medium", "high"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
With the OpenAI models that support reasoning effort (eg: o4-mini), you can specify its reasoning effort via `config` section. The default value is `medium`. You can change it to `high` or `low` based on your usage.
|
||||
|
||||
### Anthropic models
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
enable_claude_extended_thinking = false # Set to true to enable extended thinking feature
|
||||
extended_thinking_budget_tokens = 2048
|
||||
extended_thinking_max_output_tokens = 4096
|
||||
```
|
||||
(3) Go to [litellm documentation](https://litellm.vercel.app/docs/proxy/quick_start#supported-llms), find the model you want to use, and set the relevant environment variables.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -20,9 +20,10 @@ In terms of precedence, wiki configurations will override local configurations,
|
||||
|
||||
`Platforms supported: GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket`
|
||||
|
||||
With Qodo Merge, you can set configurations by creating a page called `.pr_agent.toml` in the [wiki](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/wiki/pr_agent.toml) of the repo.
|
||||
With Qodo Merge Pro, you can set configurations by creating a page called `.pr_agent.toml` in the [wiki](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/wiki/pr_agent.toml) of the repo.
|
||||
The advantage of this method is that it allows to set configurations without needing to commit new content to the repo - just edit the wiki page and **save**.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
Click [here](https://codium.ai/images/pr_agent/wiki_configuration_pr_agent.mp4) to see a short instructional video. We recommend surrounding the configuration content with triple-quotes (or \`\`\`toml), to allow better presentation when displayed in the wiki as markdown.
|
||||
@ -39,7 +40,8 @@ Qodo Merge will know to remove the surrounding quotes when reading the configura
|
||||
|
||||
`Platforms supported: GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, Azure DevOps`
|
||||
|
||||
By uploading a local `.pr_agent.toml` file to the root of the repo's default branch, you can edit and customize any configuration parameter. Note that you need to upload or update `.pr_agent.toml` before using the PR Agent tools (either at PR creation or via manual trigger) for the configuration to take effect.
|
||||
|
||||
By uploading a local `.pr_agent.toml` file to the root of the repo's main branch, you can edit and customize any configuration parameter. Note that you need to upload `.pr_agent.toml` prior to creating a PR, in order for the configuration to take effect.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, if you set in `.pr_agent.toml`:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -54,11 +56,12 @@ extra_instructions="""\
|
||||
|
||||
Then you can give a list of extra instructions to the `review` tool.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Global configuration file 💎
|
||||
|
||||
`Platforms supported: GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket`
|
||||
|
||||
If you create a repo called `pr-agent-settings` in your **organization**, its configuration file `.pr_agent.toml` will be used as a global configuration file for any other repo that belongs to the same organization.
|
||||
If you create a repo called `pr-agent-settings` in your **organization**, it's configuration file `.pr_agent.toml` will be used as a global configuration file for any other repo that belongs to the same organization.
|
||||
Parameters from a local `.pr_agent.toml` file, in a specific repo, will override the global configuration parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, in the GitHub organization `Codium-ai`:
|
||||
@ -66,29 +69,3 @@ For example, in the GitHub organization `Codium-ai`:
|
||||
- The file [`https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent-settings/.pr_agent.toml`](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent-settings/blob/main/.pr_agent.toml) serves as a global configuration file for all the repos in the GitHub organization `Codium-ai`.
|
||||
|
||||
- The repo [`https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent`](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/.pr_agent.toml) inherits the global configuration file from `pr-agent-settings`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Bitbucket Organization level configuration file 💎
|
||||
|
||||
`Relevant platforms: Bitbucket Data Center`
|
||||
|
||||
In Bitbucket Data Center, there are two levels where you can define a global configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
- Project-level global configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
Create a repository named `pr-agent-settings` within a specific project. The configuration file in this repository will apply to all repositories under the same project.
|
||||
|
||||
- Organization-level global configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
Create a dedicated project to hold a global configuration file that affects all repositories across all projects in your organization.
|
||||
|
||||
**Setting up organization-level global configuration:**
|
||||
|
||||
1. Create a new project with both the name and key: PR_AGENT_SETTINGS.
|
||||
2. Inside the PR_AGENT_SETTINGS project, create a repository named pr-agent-settings.
|
||||
3. In this repository, add a `.pr_agent.toml` configuration file—structured similarly to the global configuration file described above.
|
||||
4. Optionally, you can add organizational-level [global best practices file](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/#global-configuration-file).
|
||||
|
||||
Repositories across your entire Bitbucket organization will inherit the configuration from this file.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Note"
|
||||
If both organization-level and project-level global settings are defined, the project-level settings will take precedence over the organization-level configuration. Additionally, parameters from a repository’s local .pr_agent.toml file will always override both global settings.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,30 +0,0 @@
|
||||
`Supported Git Platforms: GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket`
|
||||
|
||||
For optimal functionality of Qodo Merge, we recommend enabling a wiki for each repository where Qodo Merge is installed. The wiki serves several important purposes:
|
||||
|
||||
**Key Wiki Features: 💎**
|
||||
|
||||
- Storing a [configuration file](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/#wiki-configuration-file)
|
||||
- Track [accepted suggestions](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#suggestion-tracking)
|
||||
- Facilitates learning over time by creating an [auto_best_practices.md](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/auto_best_practices) file
|
||||
|
||||
**Setup Instructions (GitHub):**
|
||||
|
||||
To enable a wiki for your repository:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Navigate to your repository's main page on GitHub
|
||||
2. Select "Settings" from the top navigation bar
|
||||
3. Locate the "Features" section
|
||||
4. Enable the "Wikis" option by checking the corresponding box
|
||||
5. Return to your repository's main page
|
||||
6. Look for the newly added "Wiki" tab in the top navigation
|
||||
7. Initialize your wiki by clicking "Create the first page" and saving (this step is important - without creating an initial page, the wiki will not be fully functional)
|
||||
|
||||
### Why Wiki?
|
||||
|
||||
- Your code (and its derivatives, including accepted code suggestions) is yours. Qodo Merge will never store it on external servers.
|
||||
- Repository changes typically require pull requests, which create overhead and are time-consuming. This process is too cumbersome for auto data aggregation, and is not very convenient even for managing frequently updated content like configuration files.
|
||||
- A repository wiki page provides an ideal balance:
|
||||
- It lives within your repository, making it suitable for code-related documentation
|
||||
- It enables quick updates without the overhead of pull requests
|
||||
- It maintains full Git version control, allowing you to track changes over time.
|
||||
@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
|
||||
# Usage guide
|
||||
|
||||
This section provides a detailed guide on how to use Qodo Merge.
|
||||
This page provides a detailed guide on how to use Qodo Merge.
|
||||
It includes information on how to adjust Qodo Merge configurations, define which tools will run automatically, and other advanced configurations.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- [Introduction](./introduction.md)
|
||||
- [Enabling a Wiki](./enabling_a_wiki)
|
||||
- [Configuration File](./configuration_options.md)
|
||||
- [Usage and Automation](./automations_and_usage.md)
|
||||
- [Local Repo (CLI)](./automations_and_usage.md#local-repo-cli)
|
||||
@ -16,11 +16,11 @@ It includes information on how to adjust Qodo Merge configurations, define which
|
||||
- [Azure DevOps Provider](./automations_and_usage.md#azure-devops-provider)
|
||||
- [Managing Mail Notifications](./mail_notifications.md)
|
||||
- [Changing a Model](./changing_a_model.md)
|
||||
- [Additional Configurations](./additional_configurations.md)
|
||||
- [Additional Configurations Walkthrough](./additional_configurations.md)
|
||||
- [Ignoring files from analysis](./additional_configurations.md#ignoring-files-from-analysis)
|
||||
- [Extra instructions](./additional_configurations.md#extra-instructions)
|
||||
- [Working with large PRs](./additional_configurations.md#working-with-large-prs)
|
||||
- [Changing a model](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/changing_a_model/)
|
||||
- [Changing a model](./additional_configurations.md#changing-a-model)
|
||||
- [Patch Extra Lines](./additional_configurations.md#patch-extra-lines)
|
||||
- [FAQ](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/faq/)
|
||||
- [Qodo Merge Models](./qodo_merge_models)
|
||||
- [Editing the prompts](./additional_configurations.md#editing-the-prompts)
|
||||
- [Qodo Merge Pro Models](./PR_agent_pro_models.md)
|
||||
@ -2,10 +2,12 @@
|
||||
After [installation](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/), there are three basic ways to invoke Qodo Merge:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Locally running a CLI command
|
||||
2. Online usage - by [commenting](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/229#issuecomment-1695021901){:target="_blank"} on a PR
|
||||
2. Online usage - by [commenting](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/229#issuecomment-1695021901) on a PR
|
||||
3. Enabling Qodo Merge tools to run automatically when a new PR is opened
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Specifically, CLI commands can be issued by invoking a pre-built [docker image](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/locally/#using-docker-image), or by invoking a [locally cloned repo](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/locally/#run-from-source).
|
||||
|
||||
For online usage, you will need to setup either a [GitHub App](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/github/#run-as-a-github-app) or a [GitHub Action](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/github/#run-as-a-github-action) (GitHub), a [GitLab webhook](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/gitlab/#run-a-gitlab-webhook-server) (GitLab), or a [BitBucket App](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/bitbucket/#run-using-codiumai-hosted-bitbucket-app) (BitBucket).
|
||||
These platforms also enable to run Qodo Merge specific tools automatically when a new PR is opened, or on each push to a branch.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -8,11 +8,11 @@ As an alternative, you can filter in your mail provider the notifications specif
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
Another option to reduce the mail overload, yet still receive notifications on Qodo Merge tools, is to disable the help collapsible section in Qodo Merge bot comments.
|
||||
|
||||
Another option to reduce the mail overload, yet still receive notifications on Qodo Merge tools, is to disable the help collapsible section in Qodo Merge bot comments.
|
||||
This can done by setting `enable_help_text=false` for the relevant tool in the configuration file.
|
||||
For example, to disable the help text for the `pr_reviewer` tool, set:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[pr_reviewer]
|
||||
enable_help_text = false
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -1,42 +0,0 @@
|
||||
|
||||
The default models used by Qodo Merge (April 2025) are a combination of Claude Sonnet 3.7 and Gemini 2.5 Pro.
|
||||
|
||||
### Selecting a Specific Model
|
||||
|
||||
Users can configure Qodo Merge to use only a specific model by editing the [configuration](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/) file.
|
||||
The models supported by Qodo Merge are:
|
||||
|
||||
- `claude-3-7-sonnet`
|
||||
- `o4-mini`
|
||||
- `gpt-4.1`
|
||||
- `gemini-2.5-pro`
|
||||
- `deepseek/r1`
|
||||
|
||||
To restrict Qodo Merge to using only `o4-mini`, add this setting:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
model="o4-mini"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To restrict Qodo Merge to using only `GPT-4.1`, add this setting:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
model="gpt-4.1"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To restrict Qodo Merge to using only `gemini-2.5-pro`, add this setting:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
model="gemini-2.5-pro"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
To restrict Qodo Merge to using only `deepseek-r1` us-hosted, add this setting:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
model="deepseek/r1"
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -1,27 +1,29 @@
|
||||
site_name: Qodo Merge (and open-source PR-Agent)
|
||||
repo_url: https://github.com/qodo-ai/pr-agent
|
||||
repo_name: Qodo-ai/pr-agent
|
||||
site_name: Qodo Merge (formerly known as PR-Agent)
|
||||
repo_url: https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent
|
||||
repo_name: Codium-ai/pr-agent
|
||||
|
||||
nav:
|
||||
- Overview:
|
||||
- 'index.md'
|
||||
- 💎 Qodo Merge: 'overview/pr_agent_pro.md'
|
||||
- 💎 Qodo Merge Pro: 'overview/pr_agent_pro.md'
|
||||
- Data Privacy: 'overview/data_privacy.md'
|
||||
- Installation:
|
||||
- 'installation/index.md'
|
||||
- PR-Agent: 'installation/pr_agent.md'
|
||||
- 💎 Qodo Merge: 'installation/qodo_merge.md'
|
||||
- Locally: 'installation/locally.md'
|
||||
- GitHub: 'installation/github.md'
|
||||
- GitLab: 'installation/gitlab.md'
|
||||
- BitBucket: 'installation/bitbucket.md'
|
||||
- Azure DevOps: 'installation/azure.md'
|
||||
- 💎 Qodo Merge Pro: 'installation/pr_agent_pro.md'
|
||||
- Usage Guide:
|
||||
- 'usage-guide/index.md'
|
||||
- Introduction: 'usage-guide/introduction.md'
|
||||
- Enabling a Wiki: 'usage-guide/enabling_a_wiki.md'
|
||||
- Configuration File: 'usage-guide/configuration_options.md'
|
||||
- Usage and Automation: 'usage-guide/automations_and_usage.md'
|
||||
- Managing Mail Notifications: 'usage-guide/mail_notifications.md'
|
||||
- Changing a Model: 'usage-guide/changing_a_model.md'
|
||||
- Additional Configurations: 'usage-guide/additional_configurations.md'
|
||||
- Frequently Asked Questions: 'faq/index.md'
|
||||
- 💎 Qodo Merge Models: 'usage-guide/qodo_merge_models.md'
|
||||
- 💎 Qodo Merge Pro Models: 'usage-guide/PR_agent_pro_models'
|
||||
- Tools:
|
||||
- 'tools/index.md'
|
||||
- Describe: 'tools/describe.md'
|
||||
@ -29,7 +31,7 @@ nav:
|
||||
- Improve: 'tools/improve.md'
|
||||
- Ask: 'tools/ask.md'
|
||||
- Update Changelog: 'tools/update_changelog.md'
|
||||
- Help Docs: 'tools/help_docs.md'
|
||||
- Similar Issues: 'tools/similar_issues.md'
|
||||
- Help: 'tools/help.md'
|
||||
- 💎 Analyze: 'tools/analyze.md'
|
||||
- 💎 Test: 'tools/test.md'
|
||||
@ -39,32 +41,23 @@ nav:
|
||||
- 💎 Custom Prompt: 'tools/custom_prompt.md'
|
||||
- 💎 CI Feedback: 'tools/ci_feedback.md'
|
||||
- 💎 Similar Code: 'tools/similar_code.md'
|
||||
- 💎 Implement: 'tools/implement.md'
|
||||
- 💎 Scan Repo Discussions: 'tools/scan_repo_discussions.md'
|
||||
- 💎 Repo Statistics: 'tools/repo_statistics.md'
|
||||
- Core Abilities:
|
||||
- 'core-abilities/index.md'
|
||||
- Auto best practices: 'core-abilities/auto_best_practices.md'
|
||||
- Code validation: 'core-abilities/code_validation.md'
|
||||
- Compression strategy: 'core-abilities/compression_strategy.md'
|
||||
- Local and global metadata: 'core-abilities/metadata.md'
|
||||
- Dynamic context: 'core-abilities/dynamic_context.md'
|
||||
- Fetching ticket context: 'core-abilities/fetching_ticket_context.md'
|
||||
- Self-reflection: 'core-abilities/self_reflection.md'
|
||||
- Impact evaluation: 'core-abilities/impact_evaluation.md'
|
||||
- Interactivity: 'core-abilities/interactivity.md'
|
||||
- Local and global metadata: 'core-abilities/metadata.md'
|
||||
- RAG context enrichment: 'core-abilities/rag_context_enrichment.md'
|
||||
- Self-reflection: 'core-abilities/self_reflection.md'
|
||||
- Compression strategy: 'core-abilities/compression_strategy.md'
|
||||
- Code-oriented YAML: 'core-abilities/code_oriented_yaml.md'
|
||||
- Static code analysis: 'core-abilities/static_code_analysis.md'
|
||||
- Code Fine-tuning Benchmark: 'finetuning_benchmark/index.md'
|
||||
- Chrome Extension:
|
||||
- Qodo Merge Chrome Extension: 'chrome-extension/index.md'
|
||||
- Features: 'chrome-extension/features.md'
|
||||
- Data Privacy: 'chrome-extension/data_privacy.md'
|
||||
- Options: 'chrome-extension/options.md'
|
||||
- PR Benchmark:
|
||||
- PR Benchmark: 'pr_benchmark/index.md'
|
||||
- Recent Updates:
|
||||
- Recent Updates: 'recent_updates/index.md'
|
||||
- AI Docs Search: 'ai_search/index.md'
|
||||
- FAQ:
|
||||
- FAQ: 'faq/index.md'
|
||||
# - Code Fine-tuning Benchmark: 'finetuning_benchmark/index.md'
|
||||
|
||||
theme:
|
||||
@ -85,6 +78,7 @@ theme:
|
||||
- content.tabs.link
|
||||
- content.code.annotation
|
||||
- content.code.copy
|
||||
- content.tabs.link
|
||||
language: en
|
||||
custom_dir: overrides
|
||||
|
||||
@ -152,8 +146,6 @@ markdown_extensions:
|
||||
- pymdownx.emoji:
|
||||
emoji_index: !!python/name:material.extensions.emoji.twemoji
|
||||
emoji_generator: !!python/name:material.extensions.emoji.to_svg
|
||||
- pymdownx.tabbed:
|
||||
alternate_style: true
|
||||
- toc:
|
||||
title: On this page
|
||||
toc_depth: 3
|
||||
@ -161,4 +153,4 @@ markdown_extensions:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
copyright: |
|
||||
© 2025 <a href="https://www.codium.ai/" target="_blank" rel="noopener">QodoAI</a>
|
||||
© 2024 <a href="https://www.codium.ai/" target="_blank" rel="noopener">CodiumAI</a>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2,9 +2,9 @@
|
||||
|
||||
{% block scripts %}
|
||||
{{ super() }}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- Google Tag Manager (noscript) -->
|
||||
<noscript><iframe src="https://www.googletagmanager.com/ns.html?id=GTM-5C9KZBM3"
|
||||
height="0" width="0" style="display:none;visibility:hidden"></iframe></noscript>
|
||||
<!-- End Google Tag Manager (noscript) -->
|
||||
{% endblock %}
|
||||
{% endblock %}
|
||||
@ -42,7 +42,7 @@
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.social-icons svg {
|
||||
width: 24px;
|
||||
width: 24px;
|
||||
height: auto;
|
||||
fill: white;
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -82,7 +82,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
<footer class="wrapper">
|
||||
<div class="container">
|
||||
<p class="footer-text">© 2025 <a href="https://www.qodo.ai/" target="_blank" rel="noopener">Qodo</a></p>
|
||||
<p class="footer-text">© 2024 <a href="https://www.qodo.ai/" target="_blank" rel="noopener">Qodo</a></p>
|
||||
<div class="footer-links">
|
||||
<a href="https://qodo-gen-docs.qodo.ai/">Qodo Gen</a>
|
||||
<p>|</p>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -3,5 +3,5 @@
|
||||
new Date().getTime(),event:'gtm.js'});var f=d.getElementsByTagName(s)[0],
|
||||
j=d.createElement(s),dl=l!='dataLayer'?'&l='+l:'';j.async=true;j.src=
|
||||
'https://www.googletagmanager.com/gtm.js?id='+i+dl;f.parentNode.insertBefore(j,f);
|
||||
})(window,document,'script','dataLayer','GTM-M6PJSFV');</script>
|
||||
<!-- End Google Tag Manager -->
|
||||
})(window,document,'script','dataLayer','GTM-5C9KZBM3');</script>
|
||||
<!-- End Google Tag Manager -->
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ from functools import partial
|
||||
|
||||
from pr_agent.algo.ai_handlers.base_ai_handler import BaseAiHandler
|
||||
from pr_agent.algo.ai_handlers.litellm_ai_handler import LiteLLMAIHandler
|
||||
from pr_agent.algo.cli_args import CliArgs
|
||||
|
||||
from pr_agent.algo.utils import update_settings_from_args
|
||||
from pr_agent.config_loader import get_settings
|
||||
from pr_agent.git_providers.utils import apply_repo_settings
|
||||
@ -13,8 +13,8 @@ from pr_agent.tools.pr_code_suggestions import PRCodeSuggestions
|
||||
from pr_agent.tools.pr_config import PRConfig
|
||||
from pr_agent.tools.pr_description import PRDescription
|
||||
from pr_agent.tools.pr_generate_labels import PRGenerateLabels
|
||||
from pr_agent.tools.pr_help_docs import PRHelpDocs
|
||||
from pr_agent.tools.pr_help_message import PRHelpMessage
|
||||
from pr_agent.tools.pr_information_from_user import PRInformationFromUser
|
||||
from pr_agent.tools.pr_line_questions import PR_LineQuestions
|
||||
from pr_agent.tools.pr_questions import PRQuestions
|
||||
from pr_agent.tools.pr_reviewer import PRReviewer
|
||||
@ -26,6 +26,8 @@ command2class = {
|
||||
"answer": PRReviewer,
|
||||
"review": PRReviewer,
|
||||
"review_pr": PRReviewer,
|
||||
"reflect": PRInformationFromUser,
|
||||
"reflect_and_review": PRInformationFromUser,
|
||||
"describe": PRDescription,
|
||||
"describe_pr": PRDescription,
|
||||
"improve": PRCodeSuggestions,
|
||||
@ -40,16 +42,15 @@ command2class = {
|
||||
"similar_issue": PRSimilarIssue,
|
||||
"add_docs": PRAddDocs,
|
||||
"generate_labels": PRGenerateLabels,
|
||||
"help_docs": PRHelpDocs,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
commands = list(command2class.keys())
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class PRAgent:
|
||||
def __init__(self, ai_handler: partial[BaseAiHandler,] = LiteLLMAIHandler):
|
||||
self.ai_handler = ai_handler # will be initialized in run_action
|
||||
self.forbidden_cli_args = ['enable_auto_approval']
|
||||
|
||||
async def handle_request(self, pr_url, request, notify=None) -> bool:
|
||||
# First, apply repo specific settings if exists
|
||||
@ -64,45 +65,24 @@ class PRAgent:
|
||||
else:
|
||||
action, *args = request
|
||||
|
||||
# validate args
|
||||
is_valid, arg = CliArgs.validate_user_args(args)
|
||||
if not is_valid:
|
||||
get_logger().error(
|
||||
f"CLI argument for param '{arg}' is forbidden. Use instead a configuration file."
|
||||
)
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
# Update settings from args
|
||||
if args:
|
||||
for forbidden_arg in self.forbidden_cli_args:
|
||||
for arg in args:
|
||||
if forbidden_arg in arg:
|
||||
get_logger().error(
|
||||
f"CLI argument for param '{forbidden_arg}' is forbidden. Use instead a configuration file."
|
||||
)
|
||||
return False
|
||||
args = update_settings_from_args(args)
|
||||
|
||||
# Append the response language in the extra instructions
|
||||
response_language = get_settings().config.get('response_language', 'en-us')
|
||||
if response_language.lower() != 'en-us':
|
||||
get_logger().info(f'User has set the response language to: {response_language}')
|
||||
for key in get_settings():
|
||||
setting = get_settings().get(key)
|
||||
if str(type(setting)) == "<class 'dynaconf.utils.boxing.DynaBox'>":
|
||||
if hasattr(setting, 'extra_instructions'):
|
||||
current_extra_instructions = setting.extra_instructions
|
||||
|
||||
# Define the language-specific instruction and the separator
|
||||
lang_instruction_text = f"Your response MUST be written in the language corresponding to locale code: '{response_language}'. This is crucial."
|
||||
separator_text = "\n======\n\nIn addition, "
|
||||
|
||||
# Check if the specific language instruction is already present to avoid duplication
|
||||
if lang_instruction_text not in str(current_extra_instructions):
|
||||
if current_extra_instructions: # If there's existing text
|
||||
setting.extra_instructions = str(current_extra_instructions) + separator_text + lang_instruction_text
|
||||
else: # If extra_instructions was None or empty
|
||||
setting.extra_instructions = lang_instruction_text
|
||||
# If lang_instruction_text is already present, do nothing.
|
||||
|
||||
action = action.lstrip("/").lower()
|
||||
if action not in command2class:
|
||||
get_logger().warning(f"Unknown command: {action}")
|
||||
get_logger().debug(f"Unknown command: {action}")
|
||||
return False
|
||||
with get_logger().contextualize(command=action, pr_url=pr_url):
|
||||
get_logger().info("PR-Agent request handler started", analytics=True)
|
||||
if action == "reflect_and_review":
|
||||
get_settings().pr_reviewer.ask_and_reflect = True
|
||||
if action == "answer":
|
||||
if notify:
|
||||
notify()
|
||||
|
||||