Compare commits
1 Commits
hl/fix_azu
...
ofir-frd-p
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 661a4571f9 |
@ -1,4 +1,3 @@
|
||||
.venv/
|
||||
venv/
|
||||
pr_agent/settings/.secrets.toml
|
||||
pics/
|
||||
|
||||
6
.github/workflows/build-and-test.yaml
vendored
@ -14,15 +14,15 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- id: checkout
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
||||
|
||||
- id: dockerx
|
||||
name: Setup Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v2
|
||||
|
||||
- id: build
|
||||
name: Build dev docker
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v6
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
context: .
|
||||
file: ./docker/Dockerfile
|
||||
|
||||
9
.github/workflows/code_coverage.yaml
vendored
@ -15,15 +15,15 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- id: checkout
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
||||
|
||||
- id: dockerx
|
||||
name: Setup Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v2
|
||||
|
||||
- id: build
|
||||
name: Build dev docker
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v6
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
context: .
|
||||
file: ./docker/Dockerfile
|
||||
@ -41,6 +41,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
docker cp test_container:/app/coverage.xml coverage.xml
|
||||
docker rm test_container
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Validate coverage report
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
if [ ! -f coverage.xml ]; then
|
||||
@ -48,6 +49,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
exit 1
|
||||
fi
|
||||
- name: Upload coverage to Codecov
|
||||
uses: codecov/codecov-action@v5
|
||||
uses: codecov/codecov-action@v4.0.1
|
||||
with:
|
||||
token: ${{ secrets.CODECOV_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
7
.github/workflows/e2e_tests.yaml
vendored
@ -11,14 +11,14 @@ jobs:
|
||||
name: PR-Agent E2E GitHub App Test
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout repository
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Setup Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v2
|
||||
|
||||
- id: build
|
||||
name: Build dev docker
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v6
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
context: .
|
||||
file: ./docker/Dockerfile
|
||||
@ -39,6 +39,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
docker run -e gitlab.PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN=${{ secrets.TOKEN_GITLAB }} --rm codiumai/pr-agent:test pytest -v tests/e2e_tests/test_gitlab_webhook.py
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- id: test3
|
||||
name: E2E bitbucket app
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
|
||||
2
.github/workflows/pre-commit.yml
vendored
@ -11,7 +11,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
pre-commit:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
- uses: actions/setup-python@v5
|
||||
# SEE https://github.com/pre-commit/action
|
||||
- uses: pre-commit/action@v3.0.1
|
||||
|
||||
2
.gitignore
vendored
@ -2,7 +2,6 @@
|
||||
.lsp/
|
||||
.vscode/
|
||||
.env
|
||||
.venv/
|
||||
venv/
|
||||
pr_agent/settings/.secrets.toml
|
||||
__pycache__
|
||||
@ -12,4 +11,3 @@ build/
|
||||
.DS_Store
|
||||
docs/.cache/
|
||||
.qodo
|
||||
poetry.lock
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,7 +1,6 @@
|
||||
## 2023-08-03
|
||||
|
||||
### Optimized
|
||||
|
||||
- Optimized PR diff processing by introducing caching for diff files, reducing the number of API calls.
|
||||
- Refactored `load_large_diff` function to generate a patch only when necessary.
|
||||
- Fixed a bug in the GitLab provider where the new file was not retrieved correctly.
|
||||
@ -9,7 +8,6 @@
|
||||
## 2023-08-02
|
||||
|
||||
### Enhanced
|
||||
|
||||
- Updated several tools in the `pr_agent` package to use commit messages in their functionality.
|
||||
- Commit messages are now retrieved and stored in the `vars` dictionary for each tool.
|
||||
- Added a section to display the commit messages in the prompts of various tools.
|
||||
@ -17,7 +15,6 @@
|
||||
## 2023-08-01
|
||||
|
||||
### Enhanced
|
||||
|
||||
- Introduced the ability to retrieve commit messages from pull requests across different git providers.
|
||||
- Implemented commit messages retrieval for GitHub and GitLab providers.
|
||||
- Updated the PR description template to include a section for commit messages if they exist.
|
||||
@ -25,10 +22,10 @@
|
||||
- Implemented this feature for both GitHub and GitLab providers.
|
||||
- Added a new configuration option 'use_repo_settings_file' to enable or disable the use of a repo-specific settings file.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 2023-07-30
|
||||
|
||||
### Enhanced
|
||||
|
||||
- Added the ability to modify any configuration parameter from 'configuration.toml' on-the-fly.
|
||||
- Updated the command line interface and bot commands to accept configuration changes as arguments.
|
||||
- Improved the PR agent to handle additional arguments for each action.
|
||||
@ -36,7 +33,6 @@
|
||||
## 2023-07-28
|
||||
|
||||
### Improved
|
||||
|
||||
- Enhanced error handling and logging in the GitLab provider.
|
||||
- Improved handling of inline comments and code suggestions in GitLab.
|
||||
- Fixed a bug where an additional unneeded line was added to code suggestions in GitLab.
|
||||
@ -44,7 +40,6 @@
|
||||
## 2023-07-26
|
||||
|
||||
### Added
|
||||
|
||||
- New feature for updating the CHANGELOG.md based on the contents of a PR.
|
||||
- Added support for this feature for the Github provider.
|
||||
- New configuration settings and prompts for the changelog update feature.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -42,3 +42,4 @@ with regard to the reporter of an incident.
|
||||
This Code of Conduct is adapted from the
|
||||
[Contributor Covenant](https://contributor-covenant.org), version 1.3.0, available at
|
||||
[contributor-covenant.org/version/1/3/0/](https://contributor-covenant.org/version/1/3/0/)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,4 @@
|
||||
FROM python:3.12.10-slim AS base
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install --no-install-recommends -y git curl && apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
|
||||
FROM python:3.12 as base
|
||||
|
||||
WORKDIR /app
|
||||
ADD pyproject.toml .
|
||||
|
||||
845
LICENSE
@ -1,661 +1,202 @@
|
||||
GNU AFFERO GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE
|
||||
Version 3, 19 November 2007
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright (C) 2007 Free Software Foundation, Inc. <https://fsf.org/>
|
||||
Everyone is permitted to copy and distribute verbatim copies
|
||||
of this license document, but changing it is not allowed.
|
||||
|
||||
Preamble
|
||||
|
||||
The GNU Affero General Public License is a free, copyleft license for
|
||||
software and other kinds of works, specifically designed to ensure
|
||||
cooperation with the community in the case of network server software.
|
||||
|
||||
The licenses for most software and other practical works are designed
|
||||
to take away your freedom to share and change the works. By contrast,
|
||||
our General Public Licenses are intended to guarantee your freedom to
|
||||
share and change all versions of a program--to make sure it remains free
|
||||
software for all its users.
|
||||
|
||||
When we speak of free software, we are referring to freedom, not
|
||||
price. Our General Public Licenses are designed to make sure that you
|
||||
have the freedom to distribute copies of free software (and charge for
|
||||
them if you wish), that you receive source code or can get it if you
|
||||
want it, that you can change the software or use pieces of it in new
|
||||
free programs, and that you know you can do these things.
|
||||
|
||||
Developers that use our General Public Licenses protect your rights
|
||||
with two steps: (1) assert copyright on the software, and (2) offer
|
||||
you this License which gives you legal permission to copy, distribute
|
||||
and/or modify the software.
|
||||
|
||||
A secondary benefit of defending all users' freedom is that
|
||||
improvements made in alternate versions of the program, if they
|
||||
receive widespread use, become available for other developers to
|
||||
incorporate. Many developers of free software are heartened and
|
||||
encouraged by the resulting cooperation. However, in the case of
|
||||
software used on network servers, this result may fail to come about.
|
||||
The GNU General Public License permits making a modified version and
|
||||
letting the public access it on a server without ever releasing its
|
||||
source code to the public.
|
||||
|
||||
The GNU Affero General Public License is designed specifically to
|
||||
ensure that, in such cases, the modified source code becomes available
|
||||
to the community. It requires the operator of a network server to
|
||||
provide the source code of the modified version running there to the
|
||||
users of that server. Therefore, public use of a modified version, on
|
||||
a publicly accessible server, gives the public access to the source
|
||||
code of the modified version.
|
||||
|
||||
An older license, called the Affero General Public License and
|
||||
published by Affero, was designed to accomplish similar goals. This is
|
||||
a different license, not a version of the Affero GPL, but Affero has
|
||||
released a new version of the Affero GPL which permits relicensing under
|
||||
this license.
|
||||
|
||||
The precise terms and conditions for copying, distribution and
|
||||
modification follow.
|
||||
|
||||
TERMS AND CONDITIONS
|
||||
|
||||
0. Definitions.
|
||||
|
||||
"This License" refers to version 3 of the GNU Affero General Public License.
|
||||
|
||||
"Copyright" also means copyright-like laws that apply to other kinds of
|
||||
works, such as semiconductor masks.
|
||||
|
||||
"The Program" refers to any copyrightable work licensed under this
|
||||
License. Each licensee is addressed as "you". "Licensees" and
|
||||
"recipients" may be individuals or organizations.
|
||||
|
||||
To "modify" a work means to copy from or adapt all or part of the work
|
||||
in a fashion requiring copyright permission, other than the making of an
|
||||
exact copy. The resulting work is called a "modified version" of the
|
||||
earlier work or a work "based on" the earlier work.
|
||||
|
||||
A "covered work" means either the unmodified Program or a work based
|
||||
on the Program.
|
||||
|
||||
To "propagate" a work means to do anything with it that, without
|
||||
permission, would make you directly or secondarily liable for
|
||||
infringement under applicable copyright law, except executing it on a
|
||||
computer or modifying a private copy. Propagation includes copying,
|
||||
distribution (with or without modification), making available to the
|
||||
public, and in some countries other activities as well.
|
||||
|
||||
To "convey" a work means any kind of propagation that enables other
|
||||
parties to make or receive copies. Mere interaction with a user through
|
||||
a computer network, with no transfer of a copy, is not conveying.
|
||||
|
||||
An interactive user interface displays "Appropriate Legal Notices"
|
||||
to the extent that it includes a convenient and prominently visible
|
||||
feature that (1) displays an appropriate copyright notice, and (2)
|
||||
tells the user that there is no warranty for the work (except to the
|
||||
extent that warranties are provided), that licensees may convey the
|
||||
work under this License, and how to view a copy of this License. If
|
||||
the interface presents a list of user commands or options, such as a
|
||||
menu, a prominent item in the list meets this criterion.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Source Code.
|
||||
|
||||
The "source code" for a work means the preferred form of the work
|
||||
for making modifications to it. "Object code" means any non-source
|
||||
form of a work.
|
||||
|
||||
A "Standard Interface" means an interface that either is an official
|
||||
standard defined by a recognized standards body, or, in the case of
|
||||
interfaces specified for a particular programming language, one that
|
||||
is widely used among developers working in that language.
|
||||
|
||||
The "System Libraries" of an executable work include anything, other
|
||||
than the work as a whole, that (a) is included in the normal form of
|
||||
packaging a Major Component, but which is not part of that Major
|
||||
Component, and (b) serves only to enable use of the work with that
|
||||
Major Component, or to implement a Standard Interface for which an
|
||||
implementation is available to the public in source code form. A
|
||||
"Major Component", in this context, means a major essential component
|
||||
(kernel, window system, and so on) of the specific operating system
|
||||
(if any) on which the executable work runs, or a compiler used to
|
||||
produce the work, or an object code interpreter used to run it.
|
||||
|
||||
The "Corresponding Source" for a work in object code form means all
|
||||
the source code needed to generate, install, and (for an executable
|
||||
work) run the object code and to modify the work, including scripts to
|
||||
control those activities. However, it does not include the work's
|
||||
System Libraries, or general-purpose tools or generally available free
|
||||
programs which are used unmodified in performing those activities but
|
||||
which are not part of the work. For example, Corresponding Source
|
||||
includes interface definition files associated with source files for
|
||||
the work, and the source code for shared libraries and dynamically
|
||||
linked subprograms that the work is specifically designed to require,
|
||||
such as by intimate data communication or control flow between those
|
||||
subprograms and other parts of the work.
|
||||
|
||||
The Corresponding Source need not include anything that users
|
||||
can regenerate automatically from other parts of the Corresponding
|
||||
Source.
|
||||
|
||||
The Corresponding Source for a work in source code form is that
|
||||
same work.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Basic Permissions.
|
||||
|
||||
All rights granted under this License are granted for the term of
|
||||
copyright on the Program, and are irrevocable provided the stated
|
||||
conditions are met. This License explicitly affirms your unlimited
|
||||
permission to run the unmodified Program. The output from running a
|
||||
covered work is covered by this License only if the output, given its
|
||||
content, constitutes a covered work. This License acknowledges your
|
||||
rights of fair use or other equivalent, as provided by copyright law.
|
||||
|
||||
You may make, run and propagate covered works that you do not
|
||||
convey, without conditions so long as your license otherwise remains
|
||||
in force. You may convey covered works to others for the sole purpose
|
||||
of having them make modifications exclusively for you, or provide you
|
||||
with facilities for running those works, provided that you comply with
|
||||
the terms of this License in conveying all material for which you do
|
||||
not control copyright. Those thus making or running the covered works
|
||||
for you must do so exclusively on your behalf, under your direction
|
||||
and control, on terms that prohibit them from making any copies of
|
||||
your copyrighted material outside their relationship with you.
|
||||
|
||||
Conveying under any other circumstances is permitted solely under
|
||||
the conditions stated below. Sublicensing is not allowed; section 10
|
||||
makes it unnecessary.
|
||||
|
||||
3. Protecting Users' Legal Rights From Anti-Circumvention Law.
|
||||
|
||||
No covered work shall be deemed part of an effective technological
|
||||
measure under any applicable law fulfilling obligations under article
|
||||
11 of the WIPO copyright treaty adopted on 20 December 1996, or
|
||||
similar laws prohibiting or restricting circumvention of such
|
||||
measures.
|
||||
|
||||
When you convey a covered work, you waive any legal power to forbid
|
||||
circumvention of technological measures to the extent such circumvention
|
||||
is effected by exercising rights under this License with respect to
|
||||
the covered work, and you disclaim any intention to limit operation or
|
||||
modification of the work as a means of enforcing, against the work's
|
||||
users, your or third parties' legal rights to forbid circumvention of
|
||||
technological measures.
|
||||
|
||||
4. Conveying Verbatim Copies.
|
||||
|
||||
You may convey verbatim copies of the Program's source code as you
|
||||
receive it, in any medium, provided that you conspicuously and
|
||||
appropriately publish on each copy an appropriate copyright notice;
|
||||
keep intact all notices stating that this License and any
|
||||
non-permissive terms added in accord with section 7 apply to the code;
|
||||
keep intact all notices of the absence of any warranty; and give all
|
||||
recipients a copy of this License along with the Program.
|
||||
|
||||
You may charge any price or no price for each copy that you convey,
|
||||
and you may offer support or warranty protection for a fee.
|
||||
|
||||
5. Conveying Modified Source Versions.
|
||||
|
||||
You may convey a work based on the Program, or the modifications to
|
||||
produce it from the Program, in the form of source code under the
|
||||
terms of section 4, provided that you also meet all of these conditions:
|
||||
|
||||
a) The work must carry prominent notices stating that you modified
|
||||
it, and giving a relevant date.
|
||||
|
||||
b) The work must carry prominent notices stating that it is
|
||||
released under this License and any conditions added under section
|
||||
7. This requirement modifies the requirement in section 4 to
|
||||
"keep intact all notices".
|
||||
|
||||
c) You must license the entire work, as a whole, under this
|
||||
License to anyone who comes into possession of a copy. This
|
||||
License will therefore apply, along with any applicable section 7
|
||||
additional terms, to the whole of the work, and all its parts,
|
||||
regardless of how they are packaged. This License gives no
|
||||
permission to license the work in any other way, but it does not
|
||||
invalidate such permission if you have separately received it.
|
||||
|
||||
d) If the work has interactive user interfaces, each must display
|
||||
Appropriate Legal Notices; however, if the Program has interactive
|
||||
interfaces that do not display Appropriate Legal Notices, your
|
||||
work need not make them do so.
|
||||
|
||||
A compilation of a covered work with other separate and independent
|
||||
works, which are not by their nature extensions of the covered work,
|
||||
and which are not combined with it such as to form a larger program,
|
||||
in or on a volume of a storage or distribution medium, is called an
|
||||
"aggregate" if the compilation and its resulting copyright are not
|
||||
used to limit the access or legal rights of the compilation's users
|
||||
beyond what the individual works permit. Inclusion of a covered work
|
||||
in an aggregate does not cause this License to apply to the other
|
||||
parts of the aggregate.
|
||||
|
||||
6. Conveying Non-Source Forms.
|
||||
|
||||
You may convey a covered work in object code form under the terms
|
||||
of sections 4 and 5, provided that you also convey the
|
||||
machine-readable Corresponding Source under the terms of this License,
|
||||
in one of these ways:
|
||||
|
||||
a) Convey the object code in, or embodied in, a physical product
|
||||
(including a physical distribution medium), accompanied by the
|
||||
Corresponding Source fixed on a durable physical medium
|
||||
customarily used for software interchange.
|
||||
|
||||
b) Convey the object code in, or embodied in, a physical product
|
||||
(including a physical distribution medium), accompanied by a
|
||||
written offer, valid for at least three years and valid for as
|
||||
long as you offer spare parts or customer support for that product
|
||||
model, to give anyone who possesses the object code either (1) a
|
||||
copy of the Corresponding Source for all the software in the
|
||||
product that is covered by this License, on a durable physical
|
||||
medium customarily used for software interchange, for a price no
|
||||
more than your reasonable cost of physically performing this
|
||||
conveying of source, or (2) access to copy the
|
||||
Corresponding Source from a network server at no charge.
|
||||
|
||||
c) Convey individual copies of the object code with a copy of the
|
||||
written offer to provide the Corresponding Source. This
|
||||
alternative is allowed only occasionally and noncommercially, and
|
||||
only if you received the object code with such an offer, in accord
|
||||
with subsection 6b.
|
||||
|
||||
d) Convey the object code by offering access from a designated
|
||||
place (gratis or for a charge), and offer equivalent access to the
|
||||
Corresponding Source in the same way through the same place at no
|
||||
further charge. You need not require recipients to copy the
|
||||
Corresponding Source along with the object code. If the place to
|
||||
copy the object code is a network server, the Corresponding Source
|
||||
may be on a different server (operated by you or a third party)
|
||||
that supports equivalent copying facilities, provided you maintain
|
||||
clear directions next to the object code saying where to find the
|
||||
Corresponding Source. Regardless of what server hosts the
|
||||
Corresponding Source, you remain obligated to ensure that it is
|
||||
available for as long as needed to satisfy these requirements.
|
||||
|
||||
e) Convey the object code using peer-to-peer transmission, provided
|
||||
you inform other peers where the object code and Corresponding
|
||||
Source of the work are being offered to the general public at no
|
||||
charge under subsection 6d.
|
||||
|
||||
A separable portion of the object code, whose source code is excluded
|
||||
from the Corresponding Source as a System Library, need not be
|
||||
included in conveying the object code work.
|
||||
|
||||
A "User Product" is either (1) a "consumer product", which means any
|
||||
tangible personal property which is normally used for personal, family,
|
||||
or household purposes, or (2) anything designed or sold for incorporation
|
||||
into a dwelling. In determining whether a product is a consumer product,
|
||||
doubtful cases shall be resolved in favor of coverage. For a particular
|
||||
product received by a particular user, "normally used" refers to a
|
||||
typical or common use of that class of product, regardless of the status
|
||||
of the particular user or of the way in which the particular user
|
||||
actually uses, or expects or is expected to use, the product. A product
|
||||
is a consumer product regardless of whether the product has substantial
|
||||
commercial, industrial or non-consumer uses, unless such uses represent
|
||||
the only significant mode of use of the product.
|
||||
|
||||
"Installation Information" for a User Product means any methods,
|
||||
procedures, authorization keys, or other information required to install
|
||||
and execute modified versions of a covered work in that User Product from
|
||||
a modified version of its Corresponding Source. The information must
|
||||
suffice to ensure that the continued functioning of the modified object
|
||||
code is in no case prevented or interfered with solely because
|
||||
modification has been made.
|
||||
|
||||
If you convey an object code work under this section in, or with, or
|
||||
specifically for use in, a User Product, and the conveying occurs as
|
||||
part of a transaction in which the right of possession and use of the
|
||||
User Product is transferred to the recipient in perpetuity or for a
|
||||
fixed term (regardless of how the transaction is characterized), the
|
||||
Corresponding Source conveyed under this section must be accompanied
|
||||
by the Installation Information. But this requirement does not apply
|
||||
if neither you nor any third party retains the ability to install
|
||||
modified object code on the User Product (for example, the work has
|
||||
been installed in ROM).
|
||||
|
||||
The requirement to provide Installation Information does not include a
|
||||
requirement to continue to provide support service, warranty, or updates
|
||||
for a work that has been modified or installed by the recipient, or for
|
||||
the User Product in which it has been modified or installed. Access to a
|
||||
network may be denied when the modification itself materially and
|
||||
adversely affects the operation of the network or violates the rules and
|
||||
protocols for communication across the network.
|
||||
|
||||
Corresponding Source conveyed, and Installation Information provided,
|
||||
in accord with this section must be in a format that is publicly
|
||||
documented (and with an implementation available to the public in
|
||||
source code form), and must require no special password or key for
|
||||
unpacking, reading or copying.
|
||||
|
||||
7. Additional Terms.
|
||||
|
||||
"Additional permissions" are terms that supplement the terms of this
|
||||
License by making exceptions from one or more of its conditions.
|
||||
Additional permissions that are applicable to the entire Program shall
|
||||
be treated as though they were included in this License, to the extent
|
||||
that they are valid under applicable law. If additional permissions
|
||||
apply only to part of the Program, that part may be used separately
|
||||
under those permissions, but the entire Program remains governed by
|
||||
this License without regard to the additional permissions.
|
||||
|
||||
When you convey a copy of a covered work, you may at your option
|
||||
remove any additional permissions from that copy, or from any part of
|
||||
it. (Additional permissions may be written to require their own
|
||||
removal in certain cases when you modify the work.) You may place
|
||||
additional permissions on material, added by you to a covered work,
|
||||
for which you have or can give appropriate copyright permission.
|
||||
|
||||
Notwithstanding any other provision of this License, for material you
|
||||
add to a covered work, you may (if authorized by the copyright holders of
|
||||
that material) supplement the terms of this License with terms:
|
||||
|
||||
a) Disclaiming warranty or limiting liability differently from the
|
||||
terms of sections 15 and 16 of this License; or
|
||||
|
||||
b) Requiring preservation of specified reasonable legal notices or
|
||||
author attributions in that material or in the Appropriate Legal
|
||||
Notices displayed by works containing it; or
|
||||
|
||||
c) Prohibiting misrepresentation of the origin of that material, or
|
||||
requiring that modified versions of such material be marked in
|
||||
reasonable ways as different from the original version; or
|
||||
|
||||
d) Limiting the use for publicity purposes of names of licensors or
|
||||
authors of the material; or
|
||||
|
||||
e) Declining to grant rights under trademark law for use of some
|
||||
trade names, trademarks, or service marks; or
|
||||
|
||||
f) Requiring indemnification of licensors and authors of that
|
||||
material by anyone who conveys the material (or modified versions of
|
||||
it) with contractual assumptions of liability to the recipient, for
|
||||
any liability that these contractual assumptions directly impose on
|
||||
those licensors and authors.
|
||||
|
||||
All other non-permissive additional terms are considered "further
|
||||
restrictions" within the meaning of section 10. If the Program as you
|
||||
received it, or any part of it, contains a notice stating that it is
|
||||
governed by this License along with a term that is a further
|
||||
restriction, you may remove that term. If a license document contains
|
||||
a further restriction but permits relicensing or conveying under this
|
||||
License, you may add to a covered work material governed by the terms
|
||||
of that license document, provided that the further restriction does
|
||||
not survive such relicensing or conveying.
|
||||
|
||||
If you add terms to a covered work in accord with this section, you
|
||||
must place, in the relevant source files, a statement of the
|
||||
additional terms that apply to those files, or a notice indicating
|
||||
where to find the applicable terms.
|
||||
|
||||
Additional terms, permissive or non-permissive, may be stated in the
|
||||
form of a separately written license, or stated as exceptions;
|
||||
the above requirements apply either way.
|
||||
|
||||
8. Termination.
|
||||
|
||||
You may not propagate or modify a covered work except as expressly
|
||||
provided under this License. Any attempt otherwise to propagate or
|
||||
modify it is void, and will automatically terminate your rights under
|
||||
this License (including any patent licenses granted under the third
|
||||
paragraph of section 11).
|
||||
|
||||
However, if you cease all violation of this License, then your
|
||||
license from a particular copyright holder is reinstated (a)
|
||||
provisionally, unless and until the copyright holder explicitly and
|
||||
finally terminates your license, and (b) permanently, if the copyright
|
||||
holder fails to notify you of the violation by some reasonable means
|
||||
prior to 60 days after the cessation.
|
||||
|
||||
Moreover, your license from a particular copyright holder is
|
||||
reinstated permanently if the copyright holder notifies you of the
|
||||
violation by some reasonable means, this is the first time you have
|
||||
received notice of violation of this License (for any work) from that
|
||||
copyright holder, and you cure the violation prior to 30 days after
|
||||
your receipt of the notice.
|
||||
|
||||
Termination of your rights under this section does not terminate the
|
||||
licenses of parties who have received copies or rights from you under
|
||||
this License. If your rights have been terminated and not permanently
|
||||
reinstated, you do not qualify to receive new licenses for the same
|
||||
material under section 10.
|
||||
|
||||
9. Acceptance Not Required for Having Copies.
|
||||
|
||||
You are not required to accept this License in order to receive or
|
||||
run a copy of the Program. Ancillary propagation of a covered work
|
||||
occurring solely as a consequence of using peer-to-peer transmission
|
||||
to receive a copy likewise does not require acceptance. However,
|
||||
nothing other than this License grants you permission to propagate or
|
||||
modify any covered work. These actions infringe copyright if you do
|
||||
not accept this License. Therefore, by modifying or propagating a
|
||||
covered work, you indicate your acceptance of this License to do so.
|
||||
|
||||
10. Automatic Licensing of Downstream Recipients.
|
||||
|
||||
Each time you convey a covered work, the recipient automatically
|
||||
receives a license from the original licensors, to run, modify and
|
||||
propagate that work, subject to this License. You are not responsible
|
||||
for enforcing compliance by third parties with this License.
|
||||
|
||||
An "entity transaction" is a transaction transferring control of an
|
||||
organization, or substantially all assets of one, or subdividing an
|
||||
organization, or merging organizations. If propagation of a covered
|
||||
work results from an entity transaction, each party to that
|
||||
transaction who receives a copy of the work also receives whatever
|
||||
licenses to the work the party's predecessor in interest had or could
|
||||
give under the previous paragraph, plus a right to possession of the
|
||||
Corresponding Source of the work from the predecessor in interest, if
|
||||
the predecessor has it or can get it with reasonable efforts.
|
||||
|
||||
You may not impose any further restrictions on the exercise of the
|
||||
rights granted or affirmed under this License. For example, you may
|
||||
not impose a license fee, royalty, or other charge for exercise of
|
||||
rights granted under this License, and you may not initiate litigation
|
||||
(including a cross-claim or counterclaim in a lawsuit) alleging that
|
||||
any patent claim is infringed by making, using, selling, offering for
|
||||
sale, or importing the Program or any portion of it.
|
||||
|
||||
11. Patents.
|
||||
|
||||
A "contributor" is a copyright holder who authorizes use under this
|
||||
License of the Program or a work on which the Program is based. The
|
||||
work thus licensed is called the contributor's "contributor version".
|
||||
|
||||
A contributor's "essential patent claims" are all patent claims
|
||||
owned or controlled by the contributor, whether already acquired or
|
||||
hereafter acquired, that would be infringed by some manner, permitted
|
||||
by this License, of making, using, or selling its contributor version,
|
||||
but do not include claims that would be infringed only as a
|
||||
consequence of further modification of the contributor version. For
|
||||
purposes of this definition, "control" includes the right to grant
|
||||
patent sublicenses in a manner consistent with the requirements of
|
||||
this License.
|
||||
|
||||
Each contributor grants you a non-exclusive, worldwide, royalty-free
|
||||
patent license under the contributor's essential patent claims, to
|
||||
make, use, sell, offer for sale, import and otherwise run, modify and
|
||||
propagate the contents of its contributor version.
|
||||
|
||||
In the following three paragraphs, a "patent license" is any express
|
||||
agreement or commitment, however denominated, not to enforce a patent
|
||||
(such as an express permission to practice a patent or covenant not to
|
||||
sue for patent infringement). To "grant" such a patent license to a
|
||||
party means to make such an agreement or commitment not to enforce a
|
||||
patent against the party.
|
||||
|
||||
If you convey a covered work, knowingly relying on a patent license,
|
||||
and the Corresponding Source of the work is not available for anyone
|
||||
to copy, free of charge and under the terms of this License, through a
|
||||
publicly available network server or other readily accessible means,
|
||||
then you must either (1) cause the Corresponding Source to be so
|
||||
available, or (2) arrange to deprive yourself of the benefit of the
|
||||
patent license for this particular work, or (3) arrange, in a manner
|
||||
consistent with the requirements of this License, to extend the patent
|
||||
license to downstream recipients. "Knowingly relying" means you have
|
||||
actual knowledge that, but for the patent license, your conveying the
|
||||
covered work in a country, or your recipient's use of the covered work
|
||||
in a country, would infringe one or more identifiable patents in that
|
||||
country that you have reason to believe are valid.
|
||||
|
||||
If, pursuant to or in connection with a single transaction or
|
||||
arrangement, you convey, or propagate by procuring conveyance of, a
|
||||
covered work, and grant a patent license to some of the parties
|
||||
receiving the covered work authorizing them to use, propagate, modify
|
||||
or convey a specific copy of the covered work, then the patent license
|
||||
you grant is automatically extended to all recipients of the covered
|
||||
work and works based on it.
|
||||
|
||||
A patent license is "discriminatory" if it does not include within
|
||||
the scope of its coverage, prohibits the exercise of, or is
|
||||
conditioned on the non-exercise of one or more of the rights that are
|
||||
specifically granted under this License. You may not convey a covered
|
||||
work if you are a party to an arrangement with a third party that is
|
||||
in the business of distributing software, under which you make payment
|
||||
to the third party based on the extent of your activity of conveying
|
||||
the work, and under which the third party grants, to any of the
|
||||
parties who would receive the covered work from you, a discriminatory
|
||||
patent license (a) in connection with copies of the covered work
|
||||
conveyed by you (or copies made from those copies), or (b) primarily
|
||||
for and in connection with specific products or compilations that
|
||||
contain the covered work, unless you entered into that arrangement,
|
||||
or that patent license was granted, prior to 28 March 2007.
|
||||
|
||||
Nothing in this License shall be construed as excluding or limiting
|
||||
any implied license or other defenses to infringement that may
|
||||
otherwise be available to you under applicable patent law.
|
||||
|
||||
12. No Surrender of Others' Freedom.
|
||||
|
||||
If conditions are imposed on you (whether by court order, agreement or
|
||||
otherwise) that contradict the conditions of this License, they do not
|
||||
excuse you from the conditions of this License. If you cannot convey a
|
||||
covered work so as to satisfy simultaneously your obligations under this
|
||||
License and any other pertinent obligations, then as a consequence you may
|
||||
not convey it at all. For example, if you agree to terms that obligate you
|
||||
to collect a royalty for further conveying from those to whom you convey
|
||||
the Program, the only way you could satisfy both those terms and this
|
||||
License would be to refrain entirely from conveying the Program.
|
||||
|
||||
13. Remote Network Interaction; Use with the GNU General Public License.
|
||||
|
||||
Notwithstanding any other provision of this License, if you modify the
|
||||
Program, your modified version must prominently offer all users
|
||||
interacting with it remotely through a computer network (if your version
|
||||
supports such interaction) an opportunity to receive the Corresponding
|
||||
Source of your version by providing access to the Corresponding Source
|
||||
from a network server at no charge, through some standard or customary
|
||||
means of facilitating copying of software. This Corresponding Source
|
||||
shall include the Corresponding Source for any work covered by version 3
|
||||
of the GNU General Public License that is incorporated pursuant to the
|
||||
following paragraph.
|
||||
|
||||
Notwithstanding any other provision of this License, you have
|
||||
permission to link or combine any covered work with a work licensed
|
||||
under version 3 of the GNU General Public License into a single
|
||||
combined work, and to convey the resulting work. The terms of this
|
||||
License will continue to apply to the part which is the covered work,
|
||||
but the work with which it is combined will remain governed by version
|
||||
3 of the GNU General Public License.
|
||||
|
||||
14. Revised Versions of this License.
|
||||
|
||||
The Free Software Foundation may publish revised and/or new versions of
|
||||
the GNU Affero General Public License from time to time. Such new versions
|
||||
will be similar in spirit to the present version, but may differ in detail to
|
||||
address new problems or concerns.
|
||||
|
||||
Each version is given a distinguishing version number. If the
|
||||
Program specifies that a certain numbered version of the GNU Affero General
|
||||
Public License "or any later version" applies to it, you have the
|
||||
option of following the terms and conditions either of that numbered
|
||||
version or of any later version published by the Free Software
|
||||
Foundation. If the Program does not specify a version number of the
|
||||
GNU Affero General Public License, you may choose any version ever published
|
||||
by the Free Software Foundation.
|
||||
|
||||
If the Program specifies that a proxy can decide which future
|
||||
versions of the GNU Affero General Public License can be used, that proxy's
|
||||
public statement of acceptance of a version permanently authorizes you
|
||||
to choose that version for the Program.
|
||||
|
||||
Later license versions may give you additional or different
|
||||
permissions. However, no additional obligations are imposed on any
|
||||
author or copyright holder as a result of your choosing to follow a
|
||||
later version.
|
||||
|
||||
15. Disclaimer of Warranty.
|
||||
|
||||
THERE IS NO WARRANTY FOR THE PROGRAM, TO THE EXTENT PERMITTED BY
|
||||
APPLICABLE LAW. EXCEPT WHEN OTHERWISE STATED IN WRITING THE COPYRIGHT
|
||||
HOLDERS AND/OR OTHER PARTIES PROVIDE THE PROGRAM "AS IS" WITHOUT WARRANTY
|
||||
OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO,
|
||||
THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
|
||||
PURPOSE. THE ENTIRE RISK AS TO THE QUALITY AND PERFORMANCE OF THE PROGRAM
|
||||
IS WITH YOU. SHOULD THE PROGRAM PROVE DEFECTIVE, YOU ASSUME THE COST OF
|
||||
ALL NECESSARY SERVICING, REPAIR OR CORRECTION.
|
||||
|
||||
16. Limitation of Liability.
|
||||
|
||||
IN NO EVENT UNLESS REQUIRED BY APPLICABLE LAW OR AGREED TO IN WRITING
|
||||
WILL ANY COPYRIGHT HOLDER, OR ANY OTHER PARTY WHO MODIFIES AND/OR CONVEYS
|
||||
THE PROGRAM AS PERMITTED ABOVE, BE LIABLE TO YOU FOR DAMAGES, INCLUDING ANY
|
||||
GENERAL, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF THE
|
||||
USE OR INABILITY TO USE THE PROGRAM (INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO LOSS OF
|
||||
DATA OR DATA BEING RENDERED INACCURATE OR LOSSES SUSTAINED BY YOU OR THIRD
|
||||
PARTIES OR A FAILURE OF THE PROGRAM TO OPERATE WITH ANY OTHER PROGRAMS),
|
||||
EVEN IF SUCH HOLDER OR OTHER PARTY HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF
|
||||
SUCH DAMAGES.
|
||||
|
||||
17. Interpretation of Sections 15 and 16.
|
||||
|
||||
If the disclaimer of warranty and limitation of liability provided
|
||||
above cannot be given local legal effect according to their terms,
|
||||
reviewing courts shall apply local law that most closely approximates
|
||||
an absolute waiver of all civil liability in connection with the
|
||||
Program, unless a warranty or assumption of liability accompanies a
|
||||
copy of the Program in return for a fee.
|
||||
Apache License
|
||||
Version 2.0, January 2004
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/
|
||||
|
||||
TERMS AND CONDITIONS FOR USE, REPRODUCTION, AND DISTRIBUTION
|
||||
|
||||
1. Definitions.
|
||||
|
||||
"License" shall mean the terms and conditions for use, reproduction,
|
||||
and distribution as defined by Sections 1 through 9 of this document.
|
||||
|
||||
"Licensor" shall mean the copyright owner or entity authorized by
|
||||
the copyright owner that is granting the License.
|
||||
|
||||
"Legal Entity" shall mean the union of the acting entity and all
|
||||
other entities that control, are controlled by, or are under common
|
||||
control with that entity. For the purposes of this definition,
|
||||
"control" means (i) the power, direct or indirect, to cause the
|
||||
direction or management of such entity, whether by contract or
|
||||
otherwise, or (ii) ownership of fifty percent (50%) or more of the
|
||||
outstanding shares, or (iii) beneficial ownership of such entity.
|
||||
|
||||
"You" (or "Your") shall mean an individual or Legal Entity
|
||||
exercising permissions granted by this License.
|
||||
|
||||
"Source" form shall mean the preferred form for making modifications,
|
||||
including but not limited to software source code, documentation
|
||||
source, and configuration files.
|
||||
|
||||
"Object" form shall mean any form resulting from mechanical
|
||||
transformation or translation of a Source form, including but
|
||||
not limited to compiled object code, generated documentation,
|
||||
and conversions to other media types.
|
||||
|
||||
"Work" shall mean the work of authorship, whether in Source or
|
||||
Object form, made available under the License, as indicated by a
|
||||
copyright notice that is included in or attached to the work
|
||||
(an example is provided in the Appendix below).
|
||||
|
||||
"Derivative Works" shall mean any work, whether in Source or Object
|
||||
form, that is based on (or derived from) the Work and for which the
|
||||
editorial revisions, annotations, elaborations, or other modifications
|
||||
represent, as a whole, an original work of authorship. For the purposes
|
||||
of this License, Derivative Works shall not include works that remain
|
||||
separable from, or merely link (or bind by name) to the interfaces of,
|
||||
the Work and Derivative Works thereof.
|
||||
|
||||
"Contribution" shall mean any work of authorship, including
|
||||
the original version of the Work and any modifications or additions
|
||||
to that Work or Derivative Works thereof, that is intentionally
|
||||
submitted to Licensor for inclusion in the Work by the copyright owner
|
||||
or by an individual or Legal Entity authorized to submit on behalf of
|
||||
the copyright owner. For the purposes of this definition, "submitted"
|
||||
means any form of electronic, verbal, or written communication sent
|
||||
to the Licensor or its representatives, including but not limited to
|
||||
communication on electronic mailing lists, source code control systems,
|
||||
and issue tracking systems that are managed by, or on behalf of, the
|
||||
Licensor for the purpose of discussing and improving the Work, but
|
||||
excluding communication that is conspicuously marked or otherwise
|
||||
designated in writing by the copyright owner as "Not a Contribution."
|
||||
|
||||
"Contributor" shall mean Licensor and any individual or Legal Entity
|
||||
on behalf of whom a Contribution has been received by Licensor and
|
||||
subsequently incorporated within the Work.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Grant of Copyright License. Subject to the terms and conditions of
|
||||
this License, each Contributor hereby grants to You a perpetual,
|
||||
worldwide, non-exclusive, no-charge, royalty-free, irrevocable
|
||||
copyright license to reproduce, prepare Derivative Works of,
|
||||
publicly display, publicly perform, sublicense, and distribute the
|
||||
Work and such Derivative Works in Source or Object form.
|
||||
|
||||
3. Grant of Patent License. Subject to the terms and conditions of
|
||||
this License, each Contributor hereby grants to You a perpetual,
|
||||
worldwide, non-exclusive, no-charge, royalty-free, irrevocable
|
||||
(except as stated in this section) patent license to make, have made,
|
||||
use, offer to sell, sell, import, and otherwise transfer the Work,
|
||||
where such license applies only to those patent claims licensable
|
||||
by such Contributor that are necessarily infringed by their
|
||||
Contribution(s) alone or by combination of their Contribution(s)
|
||||
with the Work to which such Contribution(s) was submitted. If You
|
||||
institute patent litigation against any entity (including a
|
||||
cross-claim or counterclaim in a lawsuit) alleging that the Work
|
||||
or a Contribution incorporated within the Work constitutes direct
|
||||
or contributory patent infringement, then any patent licenses
|
||||
granted to You under this License for that Work shall terminate
|
||||
as of the date such litigation is filed.
|
||||
|
||||
4. Redistribution. You may reproduce and distribute copies of the
|
||||
Work or Derivative Works thereof in any medium, with or without
|
||||
modifications, and in Source or Object form, provided that You
|
||||
meet the following conditions:
|
||||
|
||||
(a) You must give any other recipients of the Work or
|
||||
Derivative Works a copy of this License; and
|
||||
|
||||
(b) You must cause any modified files to carry prominent notices
|
||||
stating that You changed the files; and
|
||||
|
||||
(c) You must retain, in the Source form of any Derivative Works
|
||||
that You distribute, all copyright, patent, trademark, and
|
||||
attribution notices from the Source form of the Work,
|
||||
excluding those notices that do not pertain to any part of
|
||||
the Derivative Works; and
|
||||
|
||||
(d) If the Work includes a "NOTICE" text file as part of its
|
||||
distribution, then any Derivative Works that You distribute must
|
||||
include a readable copy of the attribution notices contained
|
||||
within such NOTICE file, excluding those notices that do not
|
||||
pertain to any part of the Derivative Works, in at least one
|
||||
of the following places: within a NOTICE text file distributed
|
||||
as part of the Derivative Works; within the Source form or
|
||||
documentation, if provided along with the Derivative Works; or,
|
||||
within a display generated by the Derivative Works, if and
|
||||
wherever such third-party notices normally appear. The contents
|
||||
of the NOTICE file are for informational purposes only and
|
||||
do not modify the License. You may add Your own attribution
|
||||
notices within Derivative Works that You distribute, alongside
|
||||
or as an addendum to the NOTICE text from the Work, provided
|
||||
that such additional attribution notices cannot be construed
|
||||
as modifying the License.
|
||||
|
||||
You may add Your own copyright statement to Your modifications and
|
||||
may provide additional or different license terms and conditions
|
||||
for use, reproduction, or distribution of Your modifications, or
|
||||
for any such Derivative Works as a whole, provided Your use,
|
||||
reproduction, and distribution of the Work otherwise complies with
|
||||
the conditions stated in this License.
|
||||
|
||||
5. Submission of Contributions. Unless You explicitly state otherwise,
|
||||
any Contribution intentionally submitted for inclusion in the Work
|
||||
by You to the Licensor shall be under the terms and conditions of
|
||||
this License, without any additional terms or conditions.
|
||||
Notwithstanding the above, nothing herein shall supersede or modify
|
||||
the terms of any separate license agreement you may have executed
|
||||
with Licensor regarding such Contributions.
|
||||
|
||||
6. Trademarks. This License does not grant permission to use the trade
|
||||
names, trademarks, service marks, or product names of the Licensor,
|
||||
except as required for reasonable and customary use in describing the
|
||||
origin of the Work and reproducing the content of the NOTICE file.
|
||||
|
||||
7. Disclaimer of Warranty. Unless required by applicable law or
|
||||
agreed to in writing, Licensor provides the Work (and each
|
||||
Contributor provides its Contributions) on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or
|
||||
implied, including, without limitation, any warranties or conditions
|
||||
of TITLE, NON-INFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY, or FITNESS FOR A
|
||||
PARTICULAR PURPOSE. You are solely responsible for determining the
|
||||
appropriateness of using or redistributing the Work and assume any
|
||||
risks associated with Your exercise of permissions under this License.
|
||||
|
||||
8. Limitation of Liability. In no event and under no legal theory,
|
||||
whether in tort (including negligence), contract, or otherwise,
|
||||
unless required by applicable law (such as deliberate and grossly
|
||||
negligent acts) or agreed to in writing, shall any Contributor be
|
||||
liable to You for damages, including any direct, indirect, special,
|
||||
incidental, or consequential damages of any character arising as a
|
||||
result of this License or out of the use or inability to use the
|
||||
Work (including but not limited to damages for loss of goodwill,
|
||||
work stoppage, computer failure or malfunction, or any and all
|
||||
other commercial damages or losses), even if such Contributor
|
||||
has been advised of the possibility of such damages.
|
||||
|
||||
9. Accepting Warranty or Additional Liability. While redistributing
|
||||
the Work or Derivative Works thereof, You may choose to offer,
|
||||
and charge a fee for, acceptance of support, warranty, indemnity,
|
||||
or other liability obligations and/or rights consistent with this
|
||||
License. However, in accepting such obligations, You may act only
|
||||
on Your own behalf and on Your sole responsibility, not on behalf
|
||||
of any other Contributor, and only if You agree to indemnify,
|
||||
defend, and hold each Contributor harmless for any liability
|
||||
incurred by, or claims asserted against, such Contributor by reason
|
||||
of your accepting any such warranty or additional liability.
|
||||
|
||||
END OF TERMS AND CONDITIONS
|
||||
|
||||
How to Apply These Terms to Your New Programs
|
||||
APPENDIX: How to apply the Apache License to your work.
|
||||
|
||||
If you develop a new program, and you want it to be of the greatest
|
||||
possible use to the public, the best way to achieve this is to make it
|
||||
free software which everyone can redistribute and change under these terms.
|
||||
To apply the Apache License to your work, attach the following
|
||||
boilerplate notice, with the fields enclosed by brackets "[]"
|
||||
replaced with your own identifying information. (Don't include
|
||||
the brackets!) The text should be enclosed in the appropriate
|
||||
comment syntax for the file format. We also recommend that a
|
||||
file or class name and description of purpose be included on the
|
||||
same "printed page" as the copyright notice for easier
|
||||
identification within third-party archives.
|
||||
|
||||
To do so, attach the following notices to the program. It is safest
|
||||
to attach them to the start of each source file to most effectively
|
||||
state the exclusion of warranty; and each file should have at least
|
||||
the "copyright" line and a pointer to where the full notice is found.
|
||||
Copyright [2023] [Codium ltd]
|
||||
|
||||
<one line to give the program's name and a brief idea of what it does.>
|
||||
Copyright (C) <year> <name of author>
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
|
||||
it under the terms of the GNU Affero General Public License as published
|
||||
by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
|
||||
(at your option) any later version.
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
||||
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
||||
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
|
||||
GNU Affero General Public License for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
You should have received a copy of the GNU Affero General Public License
|
||||
along with this program. If not, see <https://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
|
||||
|
||||
Also add information on how to contact you by electronic and paper mail.
|
||||
|
||||
If your software can interact with users remotely through a computer
|
||||
network, you should also make sure that it provides a way for users to
|
||||
get its source. For example, if your program is a web application, its
|
||||
interface could display a "Source" link that leads users to an archive
|
||||
of the code. There are many ways you could offer source, and different
|
||||
solutions will be better for different programs; see section 13 for the
|
||||
specific requirements.
|
||||
|
||||
You should also get your employer (if you work as a programmer) or school,
|
||||
if any, to sign a "copyright disclaimer" for the program, if necessary.
|
||||
For more information on this, and how to apply and follow the GNU AGPL, see
|
||||
<https://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
177
README.md
@ -2,15 +2,16 @@
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<picture>
|
||||
<source media="(prefers-color-scheme: dark)" srcset="https://www.qodo.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/PR-Agent-Purple-2.png">
|
||||
<source media="(prefers-color-scheme: light)" srcset="https://www.qodo.ai/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/PR-Agent-Purple-2.png">
|
||||
<source media="(prefers-color-scheme: dark)" srcset="https://codium.ai/images/pr_agent/logo-dark.png" width="330">
|
||||
<source media="(prefers-color-scheme: light)" srcset="https://codium.ai/images/pr_agent/logo-light.png" width="330">
|
||||
<img src="https://codium.ai/images/pr_agent/logo-light.png" alt="logo" width="330">
|
||||
|
||||
</picture>
|
||||
<br/>
|
||||
|
||||
[Installation Guide](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/) |
|
||||
[Installation Guide](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/) |
|
||||
[Usage Guide](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/) |
|
||||
[Tools Guide](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/) |
|
||||
[Qodo Merge](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/overview/pr_agent_pro/) 💎
|
||||
@ -21,12 +22,24 @@ PR-Agent aims to help efficiently review and handle pull requests, by providing
|
||||
[](https://chromewebstore.google.com/detail/qodo-merge-ai-powered-cod/ephlnjeghhogofkifjloamocljapahnl)
|
||||
[](https://github.com/apps/qodo-merge-pro/)
|
||||
[](https://github.com/apps/qodo-merge-pro-for-open-source/)
|
||||
[](https://discord.com/invite/SgSxuQ65GF)
|
||||
[](https://discord.com/channels/1057273017547378788/1126104260430528613)
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/commits/main">
|
||||
<img alt="GitHub" src="https://img.shields.io/github/last-commit/Codium-ai/pr-agent/main?style=for-the-badge" height="20">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (### [Documentation](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/))
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ()
|
||||
[//]: # (- See the [Installation Guide](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/) for instructions on installing PR-Agent on different platforms.)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ()
|
||||
[//]: # (- See the [Usage Guide](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/) for instructions on running PR-Agent tools via different interfaces, such as CLI, PR Comments, or by automatically triggering them when a new PR is opened.)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ()
|
||||
[//]: # (- See the [Tools Guide](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/) for a detailed description of the different tools, and the available configurations for each tool.)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Table of Contents
|
||||
|
||||
- [News and Updates](#news-and-updates)
|
||||
@ -36,82 +49,85 @@ PR-Agent aims to help efficiently review and handle pull requests, by providing
|
||||
- [Qodo Merge](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/overview/pr_agent_pro/)
|
||||
- [How it works](#how-it-works)
|
||||
- [Why use PR-Agent?](#why-use-pr-agent)
|
||||
- [Data privacy](#data-privacy)
|
||||
- [Contributing](#contributing)
|
||||
- [Links](#links)
|
||||
|
||||
## News and Updates
|
||||
|
||||
## May 17, 2025
|
||||
### Feb 6, 2025
|
||||
New design for the `/improve` tool:
|
||||
|
||||
- v0.29 was [released](https://github.com/qodo-ai/pr-agent/releases)
|
||||
- `Qodo Merge Pull Request Benchmark` was [released](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/pr_benchmark/). This benchmark evaluates and compares the performance of LLMs in analyzing pull request code.
|
||||
- `Recent Updates and Future Roadmap` page was added to the [Qodo Merge Docs](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/recent_updates/)
|
||||
<kbd><img src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/26506430-550e-469a-adaa-af0a09b70c6d" width="512"></kbd>
|
||||
|
||||
## Apr 30, 2025
|
||||
### Jan 25, 2025
|
||||
|
||||
A new feature is now available in the `/improve` tool for Qodo Merge 💎 - Chat on code suggestions.
|
||||
The open-source GitHub organization was updated:
|
||||
`https://github.com/codium-ai/pr-agent` →
|
||||
`https://github.com/qodo-ai/pr-agent`
|
||||
|
||||
<img width="512" alt="image" src="https://codium.ai/images/pr_agent/improve_chat_on_code_suggestions_ask.png" />
|
||||
The docker should be redirected automatically to the new location.
|
||||
However, if you have any issues, please update the GitHub action docker image from
|
||||
`uses: Codium-ai/pr-agent@main`
|
||||
to
|
||||
`uses: qodo-ai/pr-agent@main`
|
||||
|
||||
Read more about it [here](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#chat-on-code-suggestions).
|
||||
|
||||
## Apr 16, 2025
|
||||
### Jan 2, 2025
|
||||
|
||||
New tool for Qodo Merge 💎 - `/scan_repo_discussions`.
|
||||
New tool [/Implement](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/implement/) (💎), which converts human code review discussions and feedback into ready-to-commit code changes.
|
||||
|
||||
<img width="635" alt="image" src="https://codium.ai/images/pr_agent/scan_repo_discussions_2.png" />
|
||||
<kbd><img src="https://www.qodo.ai/images/pr_agent/implement1.png" width="512"></kbd>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Jan 1, 2025
|
||||
|
||||
Update logic and [documentation](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/changing_a_model/#ollama) for running local models via Ollama.
|
||||
|
||||
### December 30, 2024
|
||||
|
||||
Following feedback from the community, we have addressed two vulnerabilities identified in the open-source PR-Agent project. The [fixes](https://github.com/qodo-ai/pr-agent/pull/1425) are now included in the newly released version (v0.26), available as of today.
|
||||
|
||||
Read more about it [here](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/scan_repo_discussions/).
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="text-align:left;">
|
||||
|
||||
Supported commands per platform:
|
||||
|
||||
| | | GitHub | GitLab | Bitbucket | Azure DevOps | Gitea |
|
||||
| ----- |---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|:------:|:------:|:---------:|:------------:|:-----:|
|
||||
| TOOLS | [Review](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/review/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Describe](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/describe/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Improve](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Ask](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/ask/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | ⮑ [Ask on code lines](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/ask/#ask-lines) | ✅ | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | [Update CHANGELOG](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/update_changelog/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | [Help Docs](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/help_docs/?h=auto#auto-approval) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Ticket Context](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/fetching_ticket_context/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Utilizing Best Practices](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#best-practices) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [PR Chat](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/chrome-extension/features/#pr-chat) 💎 | ✅ | | | | |
|
||||
| | [Suggestion Tracking](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#suggestion-tracking) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | [CI Feedback](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/ci_feedback/) 💎 | ✅ | | | | |
|
||||
| | [PR Documentation](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/documentation/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | [Custom Labels](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/custom_labels/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | [Analyze](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/analyze/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | [Similar Code](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/similar_code/) 💎 | ✅ | | | | |
|
||||
| | [Custom Prompt](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/custom_prompt/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Test](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/test/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | [Implement](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/implement/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Scan Repo Discussions](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/scan_repo_discussions/) 💎 | ✅ | | | | |
|
||||
| | [Auto-Approve](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/?h=auto#auto-approval) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | | | | | | |
|
||||
| USAGE | [CLI](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/automations_and_usage/#local-repo-cli) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [App / webhook](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/automations_and_usage/#github-app) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Tagging bot](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent#try-it-now) | ✅ | | | | |
|
||||
| | [Actions](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/github/#run-as-a-github-action) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | | | | | | |
|
||||
| CORE | [PR compression](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/compression_strategy/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | Adaptive and token-aware file patch fitting | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | [Multiple models support](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/changing_a_model/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | [Local and global metadata](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/metadata/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | [Dynamic context](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/dynamic_context/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | [Self reflection](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/self_reflection/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | [Static code analysis](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/static_code_analysis/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | [Global and wiki configurations](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [PR interactive actions](https://www.qodo.ai/images/pr_agent/pr-actions.mp4) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | [Impact Evaluation](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/impact_evaluation/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | [Code Validation 💎](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/code_validation/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | [Auto Best Practices 💎](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/auto_best_practices/) | ✅ | | | | |
|
||||
- 💎 means this feature is available only in [Qodo Merge](https://www.qodo.ai/pricing/)
|
||||
| | | GitHub | GitLab | Bitbucket | Azure DevOps |
|
||||
|-------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|:--------------------:|:--------------------:|:--------------------:|:------------:|
|
||||
| TOOLS | [Review](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/review/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Describe](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/describe/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Improve](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Ask](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/ask/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | ⮑ [Ask on code lines](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/ask/#ask-lines) | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Update CHANGELOG](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/update_changelog/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Ticket Context](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/fetching_ticket_context/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | [Utilizing Best Practices](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#best-practices) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | [PR Chat](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/chrome-extension/features/#pr-chat) 💎 | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | [Suggestion Tracking](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#suggestion-tracking) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [CI Feedback](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/ci_feedback/) 💎 | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | [PR Documentation](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/documentation/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Custom Labels](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/custom_labels/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Analyze](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/analyze/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Similar Code](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/similar_code/) 💎 | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | [Custom Prompt](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/custom_prompt/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | [Test](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/test/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Implement](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/implement/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | | | | | |
|
||||
| USAGE | [CLI](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/automations_and_usage/#local-repo-cli) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [App / webhook](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/automations_and_usage/#github-app) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Tagging bot](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent#try-it-now) | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | [Actions](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/github/#run-as-a-github-action) | ✅ |✅| ✅ |✅|
|
||||
| | | | | | |
|
||||
| CORE | [PR compression](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/compression_strategy/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | Adaptive and token-aware file patch fitting | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Multiple models support](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/changing_a_model/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Local and global metadata](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/metadata/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Dynamic context](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/dynamic_context/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Self reflection](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/self_reflection/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Static code analysis](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/static_code_analysis/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | [Global and wiki configurations](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | [PR interactive actions](https://www.qodo.ai/images/pr_agent/pr-actions.mp4) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Impact Evaluation](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/impact_evaluation/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
- 💎 means this feature is available only in [Qodo-Merge](https://www.qodo.ai/pricing/)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (- Support for additional git providers is described in [here](./docs/Full_environments.md))
|
||||
___
|
||||
@ -126,7 +142,7 @@ ___
|
||||
\
|
||||
‣ **Update Changelog ([`/update_changelog`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/update_changelog/))**: Automatically updating the CHANGELOG.md file with the PR changes.
|
||||
\
|
||||
‣ **Help Docs ([`/help_docs`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/help_docs/))**: Answers a question on any repository by utilizing given documentation.
|
||||
‣ **Find Similar Issue ([`/similar_issue`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/similar_issues/))**: Automatically retrieves and presents similar issues.
|
||||
\
|
||||
‣ **Add Documentation 💎 ([`/add_docs`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/documentation/))**: Generates documentation to methods/functions/classes that changed in the PR.
|
||||
\
|
||||
@ -148,7 +164,6 @@ ___
|
||||
___
|
||||
|
||||
## Example results
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<h4><a href="https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/530">/describe</a></h4>
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
@ -177,37 +192,46 @@ ___
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="left">
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<hr>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Try it now
|
||||
|
||||
Try the Claude Sonnet powered PR-Agent instantly on _your public GitHub repository_. Just mention `@CodiumAI-Agent` and add the desired command in any PR comment. The agent will generate a response based on your command.
|
||||
Try the GPT-4 powered PR-Agent instantly on _your public GitHub repository_. Just mention `@CodiumAI-Agent` and add the desired command in any PR comment. The agent will generate a response based on your command.
|
||||
For example, add a comment to any pull request with the following text:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
@CodiumAI-Agent /review
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and the agent will respond with a review of your PR.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that this is a promotional bot, suitable only for initial experimentation.
|
||||
It does not have 'edit' access to your repo, for example, so it cannot update the PR description or add labels (`@CodiumAI-Agent /describe` will publish PR description as a comment). In addition, the bot cannot be used on private repositories, as it does not have access to the files there.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
To set up your own PR-Agent, see the [Installation](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/) section below.
|
||||
Note that when you set your own PR-Agent or use Qodo hosted PR-Agent, there is no need to mention `@CodiumAI-Agent ...`. Instead, directly start with the command, e.g., `/ask ...`.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Qodo Merge 💎
|
||||
|
||||
[Qodo Merge](https://www.qodo.ai/pricing/) is a hosted version of PR-Agent, provided by Qodo. It is available for a monthly fee, and provides the following benefits:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Fully managed** - We take care of everything for you - hosting, models, regular updates, and more. Installation is as simple as signing up and adding the Qodo Merge app to your GitHub/GitLab/BitBucket repo.
|
||||
1. **Fully managed** - We take care of everything for you - hosting, models, regular updates, and more. Installation is as simple as signing up and adding the Qodo Merge app to your GitHub\GitLab\BitBucket repo.
|
||||
2. **Improved privacy** - No data will be stored or used to train models. Qodo Merge will employ zero data retention, and will use an OpenAI account with zero data retention.
|
||||
3. **Improved support** - Qodo Merge users will receive priority support, and will be able to request new features and capabilities.
|
||||
4. **Extra features** - In addition to the benefits listed above, Qodo Merge will emphasize more customization, and the usage of static code analysis, in addition to LLM logic, to improve results.
|
||||
4. **Extra features** -In addition to the benefits listed above, Qodo Merge will emphasize more customization, and the usage of static code analysis, in addition to LLM logic, to improve results.
|
||||
See [here](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/overview/pr_agent_pro/) for a list of features available in Qodo Merge.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## How it works
|
||||
|
||||
The following diagram illustrates PR-Agent tools and their flow:
|
||||
@ -222,10 +246,11 @@ A reasonable question that can be asked is: `"Why use PR-Agent? What makes it st
|
||||
|
||||
Here are some advantages of PR-Agent:
|
||||
|
||||
- We emphasize **real-life practical usage**. Each tool (review, improve, ask, ...) has a single LLM call, no more. We feel that this is critical for realistic team usage - obtaining an answer quickly (~30 seconds) and affordably.
|
||||
- We emphasize **real-life practical usage**. Each tool (review, improve, ask, ...) has a single GPT-4 call, no more. We feel that this is critical for realistic team usage - obtaining an answer quickly (~30 seconds) and affordably.
|
||||
- Our [PR Compression strategy](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/#pr-compression-strategy) is a core ability that enables to effectively tackle both short and long PRs.
|
||||
- Our JSON prompting strategy enables to have **modular, customizable tools**. For example, the '/review' tool categories can be controlled via the [configuration](pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml) file. Adding additional categories is easy and accessible.
|
||||
- We support **multiple git providers** (GitHub, GitLab, BitBucket), **multiple ways** to use the tool (CLI, GitHub Action, GitHub App, Docker, ...), and **multiple models** (GPT, Claude, Deepseek, ...)
|
||||
- We support **multiple git providers** (GitHub, Gitlab, Bitbucket), **multiple ways** to use the tool (CLI, GitHub Action, GitHub App, Docker, ...), and **multiple models** (GPT-4, GPT-3.5, Anthropic, Cohere, Llama2).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Data privacy
|
||||
|
||||
@ -246,12 +271,10 @@ https://openai.com/enterprise-privacy
|
||||
|
||||
- The [Qodo Merge Chrome extension](https://chromewebstore.google.com/detail/qodo-merge-ai-powered-cod/ephlnjeghhogofkifjloamocljapahnl) serves solely to modify the visual appearance of a GitHub PR screen. It does not transmit any user's repo or pull request code. Code is only sent for processing when a user submits a GitHub comment that activates a PR-Agent tool, in accordance with the standard privacy policy of Qodo-Merge.
|
||||
|
||||
## Contributing
|
||||
|
||||
To contribute to the project, get started by reading our [Contributing Guide](https://github.com/qodo-ai/pr-agent/blob/b09eec265ef7d36c232063f76553efb6b53979ff/CONTRIBUTING.md).
|
||||
|
||||
## Links
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://discord.gg/kG35uSHDBc)
|
||||
|
||||
- Discord community: https://discord.gg/kG35uSHDBc
|
||||
- Qodo site: https://www.qodo.ai/
|
||||
- Blog: https://www.qodo.ai/blog/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,4 @@
|
||||
## [Version 0.11] - 2023-12-07
|
||||
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.11
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.11-github_app
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.11-bitbucket-app
|
||||
@ -8,18 +7,16 @@
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.11-github_action
|
||||
|
||||
### Added::Algo
|
||||
|
||||
- New section in `/describe` tool - [PR changes walkthrough](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/509)
|
||||
- Improving PR Agent [prompts](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/501)
|
||||
- Persistent tools (`/review`, `/describe`) now send an [update message](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/499) after finishing
|
||||
- Add Amazon Bedrock [support](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/483)
|
||||
|
||||
### Fixed
|
||||
|
||||
- Update [dependencies](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/503) in requirements.txt for Python 3.12
|
||||
|
||||
## [Version 0.10] - 2023-11-15
|
||||
|
||||
## [Version 0.10] - 2023-11-15
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.10
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.10-github_app
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.10-bitbucket-app
|
||||
@ -28,7 +25,6 @@
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.10-github_action
|
||||
|
||||
### Added::Algo
|
||||
|
||||
- Review tool now works with [persistent comments](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/451) by default
|
||||
- Bitbucket now publishes review suggestions with [code links](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/428)
|
||||
- Enabling to limit [max number of tokens](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/437/files)
|
||||
@ -38,13 +34,11 @@
|
||||
- Decoupled custom labels from [PR type](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/431)
|
||||
|
||||
### Fixed
|
||||
|
||||
- Fixed bug in [parsing quotes](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/446) in CLI
|
||||
- Preserve [user-added labels](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/433) in pull requests
|
||||
- Bug fixes in GitLab and BitBucket
|
||||
|
||||
## [Version 0.9] - 2023-10-29
|
||||
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.9
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.9-github_app
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.9-bitbucket-app
|
||||
@ -53,7 +47,6 @@
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.9-github_action
|
||||
|
||||
### Added::Algo
|
||||
|
||||
- New tool - [generate_labels](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/docs/GENERATE_CUSTOM_LABELS.md)
|
||||
- New ability to use [customize labels](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/docs/GENERATE_CUSTOM_LABELS.md#how-to-enable-custom-labels) on the `review` and `describe` tools.
|
||||
- New tool - [add_docs](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/docs/ADD_DOCUMENTATION.md)
|
||||
@ -63,17 +56,14 @@
|
||||
- PR Description default mode is now in [bullet points](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml#L35).
|
||||
|
||||
### Added::Documentation
|
||||
|
||||
Significant documentation updates (see [Installation Guide](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/INSTALL.md), [Usage Guide](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/Usage.md), and [Tools Guide](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/docs/TOOLS_GUIDE.md))
|
||||
|
||||
### Fixed
|
||||
|
||||
- Fixed support for BitBucket pipeline (see [link](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/386))
|
||||
- Fixed a bug in `review -i` tool
|
||||
- Added blacklist for specific file extensions in `add_docs` tool (see [link](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/385/))
|
||||
|
||||
## [Version 0.8] - 2023-09-27
|
||||
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.8
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.8-github_app
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.8-bitbucket-app
|
||||
@ -82,18 +72,16 @@ Significant documentation updates (see [Installation Guide](https://github.com/C
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.8-github_action
|
||||
|
||||
### Added::Algo
|
||||
|
||||
- GitHub Action: Can control which tools will run automatically when a new PR is created. (see usage guide: https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/Usage.md#working-with-github-action)
|
||||
- Code suggestion tool: Will try to avoid an 'add comments' suggestion (see https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/327)
|
||||
|
||||
### Fixed
|
||||
|
||||
- Gitlab: Fixed a bug of improper usage of pr_id
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## [Version 0.7] - 2023-09-20
|
||||
|
||||
### Docker Tags
|
||||
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.7
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.7-github_app
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.7-bitbucket-app
|
||||
@ -102,17 +90,14 @@ Significant documentation updates (see [Installation Guide](https://github.com/C
|
||||
- codiumai/pr-agent:0.7-github_action
|
||||
|
||||
### Added::Algo
|
||||
|
||||
- New tool /similar_issue - Currently on GitHub app and CLI: indexes the issues in the repo, find the most similar issues to the target issue.
|
||||
- Describe markers: Empower the /describe tool with a templating capability (see more details in https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/273).
|
||||
- New feature in the /review tool - added an estimated effort estimation to the review (https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/306).
|
||||
|
||||
### Added::Infrastructure
|
||||
|
||||
- Implementation of a GitLab webhook.
|
||||
- Implementation of a BitBucket app.
|
||||
|
||||
### Fixed
|
||||
|
||||
- Protection against no code suggestions generated.
|
||||
- Resilience to repositories where the languages cannot be automatically detected.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -9,13 +9,13 @@ This document describes the security policy of PR-Agent. For Qodo Merge's securi
|
||||
When using PR-Agent with your OpenAI (or other LLM provider) API key, the security relationship is directly between you and the provider. We do not send your code to Qodo servers.
|
||||
|
||||
Types of [self-hosted solutions](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation):
|
||||
|
||||
- Locally
|
||||
- GitHub integration
|
||||
- GitLab integration
|
||||
- BitBucket integration
|
||||
- Azure DevOps integration
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## PR-Agent Supported Versions
|
||||
|
||||
This section outlines which versions of PR-Agent are currently supported with security updates.
|
||||
@ -25,7 +25,6 @@ This section outlines which versions of PR-Agent are currently supported with se
|
||||
#### Latest Version
|
||||
|
||||
For the most recent updates, use our latest Docker image which is automatically built nightly:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
uses: qodo-ai/pr-agent@main
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -47,7 +46,6 @@ steps:
|
||||
#### Enhanced Security with Docker Digest
|
||||
|
||||
For maximum security, you can specify the Docker image using its digest:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: PR Agent action step
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,4 @@
|
||||
FROM python:3.12.10-slim AS base
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt update && apt install --no-install-recommends -y git curl && apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
|
||||
FROM python:3.12.3 AS base
|
||||
|
||||
WORKDIR /app
|
||||
ADD pyproject.toml .
|
||||
@ -33,11 +31,6 @@ FROM base AS azure_devops_webhook
|
||||
ADD pr_agent pr_agent
|
||||
CMD ["python", "pr_agent/servers/azuredevops_server_webhook.py"]
|
||||
|
||||
FROM base AS gitea_app
|
||||
ADD pr_agent pr_agent
|
||||
CMD ["python", "-m", "gunicorn", "-k", "uvicorn.workers.UvicornWorker", "-c", "pr_agent/servers/gunicorn_config.py","pr_agent.servers.gitea_app:app"]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
FROM base AS test
|
||||
ADD requirements-dev.txt .
|
||||
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir -r requirements-dev.txt && rm requirements-dev.txt
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
|
||||
FROM public.ecr.aws/lambda/python:3.12
|
||||
FROM public.ecr.aws/lambda/python:3.10
|
||||
|
||||
RUN dnf update -y && \
|
||||
dnf install -y gcc python3-devel git && \
|
||||
dnf clean all
|
||||
RUN yum update -y && \
|
||||
yum install -y gcc python3-devel git && \
|
||||
yum clean all
|
||||
|
||||
ADD pyproject.toml requirements.txt ./
|
||||
ADD pyproject.toml requirements.txt .
|
||||
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir . && rm pyproject.toml
|
||||
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir mangum==0.17.0
|
||||
COPY pr_agent/ ${LAMBDA_TASK_ROOT}/pr_agent/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,315 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<div class="search-section">
|
||||
<h1>AI Docs Search</h1>
|
||||
<p class="search-description">
|
||||
Search through our documentation using AI-powered natural language queries.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
<div class="search-container">
|
||||
<input
|
||||
type="text"
|
||||
id="searchInput"
|
||||
class="search-input"
|
||||
placeholder="Enter your search term..."
|
||||
>
|
||||
<button id="searchButton" class="search-button">Search</button>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div id="spinner" class="spinner-container" style="display: none;">
|
||||
<div class="spinner"></div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div id="results" class="results-container"></div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<style>
|
||||
Untitled
|
||||
.search-section {
|
||||
max-width: 800px;
|
||||
margin: 0 auto;
|
||||
padding: 0 1rem 2rem;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
h1 {
|
||||
color: #666;
|
||||
font-size: 2.125rem;
|
||||
font-weight: normal;
|
||||
margin-bottom: 1rem;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.search-description {
|
||||
color: #666;
|
||||
font-size: 1rem;
|
||||
line-height: 1.5;
|
||||
margin-bottom: 2rem;
|
||||
max-width: 800px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.search-container {
|
||||
display: flex;
|
||||
gap: 1rem;
|
||||
max-width: 800px;
|
||||
margin: 0; /* Changed from auto to 0 to align left */
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.search-input {
|
||||
flex: 1;
|
||||
padding: 0 0.875rem;
|
||||
border: 1px solid #ddd;
|
||||
border-radius: 4px;
|
||||
font-size: 0.9375rem;
|
||||
outline: none;
|
||||
height: 40px; /* Explicit height */
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.search-input:focus {
|
||||
border-color: #6c63ff;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.search-button {
|
||||
padding: 0 1.25rem;
|
||||
background-color: #2196F3;
|
||||
color: white;
|
||||
border: none;
|
||||
border-radius: 4px;
|
||||
cursor: pointer;
|
||||
font-size: 0.875rem;
|
||||
transition: background-color 0.2s;
|
||||
height: 40px; /* Match the height of search input */
|
||||
display: flex;
|
||||
align-items: center;
|
||||
justify-content: center;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.search-button:hover {
|
||||
background-color: #1976D2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.spinner-container {
|
||||
display: flex;
|
||||
justify-content: center;
|
||||
margin-top: 2rem;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.spinner {
|
||||
width: 40px;
|
||||
height: 40px;
|
||||
border: 4px solid #f3f3f3;
|
||||
border-top: 4px solid #2196F3;
|
||||
border-radius: 50%;
|
||||
animation: spin 1s linear infinite;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@keyframes spin {
|
||||
0% { transform: rotate(0deg); }
|
||||
100% { transform: rotate(360deg); }
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.results-container {
|
||||
margin-top: 2rem;
|
||||
max-width: 800px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.result-item {
|
||||
padding: 1rem;
|
||||
border: 1px solid #ddd;
|
||||
border-radius: 4px;
|
||||
margin-bottom: 1rem;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.result-title {
|
||||
font-size: 1.2rem;
|
||||
color: #2196F3;
|
||||
margin-bottom: 0.5rem;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.result-description {
|
||||
color: #666;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.error-message {
|
||||
color: #dc3545;
|
||||
padding: 1rem;
|
||||
border: 1px solid #dc3545;
|
||||
border-radius: 4px;
|
||||
margin-top: 1rem;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.markdown-content {
|
||||
line-height: 1.6;
|
||||
color: var(--md-typeset-color);
|
||||
background: var(--md-default-bg-color);
|
||||
border: 1px solid var(--md-default-fg-color--lightest);
|
||||
border-radius: 12px;
|
||||
padding: 1.5rem;
|
||||
box-shadow: 0 2px 4px rgba(0,0,0,0.05);
|
||||
position: relative;
|
||||
margin-top: 2rem;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.markdown-content::before {
|
||||
content: '';
|
||||
position: absolute;
|
||||
top: -8px;
|
||||
left: 24px;
|
||||
width: 16px;
|
||||
height: 16px;
|
||||
background: var(--md-default-bg-color);
|
||||
border-left: 1px solid var(--md-default-fg-color--lightest);
|
||||
border-top: 1px solid var(--md-default-fg-color--lightest);
|
||||
transform: rotate(45deg);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.markdown-content > *:first-child {
|
||||
margin-top: 0;
|
||||
padding-top: 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.markdown-content p {
|
||||
margin-bottom: 1rem;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.markdown-content p:last-child {
|
||||
margin-bottom: 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.markdown-content code {
|
||||
background: var(--md-code-bg-color);
|
||||
color: var(--md-code-fg-color);
|
||||
padding: 0.2em 0.4em;
|
||||
border-radius: 3px;
|
||||
font-size: 0.9em;
|
||||
font-family: ui-monospace, SFMono-Regular, SF Mono, Menlo, Consolas, Liberation Mono, monospace;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.markdown-content pre {
|
||||
background: var(--md-code-bg-color);
|
||||
padding: 1rem;
|
||||
border-radius: 6px;
|
||||
overflow-x: auto;
|
||||
margin: 1rem 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.markdown-content pre code {
|
||||
background: none;
|
||||
padding: 0;
|
||||
font-size: 0.9em;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
[data-md-color-scheme="slate"] .markdown-content {
|
||||
box-shadow: 0 2px 4px rgba(0,0,0,0.1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</style>
|
||||
|
||||
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/marked/9.1.6/marked.min.js"></script>
|
||||
|
||||
<script>
|
||||
window.addEventListener('load', function() {
|
||||
function displayResults(responseText) {
|
||||
const resultsContainer = document.getElementById('results');
|
||||
const spinner = document.getElementById('spinner');
|
||||
const searchContainer = document.querySelector('.search-container');
|
||||
|
||||
// Hide spinner
|
||||
spinner.style.display = 'none';
|
||||
|
||||
// Scroll to search bar
|
||||
searchContainer.scrollIntoView({ behavior: 'smooth', block: 'start' });
|
||||
|
||||
try {
|
||||
const results = JSON.parse(responseText);
|
||||
|
||||
marked.setOptions({
|
||||
breaks: true,
|
||||
gfm: true,
|
||||
headerIds: false,
|
||||
sanitize: false
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
const htmlContent = marked.parse(results.message);
|
||||
|
||||
resultsContainer.className = 'markdown-content';
|
||||
resultsContainer.innerHTML = htmlContent;
|
||||
|
||||
// Scroll after content is rendered
|
||||
setTimeout(() => {
|
||||
const searchContainer = document.querySelector('.search-container');
|
||||
const offset = 55; // Offset from top in pixels
|
||||
const elementPosition = searchContainer.getBoundingClientRect().top;
|
||||
const offsetPosition = elementPosition + window.pageYOffset - offset;
|
||||
|
||||
window.scrollTo({
|
||||
top: offsetPosition,
|
||||
behavior: 'smooth'
|
||||
});
|
||||
}, 100);
|
||||
} catch (error) {
|
||||
console.error('Error parsing results:', error);
|
||||
resultsContainer.innerHTML = '<div class="error-message">Error processing results</div>';
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
async function performSearch() {
|
||||
const searchInput = document.getElementById('searchInput');
|
||||
const resultsContainer = document.getElementById('results');
|
||||
const spinner = document.getElementById('spinner');
|
||||
const searchTerm = searchInput.value.trim();
|
||||
|
||||
if (!searchTerm) {
|
||||
resultsContainer.innerHTML = '<div class="error-message">Please enter a search term</div>';
|
||||
return;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Show spinner, clear results
|
||||
spinner.style.display = 'flex';
|
||||
resultsContainer.innerHTML = '';
|
||||
|
||||
try {
|
||||
const data = {
|
||||
"query": searchTerm
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
const options = {
|
||||
method: 'POST',
|
||||
headers: {
|
||||
'accept': 'text/plain',
|
||||
'content-type': 'application/json',
|
||||
},
|
||||
body: JSON.stringify(data)
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// const API_ENDPOINT = 'http://0.0.0.0:3000/api/v1/docs_help';
|
||||
const API_ENDPOINT = 'https://help.merge.qodo.ai/api/v1/docs_help';
|
||||
|
||||
const response = await fetch(API_ENDPOINT, options);
|
||||
|
||||
if (!response.ok) {
|
||||
throw new Error(`HTTP error! status: ${response.status}`);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
const responseText = await response.text();
|
||||
displayResults(responseText);
|
||||
} catch (error) {
|
||||
spinner.style.display = 'none';
|
||||
resultsContainer.innerHTML = `
|
||||
<div class="error-message">
|
||||
An error occurred while searching. Please try again later.
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
`;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Add event listeners
|
||||
const searchButton = document.getElementById('searchButton');
|
||||
const searchInput = document.getElementById('searchInput');
|
||||
|
||||
if (searchButton) {
|
||||
searchButton.addEventListener('click', performSearch);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if (searchInput) {
|
||||
searchInput.addEventListener('keypress', function(e) {
|
||||
if (e.key === 'Enter') {
|
||||
performSearch();
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
</script>
|
||||
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 15 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 4.2 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 57 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 263 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 24 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 1.2 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 17 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 8.7 KiB |
@ -17,8 +17,8 @@ Qodo Merge constructs a comprehensive context for each pull request, incorporati
|
||||
<img src="https://codium.ai/images/pr_agent/pr_chat_1.png" width="768">
|
||||
<img src="https://codium.ai/images/pr_agent/pr_chat_2.png" width="768">
|
||||
|
||||
### Toolbar extension
|
||||
|
||||
### Toolbar extension
|
||||
With Qodo Merge Chrome extension, it's [easier than ever](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gT5tli7X4H4) to interactively configure and experiment with the different tools and configuration options.
|
||||
|
||||
For private repositories, after you found the setup that works for you, you can also easily export it as a persistent configuration file, and use it for automatic commands.
|
||||
@ -37,6 +37,7 @@ For example, you can choose to present only message from Qodo Merge, or filter t
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://codium.ai/images/pr_agent/pr_agent_filters2.png" width="256">
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Enhanced code suggestions
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge Chrome extension adds the following capabilities to code suggestions tool's comments:
|
||||
@ -44,6 +45,7 @@ Qodo Merge Chrome extension adds the following capabilities to code suggestions
|
||||
- Auto-expand the table when you are viewing a code block, to avoid clipping.
|
||||
- Adding a "quote-and-reply" button, that enables to address and comment on a specific suggestion (for example, asking the author to fix the issue)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://codium.ai/images/pr_agent/chrome_extension_code_suggestion1.png" width="512">
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://codium.ai/images/pr_agent/chrome_extension_code_suggestion2.png" width="512">
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
With a single-click installation you will gain access to a context-aware chat on your pull requests code, a toolbar extension with multiple AI feedbacks, Qodo Merge filters, and additional abilities.
|
||||
|
||||
The extension is powered by top code models like Claude 3.7 Sonnet and o4-mini. All the extension's features are free to use on public repositories.
|
||||
The extension is powered by top code models like Claude 3.5 Sonnet and GPT4. All the extension's features are free to use on public repositories.
|
||||
|
||||
For private repositories, you will need to install [Qodo Merge](https://github.com/apps/qodo-merge-pro){:target="_blank"} in addition to the extension (Quick GitHub app setup with a 14-day free trial. No credit card needed).
|
||||
For a demonstration of how to install Qodo Merge and use it with the Chrome extension, please refer to the tutorial video at the provided [link](https://codium.ai/images/pr_agent/private_repos.mp4){:target="_blank"}.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,39 +0,0 @@
|
||||
## Options and Configurations
|
||||
|
||||
### Accessing the Options Page
|
||||
|
||||
To access the options page for the Qodo Merge Chrome extension:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Find the extension icon in your Chrome toolbar (usually in the top-right corner of your browser)
|
||||
2. Right-click on the extension icon
|
||||
3. Select "Options" from the context menu that appears
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively, you can access the options page directly using this URL:
|
||||
|
||||
[chrome-extension://ephlnjeghhogofkifjloamocljapahnl/options.html](chrome-extension://ephlnjeghhogofkifjloamocljapahnl/options.html)
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://codium.ai/images/pr_agent/chrome_ext_options.png" width="256">
|
||||
|
||||
### Configuration Options
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://codium.ai/images/pr_agent/chrome_ext_settings_page.png" width="512">
|
||||
|
||||
#### API Base Host
|
||||
|
||||
For single-tenant customers, you can configure the extension to communicate directly with your company's Qodo Merge server instance.
|
||||
|
||||
To set this up:
|
||||
|
||||
- Enter your organization's Qodo Merge API endpoint in the "API Base Host" field
|
||||
- This endpoint should be provided by your Qodo DevOps Team
|
||||
|
||||
*Note: The extension does not send your code to the server, but only triggers your previously installed Qodo Merge application.*
|
||||
|
||||
#### Interface Options
|
||||
|
||||
You can customize the extension's interface by:
|
||||
|
||||
- Toggling the "Show Qodo Merge Toolbar" option
|
||||
- When disabled, the toolbar will not appear in your Github comment bar
|
||||
|
||||
Remember to click "Save Settings" after making any changes.
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,4 @@
|
||||
# Auto Best Practices 💎
|
||||
|
||||
`Supported Git Platforms: GitHub`
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
@ -20,6 +19,7 @@ The analysis intentionally takes a flexible, _exploratory_ approach to identify
|
||||
Qodo Merge features a novel [tracking system](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#suggestion-tracking) that automatically detects when PR authors implement AI-generated code suggestions.
|
||||
All accepted suggestions are aggregated in a repository-specific wiki page called [`.pr_agent_accepted_suggestions`](https://github.com/qodo-ai/pr-agent/wiki/.pr_agent_accepted_suggestions)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Learning and Applying Auto Best Practices
|
||||
|
||||
Monthly, Qodo Merge analyzes the collection of accepted suggestions to generate repository-specific best practices, stored in [`.pr_agent_auto_best_practices`](https://github.com/qodo-ai/pr-agent/wiki/.pr_agent_auto_best_practices) wiki file.
|
||||
@ -33,10 +33,12 @@ This creates a two-phase analysis:
|
||||
|
||||
By keeping these phases decoupled, the tool remains free to discover new or unseen issues and problems, while also learning from past experiences.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
When presenting the suggestions generated by the `improve` tool, Qodo Merge will add a dedicated label for each suggestion generated from the auto best practices - 'Learned best practice':
|
||||
|
||||
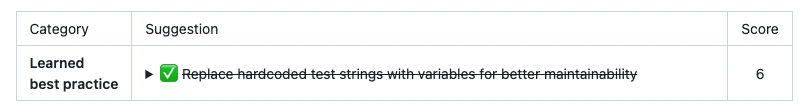{width=684}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Auto Best Practices vs Custom Best Practices
|
||||
|
||||
Teams and companies can also manually define their own [custom best practices](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#best-practices) in Qodo Merge.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,55 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Chat on code suggestions 💎
|
||||
|
||||
`Supported Git Platforms: GitHub, GitLab`
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge implements an orchestrator agent that enables interactive code discussions, listening and responding to comments without requiring explicit tool calls.
|
||||
The orchestrator intelligently analyzes your responses to determine if you want to implement a suggestion, ask a question, or request help, then delegates to the appropriate specialized tool.
|
||||
|
||||
To minimize unnecessary notifications and maintain focused discussions, the orchestrator agent will only respond to comments made directly within the inline code suggestion discussions it has created (`/improve`) or within discussions initiated by the `/implement` command.
|
||||
|
||||
## Getting Started
|
||||
|
||||
### Setup
|
||||
|
||||
Enable interactive code discussions by adding the following to your configuration file (default is `True`):
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[pr_code_suggestions]
|
||||
enable_chat_in_code_suggestions = true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Activation
|
||||
|
||||
#### `/improve`
|
||||
|
||||
To obtain dynamic responses, the following steps are required:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Run the `/improve` command (mostly automatic)
|
||||
2. Check the `/improve` recommendation checkboxes (_Apply this suggestion_) to have Qodo Merge generate a new inline code suggestion discussion
|
||||
3. The orchestrator agent will then automatically listen to and reply to comments within the discussion without requiring additional commands
|
||||
|
||||
#### `/implement`
|
||||
|
||||
To obtain dynamic responses, the following steps are required:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Select code lines in the PR diff and run the `/implement` command
|
||||
2. Wait for Qodo Merge to generate a new inline code suggestion
|
||||
3. The orchestrator agent will then automatically listen to and reply to comments within the discussion without requiring additional commands
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Explore the available interaction patterns
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip "Tip: Direct the agent with keywords"
|
||||
Use "implement" or "apply" for code generation. Use "explain", "why", or "how" for information and help.
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Asking for Details"
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Implementing Suggestions"
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Providing Additional Help"
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
2
docs/docs/core-abilities/code_oriented_yaml.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
TBD
|
||||
@ -1,40 +0,0 @@
|
||||
## Introduction
|
||||
|
||||
The Git environment usually represents the final stage before code enters production. Hence, Detecting bugs and issues during the review process is critical.
|
||||
|
||||
The [`improve`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/) tool provides actionable code suggestions for your pull requests, aiming to help detect and fix bugs and problems.
|
||||
By default, suggestions appear as a comment in a table format:
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
## Validation of Code Suggestions
|
||||
|
||||
Each suggestion in the table can be "applied" by clicking on the `Apply this suggestion` checkbox, converting it to a committable Git code change that can be committed directly to the PR.
|
||||
This approach allows to fix issues without returning to your IDE for manual edits — significantly faster and more convenient.
|
||||
|
||||
However, committing a suggestion in a Git environment carries more risk than in a local IDE, as you don't have the opportunity to fully run and test the code before committing.
|
||||
|
||||
To balance convenience with safety, Qodo Merge implements a dual validation system for each generated code suggestion:
|
||||
|
||||
1) **Localization** - Qodo Merge confirms that the suggestion's line numbers and surrounding code, as predicted by the model, actually match the repo code. This means that the model correctly identified the context and location of the code to be changed.
|
||||
|
||||
2) **"Compilation"** - Using static code analysis, Qodo Merge verifies that after applying the suggestion, the modified file will still be valid, meaning tree-sitter syntax processing will not throw an error. This process is relevant for multiple programming languages, see [here](https://pypi.org/project/tree-sitter-languages/) for the full list of supported languages.
|
||||
|
||||
When a suggestion fails to meet these validation criteria, it may still provide valuable feedback, but isn't suitable for direct application to the PR.
|
||||
In such cases, Qodo Merge will omit the 'apply' checkbox and instead display:
|
||||
|
||||
`[To ensure code accuracy, apply this suggestion manually]`
|
||||
|
||||
All suggestions that pass these validations undergo a final stage of **self-reflection**, where the AI model evaluates, scores, and re-ranks its own suggestions, eliminating any that are irrelevant or incorrect.
|
||||
Read more about this process in the [self-reflection](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/self_reflection/) page.
|
||||
|
||||
## Conclusion
|
||||
|
||||
The validation methods described above enhance the reliability of code suggestions and help PR authors determine which suggestions are safer to apply in the Git environment.
|
||||
Of course, additional factors should be considered, such as suggestion complexity and potential code impact.
|
||||
|
||||
Human judgment remains essential. After clicking 'apply', Qodo Merge still presents the 'before' and 'after' code snippets for review, allowing you to assess the changes before finalizing the commit.
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,5 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview - PR Compression Strategy
|
||||
|
||||
There are two scenarios:
|
||||
|
||||
1. The PR is small enough to fit in a single prompt (including system and user prompt)
|
||||
@ -9,7 +8,6 @@ There are two scenarios:
|
||||
For both scenarios, we first use the following strategy
|
||||
|
||||
#### Repo language prioritization strategy
|
||||
|
||||
We prioritize the languages of the repo based on the following criteria:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Exclude binary files and non code files (e.g. images, pdfs, etc)
|
||||
@ -17,33 +15,28 @@ We prioritize the languages of the repo based on the following criteria:
|
||||
3. We sort the PR files by the most common languages in the repo (in descending order):
|
||||
* ```[[file.py, file2.py],[file3.js, file4.jsx],[readme.md]]```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Small PR
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, we can fit the entire PR in a single prompt:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Exclude binary files and non code files (e.g. images, pdfs, etc)
|
||||
2. We Expand the surrounding context of each patch to 3 lines above and below the patch
|
||||
|
||||
### Large PR
|
||||
|
||||
#### Motivation
|
||||
|
||||
Pull Requests can be very long and contain a lot of information with varying degree of relevance to the pr-agent.
|
||||
We want to be able to pack as much information as possible in a single LMM prompt, while keeping the information relevant to the pr-agent.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Compression strategy
|
||||
|
||||
We prioritize additions over deletions:
|
||||
|
||||
* Combine all deleted files into a single list (`deleted files`)
|
||||
* File patches are a list of hunks, remove all hunks of type deletion-only from the hunks in the file patch
|
||||
- Combine all deleted files into a single list (`deleted files`)
|
||||
- File patches are a list of hunks, remove all hunks of type deletion-only from the hunks in the file patch
|
||||
|
||||
#### Adaptive and token-aware file patch fitting
|
||||
|
||||
We use [tiktoken](https://github.com/openai/tiktoken) to tokenize the patches after the modifications described above, and we use the following strategy to fit the patches into the prompt:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Within each language we sort the files by the number of tokens in the file (in descending order):
|
||||
* ```[[file2.py, file.py],[file4.jsx, file3.js],[readme.md]]```
|
||||
- ```[[file2.py, file.py],[file4.jsx, file3.js],[readme.md]]```
|
||||
2. Iterate through the patches in the order described above
|
||||
3. Add the patches to the prompt until the prompt reaches a certain buffer from the max token length
|
||||
4. If there are still patches left, add the remaining patches as a list called `other modified files` to the prompt until the prompt reaches the max token length (hard stop), skip the rest of the patches.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -7,8 +7,7 @@ This approach balances providing sufficient context for accurate analysis, while
|
||||
## Introduction
|
||||
|
||||
Pull request code changes are retrieved in a unified diff format, showing three lines of context before and after each modified section, with additions marked by '+' and deletions by '-'.
|
||||
|
||||
```diff
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -12,5 +12,5 @@ def func1():
|
||||
code line that already existed in the file...
|
||||
code line that already existed in the file...
|
||||
@ -26,6 +25,7 @@ Pull request code changes are retrieved in a unified diff format, showing three
|
||||
This unified diff format can be challenging for AI models to interpret accurately, as it provides limited context for understanding the full scope of code changes.
|
||||
The presentation of code using '+', '-', and ' ' symbols to indicate additions, deletions, and unchanged lines respectively also differs from the standard code formatting typically used to train AI models.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Challenges of expanding the context window
|
||||
|
||||
While expanding the context window is technically feasible, it presents a more fundamental trade-off:
|
||||
@ -43,7 +43,6 @@ Pull requests often encompass multiple changes across many files, potentially sp
|
||||
- Increased context expands the token count, increasing processing time and cost, and may prevent the model from processing the entire pull request in a single pass.
|
||||
|
||||
## Asymmetric and dynamic context
|
||||
|
||||
To address these challenges, Qodo Merge employs an **asymmetric** and **dynamic** context strategy, providing the model with more focused and relevant context information for each code change.
|
||||
|
||||
**Asymmetric:**
|
||||
@ -63,8 +62,7 @@ To prevent overwhelming the model with excessive context, we impose a limit on t
|
||||
This balance allows for comprehensive understanding while maintaining efficiency and limiting context token usage.
|
||||
|
||||
## Appendix - relevant configuration options
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
patch_extension_skip_types =[".md",".txt"] # Skip files with these extensions when trying to extend the context
|
||||
allow_dynamic_context=true # Allow dynamic context extension
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,19 +1,15 @@
|
||||
# Fetching Ticket Context for PRs
|
||||
|
||||
`Supported Git Platforms: GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket`
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge streamlines code review workflows by seamlessly connecting with multiple ticket management systems.
|
||||
Qodo Merge PR Agent streamlines code review workflows by seamlessly connecting with multiple ticket management systems.
|
||||
This integration enriches the review process by automatically surfacing relevant ticket information and context alongside code changes.
|
||||
|
||||
**Ticket systems supported**:
|
||||
## Ticket systems supported
|
||||
- GitHub
|
||||
- Jira (💎)
|
||||
|
||||
- [GitHub](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/fetching_ticket_context/#github-issues-integration)
|
||||
- [Jira (💎)](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/fetching_ticket_context/#jira-integration)
|
||||
- [Linear (💎)](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/fetching_ticket_context/#linear-integration)
|
||||
|
||||
**Ticket data fetched:**
|
||||
Ticket data fetched:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Ticket Title
|
||||
2. Ticket Description
|
||||
@ -30,17 +26,16 @@ Ticket Recognition Requirements:
|
||||
- For Jira tickets, you should follow the instructions in [Jira Integration](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/fetching_ticket_context/#jira-integration) in order to authenticate with Jira.
|
||||
|
||||
### Describe tool
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge will recognize the ticket and use the ticket content (title, description, labels) to provide additional context for the code changes.
|
||||
Qodo Merge PR Agent will recognize the ticket and use the ticket content (title, description, labels) to provide additional context for the code changes.
|
||||
By understanding the reasoning and intent behind modifications, the LLM can offer more insightful and relevant code analysis.
|
||||
|
||||
### Review tool
|
||||
|
||||
Similarly to the `describe` tool, the `review` tool will use the ticket content to provide additional context for the code changes.
|
||||
|
||||
In addition, this feature will evaluate how well a Pull Request (PR) adheres to its original purpose/intent as defined by the associated ticket or issue mentioned in the PR description.
|
||||
Each ticket will be assigned a label (Compliance/Alignment level), Indicates the degree to which the PR fulfills its original purpose, Options: Fully compliant, Partially compliant or Not compliant.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
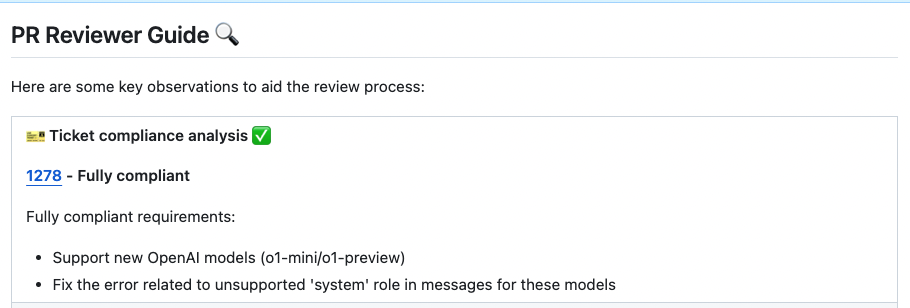{width=768}
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the tool will automatically validate if the PR complies with the referenced ticket.
|
||||
@ -51,23 +46,41 @@ If you want to disable this feedback, add the following line to your configurati
|
||||
require_ticket_analysis_review=false
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## GitHub Issues Integration
|
||||
## Providers
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge will automatically recognize GitHub issues mentioned in the PR description and fetch the issue content.
|
||||
### Github Issues Integration
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge PR Agent will automatically recognize Github issues mentioned in the PR description and fetch the issue content.
|
||||
Examples of valid GitHub issue references:
|
||||
|
||||
- `https://github.com/<ORG_NAME>/<REPO_NAME>/issues/<ISSUE_NUMBER>`
|
||||
- `#<ISSUE_NUMBER>`
|
||||
- `<ORG_NAME>/<REPO_NAME>#<ISSUE_NUMBER>`
|
||||
|
||||
Since Qodo Merge is integrated with GitHub, it doesn't require any additional configuration to fetch GitHub issues.
|
||||
Since Qodo Merge PR Agent is integrated with GitHub, it doesn't require any additional configuration to fetch GitHub issues.
|
||||
|
||||
## Jira Integration 💎
|
||||
### Jira Integration 💎
|
||||
|
||||
We support both Jira Cloud and Jira Server/Data Center.
|
||||
To integrate with Jira, you can link your PR to a ticket using either of these methods:
|
||||
|
||||
### Jira Cloud
|
||||
**Method 1: Description Reference:**
|
||||
|
||||
Include a ticket reference in your PR description using either the complete URL format https://<JIRA_ORG>.atlassian.net/browse/ISSUE-123 or the shortened ticket ID ISSUE-123.
|
||||
|
||||
**Method 2: Branch Name Detection:**
|
||||
|
||||
Name your branch with the ticket ID as a prefix (e.g., `ISSUE-123-feature-description` or `ISSUE-123/feature-description`).
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Jira Base URL"
|
||||
For shortened ticket IDs or branch detection (method 2), you must configure the Jira base URL in your configuration file under the [jira] section:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[jira]
|
||||
jira_base_url = "https://<JIRA_ORG>.atlassian.net"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Jira Cloud 💎
|
||||
There are two ways to authenticate with Jira Cloud:
|
||||
|
||||
**1) Jira App Authentication**
|
||||
@ -76,17 +89,13 @@ The recommended way to authenticate with Jira Cloud is to install the Qodo Merge
|
||||
|
||||
Installation steps:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Go to the [Qodo Merge integrations page](https://app.qodo.ai/qodo-merge/integrations)
|
||||
|
||||
2. Click on the Connect **Jira Cloud** button to connect the Jira Cloud app
|
||||
|
||||
3. Click the `accept` button.<br>
|
||||
1. Click [here](https://auth.atlassian.com/authorize?audience=api.atlassian.com&client_id=8krKmA4gMD8mM8z24aRCgPCSepZNP1xf&scope=read%3Ajira-work%20offline_access&redirect_uri=https%3A%2F%2Fregister.jira.pr-agent.codium.ai&state=qodomerge&response_type=code&prompt=consent) to install the Qodo Merge app in your Jira Cloud instance, click the `accept` button.<br>
|
||||
{width=384}
|
||||
|
||||
4. After installing the app, you will be redirected to the Qodo Merge registration page. and you will see a success message.<br>
|
||||
2. After installing the app, you will be redirected to the Qodo Merge registration page. and you will see a success message.<br>
|
||||
{width=384}
|
||||
|
||||
5. Now Qodo Merge will be able to fetch Jira ticket context for your PRs.
|
||||
3. Now you can use the Jira integration in Qodo Merge PR Agent.
|
||||
|
||||
**2) Email/Token Authentication**
|
||||
|
||||
@ -110,128 +119,46 @@ jira_api_token = "YOUR_API_TOKEN"
|
||||
jira_api_email = "YOUR_EMAIL"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Jira Data Center/Server
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ()
|
||||
[//]: # (##### Local App Authentication (For Qodo Merge On-Premise Customers))
|
||||
#### Jira Data Center/Server 💎
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ()
|
||||
[//]: # (##### 1. Step 1: Set up an application link in Jira Data Center/Server)
|
||||
##### Local App Authentication (For Qodo Merge On-Premise Customers)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (* Go to Jira Administration > Applications > Application Links > Click on `Create link`)
|
||||
##### 1. Step 1: Set up an application link in Jira Data Center/Server
|
||||
* Go to Jira Administration > Applications > Application Links > Click on `Create link`
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ()
|
||||
[//]: # (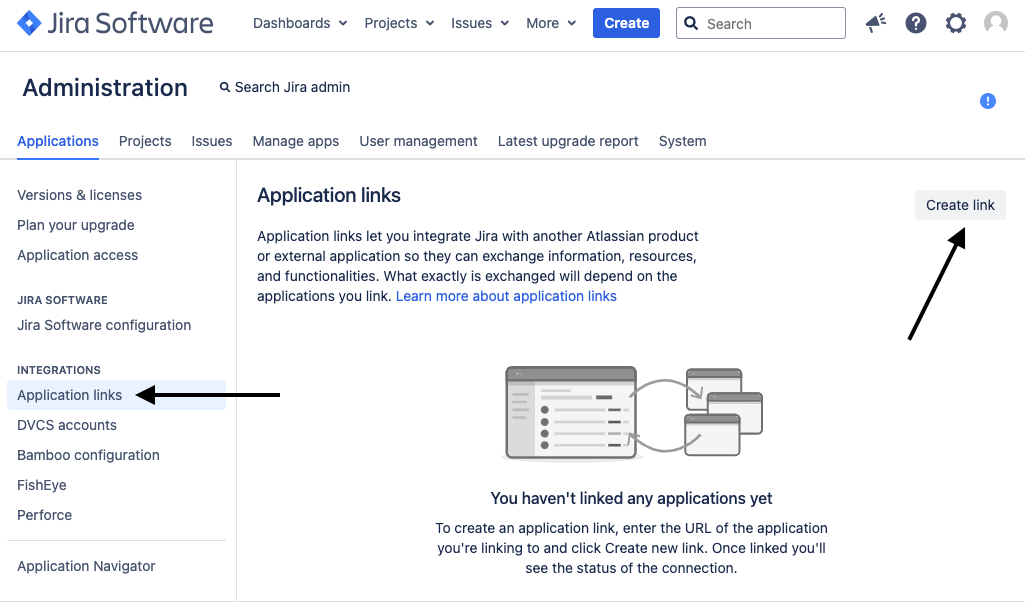{width=384})
|
||||
{width=384}
|
||||
* Choose `External application` and set the direction to `Incoming` and then click `Continue`
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (* Choose `External application` and set the direction to `Incoming` and then click `Continue`)
|
||||
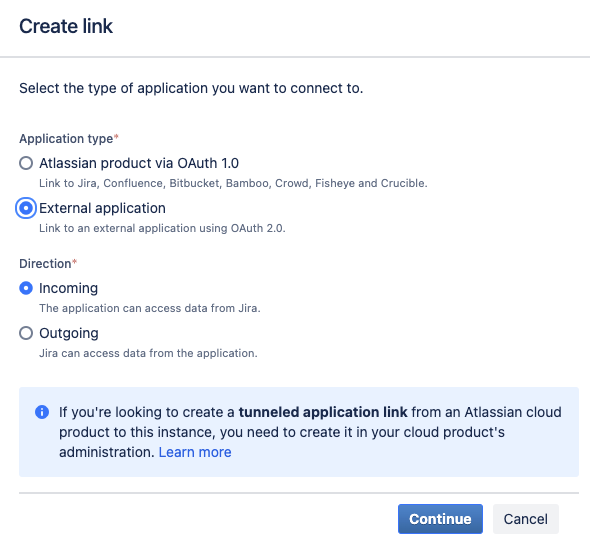{width=256}
|
||||
* In the following screen, enter the following details:
|
||||
* Name: `Qodo Merge`
|
||||
* Redirect URL: Enter your Qodo Merge URL followed `https://{QODO_MERGE_ENDPOINT}/register_ticket_provider`
|
||||
* Permission: Select `Read`
|
||||
* Click `Save`
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ()
|
||||
[//]: # ({width=256})
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (* In the following screen, enter the following details:)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ( * Name: `Qodo Merge`)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ( * Redirect URL: Enter your Qodo Merge URL followed `https://{QODO_MERGE_ENDPOINT}/register_ticket_provider`)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ( * Permission: Select `Read`)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ( * Click `Save`)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ()
|
||||
[//]: # (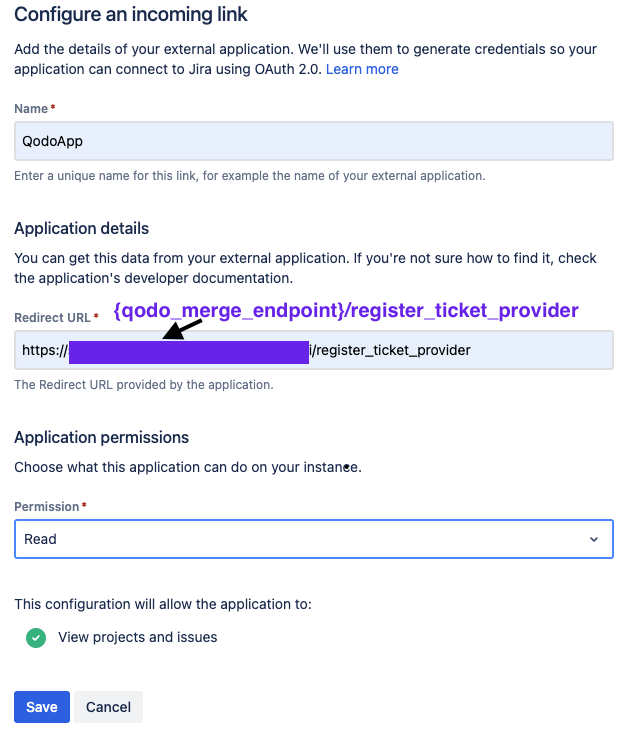{width=384})
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (* Copy the `Client ID` and `Client secret` and set them in your `.secrets` file:)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ()
|
||||
[//]: # (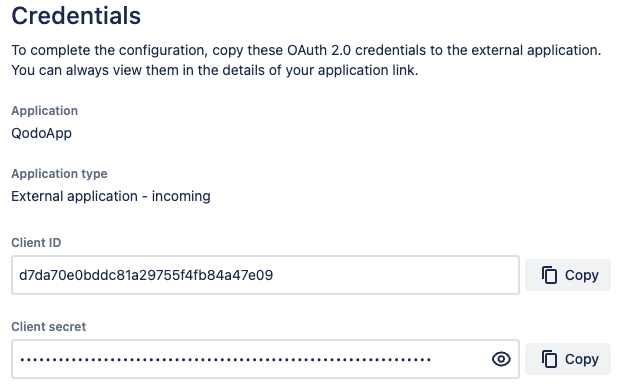{width=256})
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (```toml)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ([jira])
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (jira_app_secret = "...")
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (jira_client_id = "...")
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (```)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ()
|
||||
[//]: # (##### 2. Step 2: Authenticate with Jira Data Center/Server)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (* Open this URL in your browser: `https://{QODO_MERGE_ENDPOINT}/jira_auth`)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (* Click on link)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ()
|
||||
[//]: # ({width=384})
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ()
|
||||
[//]: # (* You will be redirected to Jira Data Center/Server, click `Allow`)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (* You will be redirected back to Qodo Merge and you will see a success message.)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (Personal Access Token (PAT) Authentication)
|
||||
|
||||
#### Using Basic Authentication for Jira Data Center/Server
|
||||
|
||||
You can use your Jira username and password to authenticate with Jira Data Center/Server.
|
||||
|
||||
In your Configuration file/Environment variables/Secrets file, add the following lines:
|
||||
{width=384}
|
||||
* Copy the `Client ID` and `Client secret` and set them in your `.secrets` file:
|
||||
|
||||
{width=256}
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
jira_api_email = "your_username"
|
||||
jira_api_token = "your_password"
|
||||
[jira]
|
||||
jira_app_secret = "..."
|
||||
jira_client_id = "..."
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
(Note that indeed the 'jira_api_email' field is used for the username, and the 'jira_api_token' field is used for the user password.)
|
||||
##### 2. Step 2: Authenticate with Jira Data Center/Server
|
||||
* Open this URL in your browser: `https://{QODO_MERGE_ENDPOINT}/jira_auth`
|
||||
* Click on link
|
||||
|
||||
##### Validating Basic authentication via Python script
|
||||
{width=384}
|
||||
|
||||
If you are facing issues retrieving tickets in Qodo Merge with Basic auth, you can validate the flow using a Python script.
|
||||
This following steps will help you check if the basic auth is working correctly, and if you can access the Jira ticket details:
|
||||
|
||||
1. run `pip install jira==3.8.0`
|
||||
|
||||
2. run the following Python script (after replacing the placeholders with your actual values):
|
||||
|
||||
??? example "Script to validate basic auth"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from jira import JIRA
|
||||
* You will be redirected to Jira Data Center/Server, click `Allow`
|
||||
* You will be redirected back to Qodo Merge PR Agent and you will see a success message.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
try:
|
||||
# Jira server URL
|
||||
server = "https://..."
|
||||
# Basic auth
|
||||
username = "..."
|
||||
password = "..."
|
||||
# Jira ticket code (e.g. "PROJ-123")
|
||||
ticket_id = "..."
|
||||
|
||||
print("Initializing JiraServerTicketProvider with JIRA server")
|
||||
# Initialize JIRA client
|
||||
jira = JIRA(
|
||||
server=server,
|
||||
basic_auth=(username, password),
|
||||
timeout=30
|
||||
)
|
||||
if jira:
|
||||
print(f"JIRA client initialized successfully")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print("Error initializing JIRA client")
|
||||
|
||||
# Fetch ticket details
|
||||
ticket = jira.issue(ticket_id)
|
||||
print(f"Ticket title: {ticket.fields.summary}")
|
||||
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
print(f"Error fetching JIRA ticket details: {e}")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Using a Personal Access Token (PAT) for Jira Data Center/Server
|
||||
##### Personal Access Token (PAT) Authentication
|
||||
We also support Personal Access Token (PAT) Authentication method.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Create a [Personal Access Token (PAT)](https://confluence.atlassian.com/enterprise/using-personal-access-tokens-1026032365.html) in your Jira account
|
||||
2. In your Configuration file/Environment variables/Secrets file, add the following lines:
|
||||
@ -241,109 +168,3 @@ This following steps will help you check if the basic auth is working correctly,
|
||||
jira_base_url = "YOUR_JIRA_BASE_URL" # e.g. https://jira.example.com
|
||||
jira_api_token = "YOUR_API_TOKEN"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
##### Validating PAT token via Python script
|
||||
|
||||
If you are facing issues retrieving tickets in Qodo Merge with PAT token, you can validate the flow using a Python script.
|
||||
This following steps will help you check if the token is working correctly, and if you can access the Jira ticket details:
|
||||
|
||||
1. run `pip install jira==3.8.0`
|
||||
|
||||
2. run the following Python script (after replacing the placeholders with your actual values):
|
||||
|
||||
??? example "Script to validate PAT token"
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from jira import JIRA
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
try:
|
||||
# Jira server URL
|
||||
server = "https://..."
|
||||
# Jira PAT token
|
||||
token_auth = "..."
|
||||
# Jira ticket code (e.g. "PROJ-123")
|
||||
ticket_id = "..."
|
||||
|
||||
print("Initializing JiraServerTicketProvider with JIRA server")
|
||||
# Initialize JIRA client
|
||||
jira = JIRA(
|
||||
server=server,
|
||||
token_auth=token_auth,
|
||||
timeout=30
|
||||
)
|
||||
if jira:
|
||||
print(f"JIRA client initialized successfully")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print("Error initializing JIRA client")
|
||||
|
||||
# Fetch ticket details
|
||||
ticket = jira.issue(ticket_id)
|
||||
print(f"Ticket title: {ticket.fields.summary}")
|
||||
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
print(f"Error fetching JIRA ticket details: {e}")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### How to link a PR to a Jira ticket
|
||||
|
||||
To integrate with Jira, you can link your PR to a ticket using either of these methods:
|
||||
|
||||
**Method 1: Description Reference:**
|
||||
|
||||
Include a ticket reference in your PR description using either the complete URL format https://<JIRA_ORG>.atlassian.net/browse/ISSUE-123 or the shortened ticket ID ISSUE-123.
|
||||
|
||||
**Method 2: Branch Name Detection:**
|
||||
|
||||
Name your branch with the ticket ID as a prefix (e.g., `ISSUE-123-feature-description` or `ISSUE-123/feature-description`).
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Jira Base URL"
|
||||
For shortened ticket IDs or branch detection (method 2 for JIRA cloud), you must configure the Jira base URL in your configuration file under the [jira] section:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[jira]
|
||||
jira_base_url = "https://<JIRA_ORG>.atlassian.net"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Linear Integration 💎
|
||||
|
||||
### Linear App Authentication
|
||||
|
||||
The recommended way to authenticate with Linear is to connect the Linear app through the Qodo Merge portal.
|
||||
|
||||
Installation steps:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Go to the [Qodo Merge integrations page](https://app.qodo.ai/qodo-merge/integrations)
|
||||
|
||||
2. Navigate to the **Integrations** tab
|
||||
|
||||
3. Click on the **Linear** button to connect the Linear app
|
||||
|
||||
4. Follow the authentication flow to authorize Qodo Merge to access your Linear workspace
|
||||
|
||||
5. Once connected, Qodo Merge will be able to fetch Linear ticket context for your PRs
|
||||
|
||||
### How to link a PR to a Linear ticket
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge will automatically detect Linear tickets using either of these methods:
|
||||
|
||||
**Method 1: Description Reference:**
|
||||
|
||||
Include a ticket reference in your PR description using either:
|
||||
- The complete Linear ticket URL: `https://linear.app/[ORG_ID]/issue/[TICKET_ID]`
|
||||
- The shortened ticket ID: `[TICKET_ID]` (e.g., `ABC-123`) - requires linear_base_url configuration (see below).
|
||||
|
||||
**Method 2: Branch Name Detection:**
|
||||
|
||||
Name your branch with the ticket ID as a prefix (e.g., `ABC-123-feature-description` or `feature/ABC-123/feature-description`).
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Linear Base URL"
|
||||
For shortened ticket IDs or branch detection (method 2), you must configure the Linear base URL in your configuration file under the [linear] section:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[linear]
|
||||
linear_base_url = "https://linear.app/[ORG_ID]"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Replace `[ORG_ID]` with your Linear organization identifier.
|
||||
@ -3,24 +3,22 @@
|
||||
Demonstrating the return on investment (ROI) of AI-powered initiatives is crucial for modern organizations.
|
||||
To address this need, Qodo Merge has developed an AI impact measurement tools and metrics, providing advanced analytics to help businesses quantify the tangible benefits of AI adoption in their PR review process.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Auto Impact Validator - Real-Time Tracking of Implemented Qodo Merge Suggestions
|
||||
|
||||
### How It Works
|
||||
|
||||
When a user pushes a new commit to the pull request, Qodo Merge automatically compares the updated code against the previous suggestions, marking them as implemented if the changes address these recommendations, whether directly or indirectly:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Direct Implementation:** The user directly addresses the suggestion as-is in the PR, either by clicking on the "apply code suggestion" checkbox or by making the changes manually.
|
||||
2. **Indirect Implementation:** Qodo Merge recognizes when a suggestion's intent is fulfilled, even if the exact code changes differ from the original recommendation. It marks these suggestions as implemented, acknowledging that users may achieve the same goal through alternative solutions.
|
||||
|
||||
### Real-Time Visual Feedback
|
||||
|
||||
Upon confirming that a suggestion was implemented, Qodo Merge automatically adds a ✅ (check mark) to the relevant suggestion, enabling transparent tracking of Qodo Merge's impact analysis.
|
||||
Qodo Merge will also add, inside the relevant suggestions, an explanation of how the new code was impacted by each suggestion.
|
||||
|
||||
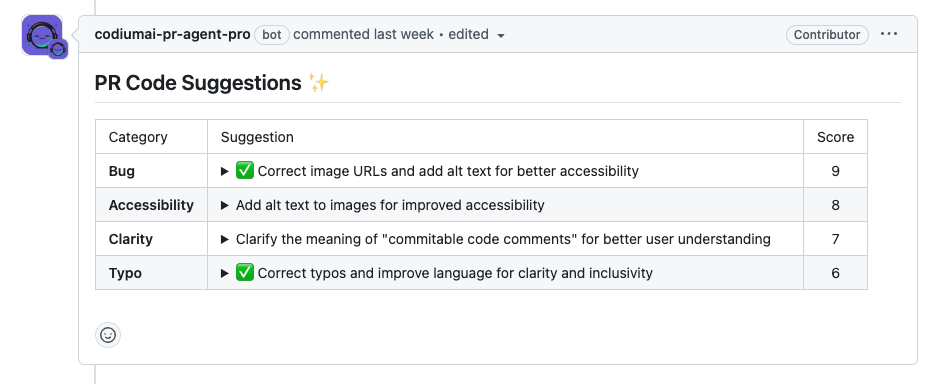{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
### Dashboard Metrics
|
||||
|
||||
The dashboard provides macro-level insights into the overall impact of Qodo Merge on the pull-request process with key productivity metrics.
|
||||
|
||||
By offering clear, data-driven evidence of Qodo Merge's impact, it empowers leadership teams to make informed decisions about the tool's effectiveness and ROI.
|
||||
@ -28,7 +26,6 @@ By offering clear, data-driven evidence of Qodo Merge's impact, it empowers lead
|
||||
Here are key metrics that the dashboard tracks:
|
||||
|
||||
#### Qodo Merge Impacts per 1K Lines
|
||||
|
||||
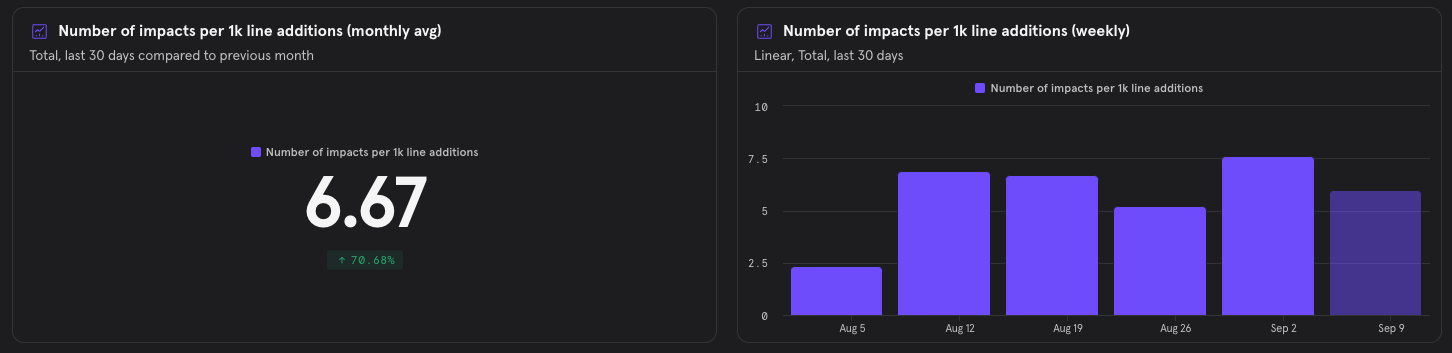{width=512}
|
||||
> Explanation: for every 1K lines of code (additions/edits), Qodo Merge had on average ~X suggestions implemented.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -39,11 +36,9 @@ Here are key metrics that the dashboard tracks:
|
||||
3. **Quantifies Value and ROI:** The metric directly correlates with the value Qodo Merge is providing, showing how frequently it offers improvements relative to the amount of new code being written. This provides a clear, quantifiable way to demonstrate Qodo Merge's return on investment to stakeholders.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Suggestion Effectiveness Across Categories
|
||||
|
||||
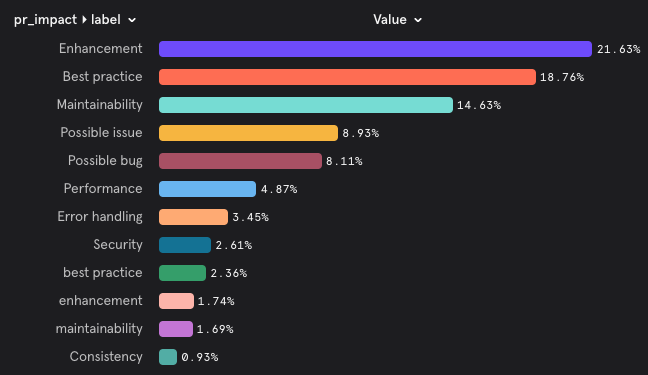{width=512}
|
||||
> Explanation: This chart illustrates the distribution of implemented suggestions across different categories, enabling teams to better understand Qodo Merge's impact on various aspects of code quality and development practices.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Suggestion Score Distribution
|
||||
|
||||
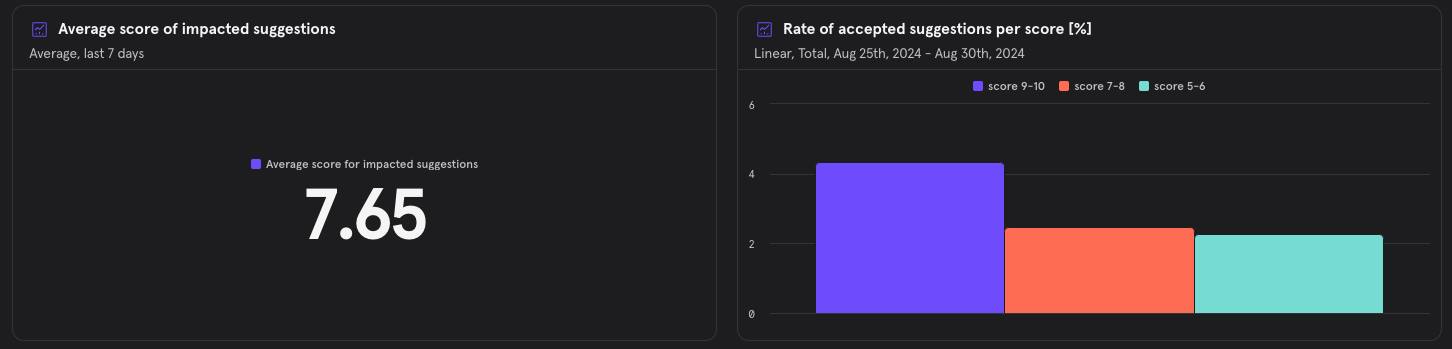{width=512}
|
||||
> Explanation: The distribution of the suggestion score for the implemented suggestions, ensuring that higher-scored suggestions truly represent more significant improvements.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,33 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Incremental Update 💎
|
||||
|
||||
`Supported Git Platforms: GitHub`
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
The Incremental Update feature helps users focus on feedback for their newest changes, making large PRs more manageable.
|
||||
|
||||
### How it works
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Update Option on Subsequent Commits"
|
||||
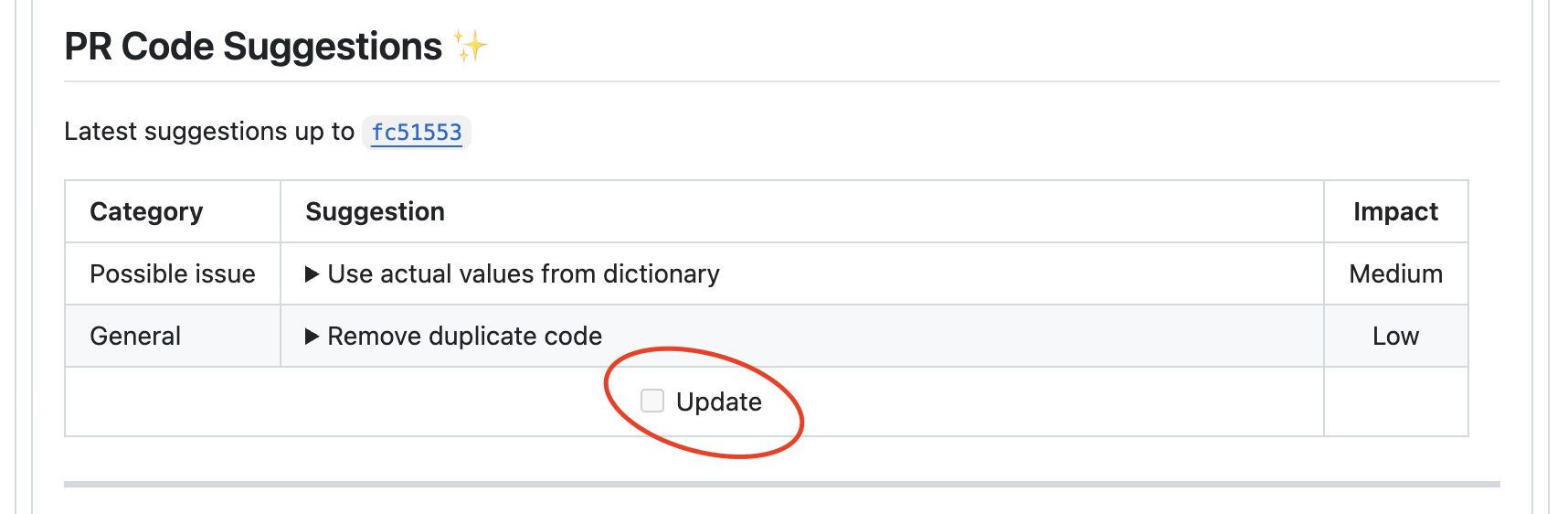{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Generation of Incremental Update"
|
||||
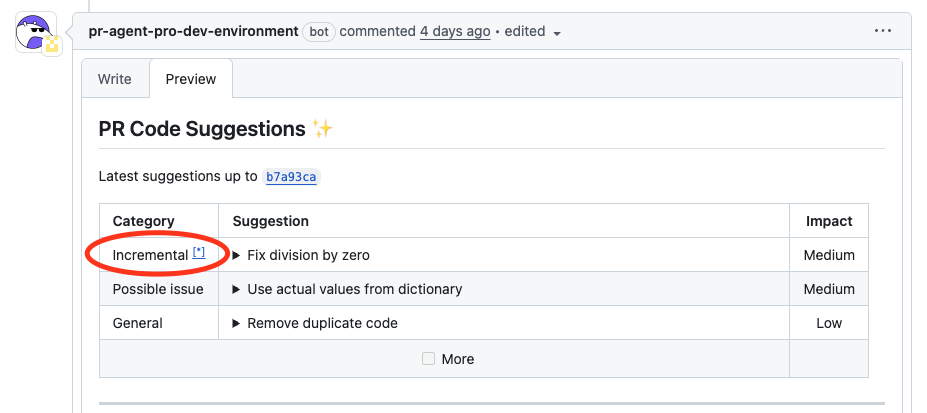{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
___
|
||||
|
||||
Whenever new commits are pushed following a recent code suggestions report for this PR, an Update button appears (as seen above).
|
||||
|
||||
Once the user clicks on the button:
|
||||
|
||||
- The `improve` tool identifies the new changes (the "delta")
|
||||
- Provides suggestions on these recent changes
|
||||
- Combines these suggestions with the overall PR feedback, prioritizing delta-related comments
|
||||
- Marks delta-related comments with a textual indication followed by an asterisk (*) with a link to this page, so they can easily be identified
|
||||
|
||||
### Benefits for Developers
|
||||
|
||||
- Focus on what matters: See feedback on newest code first
|
||||
- Clearer organization: Comments on recent changes are clearly marked
|
||||
- Better workflow: Address feedback more systematically, starting with recent changes
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,20 +1,17 @@
|
||||
# Core Abilities
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge utilizes a variety of core abilities to provide a comprehensive and efficient code review experience. These abilities include:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Auto best practices](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/auto_best_practices/)
|
||||
- [Chat on code suggestions](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/chat_on_code_suggestions/)
|
||||
- [Code validation](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/code_validation/)
|
||||
- [Compression strategy](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/compression_strategy/)
|
||||
- [Dynamic context](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/dynamic_context/)
|
||||
- [Fetching ticket context](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/fetching_ticket_context/)
|
||||
- [Impact evaluation](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/impact_evaluation/)
|
||||
- [Incremental Update](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/incremental_update/)
|
||||
- [Interactivity](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/interactivity/)
|
||||
- [Auto best practices](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/auto_best_practices/)
|
||||
- [Local and global metadata](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/metadata/)
|
||||
- [RAG context enrichment](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/rag_context_enrichment/)
|
||||
- [Dynamic context](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/dynamic_context/)
|
||||
- [Self-reflection](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/self_reflection/)
|
||||
- [Impact evaluation](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/impact_evaluation/)
|
||||
- [Interactivity](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/interactivity/)
|
||||
- [Compression strategy](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/compression_strategy/)
|
||||
- [Code-oriented YAML](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/code_oriented_yaml/)
|
||||
- [Static code analysis](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/static_code_analysis/)
|
||||
- [Code fine-tuning benchmark](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/finetuning_benchmark/)
|
||||
|
||||
## Blogs
|
||||
|
||||
@ -22,16 +19,13 @@ Here are some additional technical blogs from Qodo, that delve deeper into the c
|
||||
These resources provide more comprehensive insights into leveraging LLMs for software development.
|
||||
|
||||
### Code Generation and LLMs
|
||||
|
||||
- [Effective AI code suggestions: less is more](https://www.qodo.ai/blog/effective-code-suggestions-llms-less-is-more/)
|
||||
- [State-of-the-art Code Generation with AlphaCodium – From Prompt Engineering to Flow Engineering](https://www.qodo.ai/blog/qodoflow-state-of-the-art-code-generation-for-code-contests/)
|
||||
- [RAG for a Codebase with 10k Repos](https://www.qodo.ai/blog/rag-for-large-scale-code-repos/)
|
||||
|
||||
### Development Processes
|
||||
|
||||
- [Understanding the Challenges and Pain Points of the Pull Request Cycle](https://www.qodo.ai/blog/understanding-the-challenges-and-pain-points-of-the-pull-request-cycle/)
|
||||
- [Introduction to Code Coverage Testing](https://www.qodo.ai/blog/introduction-to-code-coverage-testing/)
|
||||
|
||||
### Cost Optimization
|
||||
|
||||
- [Reduce Your Costs by 30% When Using GPT for Python Code](https://www.qodo.ai/blog/reduce-your-costs-by-30-when-using-gpt-3-for-python-code/)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,41 +1,2 @@
|
||||
# Interactivity
|
||||
|
||||
`Supported Git Platforms: GitHub, GitLab`
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge transforms static code reviews into interactive experiences by enabling direct actions from pull request (PR) comments.
|
||||
Developers can immediately trigger actions and apply changes with simple checkbox clicks.
|
||||
|
||||
This focused workflow maintains context while dramatically reducing the time between PR creation and final merge.
|
||||
The approach eliminates manual steps, provides clear visual indicators, and creates immediate feedback loops all within the same interface.
|
||||
|
||||
## Key Interactive Features
|
||||
|
||||
### 1\. Interactive `/improve` Tool
|
||||
|
||||
The [`/improve`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/) command delivers a comprehensive interactive experience:
|
||||
|
||||
- _**Apply this suggestion**_: Clicking this checkbox instantly converts a suggestion into a committable code change. When committed to the PR, changes made to code that was flagged for improvement will be marked with a check mark, allowing developers to easily track and review implemented recommendations.
|
||||
|
||||
- _**More**_: Triggers additional suggestions generation while keeping each suggestion focused and relevant as the original set
|
||||
|
||||
- _**Update**_: Triggers a re-analysis of the code, providing updated suggestions based on the latest changes
|
||||
|
||||
- _**Author self-review**_: Interactive acknowledgment that developers have opened and reviewed collapsed suggestions
|
||||
|
||||
### 2\. Interactive `/analyze` Tool
|
||||
|
||||
The [`/analyze`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/analyze/) command provides component-level analysis with interactive options for each identified code component:
|
||||
|
||||
- Interactive checkboxes to generate tests, documentation, and code suggestions for specific components
|
||||
|
||||
- On-demand similar code search that activates when a checkbox is clicked
|
||||
|
||||
- Component-specific actions that trigger only for the selected elements, providing focused assistance
|
||||
|
||||
### 3\. Interactive `/help` Tool
|
||||
|
||||
The [`/help`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/help/) command not only lists available tools and their descriptions but also enables immediate tool invocation through interactive checkboxes.
|
||||
When a user checks a tool's checkbox, Qodo Merge instantly triggers that tool without requiring additional commands.
|
||||
This transforms the standard help menu into an interactive launch pad for all Qodo Merge capabilities, eliminating context switching by keeping developers within their PR workflow.
|
||||
## Interactive invocation 💎
|
||||
TBD
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,5 @@
|
||||
## Local and global metadata injection with multi-stage analysis
|
||||
|
||||
1\.
|
||||
(1)
|
||||
Qodo Merge initially retrieves for each PR the following data:
|
||||
|
||||
- PR title and branch name
|
||||
@ -12,7 +11,7 @@ Qodo Merge initially retrieves for each PR the following data:
|
||||
!!! tip "Tip: Organization-level metadata"
|
||||
In addition to the inputs above, Qodo Merge can incorporate supplementary preferences provided by the user, like [`extra_instructions` and `organization best practices`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#extra-instructions-and-best-practices). This information can be used to enhance the PR analysis.
|
||||
|
||||
2\.
|
||||
(2)
|
||||
By default, the first command that Qodo Merge executes is [`describe`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/describe/), which generates three types of outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
- PR Type (e.g. bug fix, feature, refactor, etc)
|
||||
@ -24,7 +23,7 @@ This effectively enables multi-stage chain-of-thought analysis, without doing an
|
||||
|
||||
For example, when generating code suggestions for different files, Qodo Merge can inject the AI-generated ["Changes walkthrough"](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/1202#issue-2511546839) file summary in the prompt:
|
||||
|
||||
```diff
|
||||
```
|
||||
## File: 'src/file1.py'
|
||||
### AI-generated file summary:
|
||||
- edited function `func1` that does X
|
||||
@ -50,7 +49,8 @@ __old hunk__
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3\. The entire PR files that were retrieved are also used to expand and enhance the PR context (see [Dynamic Context](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/dynamic_context/)).
|
||||
(3) The entire PR files that were retrieved are also used to expand and enhance the PR context (see [Dynamic Context](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/dynamic_context/)).
|
||||
|
||||
4\. All the metadata described above represents several level of cumulative analysis - ranging from hunk level, to file level, to PR level, to organization level.
|
||||
|
||||
(4) All the metadata described above represents several level of cumulative analysis - ranging from hunk level, to file level, to PR level, to organization level.
|
||||
This comprehensive approach enables Qodo Merge AI models to generate more precise and contextually relevant suggestions and feedback.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,77 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# RAG Context Enrichment 💎
|
||||
|
||||
`Supported Git Platforms: GitHub, Bitbucket Data Center`
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info "Prerequisites"
|
||||
- RAG is available only for Qodo enterprise plan users, with single tenant or on-premises setup.
|
||||
- Database setup and codebase indexing must be completed before proceeding. [Contact support](https://www.qodo.ai/contact/) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
### What is RAG Context Enrichment?
|
||||
|
||||
A feature that enhances AI analysis by retrieving and referencing relevant code patterns from your project, enabling context-aware insights during code reviews.
|
||||
|
||||
### How does RAG Context Enrichment work?
|
||||
|
||||
Using Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), it searches your configured repositories for contextually relevant code segments, enriching pull request (PR) insights and accelerating review accuracy.
|
||||
|
||||
## Getting started
|
||||
|
||||
### Configuration options
|
||||
|
||||
In order to enable the RAG feature, add the following lines to your configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[rag_arguments]
|
||||
enable_rag=true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! example "RAG Arguments Options"
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>enable_rag</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, repository enrichment using RAG will be enabled. Default is false.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>rag_repo_list</b></td>
|
||||
<td>A list of repositories that will be used by the semantic search for RAG. Use `['all']` to consider the entire codebase or a select list of repositories, for example: ['my-org/my-repo', ...]. Default: the repository from which the PR was opened.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
### Applications
|
||||
|
||||
RAG capability is exclusively available in the following tools:
|
||||
|
||||
=== "`/review`"
|
||||
The [`/review`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/review/) tool offers the _Focus area from RAG data_ which contains feedback based on the RAG references analysis.
|
||||
The complete list of references found relevant to the PR will be shown in the _References_ section, helping developers understand the broader context by exploring the provided references.
|
||||
|
||||
{width=640}
|
||||
|
||||
=== "`/implement`"
|
||||
The [`/implement`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/implement/) tool utilizes the RAG feature to provide comprehensive context of the repository codebase, allowing it to generate more refined code output.
|
||||
The _References_ section contains links to the content used to support the code generation.
|
||||
|
||||
{width=640}
|
||||
|
||||
=== "`/ask`"
|
||||
The [`/ask`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/ask/) tool can access broader repository context through the RAG feature when answering questions that go beyond the PR scope alone.
|
||||
The _References_ section displays the additional repository content consulted to formulate the answer.
|
||||
|
||||
{width=640}
|
||||
|
||||
## Limitations
|
||||
|
||||
### Querying the codebase presents significant challenges
|
||||
|
||||
- **Search Method**: RAG uses natural language queries to find semantically relevant code sections
|
||||
- **Result Quality**: No guarantee that RAG results will be useful for all queries
|
||||
- **Scope Recommendation**: To reduce noise, focus on the PR repository rather than searching across multiple repositories
|
||||
|
||||
### This feature has several requirements and restrictions
|
||||
|
||||
- **Codebase**: Must be properly indexed for search functionality
|
||||
- **Security**: Requires secure and private indexed codebase implementation
|
||||
- **Deployment**: Only available for Qodo Merge Enterprise plan using single tenant or on-premises setup
|
||||
@ -6,6 +6,7 @@ Configuration options allow users to set a score threshold for further filtering
|
||||
|
||||
## Introduction - Efficient Review with Hierarchical Presentation
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Given that not all generated code suggestions will be relevant, it is crucial to enable users to review them in a fast and efficient way, allowing quick identification and filtering of non-applicable ones.
|
||||
|
||||
To achieve this goal, Qodo Merge offers a dedicated hierarchical structure when presenting suggestions to users:
|
||||
@ -41,9 +42,9 @@ This results in a more refined and valuable set of suggestions for the user, sav
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
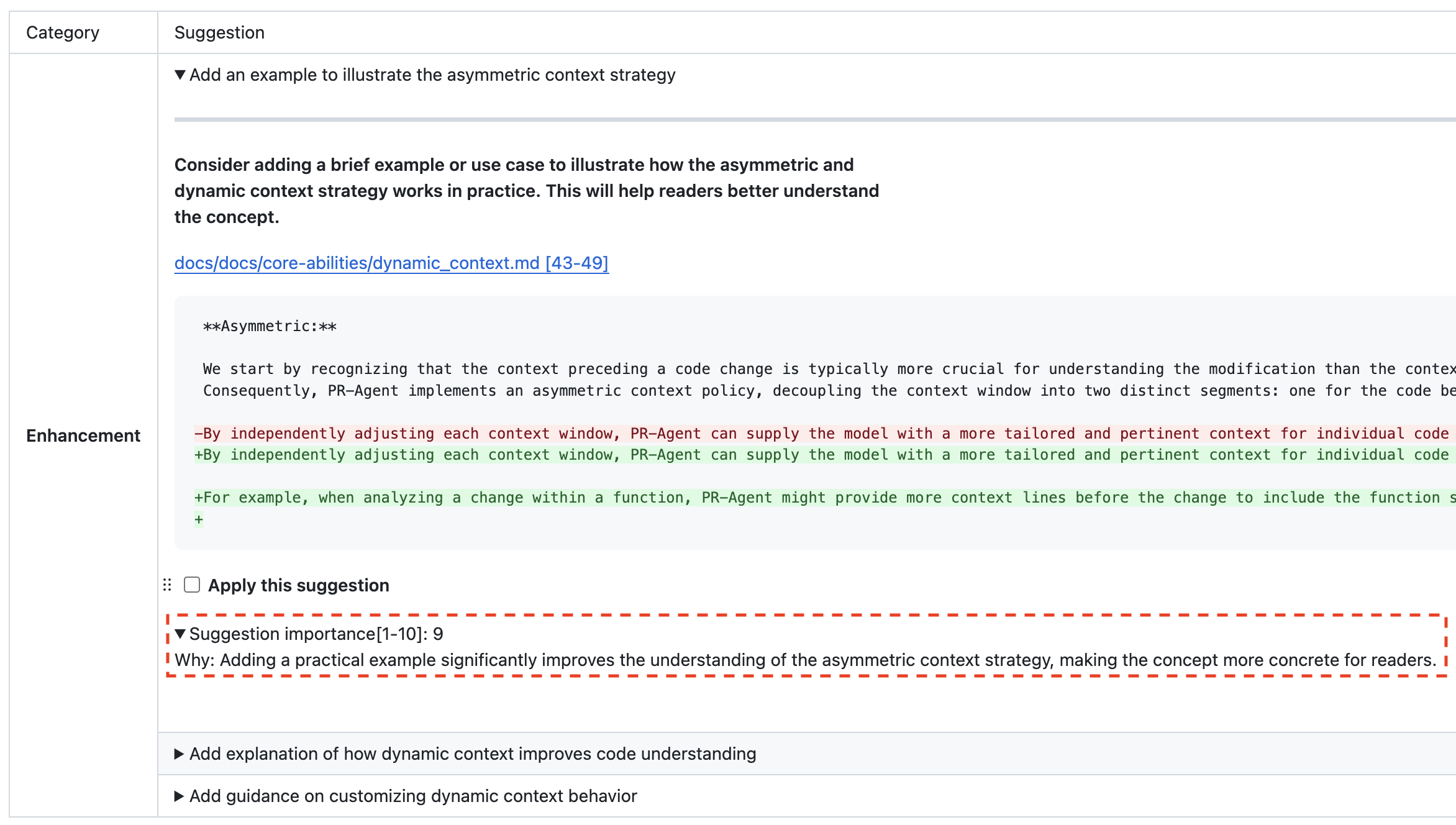{width=768}
|
||||
|
||||
## Appendix - Relevant Configuration Options
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
## Appendix - Relevant Configuration Options
|
||||
```
|
||||
[pr_code_suggestions]
|
||||
suggestions_score_threshold = 0 # Filter out suggestions with a score below this threshold (0-10)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@ -7,13 +7,14 @@ It scans the PR code changes, finds all the code components (methods, functions,
|
||||
!!! note "Language that are currently supported:"
|
||||
Python, Java, C++, JavaScript, TypeScript, C#.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Capabilities
|
||||
|
||||
### Analyze PR
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The [`analyze`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/analyze/) tool enables to interactively generate tests, docs, code suggestions and similar code search for each component that changed in the PR.
|
||||
It can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/analyze
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -28,11 +29,9 @@ Clicking on each checkbox will trigger the relevant tool for the selected compon
|
||||
|
||||
The [`test`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/test/) tool generate tests for a selected component, based on the PR code changes.
|
||||
It can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/test component_name
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
where 'component_name' is the name of a specific component in the PR, Or be triggered interactively by using the `analyze` tool.
|
||||
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
@ -41,7 +40,6 @@ where 'component_name' is the name of a specific component in the PR, Or be tri
|
||||
|
||||
The [`add_docs`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/documentation/) tool scans the PR code changes, and automatically generate docstrings for any code components that changed in the PR.
|
||||
It can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/add_docs component_name
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -51,10 +49,8 @@ Or be triggered interactively by using the `analyze` tool.
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
|
||||
### Generate Code Suggestions for a Component
|
||||
|
||||
The [`improve_component`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve_component/) tool generates code suggestions for a specific code component that changed in the PR.
|
||||
It can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/improve_component component_name
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ ___
|
||||
|
||||
#### Answer:<span style="display:none;">2</span>
|
||||
|
||||
- Modern AI models, like Claude Sonnet and GPT-4, are improving rapidly but remain imperfect. Users should critically evaluate all suggestions rather than accepting them automatically.
|
||||
- Modern AI models, like Claude 3.5 Sonnet and GPT-4, are improving rapidly but remain imperfect. Users should critically evaluate all suggestions rather than accepting them automatically.
|
||||
- AI errors are rare, but possible. A main value from reviewing the code suggestions lies in their high probability of catching **mistakes or bugs made by the PR author**. We believe it's worth spending 30-60 seconds reviewing suggestions, even if some aren't relevant, as this practice can enhance code quality and prevent bugs in production.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
93
docs/docs/finetuning_benchmark/index.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,93 @@
|
||||
# Qodo Merge Code Fine-tuning Benchmark
|
||||
|
||||
On coding tasks, the gap between open-source models and top closed-source models such as GPT4 is significant.
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
In practice, open-source models are unsuitable for most real-world code tasks, and require further fine-tuning to produce acceptable results.
|
||||
|
||||
_Qodo Merge fine-tuning benchmark_ aims to benchmark open-source models on their ability to be fine-tuned for a coding task.
|
||||
Specifically, we chose to fine-tune open-source models on the task of analyzing a pull request, and providing useful feedback and code suggestions.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are the results:
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
|
||||
**Model performance:**
|
||||
|
||||
| Model name | Model size [B] | Better than gpt-4 rate, after fine-tuning [%] |
|
||||
|-----------------------------|----------------|----------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| **DeepSeek 34B-instruct** | **34** | **40.7** |
|
||||
| DeepSeek 34B-base | 34 | 38.2 |
|
||||
| Phind-34b | 34 | 38 |
|
||||
| Granite-34B | 34 | 37.6 |
|
||||
| Codestral-22B-v0.1 | 22 | 32.7 |
|
||||
| QWEN-1.5-32B | 32 | 29 |
|
||||
| | | |
|
||||
| **CodeQwen1.5-7B** | **7** | **35.4** |
|
||||
| Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct | 8 | 35.2 |
|
||||
| Granite-8b-code-instruct | 8 | 34.2 |
|
||||
| CodeLlama-7b-hf | 7 | 31.8 |
|
||||
| Gemma-7B | 7 | 27.2 |
|
||||
| DeepSeek coder-7b-instruct | 7 | 26.8 |
|
||||
| Llama-3-8B-Instruct | 8 | 26.8 |
|
||||
| Mistral-7B-v0.1 | 7 | 16.1 |
|
||||
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
|
||||
**Fine-tuning impact:**
|
||||
|
||||
| Model name | Model size [B] | Fine-tuned | Better than gpt-4 rate [%] |
|
||||
|---------------------------|----------------|------------|----------------------------|
|
||||
| DeepSeek 34B-instruct | 34 | yes | 40.7 |
|
||||
| DeepSeek 34B-instruct | 34 | no | 3.6 |
|
||||
|
||||
## Results analysis
|
||||
|
||||
- **Fine-tuning is a must** - without fine-tuning, open-source models provide poor results on most real-world code tasks, which include complicated prompt and lengthy context. We clearly see that without fine-tuning, deepseek model was 96.4% of the time inferior to GPT-4, while after fine-tuning, it is better 40.7% of the time.
|
||||
- **Always start from a code-dedicated model** — When fine-tuning, always start from a code-dedicated model, and not from a general-usage model. The gaps in downstream results are very big.
|
||||
- **Don't believe the hype** —newer models, or models from big-tech companies (Llama3, Gemma, Mistral), are not always better for fine-tuning.
|
||||
- **The best large model** - For large 34B code-dedicated models, the gaps when doing proper fine-tuning are small. The current top model is **DeepSeek 34B-instruct**
|
||||
- **The best small model** - For small 7B code-dedicated models, the gaps when fine-tuning are much larger. **CodeQWEN 1.5-7B** is by far the best model for fine-tuning.
|
||||
- **Base vs. instruct** - For the top model (deepseek), we saw small advantage when starting from the instruct version. However, we recommend testing both versions on each specific task, as the base model is generally considered more suitable for fine-tuning.
|
||||
|
||||
## The dataset
|
||||
|
||||
### Training dataset
|
||||
|
||||
Our training dataset comprises 25,000 pull requests, aggregated from permissive license repos. For each pull request, we generated responses for the three main tools of Qodo Merge:
|
||||
[Describe](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/describe/), [Review](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/) and [Improve](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/).
|
||||
|
||||
On the raw data collected, we employed various automatic and manual cleaning techniques to ensure the outputs were of the highest quality, and suitable for instruct-tuning.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are the prompts, and example outputs, used as input-output pairs to fine-tune the models:
|
||||
|
||||
| Tool | Prompt | Example output |
|
||||
|----------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------|
|
||||
| Describe | [link](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/pr_description_prompts.toml) | [link](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/910#issue-2303989601) |
|
||||
| Review | [link](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/pr_reviewer_prompts.toml) | [link](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/910#issuecomment-2118761219) |
|
||||
| Improve | [link](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/pr_code_suggestions_prompts.toml) | [link](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/910#issuecomment-2118761309) |
|
||||
|
||||
### Evaluation dataset
|
||||
|
||||
- For each tool, we aggregated 100 additional examples to be used for evaluation. These examples were not used in the training dataset, and were manually selected to represent diverse real-world use-cases.
|
||||
- For each test example, we generated two responses: one from the fine-tuned model, and one from the best code model in the world, `gpt-4-turbo-2024-04-09`.
|
||||
|
||||
- We used a third LLM to judge which response better answers the prompt, and will likely be perceived by a human as better response.
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
|
||||
We experimented with three model as judges: `gpt-4-turbo-2024-04-09`, `gpt-4o`, and `claude-3-opus-20240229`. All three produced similar results, with the same ranking order. This strengthens the validity of our testing protocol.
|
||||
The evaluation prompt can be found [here](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/pr_evaluate_prompt_response.toml)
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example of a judge model feedback:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
command: improve
|
||||
model1_score: 9,
|
||||
model2_score: 6,
|
||||
why: |
|
||||
Response 1 is better because it provides more actionable and specific suggestions that directly
|
||||
enhance the code's maintainability, performance, and best practices. For example, it suggests
|
||||
using a variable for reusable widget instances and using named routes for navigation, which
|
||||
are practical improvements. In contrast, Response 2 focuses more on general advice and less
|
||||
actionable suggestions, such as changing variable names and adding comments, which are less
|
||||
critical for immediate code improvement."
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -9,7 +9,6 @@ Qodo Merge is a hosted version of PR-Agent, designed for companies and teams tha
|
||||
|
||||
- See the [Tools Guide](./tools/index.md) for a detailed description of the different tools.
|
||||
|
||||
- See the [Video Tutorials](https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLRTpyDOSgbwFMA_VBeKMnPLaaZKwjGBFT) for practical demonstrations on how to use the tools.
|
||||
|
||||
## Docs Smart Search
|
||||
|
||||
@ -22,82 +21,67 @@ To search the documentation site using natural language:
|
||||
|
||||
2) The bot will respond with an [answer](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/1241#issuecomment-2365259334) that includes relevant documentation links.
|
||||
|
||||
## Features
|
||||
|
||||
PR-Agent and Qodo Merge offers extensive pull request functionalities across various git providers:
|
||||
## Qodo Merge Features
|
||||
|
||||
| | | GitHub | GitLab | Bitbucket | Azure DevOps |
|
||||
| ----- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |:------:|:------:|:---------:|:------------:|
|
||||
| TOOLS | [Review](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/review/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Describe](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/describe/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Improve](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Ask](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/ask/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | ⮑ [Ask on code lines](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/ask/#ask-lines) | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Update CHANGELOG](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/update_changelog/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Help Docs](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/help_docs/?h=auto#auto-approval) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | [Ticket Context](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/fetching_ticket_context/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | [Utilizing Best Practices](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#best-practices) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | [PR Chat](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/chrome-extension/features/#pr-chat) 💎 | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | [Suggestion Tracking](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#suggestion-tracking) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [CI Feedback](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/ci_feedback/) 💎 | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | [PR Documentation](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/documentation/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Custom Labels](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/custom_labels/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Analyze](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/analyze/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Similar Code](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/similar_code/) 💎 | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | [Custom Prompt](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/custom_prompt/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | [Test](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/test/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Implement](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/implement/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | [Scan Repo Discussions](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/scan_repo_discussions/) 💎 | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | [Auto-Approve](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/?h=auto#auto-approval) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | | | | | |
|
||||
| USAGE | [CLI](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/automations_and_usage/#local-repo-cli) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [App / webhook](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/automations_and_usage/#github-app) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Tagging bot](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent#try-it-now) | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | [Actions](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/github/#run-as-a-github-action) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | | | | | |
|
||||
| CORE | [PR compression](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/compression_strategy/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
Qodo Merge offers extensive pull request functionalities across various git providers:
|
||||
|
||||
| | | GitHub | Gitlab | Bitbucket | Azure DevOps |
|
||||
|-------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|:------:|:------:|:---------:|:------------:|
|
||||
| TOOLS | Review | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | ⮑ Incremental | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | Ask | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | Describe | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | ⮑ [Inline file summary](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/describe/#inline-file-summary){:target="_blank"} 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | ✅ |
|
||||
| | Improve | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | ⮑ Extended | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Custom Prompt](./tools/custom_prompt.md){:target="_blank"} 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | Reflect and Review | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | Update CHANGELOG.md | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ️ |
|
||||
| | Find Similar Issue | ✅ | | | ️ |
|
||||
| | [Add PR Documentation](./tools/documentation.md){:target="_blank"} 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Generate Custom Labels](./tools/describe.md#handle-custom-labels-from-the-repos-labels-page-💎){:target="_blank"} 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Analyze PR Components](./tools/analyze.md){:target="_blank"} 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Test](https://pr-agent-docs.codium.ai/tools/test/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Implement](https://pr-agent-docs.codium.ai/tools/implement/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | | | | | ️ |
|
||||
| USAGE | CLI | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | App / webhook | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | Actions | ✅ | | | ️ |
|
||||
| | | | | |
|
||||
| CORE | PR compression | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | Repo language prioritization | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | Adaptive and token-aware file patch fitting | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Multiple models support](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/changing_a_model/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Local and global metadata](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/metadata/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Dynamic context](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/dynamic_context/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Self reflection](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/self_reflection/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Static code analysis](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/static_code_analysis/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Global and wiki configurations](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | |
|
||||
| | [PR interactive actions](https://www.qodo.ai/images/pr_agent/pr-actions.mp4) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Impact Evaluation](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/impact_evaluation/) 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| | [Code Validation 💎](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/code_validation/) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Auto Best Practices 💎](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/auto_best_practices/) | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | [Incremental Update 💎](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/incremental_update/) | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
!!! note "💎 means Qodo Merge only"
|
||||
All along the documentation, 💎 marks a feature available only in [Qodo Merge](https://www.codium.ai/pricing/){:target="_blank"}, and not in the open-source version.
|
||||
| | Multiple models support | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | Incremental PR review | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| | [Static code analysis](./tools/analyze.md/){:target="_blank"} 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| | [Multiple configuration options](./usage-guide/configuration_options.md){:target="_blank"} 💎 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
|
||||
💎 marks a feature available only in [Qodo Merge](https://www.codium.ai/pricing/){:target="_blank"}, and not in the open-source version.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Example Results
|
||||
|
||||
<hr>
|
||||
|
||||
#### [/describe](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/530)
|
||||
|
||||
<figure markdown="1">
|
||||
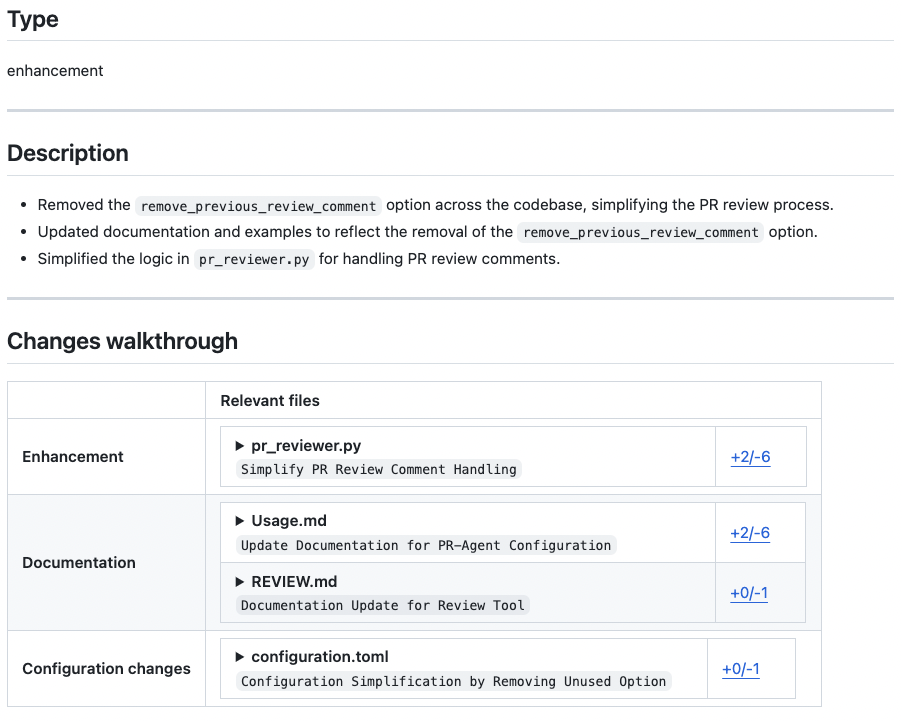{width=512}
|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
<hr>
|
||||
|
||||
#### [/review](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/732#issuecomment-1975099151)
|
||||
|
||||
<figure markdown="1">
|
||||
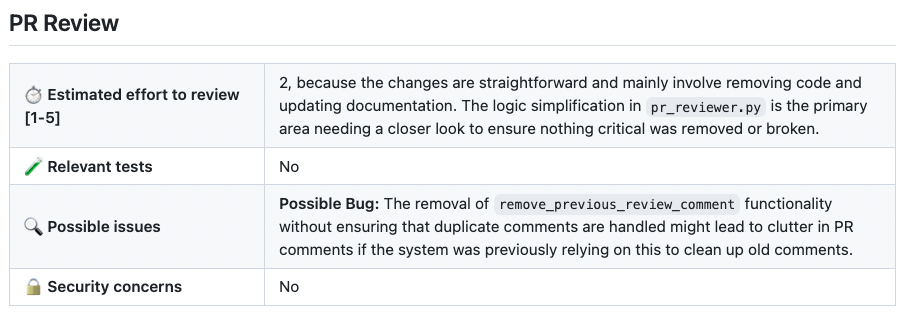{width=512}
|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
<hr>
|
||||
|
||||
#### [/improve](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/732#issuecomment-1975099159)
|
||||
|
||||
<figure markdown="1">
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
<hr>
|
||||
|
||||
#### [/generate_labels](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/530)
|
||||
|
||||
<figure markdown="1">
|
||||
{width=300}
|
||||
</figure>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
|
||||
## Azure DevOps Pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
You can use a pre-built Action Docker image to run PR-Agent as an Azure devops pipeline.
|
||||
add the following file to your repository under `azure-pipelines.yml`:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
# Opt out of CI triggers
|
||||
trigger: none
|
||||
@ -51,7 +49,6 @@ stages:
|
||||
openai__key: $(OPENAI_KEY)
|
||||
displayName: 'Run Qodo Merge'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This script will run Qodo Merge on every new merge request, with the `improve`, `review`, and `describe` commands.
|
||||
Note that you need to export the `azure_devops__pat` and `OPENAI_KEY` variables in the Azure DevOps pipeline settings (Pipelines -> Library -> + Variable group):
|
||||
|
||||
@ -64,8 +61,7 @@ Make sure to give pipeline permissions to the `pr_agent` variable group.
|
||||
## Azure DevOps from CLI
|
||||
|
||||
To use Azure DevOps provider use the following settings in configuration.toml:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
git_provider="azure"
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -78,8 +74,7 @@ If PAT was chosen, you can assign the value in .secrets.toml.
|
||||
If DefaultAzureCredential was chosen, you can assigned the additional env vars like AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET directly,
|
||||
or use managed identity/az cli (for local development) without any additional configuration.
|
||||
in any case, 'org' value must be assigned in .secrets.toml:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[azure_devops]
|
||||
org = "https://dev.azure.com/YOUR_ORGANIZATION/"
|
||||
# pat = "YOUR_PAT_TOKEN" needed only if using PAT for authentication
|
||||
@ -90,12 +85,11 @@ org = "https://dev.azure.com/YOUR_ORGANIZATION/"
|
||||
To trigger from an Azure webhook, you need to manually [add a webhook](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/devops/service-hooks/services/webhooks?view=azure-devops).
|
||||
Use the "Pull request created" type to trigger a review, or "Pull request commented on" to trigger any supported comment with /<command> <args> comment on the relevant PR. Note that for the "Pull request commented on" trigger, only API v2.0 is supported.
|
||||
|
||||
For webhook security, create a sporadic username/password pair and configure the webhook username and password on both the server and Azure DevOps webhook. These will be sent as basic Auth data by the webhook with each request:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
For webhook security, create a sporadic username/password pair and configure the webhook username and password on both the server and Azure DevOps webhook. These will be sent as basic Auth data by the webhook with each request:
|
||||
```
|
||||
[azure_devops_server]
|
||||
webhook_username = "<basic auth user>"
|
||||
webhook_password = "<basic auth password>"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> :warning: **Ensure that the webhook endpoint is only accessible over HTTPS** to mitigate the risk of credential interception when using basic authentication.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
|
||||
## Run as a Bitbucket Pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
You can use the Bitbucket Pipeline system to run PR-Agent on every pull request open or update.
|
||||
|
||||
You can use the Bitbucket Pipeline system to run Qodo Merge on every pull request open or update.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Add the following file in your repository bitbucket-pipelines.yml
|
||||
|
||||
@ -10,24 +11,23 @@ pipelines:
|
||||
'**':
|
||||
- step:
|
||||
name: PR Agent Review
|
||||
image: codiumai/pr-agent:latest
|
||||
image: python:3.10
|
||||
services:
|
||||
- docker
|
||||
script:
|
||||
- pr-agent --pr_url=https://bitbucket.org/$BITBUCKET_WORKSPACE/$BITBUCKET_REPO_SLUG/pull-requests/$BITBUCKET_PR_ID review
|
||||
- docker run -e CONFIG.GIT_PROVIDER=bitbucket -e OPENAI.KEY=$OPENAI_API_KEY -e BITBUCKET.BEARER_TOKEN=$BITBUCKET_BEARER_TOKEN codiumai/pr-agent:latest --pr_url=https://bitbucket.org/$BITBUCKET_WORKSPACE/$BITBUCKET_REPO_SLUG/pull-requests/$BITBUCKET_PR_ID review
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Add the following secure variables to your repository under Repository settings > Pipelines > Repository variables.
|
||||
|
||||
- CONFIG__GIT_PROVIDER: `bitbucket`
|
||||
- OPENAI__KEY: `<your key>`
|
||||
- BITBUCKET__AUTH_TYPE: `basic` or `bearer` (default is `bearer`)
|
||||
- BITBUCKET__BEARER_TOKEN: `<your token>` (required when auth_type is bearer)
|
||||
- BITBUCKET__BASIC_TOKEN: `<your token>` (required when auth_type is basic)
|
||||
OPENAI_API_KEY: `<your key>`
|
||||
BITBUCKET_BEARER_TOKEN: `<your token>`
|
||||
|
||||
You can get a Bitbucket token for your repository by following Repository Settings -> Security -> Access Tokens.
|
||||
For basic auth, you can generate a base64 encoded token from your username:password combination.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that comments on a PR are not supported in Bitbucket Pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Bitbucket Server and Data Center
|
||||
|
||||
Login into your on-prem instance of Bitbucket with your service account username and password.
|
||||
@ -48,16 +48,14 @@ git_provider="bitbucket_server"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and pass the Pull request URL:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
python cli.py --pr_url https://git.onpreminstanceofbitbucket.com/projects/PROJECT/repos/REPO/pull-requests/1 review
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Run it as service
|
||||
|
||||
To run PR-Agent as webhook, build the docker image:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
To run Qodo Merge as webhook, build the docker image:
|
||||
```
|
||||
docker build . -t codiumai/pr-agent:bitbucket_server_webhook --target bitbucket_server_webhook -f docker/Dockerfile
|
||||
docker push codiumai/pr-agent:bitbucket_server_webhook # Push to your Docker repository
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,46 +0,0 @@
|
||||
## Run a Gitea webhook server
|
||||
|
||||
1. In Gitea create a new user and give it "Reporter" role ("Developer" if using Pro version of the agent) for the intended group or project.
|
||||
|
||||
2. For the user from step 1. generate a `personal_access_token` with `api` access.
|
||||
|
||||
3. Generate a random secret for your app, and save it for later (`webhook_secret`). For example, you can use:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
WEBHOOK_SECRET=$(python -c "import secrets; print(secrets.token_hex(10))")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4. Clone this repository:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/qodo-ai/pr-agent.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
5. Prepare variables and secrets. Skip this step if you plan on setting these as environment variables when running the agent:
|
||||
1. In the configuration file/variables:
|
||||
- Set `config.git_provider` to "gitea"
|
||||
|
||||
2. In the secrets file/variables:
|
||||
- Set your AI model key in the respective section
|
||||
- In the [Gitea] section, set `personal_access_token` (with token from step 2) and `webhook_secret` (with secret from step 3)
|
||||
|
||||
6. Build a Docker image for the app and optionally push it to a Docker repository. We'll use Dockerhub as an example:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
docker build -f /docker/Dockerfile -t pr-agent:gitea_app --target gitea_app .
|
||||
docker push codiumai/pr-agent:gitea_webhook # Push to your Docker repository
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
7. Set the environmental variables, the method depends on your docker runtime. Skip this step if you included your secrets/configuration directly in the Docker image.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
CONFIG__GIT_PROVIDER=gitea
|
||||
GITEA__PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN=<personal_access_token>
|
||||
GITEA__WEBHOOK_SECRET=<webhook_secret>
|
||||
GITEA__URL=https://gitea.com # Or self host
|
||||
OPENAI__KEY=<your_openai_api_key>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
8. Create a webhook in your Gitea project. Set the URL to `http[s]://<PR_AGENT_HOSTNAME>/api/v1/gitea_webhooks`, the secret token to the generated secret from step 3, and enable the triggers `push`, `comments` and `merge request events`.
|
||||
|
||||
9. Test your installation by opening a merge request or commenting on a merge request using one of PR Agent's commands.
|
||||
@ -40,7 +40,6 @@ The GITHUB_TOKEN secret is automatically created by GitHub.
|
||||
When you open your next PR, you should see a comment from `github-actions` bot with a review of your PR, and instructions on how to use the rest of the tools.
|
||||
|
||||
4) You may configure Qodo Merge by adding environment variables under the env section corresponding to any configurable property in the [configuration](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml) file. Some examples:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
env:
|
||||
# ... previous environment values
|
||||
@ -48,11 +47,9 @@ When you open your next PR, you should see a comment from `github-actions` bot w
|
||||
PR_REVIEWER.REQUIRE_TESTS_REVIEW: "false" # Disable tests review
|
||||
PR_CODE_SUGGESTIONS.NUM_CODE_SUGGESTIONS: 6 # Increase number of code suggestions
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
See detailed usage instructions in the [USAGE GUIDE](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/automations_and_usage/#github-action)
|
||||
|
||||
### Using a specific release
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip ""
|
||||
if you want to pin your action to a specific release (v0.23 for example) for stability reasons, use:
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
@ -75,7 +72,6 @@ See detailed usage instructions in the [USAGE GUIDE](https://qodo-merge-docs.qod
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Action for GitHub enterprise server
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip ""
|
||||
To use the action with a GitHub enterprise server, add an environment variable `GITHUB.BASE_URL` with the API URL of your GitHub server.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -86,10 +82,10 @@ See detailed usage instructions in the [USAGE GUIDE](https://qodo-merge-docs.qod
|
||||
GITHUB.BASE_URL: "https://github.mycompany.com/api/v3"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Run as a GitHub App
|
||||
|
||||
Allowing you to automate the review process on your private or public repositories.
|
||||
|
||||
1) Create a GitHub App from the [Github Developer Portal](https://docs.github.com/en/developers/apps/creating-a-github-app).
|
||||
@ -106,7 +102,7 @@ Allowing you to automate the review process on your private or public repositori
|
||||
|
||||
2) Generate a random secret for your app, and save it for later. For example, you can use:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
```
|
||||
WEBHOOK_SECRET=$(python -c "import secrets; print(secrets.token_hex(10))")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@ -117,29 +113,28 @@ WEBHOOK_SECRET=$(python -c "import secrets; print(secrets.token_hex(10))")
|
||||
|
||||
4) Clone this repository:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
```
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
5) Copy the secrets template file and fill in the following:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
```
|
||||
cp pr_agent/settings/.secrets_template.toml pr_agent/settings/.secrets.toml
|
||||
# Edit .secrets.toml file
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- Your OpenAI key.
|
||||
- Copy your app's private key to the private_key field.
|
||||
- Copy your app's ID to the app_id field.
|
||||
- Copy your app's webhook secret to the webhook_secret field.
|
||||
- Set deployment_type to 'app' in [configuration.toml](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml)
|
||||
- Your OpenAI key.
|
||||
- Copy your app's private key to the private_key field.
|
||||
- Copy your app's ID to the app_id field.
|
||||
- Copy your app's webhook secret to the webhook_secret field.
|
||||
- Set deployment_type to 'app' in [configuration.toml](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml)
|
||||
|
||||
> The .secrets.toml file is not copied to the Docker image by default, and is only used for local development.
|
||||
> If you want to use the .secrets.toml file in your Docker image, you can add remove it from the .dockerignore file.
|
||||
> In most production environments, you would inject the secrets file as environment variables or as mounted volumes.
|
||||
> For example, in order to inject a secrets file as a volume in a Kubernetes environment you can update your pod spec to include the following,
|
||||
> assuming you have a secret named `pr-agent-settings` with a key named `.secrets.toml`:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
volumes:
|
||||
- name: settings-volume
|
||||
@ -157,7 +152,7 @@ cp pr_agent/settings/.secrets_template.toml pr_agent/settings/.secrets.toml
|
||||
|
||||
6) Build a Docker image for the app and optionally push it to a Docker repository. We'll use Dockerhub as an example:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
```
|
||||
docker build . -t codiumai/pr-agent:github_app --target github_app -f docker/Dockerfile
|
||||
docker push codiumai/pr-agent:github_app # Push to your Docker repository
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -185,18 +180,14 @@ For example: `GITHUB.WEBHOOK_SECRET` --> `GITHUB__WEBHOOK_SECRET`
|
||||
|
||||
1. Follow steps 1-5 from [here](#run-as-a-github-app).
|
||||
2. Build a docker image that can be used as a lambda function
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
docker buildx build --platform=linux/amd64 . -t codiumai/pr-agent:serverless -f docker/Dockerfile.lambda
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Push image to ECR
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
docker tag codiumai/pr-agent:serverless <AWS_ACCOUNT>.dkr.ecr.<AWS_REGION>.amazonaws.com/codiumai/pr-agent:serverless
|
||||
docker push <AWS_ACCOUNT>.dkr.ecr.<AWS_REGION>.amazonaws.com/codiumai/pr-agent:serverless
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4. Create a lambda function that uses the uploaded image. Set the lambda timeout to be at least 3m.
|
||||
5. Configure the lambda function to have a Function URL.
|
||||
6. In the environment variables of the Lambda function, specify `AZURE_DEVOPS_CACHE_DIR` to a writable location such as /tmp. (see [link](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/450#issuecomment-1840242269))
|
||||
@ -210,27 +201,28 @@ For example: `GITHUB.WEBHOOK_SECRET` --> `GITHUB__WEBHOOK_SECRET`
|
||||
Not all features have been added to CodeCommit yet. As of right now, CodeCommit has been implemented to run the Qodo Merge CLI on the command line, using AWS credentials stored in environment variables. (More features will be added in the future.) The following is a set of instructions to have Qodo Merge do a review of your CodeCommit pull request from the command line:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Create an IAM user that you will use to read CodeCommit pull requests and post comments
|
||||
- Note: That user should have CLI access only, not Console access
|
||||
* Note: That user should have CLI access only, not Console access
|
||||
2. Add IAM permissions to that user, to allow access to CodeCommit (see IAM Role example below)
|
||||
3. Generate an Access Key for your IAM user
|
||||
4. Set the Access Key and Secret using environment variables (see Access Key example below)
|
||||
5. Set the `git_provider` value to `codecommit` in the `pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml` settings file
|
||||
6. Set the `PYTHONPATH` to include your `pr-agent` project directory
|
||||
- Option A: Add `PYTHONPATH="/PATH/TO/PROJECTS/pr-agent` to your `.env` file
|
||||
- Option B: Set `PYTHONPATH` and run the CLI in one command, for example:
|
||||
- `PYTHONPATH="/PATH/TO/PROJECTS/pr-agent python pr_agent/cli.py [--ARGS]`
|
||||
* Option A: Add `PYTHONPATH="/PATH/TO/PROJECTS/pr-agent` to your `.env` file
|
||||
* Option B: Set `PYTHONPATH` and run the CLI in one command, for example:
|
||||
* `PYTHONPATH="/PATH/TO/PROJECTS/pr-agent python pr_agent/cli.py [--ARGS]`
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### AWS CodeCommit IAM Role Example
|
||||
|
||||
Example IAM permissions to that user to allow access to CodeCommit:
|
||||
|
||||
- Note: The following is a working example of IAM permissions that has read access to the repositories and write access to allow posting comments
|
||||
- Note: If you only want pr-agent to review your pull requests, you can tighten the IAM permissions further, however this IAM example will work, and allow the pr-agent to post comments to the PR
|
||||
- Note: You may want to replace the `"Resource": "*"` with your list of repos, to limit access to only those repos
|
||||
* Note: The following is a working example of IAM permissions that has read access to the repositories and write access to allow posting comments
|
||||
* Note: If you only want pr-agent to review your pull requests, you can tighten the IAM permissions further, however this IAM example will work, and allow the pr-agent to post comments to the PR
|
||||
* Note: You may want to replace the `"Resource": "*"` with your list of repos, to limit access to only those repos
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
```
|
||||
{
|
||||
"Version": "2012-10-17",
|
||||
"Statement": [
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
|
||||
## Run as a GitLab Pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
You can use a pre-built Action Docker image to run PR-Agent as a GitLab pipeline. This is a simple way to get started with Qodo Merge without setting up your own server.
|
||||
|
||||
(1) Add the following file to your repository under `.gitlab-ci.yml`:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
stages:
|
||||
- pr_agent
|
||||
@ -28,10 +26,10 @@ pr_agent_job:
|
||||
rules:
|
||||
- if: '$CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == "merge_request_event"'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This script will run Qodo Merge on every new merge request. You can modify the `rules` section to run Qodo Merge on different events.
|
||||
You can also modify the `script` section to run different Qodo Merge commands, or with different parameters by exporting different environment variables.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
(2) Add the following masked variables to your GitLab repository (CI/CD -> Variables):
|
||||
|
||||
- `GITLAB_PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN`: Your GitLab personal access token.
|
||||
@ -42,49 +40,39 @@ Note that if your base branches are not protected, don't set the variables as `p
|
||||
|
||||
> **Note**: The `$CI_SERVER_FQDN` variable is available starting from GitLab version 16.10. If you're using an earlier version, this variable will not be available. However, you can combine `$CI_SERVER_HOST` and `$CI_SERVER_PORT` to achieve the same result. Please ensure you're using a compatible version or adjust your configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Run a GitLab webhook server
|
||||
|
||||
1. In GitLab create a new user and give it "Reporter" role ("Developer" if using Pro version of the agent) for the intended group or project.
|
||||
1. From the GitLab workspace or group, create an access token with "Reporter" role ("Developer" if using Pro version of the agent) and "api" scope.
|
||||
|
||||
2. For the user from step 1. generate a `personal_access_token` with `api` access.
|
||||
2. Generate a random secret for your app, and save it for later. For example, you can use:
|
||||
|
||||
3. Generate a random secret for your app, and save it for later (`shared_secret`). For example, you can use:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
SHARED_SECRET=$(python -c "import secrets; print(secrets.token_hex(10))")
|
||||
```
|
||||
WEBHOOK_SECRET=$(python -c "import secrets; print(secrets.token_hex(10))")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4. Clone this repository:
|
||||
3. Clone this repository:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/qodo-ai/pr-agent.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
5. Prepare variables and secrets. Skip this step if you plan on setting these as environment variables when running the agent:
|
||||
1. In the configuration file/variables:
|
||||
- Set `config.git_provider` to "gitlab"
|
||||
4. Prepare variables and secrets. Skip this step if you plan on settings these as environment variables when running the agent:
|
||||
1. In the configuration file/variables:
|
||||
- Set `deployment_type` to "gitlab"
|
||||
|
||||
2. In the secrets file/variables:
|
||||
2. In the secrets file/variables:
|
||||
- Set your AI model key in the respective section
|
||||
- In the [gitlab] section, set `personal_access_token` (with token from step 2) and `shared_secret` (with secret from step 3)
|
||||
- In the [gitlab] section, set `personal_access_token` (with token from step 1) and `shared_secret` (with secret from step 2)
|
||||
|
||||
6. Build a Docker image for the app and optionally push it to a Docker repository. We'll use Dockerhub as an example:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
5. Build a Docker image for the app and optionally push it to a Docker repository. We'll use Dockerhub as an example:
|
||||
```
|
||||
docker build . -t gitlab_pr_agent --target gitlab_webhook -f docker/Dockerfile
|
||||
docker push codiumai/pr-agent:gitlab_webhook # Push to your Docker repository
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
7. Set the environmental variables, the method depends on your docker runtime. Skip this step if you included your secrets/configuration directly in the Docker image.
|
||||
6. Create a webhook in GitLab. Set the URL to ```http[s]://<PR_AGENT_HOSTNAME>/webhook```, the secret token to the generated secret from step 2, and enable the triggers `push`, `comments` and `merge request events`.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
CONFIG__GIT_PROVIDER=gitlab
|
||||
GITLAB__PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN=<personal_access_token>
|
||||
GITLAB__SHARED_SECRET=<shared_secret>
|
||||
GITLAB__URL=https://gitlab.com
|
||||
OPENAI__KEY=<your_openai_api_key>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
8. Create a webhook in your GitLab project. Set the URL to `http[s]://<PR_AGENT_HOSTNAME>/webhook`, the secret token to the generated secret from step 3, and enable the triggers `push`, `comments` and `merge request events`.
|
||||
|
||||
9. Test your installation by opening a merge request or commenting on a merge request using one of PR Agent's commands.
|
||||
7. Test your installation by opening a merge request or commenting on a merge request using one of CodiumAI's commands.
|
||||
boxes
|
||||
|
||||
@ -9,10 +9,8 @@ There are several ways to use self-hosted PR-Agent:
|
||||
- [GitLab integration](./gitlab.md)
|
||||
- [BitBucket integration](./bitbucket.md)
|
||||
- [Azure DevOps integration](./azure.md)
|
||||
- [Gitea integration](./gitea.md)
|
||||
|
||||
## Qodo Merge 💎
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge, an app hosted by QodoAI for GitHub\GitLab\BitBucket, is also available.
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
With Qodo Merge, installation is as simple as adding the Qodo Merge app to your relevant repositories.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,58 +1,40 @@
|
||||
To run PR-Agent locally, you first need to acquire two keys:
|
||||
|
||||
1. An OpenAI key from [here](https://platform.openai.com/api-keys){:target="_blank"}, with access to GPT-4 and o4-mini (or a key for other [language models](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/changing_a_model/), if you prefer).
|
||||
2. A personal access token from your Git platform (GitHub, GitLab, BitBucket,Gitea) with repo scope. GitHub token, for example, can be issued from [here](https://github.com/settings/tokens){:target="_blank"}
|
||||
1. An OpenAI key from [here](https://platform.openai.com/api-keys){:target="_blank"}, with access to GPT-4 (or a key for other [language models](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/changing_a_model/), if you prefer).
|
||||
2. A personal access token from your Git platform (GitHub, GitLab, BitBucket) with repo scope. GitHub token, for example, can be issued from [here](https://github.com/settings/tokens){:target="_blank"}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Using Docker image
|
||||
|
||||
A list of the relevant tools can be found in the [tools guide](../tools/).
|
||||
A list of the relevant tools can be found in the [tools guide](../tools/ask.md).
|
||||
|
||||
To invoke a tool (for example `review`), you can run PR-Agent directly from the Docker image. Here's how:
|
||||
|
||||
- For GitHub:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
```
|
||||
docker run --rm -it -e OPENAI.KEY=<your key> -e GITHUB.USER_TOKEN=<your token> codiumai/pr-agent:latest --pr_url <pr_url> review
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you are using GitHub enterprise server, you need to specify the custom url as variable.
|
||||
For example, if your GitHub server is at `https://github.mycompany.com`, add the following to the command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
```
|
||||
-e GITHUB.BASE_URL=https://github.mycompany.com/api/v3
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- For GitLab:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
```
|
||||
docker run --rm -it -e OPENAI.KEY=<your key> -e CONFIG.GIT_PROVIDER=gitlab -e GITLAB.PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN=<your token> codiumai/pr-agent:latest --pr_url <pr_url> review
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you have a dedicated GitLab instance, you need to specify the custom url as variable:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
```
|
||||
-e GITLAB.URL=<your gitlab instance url>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- For BitBucket:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
```
|
||||
docker run --rm -it -e CONFIG.GIT_PROVIDER=bitbucket -e OPENAI.KEY=$OPENAI_API_KEY -e BITBUCKET.BEARER_TOKEN=$BITBUCKET_BEARER_TOKEN codiumai/pr-agent:latest --pr_url=<pr_url> review
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- For Gitea:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
docker run --rm -it -e OPENAI.KEY=<your key> -e CONFIG.GIT_PROVIDER=gitea -e GITEA.PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN=<your token> codiumai/pr-agent:latest --pr_url <pr_url> review
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you have a dedicated Gitea instance, you need to specify the custom url as variable:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
-e GITEA.URL=<your gitea instance url>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
For other git providers, update `CONFIG.GIT_PROVIDER` accordingly and check the [`pr_agent/settings/.secrets_template.toml`](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/.secrets_template.toml) file for environment variables expected names and values.
|
||||
|
||||
### Utilizing environment variables
|
||||
@ -64,7 +46,7 @@ The `<TABLE>` refers to a table/section in a configuration file and `<KEY>=<VALU
|
||||
For example, suppose you want to run `pr_agent` that connects to a self-hosted GitLab instance similar to an example above.
|
||||
You can define the environment variables in a plain text file named `.env` with the following content:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
```
|
||||
CONFIG__GIT_PROVIDER="gitlab"
|
||||
GITLAB__URL="<your url>"
|
||||
GITLAB__PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN="<your token>"
|
||||
@ -94,7 +76,7 @@ Same goes for other providers, make sure to check the [documentation](https://qo
|
||||
|
||||
Install the package:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
```
|
||||
pip install pr-agent
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@ -127,17 +109,18 @@ if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
main()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Run from source
|
||||
|
||||
1. Clone this repository:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
```
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Navigate to the `/pr-agent` folder and install the requirements in your favorite virtual environment:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
```
|
||||
pip install -e .
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@ -145,7 +128,7 @@ pip install -e .
|
||||
|
||||
3. Copy the secrets template file and fill in your OpenAI key and your GitHub user token:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
```
|
||||
cp pr_agent/settings/.secrets_template.toml pr_agent/settings/.secrets.toml
|
||||
chmod 600 pr_agent/settings/.secrets.toml
|
||||
# Edit .secrets.toml file
|
||||
@ -153,7 +136,7 @@ chmod 600 pr_agent/settings/.secrets.toml
|
||||
|
||||
4. Run the cli.py script:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
```
|
||||
python3 -m pr_agent.cli --pr_url <pr_url> review
|
||||
python3 -m pr_agent.cli --pr_url <pr_url> ask <your question>
|
||||
python3 -m pr_agent.cli --pr_url <pr_url> describe
|
||||
@ -165,7 +148,6 @@ python3 -m pr_agent.cli --issue_url <issue_url> similar_issue
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[Optional] Add the pr_agent folder to your PYTHONPATH
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
```
|
||||
export PYTHONPATH=$PYTHONPATH:<PATH to pr_agent folder>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,21 +1,9 @@
|
||||
Qodo Merge is a versatile application compatible with GitHub, GitLab, and BitBucket, hosted by QodoAI.
|
||||
See [here](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/overview/pr_agent_pro/) for more details about the benefits of using Qodo Merge.
|
||||
|
||||
## Trial Period and Licensing
|
||||
|
||||
### Cloud Users with Teams Account
|
||||
|
||||
A complimentary two-week trial is provided to all new users (with three additional grace usages). When the trial period ends, users will stop receiving feedback from Qodo Merge.
|
||||
|
||||
Following the trial period, user licenses (seats) are required for continued access. Each user requires an individual seat license.
|
||||
After purchasing seats, the team owner can assign them to specific users through the management portal.
|
||||
|
||||
With an assigned seat, users can seamlessly deploy the application across any of their code repositories.
|
||||
|
||||
### Enterprise Account
|
||||
|
||||
For organizations who require an Enterprise account, please [contact](https://www.qodo.ai/contact/#pricing) us to initiate a trial period, and to discuss pricing and licensing options.
|
||||
|
||||
A complimentary two-week trial is provided to all new users. Following the trial period, user licenses (seats) are required for continued access.
|
||||
To purchase user licenses, please visit our [pricing page](https://www.qodo.ai/pricing/).
|
||||
Once subscribed, users can seamlessly deploy the application across any of their code repositories.
|
||||
|
||||
## Install Qodo Merge for GitHub
|
||||
|
||||
@ -45,6 +33,7 @@ Qodo Merge for Bitbucket Cloud is available for installation through the followi
|
||||
|
||||
To use Qodo Merge application on your private Bitbucket Server, you will need to contact us for starting an [Enterprise](https://www.qodo.ai/pricing/) trial.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Install Qodo Merge for GitLab
|
||||
|
||||
### GitLab Cloud
|
||||
|
||||
@ -10,6 +10,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
- No passive collection of Code and Pull Requests’ data — Qodo Merge will be active only when you invoke it, and it will then extract and analyze only data relevant to the executed command and queried pull request.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Qodo Merge Chrome extension
|
||||
|
||||
- The [Qodo Merge Chrome extension](https://chromewebstore.google.com/detail/pr-agent-chrome-extension/ephlnjeghhogofkifjloamocljapahnl) will not send your code to any external servers.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -15,11 +15,11 @@ Qodo Merge is designed for companies and teams that require additional features
|
||||
|
||||
### Additional features
|
||||
|
||||
Here are some of the additional features and capabilities that Qodo Merge offers, and are not available in the open-source version of PR-Agent:
|
||||
Here are some of the additional features and capabilities that Qodo Merge offers:
|
||||
|
||||
| Feature | Description |
|
||||
| -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| [**Model selection**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/PR_agent_pro_models/) | Choose the model that best fits your needs, among top models like `Claude Sonnet`, `o4-mini` |
|
||||
|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| [**Model selection**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/PR_agent_pro_models/) | Choose the model that best fits your needs, among top models like `GPT4` and `Claude-Sonnet-3.5`
|
||||
| [**Global and wiki configuration**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/) | Control configurations for many repositories from a single location; <br>Edit configuration of a single repo without committing code |
|
||||
| [**Apply suggestions**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#overview) | Generate committable code from the relevant suggestions interactively by clicking on a checkbox |
|
||||
| [**Suggestions impact**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#assessing-impact) | Automatically mark suggestions that were implemented by the user (either directly in GitHub, or indirectly in the IDE) to enable tracking of the impact of the suggestions |
|
||||
@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ Here are some of the additional features and capabilities that Qodo Merge offers
|
||||
Here are additional tools that are available only for Qodo Merge users:
|
||||
|
||||
| Feature | Description |
|
||||
| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-------------|
|
||||
| [**Custom Prompt Suggestions**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/custom_prompt/) | Generate code suggestions based on custom prompts from the user |
|
||||
| [**Analyze PR components**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/analyze/) | Identify the components that changed in the PR, and enable to interactively apply different tools to them |
|
||||
| [**Tests**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/test/) | Generate tests for code components that changed in the PR |
|
||||
@ -43,9 +43,10 @@ Here are additional tools that are available only for Qodo Merge users:
|
||||
| [**Similar code search**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/similar_code/) | Search for similar code in the repository, organization, or entire GitHub |
|
||||
| [**Code implementation**](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/implement/) | Generates implementation code from review suggestions |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Supported languages
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge leverages the world's leading code models, such as Claude 3.7 Sonnet and o3-mini.
|
||||
Qodo Merge leverages the world's leading code models - Claude 3.5 Sonnet and GPT-4.
|
||||
As a result, its primary tools such as `describe`, `review`, and `improve`, as well as the PR-chat feature, support virtually all programming languages.
|
||||
|
||||
For specialized commands that require static code analysis, Qodo Merge offers support for specific languages. For more details about features that require static code analysis, please refer to the [documentation](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/analyze/#overview).
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,201 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Qodo Merge Pull Request Benchmark
|
||||
|
||||
## Methodology
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge PR Benchmark evaluates and compares the performance of two Large Language Models (LLMs) in analyzing pull request code and providing meaningful code suggestions.
|
||||
Our diverse dataset comprises of 400 pull requests from over 100 repositories, spanning various programming languages and frameworks to reflect real-world scenarios.
|
||||
|
||||
- For each pull request, two distinct LLMs process the same prompt using the Qodo Merge `improve` tool, each generating two sets of responses. The prompt for response generation can be found [here](https://github.com/qodo-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/code_suggestions/pr_code_suggestions_prompts_not_decoupled.toml).
|
||||
|
||||
- Subsequently, a high-performing third model (an AI judge) evaluates the responses from the initial two models to determine the superior one. We utilize OpenAI's `o3` model as the judge, though other models have yielded consistent results. The prompt for this comparative judgment is available [here](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent-settings/tree/main/benchmark).
|
||||
|
||||
- We aggregate comparison outcomes across all the pull requests, calculating the win rate for each model. We also analyze the qualitative feedback (the "why" explanations from the judge) to identify each model's comparative strengths and weaknesses.
|
||||
This approach provides not just a quantitative score but also a detailed analysis of each model's strengths and weaknesses.
|
||||
|
||||
- For each model we build a "Model Card", comparing it against others. To ensure full transparency and enable community scrutiny, we also share the raw code suggestions generated by each model, and the judge's specific feedback. See example for the full output [here](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent-settings/blob/main/benchmark/sonnet_37_vs_gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06.md)
|
||||
|
||||
Note that this benchmark focuses on quality: the ability of an LLM to process complex pull request with multiple files and nuanced task to produce high-quality code suggestions.
|
||||
Other factors like speed, cost, and availability, while also relevant for model selection, are outside this benchmark's scope.
|
||||
|
||||
## TL;DR
|
||||
|
||||
Here's a summary of the win rates based on the benchmark:
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (| Model A | Model B | Model A Win Rate | Model B Win Rate |)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (|:-------------------------------|:-------------------------------|:----------------:|:----------------:|)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (| Gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06 | GPT-4.1 | 70.4% | 29.6% |)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (| Gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06 | Sonnet 3.7 | 78.1% | 21.9% |)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (| GPT-4.1 | Sonnet 3.7 | 61.0% | 39.0% |)
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<thead>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<th style="text-align:left;">Model A</th>
|
||||
<th style="text-align:left;">Model B</th>
|
||||
<th style="text-align:center;">Model A Win Rate</th> <th style="text-align:center;">Model B Win Rate</th> </tr>
|
||||
</thead>
|
||||
<tbody>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style="text-align:left;">Gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06</td>
|
||||
<td style="text-align:left;">GPT-4.1</td>
|
||||
<td style="text-align:center; color: #1E8449;"><b>70.4%</b></td> <td style="text-align:center; color: #D8000C;"><b>29.6%</b></td> </tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style="text-align:left;">Gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06</td>
|
||||
<td style="text-align:left;">Sonnet 3.7</td>
|
||||
<td style="text-align:center; color: #1E8449;"><b>78.1%</b></td> <td style="text-align:center; color: #D8000C;"><b>21.9%</b></td> </tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style="text-align:left;">Gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06</td>
|
||||
<td style="text-align:left;">Gemini-2.5-flash-preview-04-17</td>
|
||||
<td style="text-align:center; color: #1E8449;"><b>73.0%</b></td> <td style="text-align:center; color: #D8000C;"><b>27.0%</b></td> </tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style="text-align:left;">Gemini-2.5-flash-preview-04-17</td>
|
||||
<td style="text-align:left;">GPT-4.1</td>
|
||||
<td style="text-align:center; color: #1E8449;"><b>54.6%</b></td> <td style="text-align:center; color: #D8000C;"><b>45.4%</b></td> </tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style="text-align:left;">Gemini-2.5-flash-preview-04-17</td>
|
||||
<td style="text-align:left;">Sonnet 3.7</td>
|
||||
<td style="text-align:center; color: #1E8449;"><b>60.6%</b></td> <td style="text-align:center; color: #D8000C;"><b>39.4%</b></td> </tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td style="text-align:left;">GPT-4.1</td>
|
||||
<td style="text-align:left;">Sonnet 3.7</td>
|
||||
<td style="text-align:center; color: #1E8449;"><b>61.0%</b></td> <td style="text-align:center; color: #D8000C;"><b>39.0%</b></td> </tr>
|
||||
</tbody>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06 - Model Card
|
||||
|
||||
### Comparison against GPT-4.1
|
||||
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
|
||||
#### Analysis Summary
|
||||
|
||||
Model 'Gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06' is generally more useful thanks to wider and more accurate bug detection and concrete patches, but it sacrifices compliance discipline and sometimes oversteps the task rules. Model 'GPT-4.1' is safer and highly rule-abiding, yet often too timid—missing many genuine issues and providing limited insight. An ideal reviewer would combine 'GPT-4.1’ restraint with 'Gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06' thoroughness.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Detailed Analysis
|
||||
|
||||
Gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06 strengths:
|
||||
|
||||
- better_bug_coverage: Detects and explains more critical issues, winning in ~70 % of comparisons and achieving a higher average score.
|
||||
- actionable_fixes: Supplies clear code snippets, correct language labels, and often multiple coherent suggestions per diff.
|
||||
- deeper_reasoning: Shows stronger grasp of logic, edge cases, and cross-file implications, leading to broader, high-impact reviews.
|
||||
|
||||
Gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06 weaknesses:
|
||||
|
||||
- guideline_violations: More prone to over-eager advice—non-critical tweaks, touching unchanged code, suggesting new imports, or minor format errors.
|
||||
- occasional_overreach: Some fixes are speculative or risky, potentially introducing new bugs.
|
||||
- redundant_or_duplicate: At times repeats the same point or exceeds the required brevity.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Comparison against Sonnet 3.7
|
||||
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
|
||||
#### Analysis Summary
|
||||
|
||||
Model 'Gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06' is the stronger reviewer—more frequently identifies genuine, high-impact bugs and provides well-formed, actionable fixes. Model 'Sonnet 3.7' is safer against false positives and tends to be concise but often misses important defects or offers low-value or incorrect suggestions.
|
||||
|
||||
See raw results [here](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent-settings/blob/main/benchmark/sonnet_37_vs_gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06.md)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Detailed Analysis
|
||||
|
||||
Gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06 strengths:
|
||||
|
||||
- higher_accuracy_and_coverage: finds real critical bugs and supplies actionable patches in most examples (better in 78 % of cases).
|
||||
- guideline_awareness: usually respects new-lines-only scope, ≤3 suggestions, proper YAML, and stays silent when no issues exist.
|
||||
- detailed_reasoning_and_patches: explanations tie directly to the diff and fixes are concrete, often catching multiple related defects that 'Sonnet 3.7' overlooks.
|
||||
|
||||
Gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06 weaknesses:
|
||||
|
||||
- occasional_rule_violations: sometimes proposes new imports, package-version changes, or edits outside the added lines.
|
||||
- overzealous_suggestions: may add speculative or stylistic fixes that exceed the “critical” scope, or mis-label severity.
|
||||
- sporadic_technical_slips: a few patches contain minor coding errors, oversized snippets, or duplicate/contradicting advice.
|
||||
|
||||
## GPT-4.1 - Model Card
|
||||
|
||||
### Comparison against Sonnet 3.7
|
||||
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
|
||||
#### Analysis Summary
|
||||
|
||||
Model 'GPT-4.1' is safer and more compliant, preferring silence over speculation, which yields fewer rule breaches and false positives but misses some real bugs.
|
||||
Model 'Sonnet 3.7' is more adventurous and often uncovers important issues that 'GPT-4.1' ignores, yet its aggressive style leads to frequent guideline violations and a higher proportion of incorrect or non-critical advice.
|
||||
|
||||
See raw results [here](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent-settings/blob/main/benchmark/gpt-4.1_vs_sonnet_3.7_judge_o3.md)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Detailed Analysis
|
||||
|
||||
GPT-4.1 strengths:
|
||||
- Strong guideline adherence: usually stays strictly on `+` lines, avoids non-critical or stylistic advice, and rarely suggests forbidden imports; often outputs an empty list when no real bug exists.
|
||||
- Lower false-positive rate: suggestions are more accurate and seldom introduce new bugs; fixes compile more reliably.
|
||||
- Good schema discipline: YAML is almost always well-formed and fields are populated correctly.
|
||||
|
||||
GPT-4.1 weaknesses:
|
||||
- Misses bugs: often returns an empty list even when a clear critical issue is present, so coverage is narrower.
|
||||
- Sparse feedback: when it does comment, it tends to give fewer suggestions and sometimes lacks depth or completeness.
|
||||
- Occasional metadata/slip-ups (wrong language tags, overly broad code spans), though less harmful than Sonnet 3.7 errors.
|
||||
|
||||
### Comparison against Gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06
|
||||
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
|
||||
#### Analysis Summary
|
||||
|
||||
Model 'Gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06' is generally more useful thanks to wider and more accurate bug detection and concrete patches, but it sacrifices compliance discipline and sometimes oversteps the task rules. Model 'GPT-4.1' is safer and highly rule-abiding, yet often too timid—missing many genuine issues and providing limited insight. An ideal reviewer would combine 'GPT-4.1’ restraint with 'Gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06' thoroughness.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Detailed Analysis
|
||||
|
||||
GPT-4.1 strengths:
|
||||
- strict_compliance: Usually sticks to the “critical bugs only / new ‘+’ lines only” rule, so outputs rarely violate task constraints.
|
||||
- low_risk: Conservative behaviour avoids harmful or speculative fixes; safer when no obvious issue exists.
|
||||
- concise_formatting: Tends to produce minimal, correctly-structured YAML without extra noise.
|
||||
|
||||
GPT-4.1 weaknesses:
|
||||
- under_detection: Frequently returns an empty list even when real bugs are present, missing ~70 % of the time.
|
||||
- shallow_analysis: When it does suggest fixes, coverage is narrow and technical depth is limited, sometimes with wrong language tags or minor format slips.
|
||||
- occasional_inaccuracy: A few suggestions are unfounded or duplicate, and rare guideline breaches (e.g., import advice) still occur.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Sonnet 3.7 - Model Card
|
||||
|
||||
### Comparison against GPT-4.1
|
||||
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
|
||||
#### Analysis Summary
|
||||
|
||||
Model 'GPT-4.1' is safer and more compliant, preferring silence over speculation, which yields fewer rule breaches and false positives but misses some real bugs.
|
||||
Model 'Sonnet 3.7' is more adventurous and often uncovers important issues that 'GPT-4.1' ignores, yet its aggressive style leads to frequent guideline violations and a higher proportion of incorrect or non-critical advice.
|
||||
|
||||
See raw results [here](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent-settings/blob/main/benchmark/gpt-4.1_vs_sonnet_3.7_judge_o3.md)
|
||||
|
||||
#### Detailed Analysis
|
||||
|
||||
'Sonnet 3.7' strengths:
|
||||
- Better bug discovery breadth: more willing to dive into logic and spot critical problems that 'GPT-4.1' overlooks; often supplies multiple, detailed fixes.
|
||||
- Richer explanations & patches: gives fuller context and, when correct, proposes more functional or user-friendly solutions.
|
||||
- Generally correct language/context tagging and targeted code snippets.
|
||||
|
||||
'Sonnet 3.7' weaknesses:
|
||||
- Guideline violations: frequently flags non-critical issues, edits untouched code, or recommends adding imports, breaching task rules.
|
||||
- Higher error rate: suggestions are more speculative and sometimes introduce new defects or duplicate work already done.
|
||||
- Occasional schema or formatting mistakes (missing list value, duplicated suggestions), reducing reliability.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Comparison against Gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06
|
||||
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
|
||||
#### Analysis Summary
|
||||
|
||||
Model 'Gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06' is the stronger reviewer—more frequently identifies genuine, high-impact bugs and provides well-formed, actionable fixes. Model 'Sonnet 3.7' is safer against false positives and tends to be concise but often misses important defects or offers low-value or incorrect suggestions.
|
||||
|
||||
See raw results [here](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent-settings/blob/main/benchmark/sonnet_37_vs_gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06.md)
|
||||
@ -1,22 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Recent Updates and Future Roadmap
|
||||
|
||||
`Page last updated: 2025-05-11`
|
||||
|
||||
This page summarizes recent enhancements to Qodo Merge (last three months).
|
||||
|
||||
It also outlines our development roadmap for the upcoming three months. Please note that the roadmap is subject to change, and features may be adjusted, added, or reprioritized.
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Recent Updates"
|
||||
- **Qodo Merge Pull Request Benchmark** - evaluating the performance of LLMs in analyzing pull request code ([Learn more](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/pr_benchmark/))
|
||||
- **Chat on Suggestions**: Users can now chat with Qodo Merge code suggestions ([Learn more](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#chat-on-code-suggestions))
|
||||
- **Scan Repo Discussions Tool**: A new tool that analyzes past code discussions to generate a `best_practices.md` file, distilling key insights and recommendations. ([Learn more](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/scan_repo_discussions/))
|
||||
- **Enhanced Models**: Qodo Merge now defaults to a combination of top models (Claude Sonnet 3.7 and Gemini 2.5 Pro) and incorporates dedicated code validation logic for improved results. ([Details 1](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/qodo_merge_models/), [Details 2](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/code_validation/))
|
||||
- **Chrome Extension Update**: Qodo Merge Chrome extension now supports single-tenant users. ([Learn more](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/chrome-extension/options/#configuration-options/))
|
||||
- **Installation Metrics**: Upon installation, Qodo Merge analyzes past PRs for key metrics (e.g., time to merge, time to first reviewer feedback), enabling pre/post-installation comparison to calculate ROI.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Future Roadmap"
|
||||
- **Smart Update**: Upon PR updates, Qodo Merge will offer tailored code suggestions, addressing both the entire PR and the specific incremental changes since the last feedback.
|
||||
- **CLI Endpoint**: A new Qodo Merge endpoint will accept lists of before/after code changes, execute Qodo Merge commands, and return the results.
|
||||
- **Simplified Free Tier**: We plan to transition from a two-week free trial to a free tier offering a limited number of suggestions per month per organization.
|
||||
- **Best Practices Hierarchy**: Introducing support for structured best practices, such as for folders in monorepos or a unified best practice file for a group of repositories.
|
||||
@ -1,11 +1,9 @@
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The `analyze` tool combines advanced static code analysis with LLM capabilities to provide a comprehensive analysis of the PR code changes.
|
||||
|
||||
The tool scans the PR code changes, finds the code components (methods, functions, classes) that changed, and enables to interactively generate tests, docs, code suggestions and similar code search for each component.
|
||||
|
||||
It can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/analyze
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -16,5 +14,6 @@ An example result:
|
||||
|
||||
{width=750}
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Language that are currently supported:"
|
||||
Python, Java, C++, JavaScript, TypeScript, C#.
|
||||
**Notes**
|
||||
|
||||
- Language that are currently supported: Python, Java, C++, JavaScript, TypeScript, C#.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2,7 +2,6 @@
|
||||
|
||||
The `ask` tool answers questions about the PR, based on the PR code changes. Make sure to be specific and clear in your questions.
|
||||
It can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/ask "..."
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -16,7 +15,6 @@ It can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
## Ask lines
|
||||
|
||||
You can run `/ask` on specific lines of code in the PR from the PR's diff view. The tool will answer questions based on the code changes in the selected lines.
|
||||
|
||||
- Click on the '+' sign next to the line number to select the line.
|
||||
- To select multiple lines, click on the '+' sign of the first line and then hold and drag to select the rest of the lines.
|
||||
- write `/ask "..."` in the comment box and press `Add single comment` button.
|
||||
@ -30,33 +28,32 @@ Note that the tool does not have "memory" of previous questions, and answers eac
|
||||
You can also ask questions about images that appear in the comment, where the entire PR code will be used as context.
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
The basic syntax is:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/ask "..."
|
||||
|
||||
[Image](https://real_link_to_image)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
where `https://real_link_to_image` is the direct link to the image.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that GitHub has a built-in mechanism of pasting images in comments. However, pasted image does not provide a direct link.
|
||||
To get a direct link to an image, we recommend using the following scheme:
|
||||
|
||||
1\. First, post a comment that contains **only** the image:
|
||||
1) First, post a comment that contains **only** the image:
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
2\. Quote reply to that comment:
|
||||
2) Quote reply to that comment:
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
3\. In the screen opened, type the question below the image:
|
||||
3) In the screen opened, type the question below the image:
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
4\. Post the comment, and receive the answer:
|
||||
4) Post the comment, and receive the answer:
|
||||
|
||||
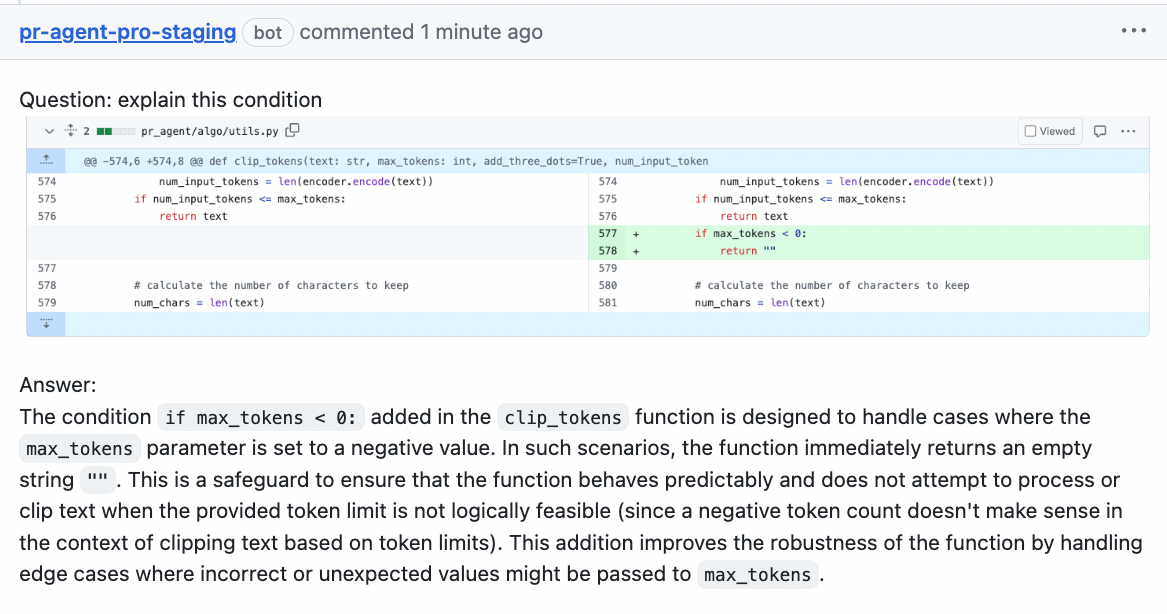{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
See a full video tutorial [here](https://codium.ai/images/pr_agent/ask_image_video.mov)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -18,24 +18,20 @@ The tool analyzes the failed checks and provides several feedbacks:
|
||||
___
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to being automatically triggered, the tool can also be invoked manually by commenting on a PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/checks "https://github.com/{repo_name}/actions/runs/{run_number}/job/{job_number}"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
where `{repo_name}` is the name of the repository, `{run_number}` is the run number of the failed check, and `{job_number}` is the job number of the failed check.
|
||||
|
||||
## Disabling the tool from running automatically
|
||||
|
||||
If you wish to disable the tool from running automatically, you can do so by adding the following configuration to the configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[checks]
|
||||
enable_auto_checks_feedback = false
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuration options
|
||||
|
||||
- `enable_auto_checks_feedback` - if set to true, the tool will automatically provide feedback when a check is failed. Default is true.
|
||||
- `excluded_checks_list` - a list of checks to exclude from the feedback, for example: ["check1", "check2"]. Default is an empty list.
|
||||
- `persistent_comment` - if set to true, the tool will overwrite a previous checks comment with the new feedback. Default is true.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The `generate_labels` tool scans the PR code changes, and given a list of labels and their descriptions, it automatically suggests labels that match the PR code changes.
|
||||
|
||||
It can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/generate_labels
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -21,26 +19,21 @@ When running the `generate_labels` tool on a PR that includes changes in SQL que
|
||||
Note that in addition to the dedicated tool `generate_labels`, the custom labels will also be used by the `describe` tool.
|
||||
|
||||
### How to enable custom labels
|
||||
|
||||
There are 3 ways to enable custom labels:
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1. CLI (local configuration file)
|
||||
|
||||
When working from CLI, you need to apply the [configuration changes](#configuration-options) to the [custom_labels file](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/custom_labels.toml):
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. Repo configuration file
|
||||
|
||||
To enable custom labels, you need to apply the [configuration changes](#configuration-options) to the local `.pr_agent.toml` file in your repository.
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3. Handle custom labels from the Repo's labels page 💎
|
||||
|
||||
> This feature is available only in Qodo Merge
|
||||
|
||||
* GitHub : `https://github.com/{owner}/{repo}/labels`, or click on the "Labels" tab in the issues or PRs page.
|
||||
* GitLab : `https://gitlab.com/{owner}/{repo}/-/labels`, or click on "Manage" -> "Labels" on the left menu.
|
||||
|
||||
b. Add/edit the custom labels. It should be formatted as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
* Label name: The name of the custom label.
|
||||
* Description: Start the description of with prefix `pr_agent:`, for example: `pr_agent: Description of when AI should suggest this label`.<br>
|
||||
The description should be comprehensive and detailed, indicating when to add the desired label.
|
||||
@ -52,9 +45,8 @@ c. Now the custom labels will be included in the `generate_labels` tool.
|
||||
> This feature is supported in GitHub and GitLab.
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuration options
|
||||
|
||||
* Change `enable_custom_labels` to True: This will turn off the default labels and enable the custom labels provided in the custom_labels.toml file.
|
||||
* Add the custom labels. It should be formatted as follows:
|
||||
- Change `enable_custom_labels` to True: This will turn off the default labels and enable the custom labels provided in the custom_labels.toml file.
|
||||
- Add the custom labels. It should be formatted as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,4 @@
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The `custom_prompt` tool scans the PR code changes, and automatically generates suggestions for improving the PR code.
|
||||
It shares similarities with the `improve` tool, but with one main difference: the `custom_prompt` tool will **only propose suggestions that follow specific guidelines defined by the prompt** in: `pr_custom_prompt.prompt` configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -18,7 +17,7 @@ The code suggestions should focus only on the following:
|
||||
|
||||
With a [configuration file](../usage-guide/automations_and_usage.md#github-app), use the following template:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[pr_custom_prompt]
|
||||
prompt="""\
|
||||
The suggestions should focus only on the following:
|
||||
@ -34,8 +33,7 @@ You might benefit from several trial-and-error iterations, until you get the cor
|
||||
## Example usage
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example of a possible prompt, defined in the configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[pr_custom_prompt]
|
||||
prompt="""\
|
||||
The code suggestions should focus only on the following:
|
||||
@ -53,8 +51,8 @@ Results obtained with the prompt above:
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuration options
|
||||
|
||||
- `prompt`: the prompt for the tool. It should be a multi-line string.
|
||||
`prompt`: the prompt for the tool. It should be a multi-line string.
|
||||
|
||||
- `num_code_suggestions_per_chunk`: number of code suggestions provided by the 'custom_prompt' tool, per chunk. Default is 3.
|
||||
`num_code_suggestions`: number of code suggestions provided by the 'custom_prompt' tool. Default is 4.
|
||||
|
||||
- `enable_help_text`: if set to true, the tool will display a help text in the comment. Default is true.
|
||||
`enable_help_text`: if set to true, the tool will display a help text in the comment. Default is true.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The `describe` tool scans the PR code changes, and generates a description for the PR - title, type, summary, walkthrough and labels.
|
||||
|
||||
The tool can be triggered automatically every time a new PR is [opened](../usage-guide/automations_and_usage.md#github-app-automatic-tools-when-a-new-pr-is-opened), or it can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/describe
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -21,7 +19,6 @@ After ~30 seconds, the tool will generate a description for the PR:
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to edit [configurations](#configuration-options), add the relevant ones to the command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/describe --pr_description.some_config1=... --pr_description.some_config2=...
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -29,7 +26,6 @@ If you want to edit [configurations](#configuration-options), add the relevant o
|
||||
### Automatic triggering
|
||||
|
||||
To run the `describe` automatically when a PR is opened, define in a [configuration file](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/#wiki-configuration-file):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[github_app]
|
||||
pr_commands = [
|
||||
@ -45,37 +41,12 @@ publish_labels = true
|
||||
- The `pr_commands` lists commands that will be executed automatically when a PR is opened.
|
||||
- The `[pr_description]` section contains the configurations for the `describe` tool you want to edit (if any).
|
||||
|
||||
## Preserving the original user description
|
||||
|
||||
By default, Qodo Merge preserves your original PR description by placing it above the generated content.
|
||||
This requires including your description during the initial PR creation.
|
||||
Be aware that if you edit the description while the automated tool is running, a race condition may occur, potentially causing your original description to be lost.
|
||||
|
||||
When updating PR descriptions, the `/describe` tool considers everything above the "PR Type" field as user content and will preserve it.
|
||||
Everything below this marker is treated as previously auto-generated content and will be replaced.
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
### Sequence Diagram Support
|
||||
When the `enable_pr_diagram` option is enabled in your configuration, the `/describe` tool will include a `Mermaid` sequence diagram in the PR description.
|
||||
|
||||
This diagram represents interactions between components/functions based on the diff content.
|
||||
|
||||
### How to enable
|
||||
|
||||
In your configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
toml
|
||||
[pr_description]
|
||||
enable_pr_diagram = true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuration options
|
||||
|
||||
!!! example "Possible configurations"
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>publish_labels</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will publish labels to the PR. Default is false.</td>
|
||||
@ -124,11 +95,8 @@ enable_pr_diagram = true
|
||||
<td><b>enable_help_text</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will display a help text in the comment. Default is false.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>enable_pr_diagram</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will generate a horizontal Mermaid flowchart summarizing the main pull request changes. This field remains empty if not applicable. Default is false.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Inline file summary 💎
|
||||
|
||||
@ -152,13 +120,13 @@ If you prefer to have the file summaries appear in the "Files changed" tab on ev
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: that this feature is currently available only for GitHub.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Markers template
|
||||
|
||||
To enable markers, set `pr_description.use_description_markers=true`.
|
||||
Markers enable to easily integrate user's content and auto-generated content, with a template-like mechanism.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, if the PR original description was:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
User content...
|
||||
|
||||
@ -171,22 +139,21 @@ pr_agent:summary
|
||||
## PR Walkthrough:
|
||||
pr_agent:walkthrough
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The marker `pr_agent:type` will be replaced with the PR type, `pr_agent:summary` will be replaced with the PR summary, and `pr_agent:walkthrough` will be replaced with the PR walkthrough.
|
||||
|
||||
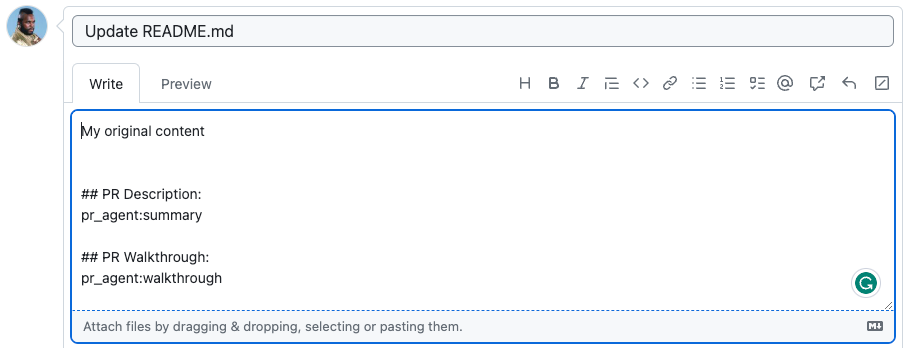{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
becomes
|
||||
→
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Configuration params**:
|
||||
|
||||
- `use_description_markers`: if set to true, the tool will use markers template. It replaces every marker of the form `pr_agent:marker_name` with the relevant content. Default is false.
|
||||
- `include_generated_by_header`: if set to true, the tool will add a dedicated header: 'Generated by PR Agent at ...' to any automatic content. Default is true.
|
||||
|
||||
## Custom labels
|
||||
|
||||
The default labels of the describe tool are quite generic, since they are meant to be used in any repo: [`Bug fix`, `Tests`, `Enhancement`, `Documentation`, `Other`].
|
||||
|
||||
You can define custom labels that are relevant for your repo and use cases.
|
||||
@ -196,9 +163,7 @@ Make sure to provide proper title, and a detailed and well-phrased description f
|
||||
Each label description should be a **conditional statement**, that indicates if to add the label to the PR or not, according to the PR content.
|
||||
|
||||
### Handle custom labels from a configuration file
|
||||
|
||||
Example for a custom labels configuration setup in a configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
enable_custom_labels=true
|
||||
@ -217,25 +182,26 @@ description = "use when a PR primarily contains new tests"
|
||||
|
||||
You can also control the custom labels that will be suggested by the `describe` tool from the repo's labels page:
|
||||
|
||||
- GitHub : go to `https://github.com/{owner}/{repo}/labels` (or click on the "Labels" tab in the issues or PRs page)
|
||||
- GitLab : go to `https://gitlab.com/{owner}/{repo}/-/labels` (or click on "Manage" -> "Labels" on the left menu)
|
||||
* GitHub : go to `https://github.com/{owner}/{repo}/labels` (or click on the "Labels" tab in the issues or PRs page)
|
||||
* GitLab : go to `https://gitlab.com/{owner}/{repo}/-/labels` (or click on "Manage" -> "Labels" on the left menu)
|
||||
|
||||
Now add/edit the custom labels. they should be formatted as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
- Label name: The name of the custom label.
|
||||
- Description: Start the description of with prefix `pr_agent:`, for example: `pr_agent: Description of when AI should suggest this label`.<br>
|
||||
* Label name: The name of the custom label.
|
||||
* Description: Start the description of with prefix `pr_agent:`, for example: `pr_agent: Description of when AI should suggest this label`.<br>
|
||||
|
||||
Examples for custom labels:
|
||||
|
||||
- `Main topic:performance` - pr_agent:The main topic of this PR is performance
|
||||
- `New endpoint` - pr_agent:A new endpoint was added in this PR
|
||||
- `SQL query` - pr_agent:A new SQL query was added in this PR
|
||||
- `Dockerfile changes` - pr_agent:The PR contains changes in the Dockerfile
|
||||
- ...
|
||||
- `Main topic:performance` - pr_agent:The main topic of this PR is performance
|
||||
- `New endpoint` - pr_agent:A new endpoint was added in this PR
|
||||
- `SQL query` - pr_agent:A new SQL query was added in this PR
|
||||
- `Dockerfile changes` - pr_agent:The PR contains changes in the Dockerfile
|
||||
- ...
|
||||
|
||||
The description should be comprehensive and detailed, indicating when to add the desired label. For example:
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage Tips
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip "Automation"
|
||||
@ -245,15 +211,14 @@ The description should be comprehensive and detailed, indicating when to add the
|
||||
```
|
||||
meaning the `describe` tool will run automatically on every PR, with the default configurations.
|
||||
|
||||
- Markers are an alternative way to control the generated description, to give maximal control to the user. If you set:
|
||||
|
||||
- Markers are an alternative way to control the generated description, to give maximal control to the user. If you set:
|
||||
```
|
||||
pr_commands = ["/describe --pr_description.use_description_markers=true", ...]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
the tool will replace every marker of the form `pr_agent:marker_name` in the PR description with the relevant content, where `marker_name` is one of the following:
|
||||
*`type`: the PR type.
|
||||
* `type`: the PR type.
|
||||
* `summary`: the PR summary.
|
||||
* `walkthrough`: the PR walkthrough.
|
||||
|
||||
- Note that when markers are enabled, if the original PR description does not contain any markers, the tool will not alter the description at all.
|
||||
- Note that when markers are enabled, if the original PR description does not contain any markers, the tool will not alter the description at all.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The `add_docs` tool scans the PR code changes, and automatically suggests documentation for any code components that changed in the PR (functions, classes, etc.).
|
||||
|
||||
It can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/add_docs
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -21,39 +19,15 @@ The tool will generate documentation for all the components that changed in the
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
|
||||
You can state a name of a specific component in the PR to get documentation only for that component:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/add_docs component_name
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Manual triggering
|
||||
|
||||
Comment `/add_docs` on a PR to invoke it manually.
|
||||
|
||||
## Automatic triggering
|
||||
|
||||
To automatically run the `add_docs` tool when a pull request is opened, define in a [configuration file](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/):
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[github_app]
|
||||
pr_commands = [
|
||||
"/add_docs",
|
||||
...
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The `pr_commands` list defines commands that run automatically when a PR is opened.
|
||||
Since this is under the [github_app] section, it only applies when using the Qodo Merge GitHub App in GitHub environments.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note
|
||||
By default, /add_docs is not triggered automatically. You must explicitly include it in pr_commands to enable this behavior.
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuration options
|
||||
- `docs_style`: The exact style of the documentation (for python docstring). you can choose between: `google`, `numpy`, `sphinx`, `restructuredtext`, `plain`. Default is `sphinx`.
|
||||
- `extra_instructions`: Optional extra instructions to the tool. For example: "focus on the changes in the file X. Ignore change in ...".
|
||||
|
||||
- `docs_style`: The exact style of the documentation (for python docstring). you can choose between: `google`, `numpy`, `sphinx`, `restructuredtext`, `plain`. Default is `sphinx`.
|
||||
- `extra_instructions`: Optional extra instructions to the tool. For example: "focus on the changes in the file X. Ignore change in ...".
|
||||
**Notes**
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Notes"
|
||||
- The following languages are currently supported: Python, Java, C++, JavaScript, TypeScript, C#.
|
||||
- This tool can also be triggered interactively by using the [`analyze`](./analyze.md) tool.
|
||||
- Language that are currently fully supported: Python, Java, C++, JavaScript, TypeScript, C#.
|
||||
- This tool can also be triggered interactively by using the [`analyze`](./analyze.md) tool.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,16 +1,13 @@
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The `help` tool provides a list of all the available tools and their descriptions.
|
||||
For Qodo Merge users, it also enables to trigger each tool by checking the relevant box.
|
||||
|
||||
It can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/help
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Example usage
|
||||
|
||||
An example [result](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/546#issuecomment-1868524805):
|
||||
|
||||
{width=750}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,110 +0,0 @@
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The `help_docs` tool can answer a free-text question based on a git documentation folder.
|
||||
|
||||
It can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR or Issue:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/help_docs "..."
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Or configured to be triggered automatically when a [new issue is opened](#run-as-a-github-action).
|
||||
|
||||
The tool assumes by default that the documentation is located in the root of the repository, at `/docs` folder.
|
||||
However, this can be customized by setting the `docs_path` configuration option:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[pr_help_docs]
|
||||
repo_url = "" # The repository to use as context
|
||||
docs_path = "docs" # The documentation folder
|
||||
repo_default_branch = "main" # The branch to use in case repo_url overwritten
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
See more configuration options in the [Configuration options](#configuration-options) section.
|
||||
|
||||
## Example usage
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (#### Asking a question about this repository:)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ({width=512})
|
||||
|
||||
**Asking a question about another repository**
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
**Response**:
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
## Run automatically when a new issue is opened
|
||||
|
||||
You can configure PR-Agent to run `help_docs` automatically on any newly created issue.
|
||||
This can be useful, for example, for providing immediate feedback to users who open issues with questions on open-source projects with extensive documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
Here's how:
|
||||
|
||||
1) Follow the steps depicted under [Run as a Github Action](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/github/#run-as-a-github-action) to create a new workflow, such as:`.github/workflows/help_docs.yml`:
|
||||
|
||||
2) Edit your yaml file to the following:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
name: Run pr agent on every opened issue, respond to user comments on an issue
|
||||
|
||||
#When the action is triggered
|
||||
on:
|
||||
issues:
|
||||
types: [opened] #New issue
|
||||
|
||||
# Read env. variables
|
||||
env:
|
||||
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
GITHUB_API_URL: ${{ github.api_url }}
|
||||
GIT_REPO_URL: ${{ github.event.repository.clone_url }}
|
||||
ISSUE_URL: ${{ github.event.issue.html_url || github.event.comment.html_url }}
|
||||
ISSUE_BODY: ${{ github.event.issue.body || github.event.comment.body }}
|
||||
OPENAI_KEY: ${{ secrets.OPENAI_KEY }}
|
||||
|
||||
# The actual set of actions
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
issue_agent:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
if: ${{ github.event.sender.type != 'Bot' }} #Do not respond to bots
|
||||
|
||||
# Set required permissions
|
||||
permissions:
|
||||
contents: read # For reading repository contents
|
||||
issues: write # For commenting on issues
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Run PR Agent on Issues
|
||||
if: ${{ env.ISSUE_URL != '' }}
|
||||
uses: docker://codiumai/pr-agent:latest
|
||||
with:
|
||||
entrypoint: /bin/bash #Replace invoking cli.py directly with a shell
|
||||
args: |
|
||||
-c "cd /app && \
|
||||
echo 'Running Issue Agent action step on ISSUE_URL=$ISSUE_URL' && \
|
||||
export config__git_provider='github' && \
|
||||
export github__user_token=$GITHUB_TOKEN && \
|
||||
export github__base_url=$GITHUB_API_URL && \
|
||||
export openai__key=$OPENAI_KEY && \
|
||||
python -m pr_agent.cli --issue_url=$ISSUE_URL --pr_help_docs.repo_url="..." --pr_help_docs.docs_path="..." --pr_help_docs.openai_key=$OPENAI_KEY && \help_docs \"$ISSUE_BODY\""
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3) Following completion of the remaining steps (such as adding secrets and relevant configurations, such as `repo_url` and `docs_path`) merge this change to your main branch.
|
||||
When a new issue is opened, you should see a comment from `github-actions` bot with an auto response, assuming the question is related to the documentation of the repository.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuration options
|
||||
|
||||
Under the section `pr_help_docs`, the [configuration file](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml#L50) contains options to customize the 'help docs' tool:
|
||||
|
||||
- `repo_url`: If not overwritten, will use the repo from where the context came from (issue or PR), otherwise - use the given repo as context.
|
||||
- `repo_default_branch`: The branch to use in case repo_url overwritten, otherwise - has no effect.
|
||||
- `docs_path`: Relative path from root of repository (either the one this PR has been issued for, or above repo url).
|
||||
- `exclude_root_readme`: Whether or not to exclude the root README file for querying the model.
|
||||
- `supported_doc_exts` : Which file extensions should be included for the purpose of querying the model.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
@ -7,51 +7,46 @@ It leverages LLM technology to transform PR comments and review suggestions into
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage Scenarios
|
||||
|
||||
=== "For Reviewers"
|
||||
|
||||
Reviewers can request code changes by:
|
||||
### For Reviewers
|
||||
|
||||
1. Selecting the code block to be modified.
|
||||
2. Adding a comment with the syntax:
|
||||
Reviewers can request code changes by: <br>
|
||||
1. Selecting the code block to be modified. <br>
|
||||
2. Adding a comment with the syntax:
|
||||
```
|
||||
/implement <code-change-description>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/implement <code-change-description>
|
||||
```
|
||||
{width=640}
|
||||
|
||||
{width=640}
|
||||
|
||||
=== "For PR Authors"
|
||||
### For PR Authors
|
||||
|
||||
PR authors can implement suggested changes by replying to a review comment using either:
|
||||
PR authors can implement suggested changes by replying to a review comment using either: <br>
|
||||
1. Add specific implementation details as described above
|
||||
```
|
||||
/implement <code-change-description>
|
||||
```
|
||||
2. Use the original review comment as instructions
|
||||
```
|
||||
/implement
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
1. Add specific implementation details as described above
|
||||
{width=640}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/implement <code-change-description>
|
||||
```
|
||||
### For Referencing Comments
|
||||
|
||||
2. Use the original review comment as instructions
|
||||
You can reference and implement changes from any comment by:
|
||||
```
|
||||
/implement <link-to-review-comment>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/implement
|
||||
```
|
||||
{width=640}
|
||||
|
||||
{width=640}
|
||||
Note that the implementation will occur within the review discussion thread.
|
||||
|
||||
=== "For Referencing Comments"
|
||||
|
||||
You can reference and implement changes from any comment by:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/implement <link-to-review-comment>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
{width=640}
|
||||
|
||||
Note that the implementation will occur within the review discussion thread.
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuration options
|
||||
|
||||
- Use `/implement` to implement code change within and based on the review discussion.
|
||||
- Use `/implement <code-change-description>` inside a review discussion to implement specific instructions.
|
||||
- Use `/implement <link-to-review-comment>` to indirectly call the tool from any comment.
|
||||
**Configuration options** <br>
|
||||
- Use `/implement` to implement code change within and based on the review discussion. <br>
|
||||
- Use `/implement <code-change-description>` inside a review discussion to implement specific instructions. <br>
|
||||
- Use `/implement <link-to-review-comment>` to indirectly call the tool from any comment. <br>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,26 +1,16 @@
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The `improve` tool scans the PR code changes, and automatically generates meaningful suggestions for improving the PR code.
|
||||
The `improve` tool scans the PR code changes, and automatically generates [meaningful](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/pr_code_suggestions_prompts.toml#L41) suggestions for improving the PR code.
|
||||
The tool can be triggered automatically every time a new PR is [opened](../usage-guide/automations_and_usage.md#github-app-automatic-tools-when-a-new-pr-is-opened), or it can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
/improve
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## How it looks
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Suggestions Overview"
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Selecting a specific suggestion"
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
Note that the `Apply this suggestion` checkbox, which interactively converts a suggestion into a commitable code comment, is available only for Qodo Merge💎 users.
|
||||
|
||||
___
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "The following features are available only for Qodo Merge 💎 users:"
|
||||
- The `Apply / Chat` checkbox, which interactively converts a suggestion into a committable code comment
|
||||
- The `More` checkbox to generate additional suggestions
|
||||
- On Bitbucket (Cloud & Data Center) and GitLab Server (v16 and earlier), you can invoke [More Suggestions manually](#manual-more-suggestions)
|
||||
|
||||
## Example usage
|
||||
|
||||
@ -28,34 +18,25 @@ ___
|
||||
|
||||
Invoke the tool manually by commenting `/improve` on any PR. The code suggestions by default are presented as a single comment:
|
||||
|
||||
To edit [configurations](#configuration-options) related to the `improve` tool, use the following template:
|
||||
|
||||
To edit [configurations](#configuration-options) related to the improve tool, use the following template:
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
/improve --pr_code_suggestions.some_config1=... --pr_code_suggestions.some_config2=...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For example, you can choose to present all the suggestions as committable code comments, by running the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
For example, you can choose to present all the suggestions as commitable code comments, by running the following command:
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
/improve --pr_code_suggestions.commitable_code_suggestions=true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
As can be seen, a single table comment has a significantly smaller PR footprint. We recommend this mode for most cases.
|
||||
Also note that collapsible are not supported in _Bitbucket_. Hence, the suggestions can only be presented in Bitbucket as code comments.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Manual more suggestions
|
||||
To generate more suggestions (distinct from the ones already generated), for git-providers that don't support interactive checkbox option, you can manually run:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/improve --more_suggestions=true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Automatic triggering
|
||||
|
||||
To run the `improve` automatically when a PR is opened, define in a [configuration file](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/#wiki-configuration-file):
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[github_app]
|
||||
pr_commands = [
|
||||
@ -71,26 +52,23 @@ num_code_suggestions_per_chunk = ...
|
||||
- The `pr_commands` lists commands that will be executed automatically when a PR is opened.
|
||||
- The `[pr_code_suggestions]` section contains the configurations for the `improve` tool you want to edit (if any)
|
||||
|
||||
### Assessing Impact
|
||||
### Assessing Impact 💎
|
||||
|
||||
>`💎 feature`
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge tracks two types of implementations for tracking implemented suggestions:
|
||||
Note that Qodo Merge tracks two types of implementations:
|
||||
|
||||
- Direct implementation - when the user directly applies the suggestion by clicking the `Apply` checkbox.
|
||||
- Indirect implementation - when the user implements the suggestion in their IDE environment. In this case, Qodo Merge will utilize, after each commit, a dedicated logic to identify if a suggestion was implemented, and will mark it as implemented.
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
In post-process, Qodo Merge counts the number of suggestions that were implemented, and provides general statistics and insights about the suggestions' impact on the PR process.
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
## Suggestion tracking
|
||||
|
||||
>`💎 feature. Platforms supported: GitHub, GitLab`
|
||||
## Suggestion tracking 💎
|
||||
`Platforms supported: GitHub, GitLab`
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge employs a novel detection system to automatically [identify](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/impact_evaluation/) AI code suggestions that PR authors have accepted and implemented.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -123,35 +101,34 @@ The `improve` tool can be further customized by providing additional instruction
|
||||
|
||||
### Extra instructions
|
||||
|
||||
>`Platforms supported: GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, Azure DevOps`
|
||||
|
||||
You can use the `extra_instructions` configuration option to give the AI model additional instructions for the `improve` tool.
|
||||
Be specific, clear, and concise in the instructions. With extra instructions, you are the prompter.
|
||||
|
||||
Examples for possible instructions:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[pr_code_suggestions]
|
||||
extra_instructions="""\
|
||||
(1) Answer in Japanese
|
||||
(1) Answer in japanese
|
||||
(2) Don't suggest to add try-except block
|
||||
(3) Ignore changes in toml files
|
||||
...
|
||||
"""
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Use triple quotes to write multi-line instructions. Use bullet points or numbers to make the instructions more readable.
|
||||
|
||||
### Best practices
|
||||
### Best practices 💎
|
||||
|
||||
> `💎 feature. Platforms supported: GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket`
|
||||
>`Platforms supported: GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket`
|
||||
|
||||
Another option to give additional guidance to the AI model is by creating a `best_practices.md` file in your repository's root directory.
|
||||
Another option to give additional guidance to the AI model is by creating a `best_practices.md` file, either in your repository's root directory or as a [**wiki page**](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/wiki) (we recommend the wiki page, as editing and maintaining it over time is easier).
|
||||
This page can contain a list of best practices, coding standards, and guidelines that are specific to your repo/organization.
|
||||
|
||||
The AI model will use this `best_practices.md` file as a reference, and in case the PR code violates any of the guidelines, it will create additional suggestions, with a dedicated label: `Organization
|
||||
The AI model will use this wiki page as a reference, and in case the PR code violates any of the guidelines, it will create additional suggestions, with a dedicated label: `Organization
|
||||
best practice`.
|
||||
|
||||
Example for a Python `best_practices.md` content:
|
||||
|
||||
Example for a python `best_practices.md` content:
|
||||
```markdown
|
||||
## Project best practices
|
||||
- Make sure that I/O operations are encapsulated in a try-except block
|
||||
@ -171,28 +148,19 @@ Tips for writing an effective `best_practices.md` file:
|
||||
- AI models may not process effectively very long documents
|
||||
- Long files tend to contain generic guidelines already known to AI
|
||||
|
||||
To control the number of best practices suggestions generated by the `improve` tool, give the following configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[best_practices]
|
||||
num_best_practice_suggestions = 2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Local and global best practices
|
||||
By default, Qodo Merge will look for a local `best_practices.md` wiki file in the root of the relevant local repo.
|
||||
|
||||
By default, Qodo Merge will look for a local `best_practices.md` in the root of the relevant local repo.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to enable also a global `best_practices.md` file, set first in the global configuration file:
|
||||
If you want to enable also a global `best_practices.md` wiki file, set first in the global configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[best_practices]
|
||||
enable_global_best_practices = true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then, create a `best_practices.md` file in the root of [global](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/#global-configuration-file) configuration repository, `pr-agent-settings`.
|
||||
Then, create a `best_practices.md` wiki file in the root of [global](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/#global-configuration-file) configuration repository, `pr-agent-settings`.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Best practices for multiple languages
|
||||
|
||||
For a git organization working with multiple programming languages, you can maintain a centralized global `best_practices.md` file containing language-specific guidelines.
|
||||
When reviewing pull requests, Qodo Merge automatically identifies the programming language and applies the relevant best practices from this file.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -208,7 +176,6 @@ To do this, structure your `best_practices.md` file using the following format:
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Dedicated label for best practices suggestions
|
||||
|
||||
Best practice suggestions are labeled as `Organization best practice` by default.
|
||||
To customize this label, modify it in your configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -219,15 +186,16 @@ organization_name = "..."
|
||||
|
||||
And the label will be: `{organization_name} best practice`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example results
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
### Auto best practices
|
||||
### Auto best practices 💎
|
||||
|
||||
>`💎 feature. Platforms supported: GitHub.`
|
||||
>`Platforms supported: GitHub`
|
||||
|
||||
`Auto best practices` is a novel Qodo Merge capability that:
|
||||
'Auto best practices' is a novel Qodo Merge capability that:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Identifies recurring patterns from accepted suggestions
|
||||
2. **Automatically** generates [best practices page](https://github.com/qodo-ai/pr-agent/wiki/.pr_agent_auto_best_practices) based on what your team consistently values
|
||||
@ -259,14 +227,8 @@ extra_instructions = ""
|
||||
max_patterns = 5
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Multiple best practices sources
|
||||
|
||||
The `improve` tool will combine best practices from all available sources - global configuration, local configuration, and auto-generated files - to provide you with comprehensive recommendations.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Combining 'extra instructions' and 'best practices'
|
||||
|
||||
> `💎 feature`
|
||||
### Combining `extra instructions` and `best practices` 💎
|
||||
|
||||
The `extra instructions` configuration is more related to the `improve` tool prompt. It can be used, for example, to avoid specific suggestions ("Don't suggest to add try-except block", "Ignore changes in toml files", ...) or to emphasize specific aspects or formats ("Answer in Japanese", "Give only short suggestions", ...)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -274,10 +236,10 @@ In contrast, the `best_practices.md` file is a general guideline for the way cod
|
||||
|
||||
Using a combination of both can help the AI model to provide relevant and tailored suggestions.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage Tips
|
||||
|
||||
### Implementing the proposed code suggestions
|
||||
|
||||
Each generated suggestion consists of three key elements:
|
||||
|
||||
1. A single-line summary of the proposed change
|
||||
@ -285,15 +247,14 @@ Each generated suggestion consists of three key elements:
|
||||
3. A diff snippet showing the recommended code modification (before and after)
|
||||
|
||||
We advise users to apply critical analysis and judgment when implementing the proposed suggestions.
|
||||
In addition to mistakes (which may happen, but are rare), sometimes the presented code modification may serve more as an _illustrative example_ than a directly applicable solution.
|
||||
In addition to mistakes (which may happen, but are rare), sometimes the presented code modification may serve more as an _illustrative example_ than a direct applicable solution.
|
||||
In such cases, we recommend prioritizing the suggestion's detailed description, using the diff snippet primarily as a supporting reference.
|
||||
|
||||
### Dual publishing mode
|
||||
|
||||
Our recommended approach for presenting code suggestions is through a [table](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#overview) (`--pr_code_suggestions.commitable_code_suggestions=false`).
|
||||
This method significantly reduces the PR footprint and allows for quick and easy digestion of multiple suggestions.
|
||||
|
||||
We also offer a complementary **dual publishing mode**. When enabled, suggestions exceeding a certain score threshold are not only displayed in the table, but also presented as committable PR comments.
|
||||
We also offer a complementary **dual publishing mode**. When enabled, suggestions exceeding a certain score threshold are not only displayed in the table, but also presented as commitable PR comments.
|
||||
This mode helps highlight suggestions deemed more critical.
|
||||
|
||||
To activate dual publishing mode, use the following setting:
|
||||
@ -303,14 +264,10 @@ To activate dual publishing mode, use the following setting:
|
||||
dual_publishing_score_threshold = x
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Where x represents the minimum score threshold (>=) for suggestions to be presented as committable PR comments in addition to the table. Default is -1 (disabled).
|
||||
Where x represents the minimum score threshold (>=) for suggestions to be presented as commitable PR comments in addition to the table. Default is -1 (disabled).
|
||||
|
||||
### Self-review
|
||||
|
||||
> `💎 feature` Platforms supported: GitHub, GitLab
|
||||
|
||||
If you set in a configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[pr_code_suggestions]
|
||||
demand_code_suggestions_self_review = true
|
||||
@ -318,7 +275,6 @@ demand_code_suggestions_self_review = true
|
||||
|
||||
The `improve` tool will add a checkbox below the suggestions, prompting user to acknowledge that they have reviewed the suggestions.
|
||||
You can set the content of the checkbox text via:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[pr_code_suggestions]
|
||||
code_suggestions_self_review_text = "... (your text here) ..."
|
||||
@ -326,6 +282,7 @@ code_suggestions_self_review_text = "... (your text here) ..."
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip "Tip - Reducing visual footprint after self-review 💎"
|
||||
|
||||
The configuration parameter `pr_code_suggestions.fold_suggestions_on_self_review` (default is True)
|
||||
@ -333,6 +290,8 @@ code_suggestions_self_review_text = "... (your text here) ..."
|
||||
|
||||
This reduces the visual footprint of the suggestions, and also indicates to the PR reviewer that the suggestions have been reviewed by the PR author, and don't require further attention.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip "Tip - Demanding self-review from the PR author 💎"
|
||||
|
||||
By setting:
|
||||
@ -351,106 +310,28 @@ code_suggestions_self_review_text = "... (your text here) ..."
|
||||
|
||||
To prevent unauthorized approvals, this configuration defaults to false, and cannot be altered through online comments; enabling requires a direct update to the configuration file and a commit to the repository. This ensures that utilizing the feature demands a deliberate documented decision by the repository owner.
|
||||
|
||||
### Auto-approval
|
||||
|
||||
> `💎 feature. Platforms supported: GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket`
|
||||
|
||||
Under specific conditions, Qodo Merge can auto-approve a PR when a specific comment is invoked, or when the PR meets certain criteria.
|
||||
|
||||
**To ensure safety, the auto-approval feature is disabled by default.**
|
||||
To enable auto-approval features, you need to actively set one or both of the following options in a pre-defined _configuration file_:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
enable_comment_approval = true # For approval via comments
|
||||
enable_auto_approval = true # For criteria-based auto-approval
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Notes"
|
||||
- Note that this specific flag cannot be set with a command line argument, only in the configuration file, committed to the repository.
|
||||
- Enabling auto-approval must be a deliberate decision by the repository owner.
|
||||
|
||||
1\. **Auto-approval by commenting**
|
||||
|
||||
To enable auto-approval by commenting, set in the configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
enable_comment_approval = true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
After enabling, by commenting on a PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/review auto_approve
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge will automatically approve the PR, and add a comment with the approval.
|
||||
|
||||
2\. **Auto-approval when the PR meets certain criteria**
|
||||
|
||||
To enable auto-approval based on specific criteria, first, you need to enable the top-level flag:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
enable_auto_approval = true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
There are several criteria that can be set for auto-approval:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Review effort score**
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
enable_auto_approval = true
|
||||
auto_approve_for_low_review_effort = X # X is a number between 1 to 5
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
When the [review effort score](https://www.qodo.ai/images/pr_agent/review3.png) is lower or equal to X, the PR will be auto-approved.
|
||||
|
||||
___
|
||||
|
||||
- **No code suggestions**
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
enable_auto_approval = true
|
||||
auto_approve_for_no_suggestions = true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
When no [code suggestions](https://www.qodo.ai/images/pr_agent/code_suggestions_as_comment_closed.png) were found for the PR, the PR will be auto-approved.
|
||||
|
||||
___
|
||||
|
||||
- **Ticket Compliance**
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
enable_auto_approval = true
|
||||
ensure_ticket_compliance = true # Default is false
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If `ensure_ticket_compliance` is set to `true`, auto-approval will be disabled if a ticket is linked to the PR and the ticket is not compliant (e.g., the `review` tool did not mark the PR as fully compliant with the ticket). This ensures that PRs are only auto-approved if their associated tickets are properly resolved.
|
||||
|
||||
### How many code suggestions are generated?
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge uses a dynamic strategy to generate code suggestions based on the size of the pull request (PR). Here's how it works:
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1. Chunking large PRs
|
||||
1) Chunking large PRs:
|
||||
|
||||
- Qodo Merge divides large PRs into 'chunks'.
|
||||
- Each chunk contains up to `pr_code_suggestions.max_context_tokens` tokens (default: 24,000).
|
||||
- Each chunk contains up to `pr_code_suggestions.max_context_tokens` tokens (default: 14,000).
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. Generating suggestions
|
||||
|
||||
2) Generating suggestions:
|
||||
|
||||
- For each chunk, Qodo Merge generates up to `pr_code_suggestions.num_code_suggestions_per_chunk` suggestions (default: 4).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
This approach has two main benefits:
|
||||
|
||||
- Scalability: The number of suggestions scales with the PR size, rather than being fixed.
|
||||
- Quality: By processing smaller chunks, the AI can maintain higher quality suggestions, as larger contexts tend to decrease AI performance.
|
||||
|
||||
Note: Chunking is primarily relevant for large PRs. For most PRs (up to 600 lines of code), Qodo Merge will be able to process the entire code in a single call.
|
||||
Note: Chunking is primarily relevant for large PRs. For most PRs (up to 500 lines of code), Qodo Merge will be able to process the entire code in a single call.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuration options
|
||||
|
||||
@ -463,15 +344,11 @@ Note: Chunking is primarily relevant for large PRs. For most PRs (up to 600 line
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>commitable_code_suggestions</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will display the suggestions as committable code comments. Default is false.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>enable_chat_in_code_suggestions</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, QM bot will interact with comments made on code changes it has proposed. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will display the suggestions as commitable code comments. Default is false.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>dual_publishing_score_threshold</b></td>
|
||||
<td>Minimum score threshold for suggestions to be presented as committable PR comments in addition to the table. Default is -1 (disabled).</td>
|
||||
<td>Minimum score threshold for suggestions to be presented as commitable PR comments in addition to the table. Default is -1 (disabled).</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>focus_only_on_problems</b></td>
|
||||
@ -479,7 +356,7 @@ Note: Chunking is primarily relevant for large PRs. For most PRs (up to 600 line
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>persistent_comment</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the improve comment will be persistent, meaning that every new improve request will edit the previous one. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the improve comment will be persistent, meaning that every new improve request will edit the previous one. Default is false.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>suggestions_score_threshold</b></td>
|
||||
@ -489,10 +366,6 @@ Note: Chunking is primarily relevant for large PRs. For most PRs (up to 600 line
|
||||
<td><b>apply_suggestions_checkbox</b></td>
|
||||
<td> Enable the checkbox to create a committable suggestion. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>enable_more_suggestions_checkbox</b></td>
|
||||
<td> Enable the checkbox to generate more suggestions. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>enable_help_text</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will display a help text in the comment. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
@ -501,16 +374,13 @@ Note: Chunking is primarily relevant for large PRs. For most PRs (up to 600 line
|
||||
<td><b>enable_chat_text</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will display a reference to the PR chat in the comment. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>publish_output_no_suggestions</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will publish a comment even if no suggestions were found. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>wiki_page_accepted_suggestions</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will automatically track accepted suggestions in a dedicated wiki page called `.pr_agent_accepted_suggestions`. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>allow_thumbs_up_down</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, all code suggestions will have thumbs up and thumbs down buttons, to encourage users to provide feedback on the suggestions. Default is false. Note that this feature is for statistics tracking. It will not affect future feedback from the AI model.</td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, all code suggestions will have thumbs up and thumbs down buttons, to encourage users to provide feedback on the suggestions. Default is false.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -523,7 +393,7 @@ Note: Chunking is primarily relevant for large PRs. For most PRs (up to 600 line
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>num_code_suggestions_per_chunk</b></td>
|
||||
<td>Number of code suggestions provided by the 'improve' tool, per chunk. Default is 3.</td>
|
||||
<td>Number of code suggestions provided by the 'improve' tool, per chunk. Default is 4.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>max_number_of_calls</b></td>
|
||||
@ -531,13 +401,14 @@ Note: Chunking is primarily relevant for large PRs. For most PRs (up to 600 line
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
## Understanding AI Code Suggestions
|
||||
## A note on code suggestions quality
|
||||
|
||||
- **AI Limitations:** AI models for code are getting better and better, but they are not flawless. Not all the suggestions will be perfect, and a user should not accept all of them automatically. Critical reading and judgment are required. Mistakes of the AI are rare but can happen, and it is usually quite easy for a human to spot them.
|
||||
- **Purpose of Suggestions:**
|
||||
- **Self-reflection:** The suggestions aim to enable developers to _self-reflect_ and improve their pull requests. This process can help to identify blind spots, uncover missed edge cases, and enhance code readability and coherency. Even when a specific code suggestion isn't suitable, the underlying issue it highlights often reveals something important that might deserve attention.
|
||||
- **Bug detection:** The suggestions also alert on any _critical bugs_ that may have been identified during the analysis. This provides an additional safety net to catch potential issues before they make it into production. It's perfectly acceptable to implement only the suggestions you find valuable for your specific context.
|
||||
- **Hierarchy:** Presenting the suggestions in a structured hierarchical table enables the user to _quickly_ understand them, and to decide which ones are relevant and which are not.
|
||||
- **Customization:** To guide the model to suggestions that are more relevant to the specific needs of your project, we recommend using the [`extra_instructions`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#extra-instructions-and-best-practices) and [`best practices`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#best-practices) fields.
|
||||
- **Model Selection:** SaaS users can also [choose](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/qodo_merge_models/) between different models. For specific programming languages or use cases, some models may perform better than others.
|
||||
- **Interactive usage:** The interactive [PR chat](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/chrome-extension/) also provides an easy way to get more tailored suggestions and feedback from the AI model.
|
||||
- AI models for code are getting better and better (Sonnet-3.5 and GPT-4), but they are not flawless. Not all the suggestions will be perfect, and a user should not accept all of them automatically. Critical reading and judgment are required.
|
||||
- While mistakes of the AI are rare but can happen, a real benefit from the suggestions of the `improve` (and [`review`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/review/)) tool is to catch, with high probability, **mistakes or bugs done by the PR author**, when they happen. So, it's a good practice to spend the needed ~30-60 seconds to review the suggestions, even if not all of them are always relevant.
|
||||
- The hierarchical structure of the suggestions is designed to help the user to _quickly_ understand them, and to decide which ones are relevant and which are not:
|
||||
|
||||
- Only if the `Category` header is relevant, the user should move to the summarized suggestion description
|
||||
- Only if the summarized suggestion description is relevant, the user should click on the collapsible, to read the full suggestion description with a code preview example.
|
||||
|
||||
- In addition, we recommend to use the [`extra_instructions`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#extra-instructions-and-best-practices) field to guide the model to suggestions that are more relevant to the specific needs of the project.
|
||||
- The interactive [PR chat](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/chrome-extension/) also provides an easy way to get more tailored suggestions and feedback from the AI model.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,14 +1,13 @@
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The `improve_component` tool generates code suggestions for a specific code component that changed in the PR.
|
||||
it can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/improve_component component_name
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To get a list of the components that changed in the PR and choose the relevant component interactively, use the [`analyze`](./analyze.md) tool.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Example usage
|
||||
|
||||
Invoke the tool manually by commenting `/improve_component` on any PR:
|
||||
@ -19,12 +18,11 @@ The tool will generate code suggestions for the selected component (if no compon
|
||||
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Notes"
|
||||
- Language that are currently supported by the tool: Python, Java, C++, JavaScript, TypeScript, C#.
|
||||
- This tool can also be triggered interactively by using the [`analyze`](./analyze.md) tool.
|
||||
**Notes**
|
||||
- Language that are currently supported by the tool: Python, Java, C++, JavaScript, TypeScript, C#.
|
||||
- This tool can also be triggered interactively by using the [`analyze`](./analyze.md) tool.
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuration options
|
||||
|
||||
- `num_code_suggestions`: number of code suggestions to provide. Default is 4
|
||||
- `extra_instructions`: Optional extra instructions to the tool. For example: "focus on ...".
|
||||
- `file`: in case there are several components with the same name, you can specify the relevant file.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -3,22 +3,21 @@
|
||||
Here is a list of Qodo Merge tools, each with a dedicated page that explains how to use it:
|
||||
|
||||
| Tool | Description |
|
||||
| ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
|
||||
|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| **[PR Description (`/describe`](./describe.md))** | Automatically generating PR description - title, type, summary, code walkthrough and labels |
|
||||
| **[PR Review (`/review`](./review.md))** | Adjustable feedback about the PR, possible issues, security concerns, review effort and more |
|
||||
| **[Code Suggestions (`/improve`](./improve.md))** | Code suggestions for improving the PR |
|
||||
| **[Question Answering (`/ask ...`](./ask.md))** | Answering free-text questions about the PR, or on specific code lines |
|
||||
| **[Update Changelog (`/update_changelog`](./update_changelog.md))** | Automatically updating the CHANGELOG.md file with the PR changes |
|
||||
| **[Find Similar Issue (`/similar_issue`](./similar_issues.md))** | Automatically retrieves and presents similar issues |
|
||||
| **[Help (`/help`](./help.md))** | Provides a list of all the available tools. Also enables to trigger them interactively (💎) |
|
||||
| **💎 [Add Documentation (`/add_docs`](./documentation.md))** | Generates documentation to methods/functions/classes that changed in the PR |
|
||||
| **💎 [Generate Custom Labels (`/generate_labels`](./custom_labels.md))** | Generates custom labels for the PR, based on specific guidelines defined by the user |
|
||||
| **💎 [Analyze (`/analyze`](./analyze.md))** | Identify code components that changed in the PR, and enables to interactively generate tests, docs, and code suggestions for each component |
|
||||
| **💎 [Analyze (`/analyze`](./analyze.md))** | Identify code components that changed in the PR, and enables to interactively generate tests, docs, and code suggestions for each component|
|
||||
| **💎 [Test (`/test`](./test.md))** | generate tests for a selected component, based on the PR code changes |
|
||||
| **💎 [Custom Prompt (`/custom_prompt`](./custom_prompt.md))** | Automatically generates custom suggestions for improving the PR code, based on specific guidelines defined by the user |
|
||||
| **💎 [Generate Tests (`/test component_name`](./test.md))** | Automatically generates unit tests for a selected component, based on the PR code changes |
|
||||
| **💎 [Improve Component (`/improve_component component_name`](./improve_component.md))** | Generates code suggestions for a specific code component that changed in the PR |
|
||||
| **💎 [CI Feedback (`/checks ci_job`](./ci_feedback.md))** | Automatically generates feedback and analysis for a failed CI job |
|
||||
| **💎 [Implement (`/implement`](./implement.md))** | Generates implementation code from review suggestions |
|
||||
| **💎 [Scan Repo Discussions (`/scan_repo_discussions`](./scan_repo_discussions.md))** | Generates `best_practices.md` file based on previous discussions in the repository |
|
||||
|
||||
Note that the tools marked with 💎 are available only for Qodo Merge users.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,9 +1,7 @@
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The `review` tool scans the PR code changes, and generates a list of feedbacks about the PR, aiming to aid the reviewing process.
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
The tool can be triggered automatically every time a new PR is [opened](../usage-guide/automations_and_usage.md#github-app-automatic-tools-when-a-new-pr-is-opened), or can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/review
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -12,6 +10,7 @@ Note that the main purpose of the `review` tool is to provide the **PR reviewer*
|
||||
|
||||
(Read more about the different personas in the PR process and how Qodo Merge aims to assist them in our [blog](https://www.codium.ai/blog/understanding-the-challenges-and-pain-points-of-the-pull-request-cycle/))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Example usage
|
||||
|
||||
### Manual triggering
|
||||
@ -25,7 +24,6 @@ After ~30 seconds, the tool will generate a review for the PR:
|
||||
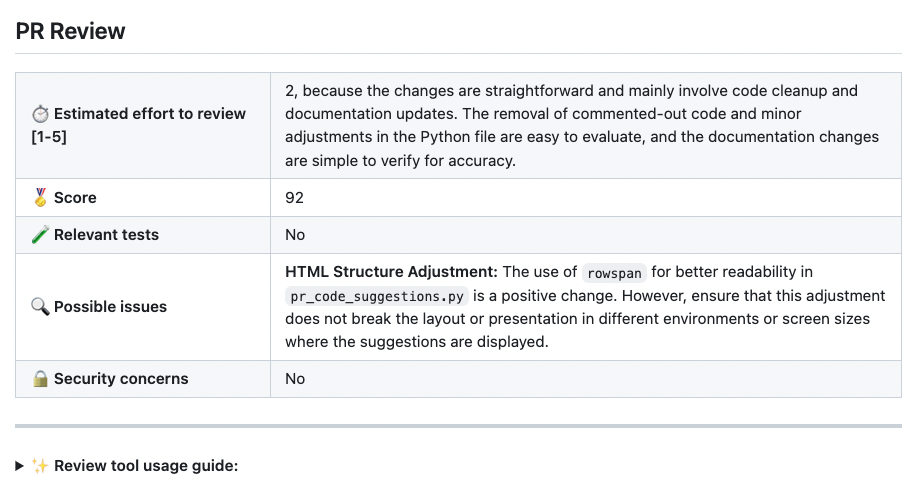{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to edit [configurations](#configuration-options), add the relevant ones to the command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/review --pr_reviewer.some_config1=... --pr_reviewer.some_config2=...
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -33,7 +31,6 @@ If you want to edit [configurations](#configuration-options), add the relevant o
|
||||
### Automatic triggering
|
||||
|
||||
To run the `review` automatically when a PR is opened, define in a [configuration file](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/#wiki-configuration-file):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[github_app]
|
||||
pr_commands = [
|
||||
@ -49,11 +46,12 @@ extra_instructions = "..."
|
||||
- The `pr_commands` lists commands that will be executed automatically when a PR is opened.
|
||||
- The `[pr_reviewer]` section contains the configurations for the `review` tool you want to edit (if any).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuration options
|
||||
|
||||
!!! example "General options"
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>persistent_comment</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the review comment will be persistent, meaning that every new review request will edit the previous one. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
@ -70,15 +68,11 @@ extra_instructions = "..."
|
||||
<td><b>enable_help_text</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will display a help text in the comment. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>num_max_findings</b></td>
|
||||
<td>Number of maximum returned findings. Default is 3.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
!!! example "Enable\\disable specific sub-sections"
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>require_score_review</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will add a section that scores the PR. Default is false.</td>
|
||||
@ -103,28 +97,37 @@ extra_instructions = "..."
|
||||
<td><b>require_ticket_analysis_review</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, and the PR contains a GitHub or Jira ticket link, the tool will add a section that checks if the PR in fact fulfilled the ticket requirements. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
!!! example "Adding PR labels"
|
||||
|
||||
You can enable\disable the `review` tool to add specific labels to the PR:
|
||||
You can enable\disable the `review` tool to add specific labels to the PR:
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>enable_review_labels_security</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will publish a 'possible security issue' label if it detects a security issue. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>enable_review_labels_effort</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will publish a 'Review effort x/5' label (1–5 scale). Default is true.</td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will publish a 'Review effort [1-5]: x' label. Default is true.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
!!! example "Auto-approval"
|
||||
|
||||
If enabled, the `review` tool can approve a PR when a specific comment, `/review auto_approve`, is invoked.
|
||||
|
||||
<table>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><b>enable_auto_approval</b></td>
|
||||
<td>If set to true, the tool will approve the PR when invoked with the 'auto_approve' command. Default is false. This flag can be changed only from a configuration file.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage Tips
|
||||
|
||||
### General guidelines
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip ""
|
||||
!!! tip "General guidelines"
|
||||
|
||||
The `review` tool provides a collection of configurable feedbacks about a PR.
|
||||
It is recommended to review the [Configuration options](#configuration-options) section, and choose the relevant options for your use case.
|
||||
@ -134,9 +137,7 @@ extra_instructions = "..."
|
||||
|
||||
On the other hand, if you find one of the enabled features to be irrelevant for your use case, disable it. No default configuration can fit all use cases.
|
||||
|
||||
### Automation
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip ""
|
||||
!!! tip "Automation"
|
||||
When you first install Qodo Merge app, the [default mode](../usage-guide/automations_and_usage.md#github-app-automatic-tools-when-a-new-pr-is-opened) for the `review` tool is:
|
||||
```
|
||||
pr_commands = ["/review", ...]
|
||||
@ -144,30 +145,16 @@ extra_instructions = "..."
|
||||
Meaning the `review` tool will run automatically on every PR, without any additional configurations.
|
||||
Edit this field to enable/disable the tool, or to change the configurations used.
|
||||
|
||||
### Auto-generated PR labels by the Review Tool
|
||||
!!! tip "Possible labels from the review tool"
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip ""
|
||||
The `review` tool can auto-generate two specific types of labels for a PR:
|
||||
|
||||
The `review` can tool automatically add labels to your Pull Requests:
|
||||
- a `possible security issue` label that detects if a possible [security issue](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/tr/user_description/pr_agent/settings/pr_reviewer_prompts.toml#L136) exists in the PR code (`enable_review_labels_security` flag)
|
||||
- a `Review effort [1-5]: x` label, where x is the estimated effort to review the PR (`enable_review_labels_effort` flag)
|
||||
|
||||
- **`possible security issue`**: This label is applied if the tool detects a potential [security vulnerability](https://github.com/qodo-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/pr_reviewer_prompts.toml#L103) in the PR's code. This feedback is controlled by the 'enable_review_labels_security' flag (default is true).
|
||||
- **`review effort [x/5]`**: This label estimates the [effort](https://github.com/qodo-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/pr_reviewer_prompts.toml#L90) required to review the PR on a relative scale of 1 to 5, where 'x' represents the assessed effort. This feedback is controlled by the 'enable_review_labels_effort' flag (default is true).
|
||||
- **`ticket compliance`**: Adds a label indicating code compliance level ("Fully compliant" | "PR Code Verified" | "Partially compliant" | "Not compliant") to any GitHub/Jira/Linea ticket linked in the PR. Controlled by the 'require_ticket_labels' flag (default: false). If 'require_no_ticket_labels' is also enabled, PRs without ticket links will receive a "No ticket found" label.
|
||||
Both modes are useful, and we recommended to enable them.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Blocking PRs from merging based on the generated labels
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip ""
|
||||
|
||||
You can configure a CI/CD Action to prevent merging PRs with specific labels. For example, implement a dedicated [GitHub Action](https://medium.com/sequra-tech/quick-tip-block-pull-request-merge-using-labels-6cc326936221).
|
||||
|
||||
This approach helps ensure PRs with potential security issues or ticket compliance problems will not be merged without further review.
|
||||
|
||||
Since AI may make mistakes or lack complete context, use this feature judiciously. For flexibility, users with appropriate permissions can remove generated labels when necessary. When a label is removed, this action will be automatically documented in the PR discussion, clearly indicating it was a deliberate override by an authorized user to allow the merge.
|
||||
|
||||
### Extra instructions
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip ""
|
||||
!!! tip "Extra instructions"
|
||||
|
||||
Extra instructions are important.
|
||||
The `review` tool can be configured with extra instructions, which can be used to guide the model to a feedback tailored to the needs of your project.
|
||||
@ -186,3 +173,29 @@ extra_instructions = "..."
|
||||
"""
|
||||
```
|
||||
Use triple quotes to write multi-line instructions. Use bullet points to make the instructions more readable.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip "Auto-approval"
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge can approve a PR when a specific comment is invoked.
|
||||
|
||||
To ensure safety, the auto-approval feature is disabled by default. To enable auto-approval, you need to actively set in a pre-defined configuration file the following:
|
||||
```
|
||||
[pr_reviewer]
|
||||
enable_auto_approval = true
|
||||
```
|
||||
(this specific flag cannot be set with a command line argument, only in the configuration file, committed to the repository)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
After enabling, by commenting on a PR:
|
||||
```
|
||||
/review auto_approve
|
||||
```
|
||||
Qodo Merge will automatically approve the PR, and add a comment with the approval.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip "Code suggestions"
|
||||
|
||||
The `review` tool previously included a legacy feature for providing code suggestions (controlled by `--pr_reviewer.num_code_suggestion`). This functionality has been deprecated and replaced by the [`improve`](./improve.md) tool, which offers higher quality and more actionable code suggestions.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,44 +0,0 @@
|
||||
`Platforms supported: GitHub`
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The `scan_repo_discussions` tool analyzes code discussions (meaning review comments over code lines) from merged pull requests over the past 12 months.
|
||||
It processes these discussions alongside other PR metadata to identify recurring patterns related to best practices in team feedback and code reviews, generating a comprehensive [`best_practices.md`](https://github.com/qodo-ai/pr-agent/blob/qodo-merge-best-practices_2025-04-16_1018/best_practices.md) document that distills key insights and recommendations.
|
||||
|
||||
This file captures repository-specific patterns derived from your team's actual workflow and discussions, rather than more generic best practices.
|
||||
It will be utilized by Qodo Merge to provide tailored suggestions for improving code quality in future pull requests.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Active repositories are needed"
|
||||
The tool is designed to work with real-life repositories, as it relies on actual discussions to generate meaningful insights.
|
||||
At least 50 merged PRs are required to generate the `best_practices.md` file.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Additional customization"
|
||||
Teams are encouraged to further customize and refine these insights to better align with their specific development priorities and contexts.
|
||||
This can be done by editing the `best_practices.md` file directly when the PR is created, or iteratively over time to enhance the 'best practices' suggestions provided by Qodo Merge.
|
||||
|
||||
The tool can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/scan_repo_discussions
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
As a response, the bot will create a new PR that contains an auto-generated `best_practices.md` file.
|
||||
Note that the scan can take several minutes to complete, since up to 250 PRs are scanned.
|
||||
|
||||
## Example usage
|
||||
|
||||
{width=640}
|
||||
|
||||
The PR created by the bot:
|
||||
|
||||
{width=640}
|
||||
|
||||
The `best_practices.md` file in the PR:
|
||||
|
||||
{width=640}
|
||||
|
||||
### Configuration options
|
||||
|
||||
- Use `/scan_repo_discussions --scan_repo_discussions.force_scan=true` to force generating a PR with a new `best_practices.md` file, even if it already exists (by default, the bot will not generate a new file if it already exists).
|
||||
- Use `/scan_repo_discussions --scan_repo_discussions.days_back=X` to specify the number of days back to scan for discussions. The default is 365 days.
|
||||
- Use `/scan_repo_discussions --scan_repo_discussions.minimal_number_of_prs=X` to specify the minimum number of merged PRs needed to generate the `best_practices.md` file. The default is 50 PRs.
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,4 @@
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The similar code tool retrieves the most similar code components from inside the organization's codebase, or from open-source code.
|
||||
|
||||
For example:
|
||||
@ -8,6 +7,7 @@ For example:
|
||||
|
||||
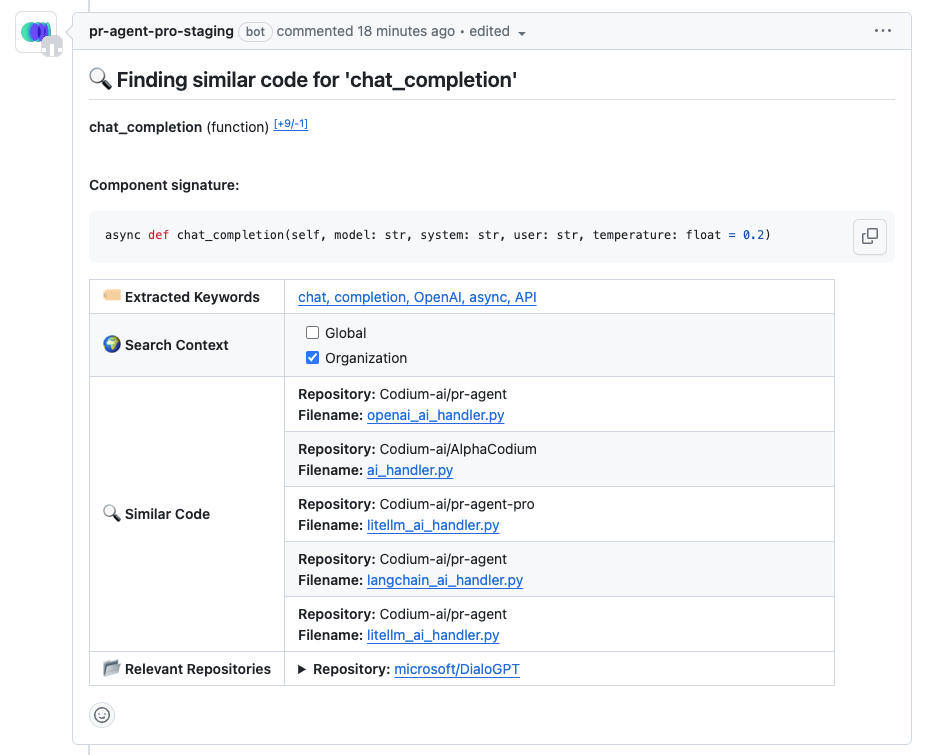{width=768}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge will examine the code component and will extract the most relevant keywords to search for similar code:
|
||||
|
||||
- `extracted keywords`: the keywords that were extracted from the code by Qodo Merge. the link will open a search page with the extracted keywords, to allow the user to modify the search if needed.
|
||||
@ -19,20 +19,18 @@ Search result link example:
|
||||
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
`Organization Search`:
|
||||
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## How to use
|
||||
|
||||
### Manually
|
||||
|
||||
To invoke the `similar code` tool manually, comment on the PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/find_similar_component COMPONENT_NAME
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Where `COMPONENT_NAME` should be the name of a code component in the PR (class, method, function).
|
||||
|
||||
If there is a name ambiguity, there are two configurations that will help the tool to find the correct component:
|
||||
@ -41,19 +39,15 @@ If there is a name ambiguity, there are two configurations that will help the to
|
||||
- `--pr_find_similar_component.class_name`: in case there are several methods with the same name in the same file, you can specify the relevant class name.
|
||||
|
||||
example:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/find_similar_component COMPONENT_NAME --pr_find_similar_component.file=FILE_NAME
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Automatically (via Analyze table)
|
||||
|
||||
It can be invoked automatically from the analyze table, can be accessed by:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/analyze
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Choose the components you want to find similar code for, and click on the `similar` checkbox.
|
||||
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
@ -62,6 +56,7 @@ You can search for similar code either within the organization's codebase or glo
|
||||
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuration options
|
||||
|
||||
- `search_from_org`: if set to true, the tool will search for similar code in the organization's codebase. Default is false.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,12 +1,11 @@
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The similar issue tool retrieves the most similar issues to the current issue.
|
||||
It can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/similar_issue
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Example usage
|
||||
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
@ -17,31 +16,24 @@ It can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
Note that to perform retrieval, the `similar_issue` tool indexes all the repo previous issues (once).
|
||||
|
||||
### Selecting a Vector Database
|
||||
|
||||
Configure your preferred database by changing the `pr_similar_issue` parameter in `configuration.toml` file.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Available Options
|
||||
|
||||
Choose from the following Vector Databases:
|
||||
**Select VectorDBs** by changing `pr_similar_issue` parameter in `configuration.toml` file
|
||||
|
||||
2 VectorDBs are available to switch in
|
||||
1. LanceDB
|
||||
2. Pinecone
|
||||
|
||||
#### Pinecone Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
To use Pinecone with the `similar issue` tool, add these credentials to `.secrets.toml` (or set as environment variables):
|
||||
To enable usage of the '**similar issue**' tool for Pinecone, you need to set the following keys in `.secrets.toml` (or in the relevant environment variables):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[pinecone]
|
||||
api_key = "..."
|
||||
environment = "..."
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
These parameters can be obtained by registering to [Pinecone](https://app.pinecone.io/?sessionType=signup/).
|
||||
|
||||
## How to use
|
||||
|
||||
## How to use
|
||||
- To invoke the 'similar issue' tool from **CLI**, run:
|
||||
`python3 cli.py --issue_url=... similar_issue`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,12 +1,9 @@
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
By combining LLM abilities with static code analysis, the `test` tool generate tests for a selected component, based on the PR code changes.
|
||||
It can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/test component_name
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
where 'component_name' is the name of a specific component in the PR.
|
||||
To get a list of the components that changed in the PR and choose the relevant component interactively, use the [`analyze`](./analyze.md) tool.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -17,14 +14,15 @@ The tool will generate tests for the selected component (if no component is stat
|
||||
|
||||
{width=768}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
(Example taken from [here](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/598#issuecomment-1913679429)):
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Notes"
|
||||
- The following languages are currently supported: Python, Java, C++, JavaScript, TypeScript, C#.
|
||||
- This tool can also be triggered interactively by using the [`analyze`](./analyze.md) tool.
|
||||
**Notes** <br>
|
||||
- The following languages are currently supported: Python, Java, C++, JavaScript, TypeScript, C#. <br>
|
||||
- This tool can also be triggered interactively by using the [`analyze`](./analyze.md) tool.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuration options
|
||||
|
||||
- `num_tests`: number of tests to generate. Default is 3.
|
||||
- `testing_framework`: the testing framework to use. If not set, for Python it will use `pytest`, for Java it will use `JUnit`, for C++ it will use `Catch2`, and for JavaScript and TypeScript it will use `jest`.
|
||||
- `avoid_mocks`: if set to true, the tool will try to avoid using mocks in the generated tests. Note that even if this option is set to true, the tool might still use mocks if it cannot generate a test without them. Default is true.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,8 +1,6 @@
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The `update_changelog` tool automatically updates the CHANGELOG.md file with the PR changes.
|
||||
It can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/update_changelog
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -17,7 +15,6 @@ It can be invoked manually by commenting on any PR:
|
||||
|
||||
Under the section `pr_update_changelog`, the [configuration file](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml#L50) contains options to customize the 'update changelog' tool:
|
||||
|
||||
- `push_changelog_changes`: whether to push the changes to CHANGELOG.md, or just publish them as a comment. Default is false (publish as comment).
|
||||
- `extra_instructions`: Optional extra instructions to the tool. For example: "Use the following structure: ..."
|
||||
- `push_changelog_changes`: whether to push the changes to CHANGELOG.md, or just print them. Default is false (print only).
|
||||
- `extra_instructions`: Optional extra instructions to the tool. For example: "focus on the changes in the file X. Ignore change in ...
|
||||
- `add_pr_link`: whether the model should try to add a link to the PR in the changelog. Default is true.
|
||||
- `skip_ci_on_push`: whether the commit message (when `push_changelog_changes` is true) will include the term "[skip ci]", preventing CI tests to be triggered on the changelog commit. Default is true.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,4 @@
|
||||
## Recommend Python Best Practices
|
||||
|
||||
This document outlines a series of recommended best practices for Python development. These guidelines aim to improve code quality, maintainability, and readability.
|
||||
|
||||
### Imports
|
||||
@ -86,7 +85,6 @@ No:
|
||||
The directory the main binary is located in should not be assumed to be in `sys.path` despite that happening in some environments. This being the case, code should assume that `import jodie` refers to a third-party or top-level package named `jodie`, not a local `jodie.py`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Default Iterators and Operators
|
||||
|
||||
Use default iterators and operators for types that support them, like lists, dictionaries, and files.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Definition
|
||||
@ -160,6 +158,7 @@ No: def foo(a, b: Mapping = {}): # Could still get passed to unchecked code.
|
||||
|
||||
### True/False Evaluations
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Use the “implicit” false if possible, e.g., `if foo:` rather than `if foo != []:`
|
||||
|
||||
### Lexical Scoping
|
||||
@ -176,11 +175,11 @@ def get_adder(summand1: float) -> Callable[[float], float]:
|
||||
|
||||
return adder
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Decision
|
||||
|
||||
Okay to use.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Threading
|
||||
|
||||
Do not rely on the atomicity of built-in types.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,35 +1,32 @@
|
||||
## Show possible configurations
|
||||
|
||||
The possible configurations of Qodo Merge are stored in [here](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml){:target="_blank"}.
|
||||
In the [tools](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/) page you can find explanations on how to use these configurations for each tool.
|
||||
|
||||
To print all the available configurations as a comment on your PR, you can use the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/config
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
To view the **actual** configurations used for a specific tool, after all the user settings are applied, you can add for each tool a `--config.output_relevant_configurations=true` suffix.
|
||||
For example:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/improve --config.output_relevant_configurations=true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Will output an additional field showing the actual configurations used for the `improve` tool.
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Ignoring files from analysis
|
||||
|
||||
In some cases, you may want to exclude specific files or directories from the analysis performed by Qodo Merge. This can be useful, for example, when you have files that are generated automatically or files that shouldn't be reviewed, like vendor code.
|
||||
|
||||
You can ignore files or folders using the following methods:
|
||||
|
||||
- `IGNORE.GLOB`
|
||||
- `IGNORE.REGEX`
|
||||
- `IGNORE.GLOB`
|
||||
- `IGNORE.REGEX`
|
||||
|
||||
which you can edit to ignore files or folders based on glob or regex patterns.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -40,67 +37,42 @@ Let's look at an example where we want to ignore all files with `.py` extension
|
||||
To ignore Python files in a PR with online usage, comment on a PR:
|
||||
`/review --ignore.glob="['*.py']"`
|
||||
|
||||
To ignore Python files in all PRs using `glob` pattern, set in a configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
To ignore Python files in all PRs using `glob` pattern, set in a configuration file:
|
||||
```
|
||||
[ignore]
|
||||
glob = ['*.py']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And to ignore Python files in all PRs using `regex` pattern, set in a configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[ignore]
|
||||
[regex]
|
||||
regex = ['.*\.py$']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Extra instructions
|
||||
|
||||
All Qodo Merge tools have a parameter called `extra_instructions`, that enables to add free-text extra instructions. Example usage:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/update_changelog --pr_update_changelog.extra_instructions="Make sure to update also the version ..."
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Language Settings
|
||||
## Working with large PRs
|
||||
|
||||
The default response language for Qodo Merge is **U.S. English**. However, some development teams may prefer to display information in a different language. For example, your team's workflow might improve if PR descriptions and code suggestions are set to your country's native language.
|
||||
The default mode of CodiumAI is to have a single call per tool, using GPT-4, which has a token limit of 8000 tokens.
|
||||
This mode provides a very good speed-quality-cost tradeoff, and can handle most PRs successfully.
|
||||
When the PR is above the token limit, it employs a [PR Compression strategy](../core-abilities/index.md).
|
||||
|
||||
To configure this, set the `response_language` parameter in the configuration file. This will prompt the model to respond in the specified language. Use a **standard locale code** based on [ISO 3166](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ISO_3166) (country codes) and [ISO 639](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ISO_639) (language codes) to define a language-country pair. See this [comprehensive list of locale codes](https://simplelocalize.io/data/locales/).
|
||||
However, for very large PRs, or in case you want to emphasize quality over speed and cost, there are two possible solutions:
|
||||
1) [Use a model](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/changing_a_model/) with larger context, like GPT-32K, or claude-100K. This solution will be applicable for all the tools.
|
||||
2) For the `/improve` tool, there is an ['extended' mode](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/) (`/improve --extended`),
|
||||
which divides the PR into chunks, and processes each chunk separately. With this mode, regardless of the model, no compression will be done (but for large PRs, multiple model calls may occur)
|
||||
|
||||
Example:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
response_language = "it-IT"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will set the response language globally for all the commands to Italian.
|
||||
|
||||
> **Important:** Note that only dynamic text generated by the AI model is translated to the configured language. Static text such as labels and table headers that are not part of the AI models response will remain in US English. In addition, the model you are using must have good support for the specified language.
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (## Working with large PRs)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ()
|
||||
[//]: # (The default mode of CodiumAI is to have a single call per tool, using GPT-4, which has a token limit of 8000 tokens.)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (This mode provides a very good speed-quality-cost tradeoff, and can handle most PRs successfully.)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (When the PR is above the token limit, it employs a [PR Compression strategy](../core-abilities/index.md).)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # ()
|
||||
[//]: # (However, for very large PRs, or in case you want to emphasize quality over speed and cost, there are two possible solutions:)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (1) [Use a model](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/changing_a_model/) with larger context, like GPT-32K, or claude-100K. This solution will be applicable for all the tools.)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (2) For the `/improve` tool, there is an ['extended' mode](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/) (`/improve --extended`),)
|
||||
|
||||
[//]: # (which divides the PR into chunks, and processes each chunk separately. With this mode, regardless of the model, no compression will be done (but for large PRs, multiple model calls may occur))
|
||||
|
||||
## Patch Extra Lines
|
||||
|
||||
By default, around any change in your PR, git patch provides three lines of context above and below the change.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -12,5 +12,5 @@ def func1():
|
||||
code line that already existed in the file...
|
||||
@ -114,7 +86,6 @@ By default, around any change in your PR, git patch provides three lines of cont
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge will try to increase the number of lines of context, via the parameter:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
patch_extra_lines_before=3
|
||||
@ -125,23 +96,30 @@ Increasing this number provides more context to the model, but will also increas
|
||||
|
||||
If the PR is too large (see [PR Compression strategy](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/PR_COMPRESSION.md)), Qodo Merge may automatically set this number to 0, and will use the original git patch.
|
||||
|
||||
## Log Level
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge allows you to control the verbosity of logging by using the `log_level` configuration parameter. This is particularly useful for troubleshooting and debugging issues with your PR workflows.
|
||||
## Editing the prompts
|
||||
|
||||
The prompts for the various Qodo Merge tools are defined in the `pr_agent/settings` folder.
|
||||
In practice, the prompts are loaded and stored as a standard setting object.
|
||||
Hence, editing them is similar to editing any other configuration value - just place the relevant key in `.pr_agent.toml`file, and override the default value.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, if you want to edit the prompts of the [describe](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/pr_description_prompts.toml) tool, you can add the following to your `.pr_agent.toml` file:
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
log_level = "DEBUG" # Options: "DEBUG", "INFO", "WARNING", "ERROR", "CRITICAL"
|
||||
[pr_description_prompt]
|
||||
system="""
|
||||
...
|
||||
"""
|
||||
user="""
|
||||
...
|
||||
"""
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The default log level is "DEBUG", which provides detailed output of all operations. If you prefer less verbose logs, you can set higher log levels like "INFO" or "WARNING".
|
||||
Note that the new prompt will need to generate an output compatible with the relevant [post-process function](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/tools/pr_description.py#L137).
|
||||
|
||||
## Integrating with Logging Observability Platforms
|
||||
|
||||
Various logging observability tools can be used out-of-the box when using the default LiteLLM AI Handler. Simply configure the LiteLLM callback settings in `configuration.toml` and set environment variables according to the LiteLLM [documentation](https://docs.litellm.ai/docs/).
|
||||
|
||||
For example, to use [LangSmith](https://www.langchain.com/langsmith) you can add the following to your `configuration.toml` file:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[litellm]
|
||||
enable_callbacks = true
|
||||
@ -164,27 +142,28 @@ Qodo Merge allows you to automatically ignore certain PRs based on various crite
|
||||
|
||||
- PRs with specific titles (using regex matching)
|
||||
- PRs between specific branches (using regex matching)
|
||||
- PRs from specific repositories (using regex matching)
|
||||
- PRs not from specific folders
|
||||
- PRs that don't include changes from specific folders (using regex matching)
|
||||
- PRs containing specific labels
|
||||
- PRs opened by specific users
|
||||
|
||||
### Ignoring PRs with specific titles
|
||||
### Example usage
|
||||
|
||||
#### Ignoring PRs with specific titles
|
||||
|
||||
To ignore PRs with a specific title such as "[Bump]: ...", you can add the following to your `configuration.toml` file:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
ignore_pr_title = ["\\[Bump\\]"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Where the `ignore_pr_title` is a list of regex patterns to match the PR title you want to ignore. Default is `ignore_pr_title = ["^\\[Auto\\]", "^Auto"]`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Ignoring PRs between specific branches
|
||||
#### Ignoring PRs between specific branches
|
||||
|
||||
To ignore PRs from specific source or target branches, you can add the following to your `configuration.toml` file:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
ignore_pr_source_branches = ['develop', 'main', 'master', 'stage']
|
||||
ignore_pr_target_branches = ["qa"]
|
||||
@ -193,19 +172,7 @@ ignore_pr_target_branches = ["qa"]
|
||||
Where the `ignore_pr_source_branches` and `ignore_pr_target_branches` are lists of regex patterns to match the source and target branches you want to ignore.
|
||||
They are not mutually exclusive, you can use them together or separately.
|
||||
|
||||
### Ignoring PRs from specific repositories
|
||||
|
||||
To ignore PRs from specific repositories, you can add the following to your `configuration.toml` file:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
ignore_repositories = ["my-org/my-repo1", "my-org/my-repo2"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Where the `ignore_repositories` is a list of regex patterns to match the repositories you want to ignore. This is useful when you have multiple repositories and want to exclude certain ones from analysis.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Ignoring PRs not from specific folders
|
||||
#### Ignoring PRs that don't include changes from specific folders
|
||||
|
||||
To allow only specific folders (often needed in large monorepos), set:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -214,11 +181,11 @@ To allow only specific folders (often needed in large monorepos), set:
|
||||
allow_only_specific_folders=['folder1','folder2']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For the configuration above, automatic feedback will only be triggered when the PR changes include files where 'folder1' or 'folder2' is in the file path
|
||||
For the configuration above, automatic feedback will only be triggered when the PR changes include files from 'folder1' or 'folder2'
|
||||
|
||||
### Ignoring PRs containing specific labels
|
||||
#### Ignoring PRs containg specific labels
|
||||
|
||||
To ignore PRs containing specific labels, you can add the following to your `configuration.toml` file:
|
||||
To ignore PRs containg specific labels, you can add the following to your `configuration.toml` file:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
@ -227,9 +194,9 @@ ignore_pr_labels = ["do-not-merge"]
|
||||
|
||||
Where the `ignore_pr_labels` is a list of labels that when present in the PR, the PR will be ignored.
|
||||
|
||||
### Ignoring PRs from specific users
|
||||
#### Ignoring PRs from specific users
|
||||
|
||||
Qodo Merge tries to automatically identify and ignore pull requests created by bots using:
|
||||
Qodo Merge automatically identifies and ignores pull requests created by bots using:
|
||||
|
||||
- GitHub's native bot detection system
|
||||
- Name-based pattern matching
|
||||
@ -240,7 +207,6 @@ While this detection is robust, it may not catch all cases, particularly when:
|
||||
- Bot names don't match common patterns
|
||||
|
||||
To supplement the automatic bot detection, you can manually specify users to ignore. Add the following to your `configuration.toml` file to ignore PRs from specific users:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
ignore_pr_authors = ["my-special-bot-user", ...]
|
||||
@ -248,5 +214,3 @@ ignore_pr_authors = ["my-special-bot-user", ...]
|
||||
|
||||
Where the `ignore_pr_authors` is a list of usernames that you want to ignore.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note
|
||||
There is one specific case where bots will receive an automatic response - when they generated a PR with a _failed test_. In that case, the [`ci_feedback`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/ci_feedback/) tool will be invoked.
|
||||
@ -7,33 +7,36 @@ Examples of invoking the different tools via the CLI:
|
||||
- **Describe**: `python -m pr_agent.cli --pr_url=<pr_url> describe`
|
||||
- **Improve**: `python -m pr_agent.cli --pr_url=<pr_url> improve`
|
||||
- **Ask**: `python -m pr_agent.cli --pr_url=<pr_url> ask "Write me a poem about this PR"`
|
||||
- **Reflect**: `python -m pr_agent.cli --pr_url=<pr_url> reflect`
|
||||
- **Update Changelog**: `python -m pr_agent.cli --pr_url=<pr_url> update_changelog`
|
||||
|
||||
`<pr_url>` is the url of the relevant PR (for example: [#50](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/50)).
|
||||
|
||||
**Notes:**
|
||||
|
||||
1. in addition to editing your local configuration file, you can also change any configuration value by adding it to the command line:
|
||||
|
||||
(1) in addition to editing your local configuration file, you can also change any configuration value by adding it to the command line:
|
||||
```
|
||||
python -m pr_agent.cli --pr_url=<pr_url> /review --pr_reviewer.extra_instructions="focus on the file: ..."
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. You can print results locally, without publishing them, by setting in `configuration.toml`:
|
||||
|
||||
(2) You can print results locally, without publishing them, by setting in `configuration.toml`:
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
publish_output=false
|
||||
verbosity_level=2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This is useful for debugging or experimenting with different tools.
|
||||
|
||||
3. **git provider**: The [git_provider](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml#L5) field in a configuration file determines the GIT provider that will be used by Qodo Merge. Currently, the following providers are supported:
|
||||
`github` **(default)**, `gitlab`, `bitbucket`, `azure`, `codecommit`, `local`,`gitea`, and `gerrit`.
|
||||
(3)
|
||||
|
||||
**git provider**: The [git_provider](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml#L5) field in a configuration file determines the GIT provider that will be used by Qodo Merge. Currently, the following providers are supported:
|
||||
`
|
||||
"github", "gitlab", "bitbucket", "azure", "codecommit", "local", "gerrit"
|
||||
`
|
||||
|
||||
Default is "github".
|
||||
|
||||
### CLI Health Check
|
||||
|
||||
To verify that Qodo Merge has been configured correctly, you can run this health check command from the repository root:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
@ -64,19 +67,21 @@ Commands for invoking the different tools via comments:
|
||||
- **Describe**: `/describe`
|
||||
- **Improve**: `/improve` (or `/improve_code` for bitbucket, since `/improve` is sometimes reserved)
|
||||
- **Ask**: `/ask "..."`
|
||||
- **Reflect**: `/reflect`
|
||||
- **Update Changelog**: `/update_changelog`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
To edit a specific configuration value, just add `--config_path=<value>` to any command.
|
||||
For example, if you want to edit the `review` tool configurations, you can run:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/review --pr_reviewer.extra_instructions="..." --pr_reviewer.require_score_review=false
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Any configuration value in [configuration file](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml) file can be similarly edited. Comment `/config` to see the list of available configurations.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Qodo Merge Automatic Feedback
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Disabling all automatic feedback
|
||||
|
||||
To easily disable all automatic feedback from Qodo Merge (GitHub App, GitLab Webhook, BitBucket App, Azure DevOps Webhook), set in a configuration file:
|
||||
@ -99,7 +104,6 @@ When this parameter is set to `true`, Qodo Merge will not run any automatic tool
|
||||
The [github_app](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml#L220) section defines GitHub app specific configurations.
|
||||
|
||||
The configuration parameter `pr_commands` defines the list of tools that will be **run automatically** when a new PR is opened:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[github_app]
|
||||
pr_commands = [
|
||||
@ -111,17 +115,6 @@ pr_commands = [
|
||||
|
||||
This means that when a new PR is opened/reopened or marked as ready for review, Qodo Merge will run the `describe`, `review` and `improve` tools.
|
||||
|
||||
**Draft PRs:**
|
||||
|
||||
By default, draft PRs are not considered for automatic tools, but you can change this by setting the `feedback_on_draft_pr` parameter to `true` in the configuration file.
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[github_app]
|
||||
feedback_on_draft_pr = true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Changing default tool parameters:**
|
||||
|
||||
You can override the default tool parameters by using one the three options for a [configuration file](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/): **wiki**, **local**, or **global**.
|
||||
For example, if your configuration file contains:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -132,12 +125,8 @@ generate_ai_title = true
|
||||
|
||||
Every time you run the `describe` tool (including automatic runs) the PR title will be generated by the AI.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Parameters for automated runs:**
|
||||
|
||||
You can customize configurations specifically for automated runs by using the `--config_path=<value>` parameter.
|
||||
For instance, to modify the `review` tool settings only for newly opened PRs, use:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[github_app]
|
||||
pr_commands = [
|
||||
@ -153,7 +142,6 @@ In addition to running automatic tools when a PR is opened, the GitHub app can a
|
||||
|
||||
The configuration toggle `handle_push_trigger` can be used to enable this feature.
|
||||
The configuration parameter `push_commands` defines the list of tools that will be **run automatically** when new code is pushed to the PR.
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[github_app]
|
||||
handle_push_trigger = true
|
||||
@ -162,15 +150,12 @@ push_commands = [
|
||||
"/review",
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This means that when new code is pushed to the PR, the Qodo Merge will run the `describe` and `review` tools, with the specified parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
### GitHub Action
|
||||
|
||||
`GitHub Action` is a different way to trigger Qodo Merge tools, and uses a different configuration mechanism than `GitHub App`.<br>
|
||||
You can configure settings for `GitHub Action` by adding environment variables under the env section in `.github/workflows/pr_agent.yml` file.
|
||||
Specifically, start by setting the following environment variables:
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
env:
|
||||
OPENAI_KEY: ${{ secrets.OPENAI_KEY }} # Make sure to add your OpenAI key to your repo secrets
|
||||
@ -180,7 +165,6 @@ Specifically, start by setting the following environment variables:
|
||||
github_action_config.auto_improve: "true" # enable\disable auto improve
|
||||
github_action_config.pr_actions: '["opened", "reopened", "ready_for_review", "review_requested"]'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`github_action_config.auto_review`, `github_action_config.auto_describe` and `github_action_config.auto_improve` are used to enable/disable automatic tools that run when a new PR is opened.
|
||||
If not set, the default configuration is for all three tools to run automatically when a new PR is opened.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -189,7 +173,7 @@ If not set, the default configuration is `["opened", "reopened", "ready_for_revi
|
||||
|
||||
`github_action_config.enable_output` are used to enable/disable github actions [output parameter](https://docs.github.com/en/actions/creating-actions/metadata-syntax-for-github-actions#outputs-for-docker-container-and-javascript-actions) (default is `true`).
|
||||
Review result is output as JSON to `steps.{step-id}.outputs.review` property.
|
||||
The JSON structure is equivalent to the yaml data structure defined in [pr_reviewer_prompts.toml](https://github.com/qodo-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/pr_reviewer_prompts.toml).
|
||||
The JSON structure is equivalent to the yaml data structure defined in [pr_reviewer_prompts.toml](https://github.com/idubnori/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/pr_reviewer_prompts.toml).
|
||||
|
||||
Note that you can give additional config parameters by adding environment variables to `.github/workflows/pr_agent.yml`, or by using a `.pr_agent.toml` [configuration file](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/#global-configuration-file) in the root of your repo
|
||||
|
||||
@ -203,7 +187,6 @@ publish_labels = false
|
||||
to prevent Qodo Merge from publishing labels when running the `describe` tool.
|
||||
|
||||
### GitLab Webhook
|
||||
|
||||
After setting up a GitLab webhook, to control which commands will run automatically when a new MR is opened, you can set the `pr_commands` parameter in the configuration file, similar to the GitHub App:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
@ -218,7 +201,6 @@ pr_commands = [
|
||||
the GitLab webhook can also respond to new code that is pushed to an open MR.
|
||||
The configuration toggle `handle_push_trigger` can be used to enable this feature.
|
||||
The configuration parameter `push_commands` defines the list of tools that will be **run automatically** when new code is pushed to the MR.
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[gitlab]
|
||||
handle_push_trigger = true
|
||||
@ -231,13 +213,11 @@ push_commands = [
|
||||
Note that to use the 'handle_push_trigger' feature, you need to give the gitlab webhook also the "Push events" scope.
|
||||
|
||||
### BitBucket App
|
||||
Similar to GitHub app, when running Qodo Merge from BitBucket App, the default [configuration file](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml) from a pre-built docker will be initially loaded.
|
||||
|
||||
Similar to GitHub app, when running Qodo Merge from BitBucket App, the default [configuration file](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml) will be initially loaded.
|
||||
|
||||
By uploading a local `.pr_agent.toml` file to the root of the repo's default branch, you can edit and customize any configuration parameter. Note that you need to upload `.pr_agent.toml` prior to creating a PR, in order for the configuration to take effect.
|
||||
By uploading a local `.pr_agent.toml` file to the root of the repo's main branch, you can edit and customize any configuration parameter. Note that you need to upload `.pr_agent.toml` prior to creating a PR, in order for the configuration to take effect.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, if your local `.pr_agent.toml` file contains:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[pr_reviewer]
|
||||
extra_instructions = "Answer in japanese"
|
||||
@ -245,10 +225,12 @@ extra_instructions = "Answer in japanese"
|
||||
|
||||
Each time you invoke a `/review` tool, it will use the extra instructions you set in the local configuration file.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Note that among other limitations, BitBucket provides relatively low rate-limits for applications (up to 1000 requests per hour), and does not provide an API to track the actual rate-limit usage.
|
||||
If you experience a lack of responses from Qodo Merge, you might want to set: `bitbucket_app.avoid_full_files=true` in your configuration file.
|
||||
This will prevent Qodo Merge from acquiring the full file content, and will only use the diff content. This will reduce the number of requests made to BitBucket, at the cost of small decrease in accuracy, as dynamic context will not be applicable.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### BitBucket Self-Hosted App automatic tools
|
||||
|
||||
To control which commands will run automatically when a new PR is opened, you can set the `pr_commands` parameter in the configuration file:
|
||||
@ -261,12 +243,10 @@ pr_commands = [
|
||||
"/improve --pr_code_suggestions.commitable_code_suggestions=true --pr_code_suggestions.suggestions_score_threshold=7",
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note that we set specifically for bitbucket, we recommend using: `--pr_code_suggestions.suggestions_score_threshold=7` and that is the default value we set for bitbucket.
|
||||
Since this platform only supports inline code suggestions, we want to limit the number of suggestions, and only present a limited number.
|
||||
|
||||
To enable BitBucket app to respond to each **push** to the PR, set (for example):
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[bitbucket_app]
|
||||
handle_push_trigger = true
|
||||
@ -279,7 +259,6 @@ push_commands = [
|
||||
### Azure DevOps provider
|
||||
|
||||
To use Azure DevOps provider use the following settings in configuration.toml:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
git_provider="azure"
|
||||
@ -293,7 +272,6 @@ If PAT was chosen, you can assign the value in .secrets.toml.
|
||||
If DefaultAzureCredential was chosen, you can assigned the additional env vars like AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET directly,
|
||||
or use managed identity/az cli (for local development) without any additional configuration.
|
||||
in any case, 'org' value must be assigned in .secrets.toml:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[azure_devops]
|
||||
org = "https://dev.azure.com/YOUR_ORGANIZATION/"
|
||||
@ -303,7 +281,6 @@ org = "https://dev.azure.com/YOUR_ORGANIZATION/"
|
||||
#### Azure DevOps Webhook
|
||||
|
||||
To control which commands will run automatically when a new PR is opened, you can set the `pr_commands` parameter in the configuration file, similar to the GitHub App:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[azure_devops_server]
|
||||
pr_commands = [
|
||||
@ -312,16 +289,3 @@ pr_commands = [
|
||||
"/improve",
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Gitea Webhook
|
||||
|
||||
After setting up a Gitea webhook, to control which commands will run automatically when a new MR is opened, you can set the `pr_commands` parameter in the configuration file, similar to the GitHub App:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[gitea]
|
||||
pr_commands = [
|
||||
"/describe",
|
||||
"/review",
|
||||
"/improve",
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,43 +1,20 @@
|
||||
## Changing a model in PR-Agent
|
||||
|
||||
See [here](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/algo/__init__.py) for a list of available models.
|
||||
To use a different model than the default (o4-mini), you need to edit in the [configuration file](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml#L2) the fields:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
To use a different model than the default (GPT-4), you need to edit in the [configuration file](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml#L2) the fields:
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
model = "..."
|
||||
fallback_models = ["..."]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For models and environments not from OpenAI, you might need to provide additional keys and other parameters.
|
||||
You can give parameters via a configuration file, or from environment variables.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Model-specific environment variables"
|
||||
See [litellm documentation](https://litellm.vercel.app/docs/proxy/quick_start#supported-llms) for the environment variables needed per model, as they may vary and change over time. Our documentation per-model may not always be up-to-date with the latest changes.
|
||||
Failing to set the needed keys of a specific model will usually result in litellm not identifying the model type, and failing to utilize it.
|
||||
|
||||
### OpenAI like API
|
||||
To use an OpenAI like API, set the following in your `.secrets.toml` file:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[openai]
|
||||
api_base = "https://api.openai.com/v1"
|
||||
api_key = "sk-..."
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
or use the environment variables (make sure to use double underscores `__`):
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
OPENAI__API_BASE=https://api.openai.com/v1
|
||||
OPENAI__KEY=sk-...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can give parameters via a configuration file (see below for instructions), or from environment variables. See [litellm documentation](https://litellm.vercel.app/docs/proxy/quick_start#supported-llms) for the environment variables relevant per model.
|
||||
|
||||
### Azure
|
||||
|
||||
To use Azure, set in your `.secrets.toml` (working from CLI), or in the GitHub `Settings > Secrets and variables` (working from GitHub App or GitHub Action):
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[openai]
|
||||
key = "" # your azure api key
|
||||
api_type = "azure"
|
||||
@ -47,39 +24,18 @@ deployment_id = "" # The deployment name you chose when you deployed the engine
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and set in your configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
model="" # the OpenAI model you've deployed on Azure (e.g. gpt-4o)
|
||||
fallback_models=["..."]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To use Azure AD (Entra id) based authentication set in your `.secrets.toml` (working from CLI), or in the GitHub `Settings > Secrets and variables` (working from GitHub App or GitHub Action):
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[azure_ad]
|
||||
client_id = "" # Your Azure AD application client ID
|
||||
client_secret = "" # Your Azure AD application client secret
|
||||
tenant_id = "" # Your Azure AD tenant ID
|
||||
api_base = "" # Your Azure OpenAI service base URL (e.g., https://openai.xyz.com/)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Passing custom headers to the underlying LLM Model API can be done by setting extra_headers parameter to litellm.
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[litellm]
|
||||
extra_headers='{"projectId": "<authorized projectId >", ...}') #The value of this setting should be a JSON string representing the desired headers, a ValueError is thrown otherwise.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This enables users to pass authorization tokens or API keys, when routing requests through an API management gateway.
|
||||
|
||||
### Ollama
|
||||
|
||||
You can run models locally through either [VLLM](https://docs.litellm.ai/docs/providers/vllm) or [Ollama](https://docs.litellm.ai/docs/providers/ollama)
|
||||
|
||||
E.g. to use a new model locally via Ollama, set in `.secrets.toml` or in a configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
model = "ollama/qwen2.5-coder:32b"
|
||||
fallback_models=["ollama/qwen2.5-coder:32b"]
|
||||
@ -90,10 +46,6 @@ duplicate_examples=true # will duplicate the examples in the prompt, to help the
|
||||
api_base = "http://localhost:11434" # or whatever port you're running Ollama on
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
By default, Ollama uses a context window size of 2048 tokens. In most cases this is not enough to cover pr-agent promt and pull-request diff. Context window size can be overridden with the `OLLAMA_CONTEXT_LENGTH` environment variable. For example, to set the default context length to 8K, use: `OLLAMA_CONTEXT_LENGTH=8192 ollama serve`. More information you can find on the [official ollama faq](https://github.com/ollama/ollama/blob/main/docs/faq.md#how-can-i-specify-the-context-window-size).
|
||||
|
||||
Please note that the `custom_model_max_tokens` setting should be configured in accordance with the `OLLAMA_CONTEXT_LENGTH`. Failure to do so may result in unexpected model output.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Local models vs commercial models"
|
||||
Qodo Merge is compatible with almost any AI model, but analyzing complex code repositories and pull requests requires a model specifically optimized for code analysis.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -106,8 +58,7 @@ Please note that the `custom_model_max_tokens` setting should be configured in a
|
||||
### Hugging Face
|
||||
|
||||
To use a new model with Hugging Face Inference Endpoints, for example, set:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config] # in configuration.toml
|
||||
model = "huggingface/meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-chat-hf"
|
||||
fallback_models=["huggingface/meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-chat-hf"]
|
||||
@ -117,59 +68,40 @@ custom_model_max_tokens=... # set the maximal input tokens for the model
|
||||
key = ... # your Hugging Face api key
|
||||
api_base = ... # the base url for your Hugging Face inference endpoint
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
(you can obtain a Llama2 key from [here](https://replicate.com/replicate/llama-2-70b-chat/api))
|
||||
|
||||
### Replicate
|
||||
|
||||
To use Llama2 model with Replicate, for example, set:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config] # in configuration.toml
|
||||
model = "replicate/llama-2-70b-chat:2c1608e18606fad2812020dc541930f2d0495ce32eee50074220b87300bc16e1"
|
||||
fallback_models=["replicate/llama-2-70b-chat:2c1608e18606fad2812020dc541930f2d0495ce32eee50074220b87300bc16e1"]
|
||||
[replicate] # in .secrets.toml
|
||||
key = ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
(you can obtain a Llama2 key from [here](https://replicate.com/replicate/llama-2-70b-chat/api))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Also, review the [AiHandler](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/algo/ai_handler.py) file for instructions on how to set keys for other models.
|
||||
|
||||
### Groq
|
||||
|
||||
To use Llama3 model with Groq, for example, set:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config] # in configuration.toml
|
||||
model = "llama3-70b-8192"
|
||||
fallback_models = ["groq/llama3-70b-8192"]
|
||||
[groq] # in .secrets.toml
|
||||
key = ... # your Groq api key
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
(you can obtain a Groq key from [here](https://console.groq.com/keys))
|
||||
|
||||
### xAI
|
||||
|
||||
To use xAI's models with PR-Agent, set:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config] # in configuration.toml
|
||||
model = "xai/grok-2-latest"
|
||||
fallback_models = ["xai/grok-2-latest"] # or any other model as fallback
|
||||
|
||||
[xai] # in .secrets.toml
|
||||
key = "..." # your xAI API key
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can obtain an xAI API key from [xAI's console](https://console.x.ai/) by creating an account and navigating to the developer settings page.
|
||||
|
||||
### Vertex AI
|
||||
|
||||
To use Google's Vertex AI platform and its associated models (chat-bison/codechat-bison) set:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config] # in configuration.toml
|
||||
model = "vertex_ai/codechat-bison"
|
||||
fallback_models="vertex_ai/codechat-bison"
|
||||
@ -189,8 +121,8 @@ To use [Google AI Studio](https://aistudio.google.com/) models, set the relevant
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config] # in configuration.toml
|
||||
model="gemini/gemini-1.5-flash"
|
||||
fallback_models=["gemini/gemini-1.5-flash"]
|
||||
model="google_ai_studio/gemini-1.5-flash"
|
||||
fallback_models=["google_ai_studio/gemini-1.5-flash"]
|
||||
|
||||
[google_ai_studio] # in .secrets.toml
|
||||
gemini_api_key = "..."
|
||||
@ -202,37 +134,37 @@ If you don't want to set the API key in the .secrets.toml file, you can set the
|
||||
|
||||
To use Anthropic models, set the relevant models in the configuration section of the configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
model="anthropic/claude-3-opus-20240229"
|
||||
fallback_models=["anthropic/claude-3-opus-20240229"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And also set the api key in the .secrets.toml file:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[anthropic]
|
||||
KEY = "..."
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
See [litellm](https://docs.litellm.ai/docs/providers/anthropic#usage) documentation for more information about the environment variables required for Anthropic.
|
||||
|
||||
### Amazon Bedrock
|
||||
|
||||
To use Amazon Bedrock and its foundational models, add the below configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config] # in configuration.toml
|
||||
model="bedrock/anthropic.claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620-v1:0"
|
||||
fallback_models=["bedrock/anthropic.claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620-v1:0"]
|
||||
|
||||
[aws]
|
||||
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID="..."
|
||||
AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY="..."
|
||||
AWS_REGION_NAME="..."
|
||||
model="bedrock/anthropic.claude-3-sonnet-20240229-v1:0"
|
||||
fallback_models=["bedrock/anthropic.claude-v2:1"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
See [litellm](https://docs.litellm.ai/docs/providers/bedrock#usage) documentation for more information about the environment variables required for Amazon Bedrock.
|
||||
Note that you have to add access to foundational models before using them. Please refer to [this document](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/bedrock/latest/userguide/setting-up.html) for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are using the claude-3 model, please configure the following settings as there are parameters incompatible with claude-3.
|
||||
```
|
||||
[litellm]
|
||||
drop_params = true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
AWS session is automatically authenticated from your environment, but you can also explicitly set `AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID`, `AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY` and `AWS_REGION_NAME` environment variables. Please refer to [this document](https://litellm.vercel.app/docs/providers/bedrock) for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
### DeepSeek
|
||||
|
||||
@ -253,104 +185,19 @@ key = ...
|
||||
|
||||
(you can obtain a deepseek-chat key from [here](https://platform.deepseek.com))
|
||||
|
||||
### DeepInfra
|
||||
|
||||
To use DeepSeek model with DeepInfra, for example, set:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config] # in configuration.toml
|
||||
model = "deepinfra/deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama-70B"
|
||||
fallback_models = ["deepinfra/deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B"]
|
||||
[deepinfra] # in .secrets.toml
|
||||
key = ... # your DeepInfra api key
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
(you can obtain a DeepInfra key from [here](https://deepinfra.com/dash/api_keys))
|
||||
|
||||
### Mistral
|
||||
|
||||
To use models like Mistral or Codestral with Mistral, for example, set:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config] # in configuration.toml
|
||||
model = "mistral/mistral-small-latest"
|
||||
fallback_models = ["mistral/mistral-medium-latest"]
|
||||
[mistral] # in .secrets.toml
|
||||
key = "..." # your Mistral api key
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
(you can obtain a Mistral key from [here](https://console.mistral.ai/api-keys))
|
||||
|
||||
### Codestral
|
||||
|
||||
To use Codestral model with Codestral, for example, set:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config] # in configuration.toml
|
||||
model = "codestral/codestral-latest"
|
||||
fallback_models = ["codestral/codestral-2405"]
|
||||
[codestral] # in .secrets.toml
|
||||
key = "..." # your Codestral api key
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
(you can obtain a Codestral key from [here](https://console.mistral.ai/codestral))
|
||||
|
||||
### Openrouter
|
||||
|
||||
To use model from Openrouter, for example, set:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config] # in configuration.toml
|
||||
model="openrouter/anthropic/claude-3.7-sonnet"
|
||||
fallback_models=["openrouter/deepseek/deepseek-chat"]
|
||||
custom_model_max_tokens=20000
|
||||
|
||||
[openrouter] # in .secrets.toml or passed an environment variable openrouter__key
|
||||
key = "..." # your openrouter api key
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
(you can obtain an Openrouter API key from [here](https://openrouter.ai/settings/keys))
|
||||
|
||||
### Custom models
|
||||
|
||||
If the relevant model doesn't appear [here](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/algo/__init__.py), you can still use it as a custom model:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Set the model name in the configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
(1) Set the model name in the configuration file:
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
model="custom_model_name"
|
||||
fallback_models=["custom_model_name"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Set the maximal tokens for the model:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
(2) Set the maximal tokens for the model:
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
custom_model_max_tokens= ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Go to [litellm documentation](https://litellm.vercel.app/docs/proxy/quick_start#supported-llms), find the model you want to use, and set the relevant environment variables.
|
||||
|
||||
4. Most reasoning models do not support chat-style inputs (`system` and `user` messages) or temperature settings.
|
||||
To bypass chat templates and temperature controls, set `config.custom_reasoning_model = true` in your configuration file.
|
||||
|
||||
## Dedicated parameters
|
||||
|
||||
### OpenAI models
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
reasoning_efffort= = "medium" # "low", "medium", "high"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
With the OpenAI models that support reasoning effort (eg: o4-mini), you can specify its reasoning effort via `config` section. The default value is `medium`. You can change it to `high` or `low` based on your usage.
|
||||
|
||||
### Anthropic models
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
enable_claude_extended_thinking = false # Set to true to enable extended thinking feature
|
||||
extended_thinking_budget_tokens = 2048
|
||||
extended_thinking_max_output_tokens = 4096
|
||||
```
|
||||
(3) Go to [litellm documentation](https://litellm.vercel.app/docs/proxy/quick_start#supported-llms), find the model you want to use, and set the relevant environment variables.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,22 +1,20 @@
|
||||
The different tools and sub-tools used by Qodo Merge are adjustable via a Git configuration file.
|
||||
There are three main ways to set persistent configurations:
|
||||
The different tools and sub-tools used by Qodo Merge are adjustable via the **[configuration file](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml)**.
|
||||
|
||||
1. [Wiki](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/#wiki-configuration-file) configuration page 💎
|
||||
2. [Local](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/#local-configuration-file) configuration file
|
||||
3. [Global](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/#global-configuration-file) configuration file 💎
|
||||
In addition to general configuration options, each tool has its own configurations. For example, the `review` tool will use parameters from the [pr_reviewer](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml#L16) section in the configuration file.
|
||||
See the [Tools Guide](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/) for a detailed description of the different tools and their configurations.
|
||||
|
||||
There are three ways to set persistent configurations:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Wiki configuration page 💎
|
||||
2. Local configuration file
|
||||
3. Global configuration file 💎
|
||||
|
||||
In terms of precedence, wiki configurations will override local configurations, and local configurations will override global configurations.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
For a list of all possible configurations, see the [configuration options](https://github.com/qodo-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml/) page.
|
||||
In addition to general configuration options, each tool has its own configurations. For example, the `review` tool will use parameters from the [pr_reviewer](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/pr_agent/settings/configuration.toml#L16) section in the configuration file.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip "Tip1: Edit only what you need"
|
||||
!!! tip "Tip1: edit only what you need"
|
||||
Your configuration file should be minimal, and edit only the relevant values. Don't copy the entire configuration options, since it can lead to legacy problems when something changes.
|
||||
!!! tip "Tip2: Show relevant configurations"
|
||||
If you set `config.output_relevant_configurations` to True, each tool will also output in a collapsible section its relevant configurations. This can be useful for debugging, or getting to know the configurations better.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip "Tip2: show relevant configurations"
|
||||
If you set `config.output_relevant_configurations=true`, each tool will also output in a collapsible section its relevant configurations. This can be useful for debugging, or getting to know the configurations better.
|
||||
|
||||
## Wiki configuration file 💎
|
||||
|
||||
@ -25,6 +23,7 @@ In addition to general configuration options, each tool has its own configuratio
|
||||
With Qodo Merge, you can set configurations by creating a page called `.pr_agent.toml` in the [wiki](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/wiki/pr_agent.toml) of the repo.
|
||||
The advantage of this method is that it allows to set configurations without needing to commit new content to the repo - just edit the wiki page and **save**.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
Click [here](https://codium.ai/images/pr_agent/wiki_configuration_pr_agent.mp4) to see a short instructional video. We recommend surrounding the configuration content with triple-quotes (or \`\`\`toml), to allow better presentation when displayed in the wiki as markdown.
|
||||
@ -41,7 +40,8 @@ Qodo Merge will know to remove the surrounding quotes when reading the configura
|
||||
|
||||
`Platforms supported: GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, Azure DevOps`
|
||||
|
||||
By uploading a local `.pr_agent.toml` file to the root of the repo's default branch, you can edit and customize any configuration parameter. Note that you need to upload or update `.pr_agent.toml` before using the PR Agent tools (either at PR creation or via manual trigger) for the configuration to take effect.
|
||||
|
||||
By uploading a local `.pr_agent.toml` file to the root of the repo's main branch, you can edit and customize any configuration parameter. Note that you need to upload `.pr_agent.toml` prior to creating a PR, in order for the configuration to take effect.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, if you set in `.pr_agent.toml`:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -56,11 +56,12 @@ extra_instructions="""\
|
||||
|
||||
Then you can give a list of extra instructions to the `review` tool.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Global configuration file 💎
|
||||
|
||||
`Platforms supported: GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket`
|
||||
|
||||
If you create a repo called `pr-agent-settings` in your **organization**, its configuration file `.pr_agent.toml` will be used as a global configuration file for any other repo that belongs to the same organization.
|
||||
If you create a repo called `pr-agent-settings` in your **organization**, it's configuration file `.pr_agent.toml` will be used as a global configuration file for any other repo that belongs to the same organization.
|
||||
Parameters from a local `.pr_agent.toml` file, in a specific repo, will override the global configuration parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, in the GitHub organization `Codium-ai`:
|
||||
@ -68,29 +69,3 @@ For example, in the GitHub organization `Codium-ai`:
|
||||
- The file [`https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent-settings/.pr_agent.toml`](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent-settings/blob/main/.pr_agent.toml) serves as a global configuration file for all the repos in the GitHub organization `Codium-ai`.
|
||||
|
||||
- The repo [`https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent`](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/blob/main/.pr_agent.toml) inherits the global configuration file from `pr-agent-settings`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Bitbucket Organization level configuration file 💎
|
||||
|
||||
`Relevant platforms: Bitbucket Data Center`
|
||||
|
||||
In Bitbucket Data Center, there are two levels where you can define a global configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
- Project-level global configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
Create a repository named `pr-agent-settings` within a specific project. The configuration file in this repository will apply to all repositories under the same project.
|
||||
|
||||
- Organization-level global configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
Create a dedicated project to hold a global configuration file that affects all repositories across all projects in your organization.
|
||||
|
||||
**Setting up organization-level global configuration:**
|
||||
|
||||
1. Create a new project with both the name and key: PR_AGENT_SETTINGS.
|
||||
2. Inside the PR_AGENT_SETTINGS project, create a repository named pr-agent-settings.
|
||||
3. In this repository, add a `.pr_agent.toml` configuration file—structured similarly to the global configuration file described above.
|
||||
4. Optionally, you can add organizational-level [global best practices file](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/#global-configuration-file).
|
||||
|
||||
Repositories across your entire Bitbucket organization will inherit the configuration from this file.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Note"
|
||||
If both organization-level and project-level global settings are defined, the project-level settings will take precedence over the organization-level configuration. Additionally, parameters from a repository’s local .pr_agent.toml file will always override both global settings.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,13 +1,16 @@
|
||||
`Supported Git Platforms: GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
For optimal functionality of Qodo Merge, we recommend enabling a wiki for each repository where Qodo Merge is installed. The wiki serves several important purposes:
|
||||
|
||||
**Key Wiki Features: 💎**
|
||||
|
||||
- Storing a [configuration file](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/#wiki-configuration-file)
|
||||
- Defining a [`best_practices.md`](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#best-practices) file
|
||||
- Track [accepted suggestions](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/tools/improve/#suggestion-tracking)
|
||||
- Facilitates learning over time by creating an [auto_best_practices.md](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/core-abilities/auto_best_practices) file
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Setup Instructions (GitHub):**
|
||||
|
||||
To enable a wiki for your repository:
|
||||
@ -23,7 +26,7 @@ To enable a wiki for your repository:
|
||||
### Why Wiki?
|
||||
|
||||
- Your code (and its derivatives, including accepted code suggestions) is yours. Qodo Merge will never store it on external servers.
|
||||
- Repository changes typically require pull requests, which create overhead and are time-consuming. This process is too cumbersome for auto data aggregation, and is not very convenient even for managing frequently updated content like configuration files.
|
||||
- Repository changes typically require pull requests, which create overhead and are time-consuming. This process is too cumbersome for auto data aggregation, and is not very convenient even for managing frequently updated content like configuration files and best practices.
|
||||
- A repository wiki page provides an ideal balance:
|
||||
- It lives within your repository, making it suitable for code-related documentation
|
||||
- It enables quick updates without the overhead of pull requests
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,8 +1,9 @@
|
||||
# Usage guide
|
||||
|
||||
This section provides a detailed guide on how to use Qodo Merge.
|
||||
This page provides a detailed guide on how to use Qodo Merge.
|
||||
It includes information on how to adjust Qodo Merge configurations, define which tools will run automatically, and other advanced configurations.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- [Introduction](./introduction.md)
|
||||
- [Enabling a Wiki](./enabling_a_wiki)
|
||||
- [Configuration File](./configuration_options.md)
|
||||
@ -12,16 +13,15 @@ It includes information on how to adjust Qodo Merge configurations, define which
|
||||
- [GitHub App](./automations_and_usage.md#github-app)
|
||||
- [GitHub Action](./automations_and_usage.md#github-action)
|
||||
- [GitLab Webhook](./automations_and_usage.md#gitlab-webhook)
|
||||
- [Gitea Webhook](./automations_and_usage.md#gitea-webhook)
|
||||
- [BitBucket App](./automations_and_usage.md#bitbucket-app)
|
||||
- [Azure DevOps Provider](./automations_and_usage.md#azure-devops-provider)
|
||||
- [Managing Mail Notifications](./mail_notifications.md)
|
||||
- [Changing a Model](./changing_a_model.md)
|
||||
- [Additional Configurations](./additional_configurations.md)
|
||||
- [Additional Configurations Walkthrough](./additional_configurations.md)
|
||||
- [Ignoring files from analysis](./additional_configurations.md#ignoring-files-from-analysis)
|
||||
- [Extra instructions](./additional_configurations.md#extra-instructions)
|
||||
- [Working with large PRs](./additional_configurations.md#working-with-large-prs)
|
||||
- [Changing a model](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/changing_a_model/)
|
||||
- [Changing a model](./additional_configurations.md#changing-a-model)
|
||||
- [Patch Extra Lines](./additional_configurations.md#patch-extra-lines)
|
||||
- [FAQ](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/faq/)
|
||||
- [Editing the prompts](./additional_configurations.md#editing-the-prompts)
|
||||
- [Qodo Merge Models](./qodo_merge_models)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -5,6 +5,7 @@ After [installation](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/), there are t
|
||||
2. Online usage - by [commenting](https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent/pull/229#issuecomment-1695021901){:target="_blank"} on a PR
|
||||
3. Enabling Qodo Merge tools to run automatically when a new PR is opened
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Specifically, CLI commands can be issued by invoking a pre-built [docker image](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/locally/#using-docker-image), or by invoking a [locally cloned repo](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/locally/#run-from-source).
|
||||
|
||||
For online usage, you will need to setup either a [GitHub App](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/github/#run-as-a-github-app) or a [GitHub Action](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/github/#run-as-a-github-action) (GitHub), a [GitLab webhook](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/gitlab/#run-a-gitlab-webhook-server) (GitLab), or a [BitBucket App](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/installation/bitbucket/#run-using-codiumai-hosted-bitbucket-app) (BitBucket).
|
||||
|
||||
@ -8,10 +8,10 @@ As an alternative, you can filter in your mail provider the notifications specif
|
||||
|
||||
{width=512}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Another option to reduce the mail overload, yet still receive notifications on Qodo Merge tools, is to disable the help collapsible section in Qodo Merge bot comments.
|
||||
This can done by setting `enable_help_text=false` for the relevant tool in the configuration file.
|
||||
For example, to disable the help text for the `pr_reviewer` tool, set:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[pr_reviewer]
|
||||
enable_help_text = false
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,42 +1,37 @@
|
||||
|
||||
The default models used by Qodo Merge (April 2025) are a combination of Claude Sonnet 3.7 and Gemini 2.5 Pro.
|
||||
The default models used by Qodo Merge are a combination of Claude-3.5-sonnet and OpenAI's GPT-4 models.
|
||||
|
||||
### Selecting a Specific Model
|
||||
|
||||
Users can configure Qodo Merge to use only a specific model by editing the [configuration](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/) file.
|
||||
Users can configure Qodo Merge to use a specific model by editing the [configuration](https://qodo-merge-docs.qodo.ai/usage-guide/configuration_options/) file.
|
||||
The models supported by Qodo Merge are:
|
||||
|
||||
- `claude-3-7-sonnet`
|
||||
- `o4-mini`
|
||||
- `gpt-4.1`
|
||||
- `gemini-2.5-pro`
|
||||
- `deepseek/r1`
|
||||
- `claude-3-5-sonnet`
|
||||
- `gpt-4o`
|
||||
- `deepseek-r1`
|
||||
- `o3-mini`
|
||||
|
||||
To restrict Qodo Merge to using only `o4-mini`, add this setting:
|
||||
To restrict Qodo Merge to using only `Claude-3.5-sonnet`, add this setting:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
model="o4-mini"
|
||||
model="claude-3-5-sonnet"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To restrict Qodo Merge to using only `GPT-4.1`, add this setting:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
To restrict Qodo Merge to using only `GPT-4o`, add this setting:
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
model="gpt-4.1"
|
||||
model="gpt-4o"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To restrict Qodo Merge to using only `gemini-2.5-pro`, add this setting:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
model="gemini-2.5-pro"
|
||||
To restrict Qodo Merge to using only `deepseek-r1`, add this setting:
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
To restrict Qodo Merge to using only `deepseek-r1` us-hosted, add this setting:
|
||||
|
||||
```toml
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
model="deepseek/r1"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To restrict Qodo Merge to using only `o3-mini`, add this setting:
|
||||
```
|
||||
[config]
|
||||
model="o3-mini"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
site_name: Qodo Merge (and open-source PR-Agent)
|
||||
repo_url: https://github.com/qodo-ai/pr-agent
|
||||
repo_name: Qodo-ai/pr-agent
|
||||
repo_url: https://github.com/Codium-ai/pr-agent
|
||||
repo_name: Codium-ai/pr-agent
|
||||
|
||||
nav:
|
||||
- Overview:
|
||||
@ -20,7 +20,6 @@ nav:
|
||||
- Managing Mail Notifications: 'usage-guide/mail_notifications.md'
|
||||
- Changing a Model: 'usage-guide/changing_a_model.md'
|
||||
- Additional Configurations: 'usage-guide/additional_configurations.md'
|
||||
- Frequently Asked Questions: 'faq/index.md'
|
||||
- 💎 Qodo Merge Models: 'usage-guide/qodo_merge_models.md'
|
||||
- Tools:
|
||||
- 'tools/index.md'
|
||||
@ -29,7 +28,7 @@ nav:
|
||||
- Improve: 'tools/improve.md'
|
||||
- Ask: 'tools/ask.md'
|
||||
- Update Changelog: 'tools/update_changelog.md'
|
||||
- Help Docs: 'tools/help_docs.md'
|
||||
- Similar Issues: 'tools/similar_issues.md'
|
||||
- Help: 'tools/help.md'
|
||||
- 💎 Analyze: 'tools/analyze.md'
|
||||
- 💎 Test: 'tools/test.md'
|
||||
@ -40,32 +39,25 @@ nav:
|
||||
- 💎 CI Feedback: 'tools/ci_feedback.md'
|
||||
- 💎 Similar Code: 'tools/similar_code.md'
|
||||
- 💎 Implement: 'tools/implement.md'
|
||||
- 💎 Scan Repo Discussions: 'tools/scan_repo_discussions.md'
|
||||
- Core Abilities:
|
||||
- 'core-abilities/index.md'
|
||||
- Auto best practices: 'core-abilities/auto_best_practices.md'
|
||||
- Chat on code suggestions: 'core-abilities/chat_on_code_suggestions.md'
|
||||
- Code validation: 'core-abilities/code_validation.md'
|
||||
- Compression strategy: 'core-abilities/compression_strategy.md'
|
||||
- Dynamic context: 'core-abilities/dynamic_context.md'
|
||||
- Fetching ticket context: 'core-abilities/fetching_ticket_context.md'
|
||||
- Impact evaluation: 'core-abilities/impact_evaluation.md'
|
||||
- Incremental Update: 'core-abilities/incremental_update.md'
|
||||
- Interactivity: 'core-abilities/interactivity.md'
|
||||
- Auto best practices: 'core-abilities/auto_best_practices.md'
|
||||
- Local and global metadata: 'core-abilities/metadata.md'
|
||||
- RAG context enrichment: 'core-abilities/rag_context_enrichment.md'
|
||||
- Dynamic context: 'core-abilities/dynamic_context.md'
|
||||
- Self-reflection: 'core-abilities/self_reflection.md'
|
||||
- Impact evaluation: 'core-abilities/impact_evaluation.md'
|
||||
- Interactivity: 'core-abilities/interactivity.md'
|
||||
- Compression strategy: 'core-abilities/compression_strategy.md'
|
||||
- Code-oriented YAML: 'core-abilities/code_oriented_yaml.md'
|
||||
- Static code analysis: 'core-abilities/static_code_analysis.md'
|
||||
- Code Fine-tuning Benchmark: 'finetuning_benchmark/index.md'
|
||||
- Chrome Extension:
|
||||
- Qodo Merge Chrome Extension: 'chrome-extension/index.md'
|
||||
- Features: 'chrome-extension/features.md'
|
||||
- Data Privacy: 'chrome-extension/data_privacy.md'
|
||||
- Options: 'chrome-extension/options.md'
|
||||
- PR Benchmark:
|
||||
- PR Benchmark: 'pr_benchmark/index.md'
|
||||
- Recent Updates:
|
||||
- Recent Updates: 'recent_updates/index.md'
|
||||
- AI Docs Search: 'ai_search/index.md'
|
||||
- FAQ:
|
||||
- FAQ: 'faq/index.md'
|
||||
# - Code Fine-tuning Benchmark: 'finetuning_benchmark/index.md'
|
||||
|
||||
theme:
|
||||
@ -86,6 +78,7 @@ theme:
|
||||
- content.tabs.link
|
||||
- content.code.annotation
|
||||
- content.code.copy
|
||||
- content.tabs.link
|
||||
language: en
|
||||
custom_dir: overrides
|
||||
|
||||
@ -153,8 +146,6 @@ markdown_extensions:
|
||||
- pymdownx.emoji:
|
||||
emoji_index: !!python/name:material.extensions.emoji.twemoji
|
||||
emoji_generator: !!python/name:material.extensions.emoji.to_svg
|
||||
- pymdownx.tabbed:
|
||||
alternate_style: true
|
||||
- toc:
|
||||
title: On this page
|
||||
toc_depth: 3
|
||||
@ -162,4 +153,4 @@ markdown_extensions:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
copyright: |
|
||||
© 2025 <a href="https://www.codium.ai/" target="_blank" rel="noopener">QodoAI</a>
|
||||
© 2024 <a href="https://www.codium.ai/" target="_blank" rel="noopener">CodiumAI</a>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -82,7 +82,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
<footer class="wrapper">
|
||||
<div class="container">
|
||||
<p class="footer-text">© 2025 <a href="https://www.qodo.ai/" target="_blank" rel="noopener">Qodo</a></p>
|
||||
<p class="footer-text">© 2024 <a href="https://www.qodo.ai/" target="_blank" rel="noopener">Qodo</a></p>
|
||||
<div class="footer-links">
|
||||
<a href="https://qodo-gen-docs.qodo.ai/">Qodo Gen</a>
|
||||
<p>|</p>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -3,7 +3,6 @@ from functools import partial
|
||||
|
||||
from pr_agent.algo.ai_handlers.base_ai_handler import BaseAiHandler
|
||||
from pr_agent.algo.ai_handlers.litellm_ai_handler import LiteLLMAIHandler
|
||||
from pr_agent.algo.cli_args import CliArgs
|
||||
from pr_agent.algo.utils import update_settings_from_args
|
||||
from pr_agent.config_loader import get_settings
|
||||
from pr_agent.git_providers.utils import apply_repo_settings
|
||||
@ -13,7 +12,6 @@ from pr_agent.tools.pr_code_suggestions import PRCodeSuggestions
|
||||
from pr_agent.tools.pr_config import PRConfig
|
||||
from pr_agent.tools.pr_description import PRDescription
|
||||
from pr_agent.tools.pr_generate_labels import PRGenerateLabels
|
||||
from pr_agent.tools.pr_help_docs import PRHelpDocs
|
||||
from pr_agent.tools.pr_help_message import PRHelpMessage
|
||||
from pr_agent.tools.pr_line_questions import PR_LineQuestions
|
||||
from pr_agent.tools.pr_questions import PRQuestions
|
||||
@ -40,13 +38,11 @@ command2class = {
|
||||
"similar_issue": PRSimilarIssue,
|
||||
"add_docs": PRAddDocs,
|
||||
"generate_labels": PRGenerateLabels,
|
||||
"help_docs": PRHelpDocs,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
commands = list(command2class.keys())
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class PRAgent:
|
||||
def __init__(self, ai_handler: partial[BaseAiHandler,] = LiteLLMAIHandler):
|
||||
self.ai_handler = ai_handler # will be initialized in run_action
|
||||
@ -64,42 +60,30 @@ class PRAgent:
|
||||
else:
|
||||
action, *args = request
|
||||
|
||||
# validate args
|
||||
is_valid, arg = CliArgs.validate_user_args(args)
|
||||
if not is_valid:
|
||||
forbidden_cli_args = ['enable_auto_approval', 'approve_pr_on_self_review', 'base_url', 'url', 'app_name', 'secret_provider',
|
||||
'git_provider', 'skip_keys', 'openai.key', 'ANALYTICS_FOLDER', 'uri', 'app_id', 'webhook_secret',
|
||||
'bearer_token', 'PERSONAL_ACCESS_TOKEN', 'override_deployment_type', 'private_key',
|
||||
'local_cache_path', 'enable_local_cache', 'jira_base_url', 'api_base', 'api_type', 'api_version',
|
||||
'skip_keys']
|
||||
if args:
|
||||
for arg in args:
|
||||
if arg.startswith('--'):
|
||||
arg_word = arg.lower()
|
||||
arg_word = arg_word.replace('__', '.') # replace double underscore with dot, e.g. --openai__key -> --openai.key
|
||||
for forbidden_arg in forbidden_cli_args:
|
||||
forbidden_arg_word = forbidden_arg.lower()
|
||||
if '.' not in forbidden_arg_word:
|
||||
forbidden_arg_word = '.' + forbidden_arg_word
|
||||
if forbidden_arg_word in arg_word:
|
||||
get_logger().error(
|
||||
f"CLI argument for param '{arg}' is forbidden. Use instead a configuration file."
|
||||
f"CLI argument for param '{forbidden_arg}' is forbidden. Use instead a configuration file."
|
||||
)
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
# Update settings from args
|
||||
args = update_settings_from_args(args)
|
||||
|
||||
# Append the response language in the extra instructions
|
||||
response_language = get_settings().config.get('response_language', 'en-us')
|
||||
if response_language.lower() != 'en-us':
|
||||
get_logger().info(f'User has set the response language to: {response_language}')
|
||||
for key in get_settings():
|
||||
setting = get_settings().get(key)
|
||||
if str(type(setting)) == "<class 'dynaconf.utils.boxing.DynaBox'>":
|
||||
if hasattr(setting, 'extra_instructions'):
|
||||
current_extra_instructions = setting.extra_instructions
|
||||
|
||||
# Define the language-specific instruction and the separator
|
||||
lang_instruction_text = f"Your response MUST be written in the language corresponding to locale code: '{response_language}'. This is crucial."
|
||||
separator_text = "\n======\n\nIn addition, "
|
||||
|
||||
# Check if the specific language instruction is already present to avoid duplication
|
||||
if lang_instruction_text not in str(current_extra_instructions):
|
||||
if current_extra_instructions: # If there's existing text
|
||||
setting.extra_instructions = str(current_extra_instructions) + separator_text + lang_instruction_text
|
||||
else: # If extra_instructions was None or empty
|
||||
setting.extra_instructions = lang_instruction_text
|
||||
# If lang_instruction_text is already present, do nothing.
|
||||
|
||||
action = action.lstrip("/").lower()
|
||||
if action not in command2class:
|
||||
get_logger().warning(f"Unknown command: {action}")
|
||||
get_logger().error(f"Unknown command: {action}")
|
||||
return False
|
||||
with get_logger().contextualize(command=action, pr_url=pr_url):
|
||||
get_logger().info("PR-Agent request handler started", analytics=True)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -20,14 +20,6 @@ MAX_TOKENS = {
|
||||
'gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18': 128000, # 128K, but may be limited by config.max_model_tokens
|
||||
'gpt-4o-2024-08-06': 128000, # 128K, but may be limited by config.max_model_tokens
|
||||
'gpt-4o-2024-11-20': 128000, # 128K, but may be limited by config.max_model_tokens
|
||||
'gpt-4.5-preview': 128000, # 128K, but may be limited by config.max_model_tokens
|
||||
'gpt-4.5-preview-2025-02-27': 128000, # 128K, but may be limited by config.max_model_tokens
|
||||
'gpt-4.1': 1047576,
|
||||
'gpt-4.1-2025-04-14': 1047576,
|
||||
'gpt-4.1-mini': 1047576,
|
||||
'gpt-4.1-mini-2025-04-14': 1047576,
|
||||
'gpt-4.1-nano': 1047576,
|
||||
'gpt-4.1-nano-2025-04-14': 1047576,
|
||||
'o1-mini': 128000, # 128K, but may be limited by config.max_model_tokens
|
||||
'o1-mini-2024-09-12': 128000, # 128K, but may be limited by config.max_model_tokens
|
||||
'o1-preview': 128000, # 128K, but may be limited by config.max_model_tokens
|
||||
@ -36,10 +28,6 @@ MAX_TOKENS = {
|
||||
'o1': 204800, # 200K, but may be limited by config.max_model_tokens
|
||||
'o3-mini': 204800, # 200K, but may be limited by config.max_model_tokens
|
||||
'o3-mini-2025-01-31': 204800, # 200K, but may be limited by config.max_model_tokens
|
||||
'o3': 200000, # 200K, but may be limited by config.max_model_tokens
|
||||
'o3-2025-04-16': 200000, # 200K, but may be limited by config.max_model_tokens
|
||||
'o4-mini': 200000, # 200K, but may be limited by config.max_model_tokens
|
||||
'o4-mini-2025-04-16': 200000, # 200K, but may be limited by config.max_model_tokens
|
||||
'claude-instant-1': 100000,
|
||||
'claude-2': 100000,
|
||||
'command-nightly': 4096,
|
||||
@ -53,74 +41,40 @@ MAX_TOKENS = {
|
||||
'vertex_ai/claude-3-5-haiku@20241022': 100000,
|
||||
'vertex_ai/claude-3-sonnet@20240229': 100000,
|
||||
'vertex_ai/claude-3-opus@20240229': 100000,
|
||||
'vertex_ai/claude-opus-4@20250514': 200000,
|
||||
'vertex_ai/claude-3-5-sonnet@20240620': 100000,
|
||||
'vertex_ai/claude-3-5-sonnet-v2@20241022': 100000,
|
||||
'vertex_ai/claude-3-7-sonnet@20250219': 200000,
|
||||
'vertex_ai/claude-sonnet-4@20250514': 200000,
|
||||
'vertex_ai/gemini-1.5-pro': 1048576,
|
||||
'vertex_ai/gemini-2.5-pro-preview-03-25': 1048576,
|
||||
'vertex_ai/gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06': 1048576,
|
||||
'vertex_ai/gemini-1.5-flash': 1048576,
|
||||
'vertex_ai/gemini-2.0-flash': 1048576,
|
||||
'vertex_ai/gemini-2.5-flash-preview-04-17': 1048576,
|
||||
'vertex_ai/gemini-2.5-flash-preview-05-20': 1048576,
|
||||
'vertex_ai/gemini-2.0-flash-exp': 1048576,
|
||||
'vertex_ai/gemma2': 8200,
|
||||
'gemini/gemini-1.5-pro': 1048576,
|
||||
'gemini/gemini-1.5-flash': 1048576,
|
||||
'gemini/gemini-2.0-flash': 1048576,
|
||||
'gemini/gemini-2.5-flash-preview-04-17': 1048576,
|
||||
'gemini/gemini-2.5-flash-preview-05-20': 1048576,
|
||||
'gemini/gemini-2.5-pro-preview-03-25': 1048576,
|
||||
'gemini/gemini-2.5-pro-preview-05-06': 1048576,
|
||||
'gemini/gemini-2.0-flash-exp': 1048576,
|
||||
'codechat-bison': 6144,
|
||||
'codechat-bison-32k': 32000,
|
||||
'anthropic.claude-instant-v1': 100000,
|
||||
'anthropic.claude-v1': 100000,
|
||||
'anthropic.claude-v2': 100000,
|
||||
'anthropic/claude-3-opus-20240229': 100000,
|
||||
'anthropic/claude-opus-4-20250514': 200000,
|
||||
'anthropic/claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620': 100000,
|
||||
'anthropic/claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022': 100000,
|
||||
'anthropic/claude-3-7-sonnet-20250219': 200000,
|
||||
'anthropic/claude-sonnet-4-20250514': 200000,
|
||||
'claude-3-7-sonnet-20250219': 200000,
|
||||
'anthropic/claude-3-5-haiku-20241022': 100000,
|
||||
'bedrock/anthropic.claude-instant-v1': 100000,
|
||||
'bedrock/anthropic.claude-v2': 100000,
|
||||
'bedrock/anthropic.claude-v2:1': 100000,
|
||||
'bedrock/anthropic.claude-3-sonnet-20240229-v1:0': 100000,
|
||||
'bedrock/anthropic.claude-opus-4-20250514-v1:0': 200000,
|
||||
'bedrock/anthropic.claude-3-haiku-20240307-v1:0': 100000,
|
||||
'bedrock/anthropic.claude-3-5-haiku-20241022-v1:0': 100000,
|
||||
'bedrock/anthropic.claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620-v1:0': 100000,
|
||||
'bedrock/anthropic.claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022-v2:0': 100000,
|
||||
'bedrock/anthropic.claude-3-7-sonnet-20250219-v1:0': 200000,
|
||||
'bedrock/anthropic.claude-sonnet-4-20250514-v1:0': 200000,
|
||||
"bedrock/us.anthropic.claude-opus-4-20250514-v1:0": 200000,
|
||||
"bedrock/us.anthropic.claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022-v2:0": 100000,
|
||||
"bedrock/us.anthropic.claude-3-7-sonnet-20250219-v1:0": 200000,
|
||||
"bedrock/us.anthropic.claude-sonnet-4-20250514-v1:0": 200000,
|
||||
'claude-3-5-sonnet': 100000,
|
||||
'groq/meta-llama/llama-4-scout-17b-16e-instruct': 131072,
|
||||
'groq/meta-llama/llama-4-maverick-17b-128e-instruct': 131072,
|
||||
'groq/llama3-8b-8192': 8192,
|
||||
'groq/llama3-70b-8192': 8192,
|
||||
'groq/llama-3.1-8b-instant': 8192,
|
||||
'groq/llama-3.3-70b-versatile': 128000,
|
||||
'groq/mixtral-8x7b-32768': 32768,
|
||||
'groq/gemma2-9b-it': 8192,
|
||||
'xai/grok-2': 131072,
|
||||
'xai/grok-2-1212': 131072,
|
||||
'xai/grok-2-latest': 131072,
|
||||
'xai/grok-3': 131072,
|
||||
'xai/grok-3-beta': 131072,
|
||||
'xai/grok-3-fast': 131072,
|
||||
'xai/grok-3-fast-beta': 131072,
|
||||
'xai/grok-3-mini': 131072,
|
||||
'xai/grok-3-mini-beta': 131072,
|
||||
'xai/grok-3-mini-fast': 131072,
|
||||
'xai/grok-3-mini-fast-beta': 131072,
|
||||
'ollama/llama3': 4096,
|
||||
'watsonx/meta-llama/llama-3-8b-instruct': 4096,
|
||||
"watsonx/meta-llama/llama-3-70b-instruct": 4096,
|
||||
@ -128,23 +82,6 @@ MAX_TOKENS = {
|
||||
"watsonx/ibm/granite-13b-chat-v2": 8191,
|
||||
"watsonx/ibm/granite-34b-code-instruct": 8191,
|
||||
"watsonx/mistralai/mistral-large": 32768,
|
||||
"deepinfra/deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B": 128000,
|
||||
"deepinfra/deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama-70B": 128000,
|
||||
"deepinfra/deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1": 128000,
|
||||
"mistral/mistral-small-latest": 8191,
|
||||
"mistral/mistral-medium-latest": 8191,
|
||||
"mistral/mistral-large-2407": 128000,
|
||||
"mistral/mistral-large-latest": 128000,
|
||||
"mistral/open-mistral-7b": 8191,
|
||||
"mistral/open-mixtral-8x7b": 8191,
|
||||
"mistral/open-mixtral-8x22b": 8191,
|
||||
"mistral/codestral-latest": 8191,
|
||||
"mistral/open-mistral-nemo": 128000,
|
||||
"mistral/open-mistral-nemo-2407": 128000,
|
||||
"mistral/open-codestral-mamba": 256000,
|
||||
"mistral/codestral-mamba-latest": 256000,
|
||||
"codestral/codestral-latest": 8191,
|
||||
"codestral/codestral-2405": 8191,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
USER_MESSAGE_ONLY_MODELS = [
|
||||
@ -162,23 +99,5 @@ NO_SUPPORT_TEMPERATURE_MODELS = [
|
||||
"o1-2024-12-17",
|
||||
"o3-mini",
|
||||
"o3-mini-2025-01-31",
|
||||
"o1-preview",
|
||||
"o3",
|
||||
"o3-2025-04-16",
|
||||
"o4-mini",
|
||||
"o4-mini-2025-04-16",
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
SUPPORT_REASONING_EFFORT_MODELS = [
|
||||
"o3-mini",
|
||||
"o3-mini-2025-01-31",
|
||||
"o3",
|
||||
"o3-2025-04-16",
|
||||
"o4-mini",
|
||||
"o4-mini-2025-04-16",
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
CLAUDE_EXTENDED_THINKING_MODELS = [
|
||||
"anthropic/claude-3-7-sonnet-20250219",
|
||||
"claude-3-7-sonnet-20250219"
|
||||
"o1-preview"
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,17 +1,13 @@
|
||||
_LANGCHAIN_INSTALLED = False
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage, SystemMessage
|
||||
from langchain_openai import AzureChatOpenAI, ChatOpenAI
|
||||
_LANGCHAIN_INSTALLED = True
|
||||
except: # we don't enforce langchain as a dependency, so if it's not installed, just move on
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
import functools
|
||||
|
||||
import openai
|
||||
from tenacity import retry, retry_if_exception_type, retry_if_not_exception_type, stop_after_attempt
|
||||
from langchain_core.runnables import Runnable
|
||||
from openai import APIError, RateLimitError, Timeout
|
||||
from retry import retry
|
||||
|
||||
from pr_agent.algo.ai_handlers.base_ai_handler import BaseAiHandler
|
||||
from pr_agent.config_loader import get_settings
|
||||
@ -22,14 +18,17 @@ OPENAI_RETRIES = 5
|
||||
|
||||
class LangChainOpenAIHandler(BaseAiHandler):
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
if not _LANGCHAIN_INSTALLED:
|
||||
error_msg = "LangChain is not installed. Please install it with `pip install langchain`."
|
||||
get_logger().error(error_msg)
|
||||
raise ImportError(error_msg)
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize OpenAIHandler specific attributes here
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.azure = get_settings().get("OPENAI.API_TYPE", "").lower() == "azure"
|
||||
|
||||
# Create a default unused chat object to trigger early validation
|
||||
self._create_chat(self.deployment_id)
|
||||
|
||||
def chat(self, messages: list, model: str, temperature: float):
|
||||
chat = self._create_chat(self.deployment_id)
|
||||
return chat.invoke(input=messages, model=model, temperature=temperature)
|
||||
|
||||
@property
|
||||
def deployment_id(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
@ -37,10 +36,26 @@ class LangChainOpenAIHandler(BaseAiHandler):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return get_settings().get("OPENAI.DEPLOYMENT_ID", None)
|
||||
|
||||
async def _create_chat_async(self, deployment_id=None):
|
||||
@retry(exceptions=(APIError, Timeout, AttributeError, RateLimitError),
|
||||
tries=OPENAI_RETRIES, delay=2, backoff=2, jitter=(1, 3))
|
||||
async def chat_completion(self, model: str, system: str, user: str, temperature: float = 0.2):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
messages = [SystemMessage(content=system), HumanMessage(content=user)]
|
||||
|
||||
# get a chat completion from the formatted messages
|
||||
resp = self.chat(messages, model=model, temperature=temperature)
|
||||
finish_reason = "completed"
|
||||
return resp.content, finish_reason
|
||||
|
||||
except (Exception) as e:
|
||||
get_logger().error("Unknown error during OpenAI inference: ", e)
|
||||
raise e
|
||||
|
||||
def _create_chat(self, deployment_id=None):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
if self.azure:
|
||||
# Using Azure OpenAI service
|
||||
# using a partial function so we can set the deployment_id later to support fallback_deployments
|
||||
# but still need to access the other settings now so we can raise a proper exception if they're missing
|
||||
return AzureChatOpenAI(
|
||||
openai_api_key=get_settings().openai.key,
|
||||
openai_api_version=get_settings().openai.api_version,
|
||||
@ -48,64 +63,14 @@ class LangChainOpenAIHandler(BaseAiHandler):
|
||||
azure_endpoint=get_settings().openai.api_base,
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# Using standard OpenAI or other LLM services
|
||||
# for llms that compatible with openai, should use custom api base
|
||||
openai_api_base = get_settings().get("OPENAI.API_BASE", None)
|
||||
if openai_api_base is None or len(openai_api_base) == 0:
|
||||
return ChatOpenAI(openai_api_key=get_settings().openai.key)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return ChatOpenAI(
|
||||
openai_api_key=get_settings().openai.key,
|
||||
openai_api_base=openai_api_base
|
||||
)
|
||||
return ChatOpenAI(openai_api_key=get_settings().openai.key, openai_api_base=openai_api_base)
|
||||
except AttributeError as e:
|
||||
# Handle configuration errors
|
||||
error_msg = f"OpenAI {e.name} is required" if getattr(e, "name") else str(e)
|
||||
get_logger().error(error_msg)
|
||||
raise ValueError(error_msg) from e
|
||||
|
||||
@retry(
|
||||
retry=retry_if_exception_type(openai.APIError) & retry_if_not_exception_type(openai.RateLimitError),
|
||||
stop=stop_after_attempt(OPENAI_RETRIES),
|
||||
)
|
||||
async def chat_completion(self, model: str, system: str, user: str, temperature: float = 0.2, img_path: str = None):
|
||||
if img_path:
|
||||
get_logger().warning(f"Image path is not supported for LangChainOpenAIHandler. Ignoring image path: {img_path}")
|
||||
try:
|
||||
messages = [SystemMessage(content=system), HumanMessage(content=user)]
|
||||
llm = await self._create_chat_async(deployment_id=self.deployment_id)
|
||||
|
||||
if not isinstance(llm, Runnable):
|
||||
error_message = (
|
||||
f"The Langchain LLM object ({type(llm)}) does not implement the Runnable interface. "
|
||||
f"Please update your Langchain library to the latest version or "
|
||||
f"check your LLM configuration to support async calls. "
|
||||
f"PR-Agent is designed to utilize Langchain's async capabilities."
|
||||
)
|
||||
get_logger().error(error_message)
|
||||
raise NotImplementedError(error_message)
|
||||
|
||||
# Handle parameters based on LLM type
|
||||
if isinstance(llm, (ChatOpenAI, AzureChatOpenAI)):
|
||||
# OpenAI models support all parameters
|
||||
resp = await llm.ainvoke(
|
||||
input=messages,
|
||||
model=model,
|
||||
temperature=temperature
|
||||
)
|
||||
if getattr(e, "name"):
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"OpenAI {e.name} is required") from e
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# Other LLMs (like Gemini) only support input parameter
|
||||
get_logger().info(f"Using simplified ainvoke for {type(llm)}")
|
||||
resp = await llm.ainvoke(input=messages)
|
||||
|
||||
finish_reason = "completed"
|
||||
return resp.content, finish_reason
|
||||
|
||||
except openai.RateLimitError as e:
|
||||
get_logger().error(f"Rate limit error during LLM inference: {e}")
|
||||
raise
|
||||
except openai.APIError as e:
|
||||
get_logger().warning(f"Error during LLM inference: {e}")
|
||||
raise
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
get_logger().warning(f"Unknown error during LLM inference: {e}")
|
||||
raise openai.APIError from e
|
||||
raise e
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,16 +1,16 @@
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
import litellm
|
||||
import openai
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
from litellm import acompletion
|
||||
from tenacity import retry, retry_if_exception_type, retry_if_not_exception_type, stop_after_attempt
|
||||
from tenacity import retry, retry_if_exception_type, stop_after_attempt
|
||||
|
||||
from pr_agent.algo import CLAUDE_EXTENDED_THINKING_MODELS, NO_SUPPORT_TEMPERATURE_MODELS, SUPPORT_REASONING_EFFORT_MODELS, USER_MESSAGE_ONLY_MODELS
|
||||
from pr_agent.algo import NO_SUPPORT_TEMPERATURE_MODELS, USER_MESSAGE_ONLY_MODELS
|
||||
from pr_agent.algo.ai_handlers.base_ai_handler import BaseAiHandler
|
||||
from pr_agent.algo.utils import ReasoningEffort, get_version
|
||||
from pr_agent.algo.utils import get_version
|
||||
from pr_agent.config_loader import get_settings
|
||||
from pr_agent.log import get_logger
|
||||
import json
|
||||
|
||||
OPENAI_RETRIES = 5
|
||||
|
||||
@ -30,7 +30,6 @@ class LiteLLMAIHandler(BaseAiHandler):
|
||||
self.azure = False
|
||||
self.api_base = None
|
||||
self.repetition_penalty = None
|
||||
|
||||
if get_settings().get("OPENAI.KEY", None):
|
||||
openai.api_key = get_settings().openai.key
|
||||
litellm.openai_key = get_settings().openai.key
|
||||
@ -41,6 +40,11 @@ class LiteLLMAIHandler(BaseAiHandler):
|
||||
os.environ["AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID"] = get_settings().aws.AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
|
||||
os.environ["AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY"] = get_settings().aws.AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
|
||||
os.environ["AWS_REGION_NAME"] = get_settings().aws.AWS_REGION_NAME
|
||||
if get_settings().get("litellm.use_client"):
|
||||
litellm_token = get_settings().get("litellm.LITELLM_TOKEN")
|
||||
assert litellm_token, "LITELLM_TOKEN is required"
|
||||
os.environ["LITELLM_TOKEN"] = litellm_token
|
||||
litellm.use_client = True
|
||||
if get_settings().get("LITELLM.DROP_PARAMS", None):
|
||||
litellm.drop_params = get_settings().litellm.drop_params
|
||||
if get_settings().get("LITELLM.SUCCESS_CALLBACK", None):
|
||||
@ -59,7 +63,6 @@ class LiteLLMAIHandler(BaseAiHandler):
|
||||
litellm.api_version = get_settings().openai.api_version
|
||||
if get_settings().get("OPENAI.API_BASE", None):
|
||||
litellm.api_base = get_settings().openai.api_base
|
||||
self.api_base = get_settings().openai.api_base
|
||||
if get_settings().get("ANTHROPIC.KEY", None):
|
||||
litellm.anthropic_key = get_settings().anthropic.key
|
||||
if get_settings().get("COHERE.KEY", None):
|
||||
@ -68,8 +71,6 @@ class LiteLLMAIHandler(BaseAiHandler):
|
||||
litellm.api_key = get_settings().groq.key
|
||||
if get_settings().get("REPLICATE.KEY", None):
|
||||
litellm.replicate_key = get_settings().replicate.key
|
||||
if get_settings().get("XAI.KEY", None):
|
||||
litellm.api_key = get_settings().xai.key
|
||||
if get_settings().get("HUGGINGFACE.KEY", None):
|
||||
litellm.huggingface_key = get_settings().huggingface.key
|
||||
if get_settings().get("HUGGINGFACE.API_BASE", None) and 'huggingface' in get_settings().config.model:
|
||||
@ -94,75 +95,12 @@ class LiteLLMAIHandler(BaseAiHandler):
|
||||
if get_settings().get("DEEPSEEK.KEY", None):
|
||||
os.environ['DEEPSEEK_API_KEY'] = get_settings().get("DEEPSEEK.KEY")
|
||||
|
||||
# Support deepinfra models
|
||||
if get_settings().get("DEEPINFRA.KEY", None):
|
||||
os.environ['DEEPINFRA_API_KEY'] = get_settings().get("DEEPINFRA.KEY")
|
||||
|
||||
# Support mistral models
|
||||
if get_settings().get("MISTRAL.KEY", None):
|
||||
os.environ["MISTRAL_API_KEY"] = get_settings().get("MISTRAL.KEY")
|
||||
|
||||
# Support codestral models
|
||||
if get_settings().get("CODESTRAL.KEY", None):
|
||||
os.environ["CODESTRAL_API_KEY"] = get_settings().get("CODESTRAL.KEY")
|
||||
|
||||
# Check for Azure AD configuration
|
||||
if get_settings().get("AZURE_AD.CLIENT_ID", None):
|
||||
self.azure = True
|
||||
# Generate access token using Azure AD credentials from settings
|
||||
access_token = self._get_azure_ad_token()
|
||||
litellm.api_key = access_token
|
||||
openai.api_key = access_token
|
||||
|
||||
# Set API base from settings
|
||||
self.api_base = get_settings().azure_ad.api_base
|
||||
litellm.api_base = self.api_base
|
||||
openai.api_base = self.api_base
|
||||
|
||||
# Support for Openrouter models
|
||||
if get_settings().get("OPENROUTER.KEY", None):
|
||||
openrouter_api_key = get_settings().get("OPENROUTER.KEY", None)
|
||||
os.environ["OPENROUTER_API_KEY"] = openrouter_api_key
|
||||
litellm.api_key = openrouter_api_key
|
||||
openai.api_key = openrouter_api_key
|
||||
|
||||
openrouter_api_base = get_settings().get("OPENROUTER.API_BASE", "https://openrouter.ai/api/v1")
|
||||
os.environ["OPENROUTER_API_BASE"] = openrouter_api_base
|
||||
self.api_base = openrouter_api_base
|
||||
litellm.api_base = openrouter_api_base
|
||||
|
||||
# Models that only use user meessage
|
||||
self.user_message_only_models = USER_MESSAGE_ONLY_MODELS
|
||||
|
||||
# Model that doesn't support temperature argument
|
||||
self.no_support_temperature_models = NO_SUPPORT_TEMPERATURE_MODELS
|
||||
|
||||
# Models that support reasoning effort
|
||||
self.support_reasoning_models = SUPPORT_REASONING_EFFORT_MODELS
|
||||
|
||||
# Models that support extended thinking
|
||||
self.claude_extended_thinking_models = CLAUDE_EXTENDED_THINKING_MODELS
|
||||
|
||||
def _get_azure_ad_token(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Generates an access token using Azure AD credentials from settings.
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
str: The access token
|
||||
"""
|
||||
from azure.identity import ClientSecretCredential
|
||||
try:
|
||||
credential = ClientSecretCredential(
|
||||
tenant_id=get_settings().azure_ad.tenant_id,
|
||||
client_id=get_settings().azure_ad.client_id,
|
||||
client_secret=get_settings().azure_ad.client_secret
|
||||
)
|
||||
# Get token for Azure OpenAI service
|
||||
token = credential.get_token("https://cognitiveservices.azure.com/.default")
|
||||
return token.token
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
get_logger().error(f"Failed to get Azure AD token: {e}")
|
||||
raise
|
||||
|
||||
def prepare_logs(self, response, system, user, resp, finish_reason):
|
||||
response_log = response.dict().copy()
|
||||
response_log['system'] = system
|
||||
@ -175,43 +113,6 @@ class LiteLLMAIHandler(BaseAiHandler):
|
||||
response_log['main_pr_language'] = 'unknown'
|
||||
return response_log
|
||||
|
||||
def _configure_claude_extended_thinking(self, model: str, kwargs: dict) -> dict:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Configure Claude extended thinking parameters if applicable.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
model (str): The AI model being used
|
||||
kwargs (dict): The keyword arguments for the model call
|
||||
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
dict: Updated kwargs with extended thinking configuration
|
||||
"""
|
||||
extended_thinking_budget_tokens = get_settings().config.get("extended_thinking_budget_tokens", 2048)
|
||||
extended_thinking_max_output_tokens = get_settings().config.get("extended_thinking_max_output_tokens", 4096)
|
||||
|
||||
# Validate extended thinking parameters
|
||||
if not isinstance(extended_thinking_budget_tokens, int) or extended_thinking_budget_tokens <= 0:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"extended_thinking_budget_tokens must be a positive integer, got {extended_thinking_budget_tokens}")
|
||||
if not isinstance(extended_thinking_max_output_tokens, int) or extended_thinking_max_output_tokens <= 0:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"extended_thinking_max_output_tokens must be a positive integer, got {extended_thinking_max_output_tokens}")
|
||||
if extended_thinking_max_output_tokens < extended_thinking_budget_tokens:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"extended_thinking_max_output_tokens ({extended_thinking_max_output_tokens}) must be greater than or equal to extended_thinking_budget_tokens ({extended_thinking_budget_tokens})")
|
||||
|
||||
kwargs["thinking"] = {
|
||||
"type": "enabled",
|
||||
"budget_tokens": extended_thinking_budget_tokens
|
||||
}
|
||||
if get_settings().config.verbosity_level >= 2:
|
||||
get_logger().info(f"Adding max output tokens {extended_thinking_max_output_tokens} to model {model}, extended thinking budget tokens: {extended_thinking_budget_tokens}")
|
||||
kwargs["max_tokens"] = extended_thinking_max_output_tokens
|
||||
|
||||
# temperature may only be set to 1 when thinking is enabled
|
||||
if get_settings().config.verbosity_level >= 2:
|
||||
get_logger().info("Temperature may only be set to 1 when thinking is enabled with claude models.")
|
||||
kwargs["temperature"] = 1
|
||||
|
||||
return kwargs
|
||||
|
||||
def add_litellm_callbacks(selfs, kwargs) -> dict:
|
||||
captured_extra = []
|
||||
|
||||
@ -274,8 +175,8 @@ class LiteLLMAIHandler(BaseAiHandler):
|
||||
return get_settings().get("OPENAI.DEPLOYMENT_ID", None)
|
||||
|
||||
@retry(
|
||||
retry=retry_if_exception_type(openai.APIError) & retry_if_not_exception_type(openai.RateLimitError),
|
||||
stop=stop_after_attempt(OPENAI_RETRIES),
|
||||
retry=retry_if_exception_type((openai.APIError, openai.APIConnectionError, openai.APITimeoutError)), # No retry on RateLimitError
|
||||
stop=stop_after_attempt(OPENAI_RETRIES)
|
||||
)
|
||||
async def chat_completion(self, model: str, system: str, user: str, temperature: float = 0.2, img_path: str = None):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
@ -304,7 +205,7 @@ class LiteLLMAIHandler(BaseAiHandler):
|
||||
{"type": "image_url", "image_url": {"url": img_path}}]
|
||||
|
||||
# Currently, some models do not support a separate system and user prompts
|
||||
if model in self.user_message_only_models or get_settings().config.custom_reasoning_model:
|
||||
if model in self.user_message_only_models:
|
||||
user = f"{system}\n\n\n{user}"
|
||||
system = ""
|
||||
get_logger().info(f"Using model {model}, combining system and user prompts")
|
||||
@ -326,21 +227,9 @@ class LiteLLMAIHandler(BaseAiHandler):
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# Add temperature only if model supports it
|
||||
if model not in self.no_support_temperature_models and not get_settings().config.custom_reasoning_model:
|
||||
# get_logger().info(f"Adding temperature with value {temperature} to model {model}.")
|
||||
if model not in self.no_support_temperature_models:
|
||||
kwargs["temperature"] = temperature
|
||||
|
||||
# Add reasoning_effort if model supports it
|
||||
if (model in self.support_reasoning_models):
|
||||
supported_reasoning_efforts = [ReasoningEffort.HIGH.value, ReasoningEffort.MEDIUM.value, ReasoningEffort.LOW.value]
|
||||
reasoning_effort = get_settings().config.reasoning_effort if (get_settings().config.reasoning_effort in supported_reasoning_efforts) else ReasoningEffort.MEDIUM.value
|
||||
get_logger().info(f"Adding reasoning_effort with value {reasoning_effort} to model {model}.")
|
||||
kwargs["reasoning_effort"] = reasoning_effort
|
||||
|
||||
# https://docs.anthropic.com/en/docs/build-with-claude/extended-thinking
|
||||
if (model in self.claude_extended_thinking_models) and get_settings().config.get("enable_claude_extended_thinking", False):
|
||||
kwargs = self._configure_claude_extended_thinking(model, kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
if get_settings().litellm.get("enable_callbacks", False):
|
||||
kwargs = self.add_litellm_callbacks(kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -354,16 +243,6 @@ class LiteLLMAIHandler(BaseAiHandler):
|
||||
if self.repetition_penalty:
|
||||
kwargs["repetition_penalty"] = self.repetition_penalty
|
||||
|
||||
#Added support for extra_headers while using litellm to call underlying model, via a api management gateway, would allow for passing custom headers for security and authorization
|
||||
if get_settings().get("LITELLM.EXTRA_HEADERS", None):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
litellm_extra_headers = json.loads(get_settings().litellm.extra_headers)
|
||||
if not isinstance(litellm_extra_headers, dict):
|
||||
raise ValueError("LITELLM.EXTRA_HEADERS must be a JSON object")
|
||||
except json.JSONDecodeError as e:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"LITELLM.EXTRA_HEADERS contains invalid JSON: {str(e)}")
|
||||
kwargs["extra_headers"] = litellm_extra_headers
|
||||
|
||||
get_logger().debug("Prompts", artifact={"system": system, "user": user})
|
||||
|
||||
if get_settings().config.verbosity_level >= 2:
|
||||
@ -371,13 +250,13 @@ class LiteLLMAIHandler(BaseAiHandler):
|
||||
get_logger().info(f"\nUser prompt:\n{user}")
|
||||
|
||||
response = await acompletion(**kwargs)
|
||||
except openai.RateLimitError as e:
|
||||
get_logger().error(f"Rate limit error during LLM inference: {e}")
|
||||
raise
|
||||
except openai.APIError as e:
|
||||
except (openai.APIError, openai.APITimeoutError) as e:
|
||||
get_logger().warning(f"Error during LLM inference: {e}")
|
||||
raise
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
except (openai.RateLimitError) as e:
|
||||
get_logger().error(f"Rate limit error during LLM inference: {e}")
|
||||
raise
|
||||
except (Exception) as e:
|
||||
get_logger().warning(f"Unknown error during LLM inference: {e}")
|
||||
raise openai.APIError from e
|
||||
if response is None or len(response["choices"]) == 0:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
|
||||
from os import environ
|
||||
from pr_agent.algo.ai_handlers.base_ai_handler import BaseAiHandler
|
||||
import openai
|
||||
from openai import AsyncOpenAI
|
||||
from tenacity import retry, retry_if_exception_type, retry_if_not_exception_type, stop_after_attempt
|
||||
from openai import APIError, AsyncOpenAI, RateLimitError, Timeout
|
||||
from retry import retry
|
||||
|
||||
from pr_agent.algo.ai_handlers.base_ai_handler import BaseAiHandler
|
||||
from pr_agent.config_loader import get_settings
|
||||
@ -38,14 +38,10 @@ class OpenAIHandler(BaseAiHandler):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return get_settings().get("OPENAI.DEPLOYMENT_ID", None)
|
||||
|
||||
@retry(
|
||||
retry=retry_if_exception_type(openai.APIError) & retry_if_not_exception_type(openai.RateLimitError),
|
||||
stop=stop_after_attempt(OPENAI_RETRIES),
|
||||
)
|
||||
async def chat_completion(self, model: str, system: str, user: str, temperature: float = 0.2, img_path: str = None):
|
||||
@retry(exceptions=(APIError, Timeout, AttributeError, RateLimitError),
|
||||
tries=OPENAI_RETRIES, delay=2, backoff=2, jitter=(1, 3))
|
||||
async def chat_completion(self, model: str, system: str, user: str, temperature: float = 0.2):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
if img_path:
|
||||
get_logger().warning(f"Image path is not supported for OpenAIHandler. Ignoring image path: {img_path}")
|
||||
get_logger().info("System: ", system)
|
||||
get_logger().info("User: ", user)
|
||||
messages = [{"role": "system", "content": system}, {"role": "user", "content": user}]
|
||||
@ -61,12 +57,12 @@ class OpenAIHandler(BaseAiHandler):
|
||||
get_logger().info("AI response", response=resp, messages=messages, finish_reason=finish_reason,
|
||||
model=model, usage=usage)
|
||||
return resp, finish_reason
|
||||
except openai.RateLimitError as e:
|
||||
get_logger().error(f"Rate limit error during LLM inference: {e}")
|
||||
except (APIError, Timeout) as e:
|
||||
get_logger().error("Error during OpenAI inference: ", e)
|
||||
raise
|
||||
except openai.APIError as e:
|
||||
get_logger().warning(f"Error during LLM inference: {e}")
|
||||
except (RateLimitError) as e:
|
||||
get_logger().error("Rate limit error during OpenAI inference: ", e)
|
||||
raise
|
||||
except (Exception) as e:
|
||||
get_logger().error("Unknown error during OpenAI inference: ", e)
|
||||
raise
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
get_logger().warning(f"Unknown error during LLM inference: {e}")
|
||||
raise openai.APIError from e
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,36 +0,0 @@
|
||||
from base64 import b64decode, encode, b64encode
|
||||
import hashlib
|
||||
|
||||
class CliArgs:
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
def validate_user_args(args: list) -> (bool, str):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
if not args:
|
||||
return True, ""
|
||||
|
||||
# decode forbidden args
|
||||
# b64encode('word'.encode()).decode()
|
||||
_encoded_args = 'c2hhcmVkX3NlY3JldA==:dXNlcg==:c3lzdGVt:ZW5hYmxlX2NvbW1lbnRfYXBwcm92YWw=:ZW5hYmxlX21hbnVhbF9hcHByb3ZhbA==:ZW5hYmxlX2F1dG9fYXBwcm92YWw=:YXBwcm92ZV9wcl9vbl9zZWxmX3Jldmlldw==:YmFzZV91cmw=:dXJs:YXBwX25hbWU=:c2VjcmV0X3Byb3ZpZGVy:Z2l0X3Byb3ZpZGVy:c2tpcF9rZXlz:b3BlbmFpLmtleQ==:QU5BTFlUSUNTX0ZPTERFUg==:dXJp:YXBwX2lk:d2ViaG9va19zZWNyZXQ=:YmVhcmVyX3Rva2Vu:UEVSU09OQUxfQUNDRVNTX1RPS0VO:b3ZlcnJpZGVfZGVwbG95bWVudF90eXBl:cHJpdmF0ZV9rZXk=:bG9jYWxfY2FjaGVfcGF0aA==:ZW5hYmxlX2xvY2FsX2NhY2hl:amlyYV9iYXNlX3VybA==:YXBpX2Jhc2U=:YXBpX3R5cGU=:YXBpX3ZlcnNpb24=:c2tpcF9rZXlz'
|
||||
|
||||
forbidden_cli_args = []
|
||||
for e in _encoded_args.split(':'):
|
||||
forbidden_cli_args.append(b64decode(e).decode())
|
||||
|
||||
# lowercase all forbidden args
|
||||
for i, _ in enumerate(forbidden_cli_args):
|
||||
forbidden_cli_args[i] = forbidden_cli_args[i].lower()
|
||||
if '.' not in forbidden_cli_args[i]:
|
||||
forbidden_cli_args[i] = '.' + forbidden_cli_args[i]
|
||||
|
||||
for arg in args:
|
||||
if arg.startswith('--'):
|
||||
arg_word = arg.lower()
|
||||
arg_word = arg_word.replace('__', '.') # replace double underscore with dot, e.g. --openai__key -> --openai.key
|
||||
for forbidden_arg_word in forbidden_cli_args:
|
||||
if forbidden_arg_word in arg_word:
|
||||
return False, forbidden_arg_word
|
||||
return True, ""
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
return False, str(e)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -58,9 +58,6 @@ def filter_ignored(files, platform = 'github'):
|
||||
files = files_o
|
||||
elif platform == 'azure':
|
||||
files = [f for f in files if not r.match(f)]
|
||||
elif platform == 'gitea':
|
||||
files = [f for f in files if not r.match(f.get("filename", ""))]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
print(f"Could not filter file list: {e}")
|
||||
|
||||
@ -9,12 +9,11 @@ from pr_agent.log import get_logger
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def extend_patch(original_file_str, patch_str, patch_extra_lines_before=0,
|
||||
patch_extra_lines_after=0, filename: str = "", new_file_str="") -> str:
|
||||
patch_extra_lines_after=0, filename: str = "") -> str:
|
||||
if not patch_str or (patch_extra_lines_before == 0 and patch_extra_lines_after == 0) or not original_file_str:
|
||||
return patch_str
|
||||
|
||||
original_file_str = decode_if_bytes(original_file_str)
|
||||
new_file_str = decode_if_bytes(new_file_str)
|
||||
if not original_file_str:
|
||||
return patch_str
|
||||
|
||||
@ -23,7 +22,7 @@ def extend_patch(original_file_str, patch_str, patch_extra_lines_before=0,
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
extended_patch_str = process_patch_lines(patch_str, original_file_str,
|
||||
patch_extra_lines_before, patch_extra_lines_after, new_file_str)
|
||||
patch_extra_lines_before, patch_extra_lines_after)
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
get_logger().warning(f"Failed to extend patch: {e}", artifact={"traceback": traceback.format_exc()})
|
||||
return patch_str
|
||||
@ -53,13 +52,12 @@ def should_skip_patch(filename):
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def process_patch_lines(patch_str, original_file_str, patch_extra_lines_before, patch_extra_lines_after, new_file_str=""):
|
||||
def process_patch_lines(patch_str, original_file_str, patch_extra_lines_before, patch_extra_lines_after):
|
||||
allow_dynamic_context = get_settings().config.allow_dynamic_context
|
||||
patch_extra_lines_before_dynamic = get_settings().config.max_extra_lines_before_dynamic_context
|
||||
|
||||
file_original_lines = original_file_str.splitlines()
|
||||
file_new_lines = new_file_str.splitlines() if new_file_str else []
|
||||
len_original_lines = len(file_original_lines)
|
||||
original_lines = original_file_str.splitlines()
|
||||
len_original_lines = len(original_lines)
|
||||
patch_lines = patch_str.splitlines()
|
||||
extended_patch_lines = []
|
||||
|
||||
@ -75,12 +73,12 @@ def process_patch_lines(patch_str, original_file_str, patch_extra_lines_before,
|
||||
if match:
|
||||
# finish processing previous hunk
|
||||
if is_valid_hunk and (start1 != -1 and patch_extra_lines_after > 0):
|
||||
delta_lines_original = [f' {line}' for line in file_original_lines[start1 + size1 - 1:start1 + size1 - 1 + patch_extra_lines_after]]
|
||||
extended_patch_lines.extend(delta_lines_original)
|
||||
delta_lines = [f' {line}' for line in original_lines[start1 + size1 - 1:start1 + size1 - 1 + patch_extra_lines_after]]
|
||||
extended_patch_lines.extend(delta_lines)
|
||||
|
||||
section_header, size1, size2, start1, start2 = extract_hunk_headers(match)
|
||||
|
||||
is_valid_hunk = check_if_hunk_lines_matches_to_file(i, file_original_lines, patch_lines, start1)
|
||||
is_valid_hunk = check_if_hunk_lines_matches_to_file(i, original_lines, patch_lines, start1)
|
||||
|
||||
if is_valid_hunk and (patch_extra_lines_before > 0 or patch_extra_lines_after > 0):
|
||||
def _calc_context_limits(patch_lines_before):
|
||||
@ -95,28 +93,20 @@ def process_patch_lines(patch_str, original_file_str, patch_extra_lines_before,
|
||||
extended_size2 = max(extended_size2 - delta_cap, size2)
|
||||
return extended_start1, extended_size1, extended_start2, extended_size2
|
||||
|
||||
if allow_dynamic_context and file_new_lines:
|
||||
if allow_dynamic_context:
|
||||
extended_start1, extended_size1, extended_start2, extended_size2 = \
|
||||
_calc_context_limits(patch_extra_lines_before_dynamic)
|
||||
|
||||
lines_before_original = file_original_lines[extended_start1 - 1:start1 - 1]
|
||||
lines_before_new = file_new_lines[extended_start2 - 1:start2 - 1]
|
||||
lines_before = original_lines[extended_start1 - 1:start1 - 1]
|
||||
found_header = False
|
||||
for i, line in enumerate(lines_before_original):
|
||||
for i, line, in enumerate(lines_before):
|
||||
if section_header in line:
|
||||
found_header = True
|
||||
# Update start and size in one line each
|
||||
extended_start1, extended_start2 = extended_start1 + i, extended_start2 + i
|
||||
extended_size1, extended_size2 = extended_size1 - i, extended_size2 - i
|
||||
lines_before_original_dynamic_context = lines_before_original[i:]
|
||||
lines_before_new_dynamic_context = lines_before_new[i:]
|
||||
if lines_before_original_dynamic_context == lines_before_new_dynamic_context:
|
||||
# get_logger().debug(f"found dynamic context match for section header: {section_header}")
|
||||
found_header = True
|
||||
# get_logger().debug(f"Found section header in line {i} before the hunk")
|
||||
section_header = ''
|
||||
else:
|
||||
pass # its ok to be here. We cant apply dynamic context if the lines are different if 'old' and 'new' hunks
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
if not found_header:
|
||||
# get_logger().debug(f"Section header not found in the extra lines before the hunk")
|
||||
extended_start1, extended_size1, extended_start2, extended_size2 = \
|
||||
@ -125,35 +115,11 @@ def process_patch_lines(patch_str, original_file_str, patch_extra_lines_before,
|
||||
extended_start1, extended_size1, extended_start2, extended_size2 = \
|
||||
_calc_context_limits(patch_extra_lines_before)
|
||||
|
||||
# check if extra lines before hunk are different in original and new file
|
||||
delta_lines_original = [f' {line}' for line in file_original_lines[extended_start1 - 1:start1 - 1]]
|
||||
if file_new_lines:
|
||||
delta_lines_new = [f' {line}' for line in file_new_lines[extended_start2 - 1:start2 - 1]]
|
||||
if delta_lines_original != delta_lines_new:
|
||||
found_mini_match = False
|
||||
for i in range(len(delta_lines_original)):
|
||||
if delta_lines_original[i:] == delta_lines_new[i:]:
|
||||
delta_lines_original = delta_lines_original[i:]
|
||||
delta_lines_new = delta_lines_new[i:]
|
||||
extended_start1 += i
|
||||
extended_size1 -= i
|
||||
extended_start2 += i
|
||||
extended_size2 -= i
|
||||
found_mini_match = True
|
||||
break
|
||||
if not found_mini_match:
|
||||
extended_start1 = start1
|
||||
extended_size1 = size1
|
||||
extended_start2 = start2
|
||||
extended_size2 = size2
|
||||
delta_lines_original = []
|
||||
# get_logger().debug(f"Extra lines before hunk are different in original and new file",
|
||||
# artifact={"delta_lines_original": delta_lines_original,
|
||||
# "delta_lines_new": delta_lines_new})
|
||||
delta_lines = [f' {line}' for line in original_lines[extended_start1 - 1:start1 - 1]]
|
||||
|
||||
# logic to remove section header if its in the extra delta lines (in dynamic context, this is also done)
|
||||
if section_header and not allow_dynamic_context:
|
||||
for line in delta_lines_original:
|
||||
for line in delta_lines:
|
||||
if section_header in line:
|
||||
section_header = '' # remove section header if it is in the extra delta lines
|
||||
break
|
||||
@ -162,12 +128,12 @@ def process_patch_lines(patch_str, original_file_str, patch_extra_lines_before,
|
||||
extended_size1 = size1
|
||||
extended_start2 = start2
|
||||
extended_size2 = size2
|
||||
delta_lines_original = []
|
||||
delta_lines = []
|
||||
extended_patch_lines.append('')
|
||||
extended_patch_lines.append(
|
||||
f'@@ -{extended_start1},{extended_size1} '
|
||||
f'+{extended_start2},{extended_size2} @@ {section_header}')
|
||||
extended_patch_lines.extend(delta_lines_original) # one to zero based
|
||||
extended_patch_lines.extend(delta_lines) # one to zero based
|
||||
continue
|
||||
extended_patch_lines.append(line)
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
@ -176,14 +142,15 @@ def process_patch_lines(patch_str, original_file_str, patch_extra_lines_before,
|
||||
|
||||
# finish processing last hunk
|
||||
if start1 != -1 and patch_extra_lines_after > 0 and is_valid_hunk:
|
||||
delta_lines_original = file_original_lines[start1 + size1 - 1:start1 + size1 - 1 + patch_extra_lines_after]
|
||||
delta_lines = original_lines[start1 + size1 - 1:start1 + size1 - 1 + patch_extra_lines_after]
|
||||
# add space at the beginning of each extra line
|
||||
delta_lines_original = [f' {line}' for line in delta_lines_original]
|
||||
extended_patch_lines.extend(delta_lines_original)
|
||||
delta_lines = [f' {line}' for line in delta_lines]
|
||||
extended_patch_lines.extend(delta_lines)
|
||||
|
||||
extended_patch_str = '\n'.join(extended_patch_lines)
|
||||
return extended_patch_str
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def check_if_hunk_lines_matches_to_file(i, original_lines, patch_lines, start1):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Check if the hunk lines match the original file content. We saw cases where the hunk header line doesn't match the original file content, and then
|
||||
@ -193,18 +160,8 @@ def check_if_hunk_lines_matches_to_file(i, original_lines, patch_lines, start1):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
if i + 1 < len(patch_lines) and patch_lines[i + 1][0] == ' ': # an existing line in the file
|
||||
if patch_lines[i + 1].strip() != original_lines[start1 - 1].strip():
|
||||
# check if different encoding is needed
|
||||
original_line = original_lines[start1 - 1].strip()
|
||||
for encoding in ['iso-8859-1', 'latin-1', 'ascii', 'utf-16']:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
if original_line.encode(encoding).decode().strip() == patch_lines[i + 1].strip():
|
||||
get_logger().info(f"Detected different encoding in hunk header line {start1}, needed encoding: {encoding}")
|
||||
return False # we still want to avoid extending the hunk. But we don't want to log an error
|
||||
except:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
is_valid_hunk = False
|
||||
get_logger().info(
|
||||
get_logger().error(
|
||||
f"Invalid hunk in PR, line {start1} in hunk header doesn't match the original file content")
|
||||
except:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
@ -297,7 +254,7 @@ def handle_patch_deletions(patch: str, original_file_content_str: str,
|
||||
return patch
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def decouple_and_convert_to_hunks_with_lines_numbers(patch: str, file) -> str:
|
||||
def convert_to_hunks_with_lines_numbers(patch: str, file) -> str:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Convert a given patch string into a string with line numbers for each hunk, indicating the new and old content of
|
||||
the file.
|
||||
@ -329,17 +286,11 @@ __old hunk__
|
||||
line6
|
||||
...
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
# Add a header for the file
|
||||
if file:
|
||||
# if the file was deleted, return a message indicating that the file was deleted
|
||||
if hasattr(file, 'edit_type') and file.edit_type == EDIT_TYPE.DELETED:
|
||||
return f"\n\n## File '{file.filename.strip()}' was deleted\n"
|
||||
return f"\n\n## file '{file.filename.strip()}' was deleted\n"
|
||||
|
||||
patch_with_lines_str = f"\n\n## File: '{file.filename.strip()}'\n"
|
||||
else:
|
||||
patch_with_lines_str = ""
|
||||
|
||||
patch_lines = patch.splitlines()
|
||||
RE_HUNK_HEADER = re.compile(
|
||||
r"^@@ -(\d+)(?:,(\d+))? \+(\d+)(?:,(\d+))? @@[ ]?(.*)")
|
||||
@ -412,7 +363,7 @@ __old hunk__
|
||||
return patch_with_lines_str.rstrip()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def extract_hunk_lines_from_patch(patch: str, file_name, line_start, line_end, side, remove_trailing_chars: bool = True) -> tuple[str, str]:
|
||||
def extract_hunk_lines_from_patch(patch: str, file_name, line_start, line_end, side) -> tuple[str, str]:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
patch_with_lines_str = f"\n\n## File: '{file_name.strip()}'\n\n"
|
||||
selected_lines = ""
|
||||
@ -460,8 +411,4 @@ def extract_hunk_lines_from_patch(patch: str, file_name, line_start, line_end, s
|
||||
get_logger().error(f"Failed to extract hunk lines from patch: {e}", artifact={"traceback": traceback.format_exc()})
|
||||
return "", ""
|
||||
|
||||
if remove_trailing_chars:
|
||||
patch_with_lines_str = patch_with_lines_str.rstrip()
|
||||
selected_lines = selected_lines.rstrip()
|
||||
|
||||
return patch_with_lines_str, selected_lines
|
||||
return patch_with_lines_str.rstrip(), selected_lines.rstrip()
|
||||
|
||||
@ -19,12 +19,6 @@ def is_valid_file(filename:str, bad_extensions=None) -> bool:
|
||||
bad_extensions = get_settings().bad_extensions.default
|
||||
if get_settings().config.use_extra_bad_extensions:
|
||||
bad_extensions += get_settings().bad_extensions.extra
|
||||
|
||||
auto_generated_files = ['package-lock.json', 'yarn.lock', 'composer.lock', 'Gemfile.lock', 'poetry.lock']
|
||||
for forbidden_file in auto_generated_files:
|
||||
if filename.endswith(forbidden_file):
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
return filename.split('.')[-1] not in bad_extensions
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -47,7 +41,6 @@ def sort_files_by_main_languages(languages: Dict, files: list):
|
||||
|
||||
# filter out files bad extensions
|
||||
files_filtered = filter_bad_extensions(files)
|
||||
|
||||
# sort files by their extension, put the files that are in the main extension first
|
||||
# and the rest files after, map languages_sorted to their respective files
|
||||
files_sorted = []
|
||||
|
||||
@ -7,12 +7,11 @@ from github import RateLimitExceededException
|
||||
|
||||
from pr_agent.algo.file_filter import filter_ignored
|
||||
from pr_agent.algo.git_patch_processing import (
|
||||
extend_patch, handle_patch_deletions,
|
||||
decouple_and_convert_to_hunks_with_lines_numbers)
|
||||
convert_to_hunks_with_lines_numbers, extend_patch, handle_patch_deletions)
|
||||
from pr_agent.algo.language_handler import sort_files_by_main_languages
|
||||
from pr_agent.algo.token_handler import TokenHandler
|
||||
from pr_agent.algo.types import EDIT_TYPE, FilePatchInfo
|
||||
from pr_agent.algo.utils import ModelType, clip_tokens, get_max_tokens, get_model
|
||||
from pr_agent.algo.utils import ModelType, clip_tokens, get_max_tokens, get_weak_model
|
||||
from pr_agent.config_loader import get_settings
|
||||
from pr_agent.git_providers.git_provider import GitProvider
|
||||
from pr_agent.log import get_logger
|
||||
@ -51,11 +50,22 @@ def get_pr_diff(git_provider: GitProvider, token_handler: TokenHandler,
|
||||
PATCH_EXTRA_LINES_AFTER = cap_and_log_extra_lines(PATCH_EXTRA_LINES_AFTER, "after")
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
diff_files = git_provider.get_diff_files()
|
||||
diff_files_original = git_provider.get_diff_files()
|
||||
except RateLimitExceededException as e:
|
||||
get_logger().error(f"Rate limit exceeded for git provider API. original message {e}")
|
||||
raise
|
||||
|
||||
diff_files = filter_ignored(diff_files_original)
|
||||
if diff_files != diff_files_original:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
get_logger().info(f"Filtered out {len(diff_files_original) - len(diff_files)} files")
|
||||
new_names = set([a.filename for a in diff_files])
|
||||
orig_names = set([a.filename for a in diff_files_original])
|
||||
get_logger().info(f"Filtered out files: {orig_names - new_names}")
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# get pr languages
|
||||
pr_languages = sort_files_by_main_languages(git_provider.get_languages(), diff_files)
|
||||
if pr_languages:
|
||||
@ -145,11 +155,21 @@ def get_pr_diff(git_provider: GitProvider, token_handler: TokenHandler,
|
||||
def get_pr_diff_multiple_patchs(git_provider: GitProvider, token_handler: TokenHandler, model: str,
|
||||
add_line_numbers_to_hunks: bool = False, disable_extra_lines: bool = False):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
diff_files = git_provider.get_diff_files()
|
||||
diff_files_original = git_provider.get_diff_files()
|
||||
except RateLimitExceededException as e:
|
||||
get_logger().error(f"Rate limit exceeded for git provider API. original message {e}")
|
||||
raise
|
||||
|
||||
diff_files = filter_ignored(diff_files_original)
|
||||
if diff_files != diff_files_original:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
get_logger().info(f"Filtered out {len(diff_files_original) - len(diff_files)} files")
|
||||
new_names = set([a.filename for a in diff_files])
|
||||
orig_names = set([a.filename for a in diff_files_original])
|
||||
get_logger().info(f"Filtered out files: {orig_names - new_names}")
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
# get pr languages
|
||||
pr_languages = sort_files_by_main_languages(git_provider.get_languages(), diff_files)
|
||||
if pr_languages:
|
||||
@ -175,24 +195,21 @@ def pr_generate_extended_diff(pr_languages: list,
|
||||
for lang in pr_languages:
|
||||
for file in lang['files']:
|
||||
original_file_content_str = file.base_file
|
||||
new_file_content_str = file.head_file
|
||||
patch = file.patch
|
||||
if not patch:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
# extend each patch with extra lines of context
|
||||
extended_patch = extend_patch(original_file_content_str, patch,
|
||||
patch_extra_lines_before, patch_extra_lines_after, file.filename,
|
||||
new_file_str=new_file_content_str)
|
||||
patch_extra_lines_before, patch_extra_lines_after, file.filename)
|
||||
if not extended_patch:
|
||||
get_logger().warning(f"Failed to extend patch for file: {file.filename}")
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
if add_line_numbers_to_hunks:
|
||||
full_extended_patch = decouple_and_convert_to_hunks_with_lines_numbers(extended_patch, file)
|
||||
full_extended_patch = convert_to_hunks_with_lines_numbers(extended_patch, file)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
extended_patch = extended_patch.replace('\n@@ ', '\n\n@@ ') # add extra line before each hunk
|
||||
full_extended_patch = f"\n\n## File: '{file.filename.strip()}'\n\n{extended_patch.strip()}\n"
|
||||
full_extended_patch = f"\n\n## File: '{file.filename.strip()}'\n{extended_patch.rstrip()}\n"
|
||||
|
||||
# add AI-summary metadata to the patch
|
||||
if file.ai_file_summary and get_settings().get("config.enable_ai_metadata", False):
|
||||
@ -235,7 +252,7 @@ def pr_generate_compressed_diff(top_langs: list, token_handler: TokenHandler, mo
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
if convert_hunks_to_line_numbers:
|
||||
patch = decouple_and_convert_to_hunks_with_lines_numbers(patch, file)
|
||||
patch = convert_to_hunks_with_lines_numbers(patch, file)
|
||||
|
||||
## add AI-summary metadata to the patch (disabled, since we are in the compressed diff)
|
||||
# if file.ai_file_summary and get_settings().config.get('config.is_auto_command', False):
|
||||
@ -339,11 +356,7 @@ async def retry_with_fallback_models(f: Callable, model_type: ModelType = ModelT
|
||||
|
||||
def _get_all_models(model_type: ModelType = ModelType.REGULAR) -> List[str]:
|
||||
if model_type == ModelType.WEAK:
|
||||
model = get_model('model_weak')
|
||||
elif model_type == ModelType.REASONING:
|
||||
model = get_model('model_reasoning')
|
||||
elif model_type == ModelType.REGULAR:
|
||||
model = get_settings().config.model
|
||||
model = get_weak_model()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
model = get_settings().config.model
|
||||
fallback_models = get_settings().config.fallback_models
|
||||
@ -371,8 +384,7 @@ def _get_all_deployments(all_models: List[str]) -> List[str]:
|
||||
def get_pr_multi_diffs(git_provider: GitProvider,
|
||||
token_handler: TokenHandler,
|
||||
model: str,
|
||||
max_calls: int = 5,
|
||||
add_line_numbers: bool = True) -> List[str]:
|
||||
max_calls: int = 5) -> List[str]:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Retrieves the diff files from a Git provider, sorts them by main language, and generates patches for each file.
|
||||
The patches are split into multiple groups based on the maximum number of tokens allowed for the given model.
|
||||
@ -395,6 +407,8 @@ def get_pr_multi_diffs(git_provider: GitProvider,
|
||||
get_logger().error(f"Rate limit exceeded for git provider API. original message {e}")
|
||||
raise
|
||||
|
||||
diff_files = filter_ignored(diff_files)
|
||||
|
||||
# Sort files by main language
|
||||
pr_languages = sort_files_by_main_languages(git_provider.get_languages(), diff_files)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -411,8 +425,7 @@ def get_pr_multi_diffs(git_provider: GitProvider,
|
||||
|
||||
# try first a single run with standard diff string, with patch extension, and no deletions
|
||||
patches_extended, total_tokens, patches_extended_tokens = pr_generate_extended_diff(
|
||||
pr_languages, token_handler,
|
||||
add_line_numbers_to_hunks=add_line_numbers,
|
||||
pr_languages, token_handler, add_line_numbers_to_hunks=True,
|
||||
patch_extra_lines_before=PATCH_EXTRA_LINES_BEFORE,
|
||||
patch_extra_lines_after=PATCH_EXTRA_LINES_AFTER)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -441,12 +454,7 @@ def get_pr_multi_diffs(git_provider: GitProvider,
|
||||
if patch is None:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
# Add line numbers and metadata to the patch
|
||||
if add_line_numbers:
|
||||
patch = decouple_and_convert_to_hunks_with_lines_numbers(patch, file)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
patch = f"\n\n## File: '{file.filename.strip()}'\n\n{patch.strip()}\n"
|
||||
|
||||
patch = convert_to_hunks_with_lines_numbers(patch, file)
|
||||
# add AI-summary metadata to the patch
|
||||
if file.ai_file_summary and get_settings().get("config.enable_ai_metadata", False):
|
||||
patch = add_ai_summary_top_patch(file, patch)
|
||||
@ -494,7 +502,7 @@ def get_pr_multi_diffs(git_provider: GitProvider,
|
||||
# Add the last chunk
|
||||
if patches:
|
||||
final_diff = "\n".join(patches)
|
||||
final_diff_list.append(final_diff.strip())
|
||||
final_diff_list.append(final_diff)
|
||||
|
||||
return final_diff_list
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,4 @@
|
||||
from threading import Lock
|
||||
from math import ceil
|
||||
import re
|
||||
|
||||
from jinja2 import Environment, StrictUndefined
|
||||
from tiktoken import encoding_for_model, get_encoding
|
||||
@ -9,16 +7,6 @@ from pr_agent.config_loader import get_settings
|
||||
from pr_agent.log import get_logger
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ModelTypeValidator:
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
def is_openai_model(model_name: str) -> bool:
|
||||
return 'gpt' in model_name or re.match(r"^o[1-9](-mini|-preview)?$", model_name)
|
||||
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
def is_anthropic_model(model_name: str) -> bool:
|
||||
return 'claude' in model_name
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TokenEncoder:
|
||||
_encoder_instance = None
|
||||
_model = None
|
||||
@ -31,11 +19,8 @@ class TokenEncoder:
|
||||
with cls._lock: # Lock acquisition to ensure thread safety
|
||||
if cls._encoder_instance is None or model != cls._model:
|
||||
cls._model = model
|
||||
try:
|
||||
cls._encoder_instance = encoding_for_model(cls._model) if "gpt" in cls._model else get_encoding(
|
||||
"o200k_base")
|
||||
except:
|
||||
cls._encoder_instance = get_encoding("o200k_base")
|
||||
"cl100k_base")
|
||||
return cls._encoder_instance
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -52,10 +37,6 @@ class TokenHandler:
|
||||
method.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
# Constants
|
||||
CLAUDE_MODEL = "claude-3-7-sonnet-20250219"
|
||||
CLAUDE_MAX_CONTENT_SIZE = 9_000_000 # Maximum allowed content size (9MB) for Claude API
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, pr=None, vars: dict = {}, system="", user=""):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Initializes the TokenHandler object.
|
||||
@ -67,7 +48,6 @@ class TokenHandler:
|
||||
- user: The user string.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.encoder = TokenEncoder.get_token_encoder()
|
||||
|
||||
if pr is not None:
|
||||
self.prompt_tokens = self._get_system_user_tokens(pr, self.encoder, vars, system, user)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -96,76 +76,14 @@ class TokenHandler:
|
||||
get_logger().error(f"Error in _get_system_user_tokens: {e}")
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
|
||||
def _calc_claude_tokens(self, patch: str) -> int:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
import anthropic
|
||||
from pr_agent.algo import MAX_TOKENS
|
||||
|
||||
client = anthropic.Anthropic(api_key=get_settings(use_context=False).get('anthropic.key'))
|
||||
max_tokens = MAX_TOKENS[get_settings().config.model]
|
||||
|
||||
if len(patch.encode('utf-8')) > self.CLAUDE_MAX_CONTENT_SIZE:
|
||||
get_logger().warning(
|
||||
"Content too large for Anthropic token counting API, falling back to local tokenizer"
|
||||
)
|
||||
return max_tokens
|
||||
|
||||
response = client.messages.count_tokens(
|
||||
model=self.CLAUDE_MODEL,
|
||||
system="system",
|
||||
messages=[{
|
||||
"role": "user",
|
||||
"content": patch
|
||||
}],
|
||||
)
|
||||
return response.input_tokens
|
||||
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
get_logger().error(f"Error in Anthropic token counting: {e}")
|
||||
return max_tokens
|
||||
|
||||
def _apply_estimation_factor(self, model_name: str, default_estimate: int) -> int:
|
||||
factor = 1 + get_settings().get('config.model_token_count_estimate_factor', 0)
|
||||
get_logger().warning(f"{model_name}'s token count cannot be accurately estimated. Using factor of {factor}")
|
||||
|
||||
return ceil(factor * default_estimate)
|
||||
|
||||
def _get_token_count_by_model_type(self, patch: str, default_estimate: int) -> int:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Get token count based on model type.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
patch: The text to count tokens for.
|
||||
default_estimate: The default token count estimate.
|
||||
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
int: The calculated token count.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
model_name = get_settings().config.model.lower()
|
||||
|
||||
if ModelTypeValidator.is_openai_model(model_name) and get_settings(use_context=False).get('openai.key'):
|
||||
return default_estimate
|
||||
|
||||
if ModelTypeValidator.is_anthropic_model(model_name) and get_settings(use_context=False).get('anthropic.key'):
|
||||
return self._calc_claude_tokens(patch)
|
||||
|
||||
return self._apply_estimation_factor(model_name, default_estimate)
|
||||
|
||||
def count_tokens(self, patch: str, force_accurate: bool = False) -> int:
|
||||
def count_tokens(self, patch: str) -> int:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Counts the number of tokens in a given patch string.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
- patch: The patch string.
|
||||
- force_accurate: If True, uses a more precise calculation method.
|
||||
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
The number of tokens in the patch string.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
encoder_estimate = len(self.encoder.encode(patch, disallowed_special=()))
|
||||
|
||||
# If an estimate is enough (for example, in cases where the maximal allowed tokens is way below the known limits), return it.
|
||||
if not force_accurate:
|
||||
return encoder_estimate
|
||||
|
||||
return self._get_token_count_by_model_type(patch, encoder_estimate)
|
||||
return len(self.encoder.encode(patch, disallowed_special=()))
|
||||
|
||||
@ -30,13 +30,12 @@ from pr_agent.config_loader import get_settings, global_settings
|
||||
from pr_agent.log import get_logger
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_model(model_type: str = "model_weak") -> str:
|
||||
if model_type == "model_weak" and get_settings().get("config.model_weak"):
|
||||
def get_weak_model() -> str:
|
||||
if get_settings().get("config.model_weak"):
|
||||
return get_settings().config.model_weak
|
||||
elif model_type == "model_reasoning" and get_settings().get("config.model_reasoning"):
|
||||
return get_settings().config.model_reasoning
|
||||
return get_settings().config.model
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Range(BaseModel):
|
||||
line_start: int # should be 0-indexed
|
||||
line_end: int
|
||||
@ -46,17 +45,11 @@ class Range(BaseModel):
|
||||
class ModelType(str, Enum):
|
||||
REGULAR = "regular"
|
||||
WEAK = "weak"
|
||||
REASONING = "reasoning"
|
||||
|
||||
class PRReviewHeader(str, Enum):
|
||||
REGULAR = "## PR Reviewer Guide"
|
||||
INCREMENTAL = "## Incremental PR Reviewer Guide"
|
||||
|
||||
class ReasoningEffort(str, Enum):
|
||||
HIGH = "high"
|
||||
MEDIUM = "medium"
|
||||
LOW = "low"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class PRDescriptionHeader(str, Enum):
|
||||
CHANGES_WALKTHROUGH = "### **Changes walkthrough** 📝"
|
||||
@ -252,7 +245,7 @@ def convert_to_markdown_v2(output_data: dict,
|
||||
if gfm_supported:
|
||||
if reference_link is not None and len(reference_link) > 0:
|
||||
if relevant_lines_str:
|
||||
issue_str = f"<details><summary><a href='{reference_link}'><strong>{issue_header}</strong></a>\n\n{issue_content}\n</summary>\n\n{relevant_lines_str}\n\n</details>"
|
||||
issue_str = f"<details><summary><a href='{reference_link}'><strong>{issue_header}</strong></a>\n\n{issue_content}</summary>\n\n{relevant_lines_str}\n\n</details>"
|
||||
else:
|
||||
issue_str = f"<a href='{reference_link}'><strong>{issue_header}</strong></a><br>{issue_content}"
|
||||
else:
|
||||
@ -706,14 +699,12 @@ def _fix_key_value(key: str, value: str):
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def load_yaml(response_text: str, keys_fix_yaml: List[str] = [], first_key="", last_key="") -> dict:
|
||||
response_text_original = copy.deepcopy(response_text)
|
||||
response_text = response_text.strip('\n').removeprefix('```yaml').rstrip().removesuffix('```')
|
||||
try:
|
||||
data = yaml.safe_load(response_text)
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
get_logger().warning(f"Initial failure to parse AI prediction: {e}")
|
||||
data = try_fix_yaml(response_text, keys_fix_yaml=keys_fix_yaml, first_key=first_key, last_key=last_key,
|
||||
response_text_original=response_text_original)
|
||||
data = try_fix_yaml(response_text, keys_fix_yaml=keys_fix_yaml, first_key=first_key, last_key=last_key)
|
||||
if not data:
|
||||
get_logger().error(f"Failed to parse AI prediction after fallbacks",
|
||||
artifact={'response_text': response_text})
|
||||
@ -727,13 +718,11 @@ def load_yaml(response_text: str, keys_fix_yaml: List[str] = [], first_key="", l
|
||||
def try_fix_yaml(response_text: str,
|
||||
keys_fix_yaml: List[str] = [],
|
||||
first_key="",
|
||||
last_key="",
|
||||
response_text_original="") -> dict:
|
||||
last_key="",) -> dict:
|
||||
response_text_lines = response_text.split('\n')
|
||||
|
||||
keys_yaml = ['relevant line:', 'suggestion content:', 'relevant file:', 'existing code:', 'improved code:', 'label:']
|
||||
keys_yaml = ['relevant line:', 'suggestion content:', 'relevant file:', 'existing code:', 'improved code:']
|
||||
keys_yaml = keys_yaml + keys_fix_yaml
|
||||
|
||||
# first fallback - try to convert 'relevant line: ...' to relevant line: |-\n ...'
|
||||
response_text_lines_copy = response_text_lines.copy()
|
||||
for i in range(0, len(response_text_lines_copy)):
|
||||
@ -748,32 +737,9 @@ def try_fix_yaml(response_text: str,
|
||||
except:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
# 1.5 fallback - try to convert '|' to '|2'. Will solve cases of indent decreasing during the code
|
||||
response_text_copy = copy.deepcopy(response_text)
|
||||
response_text_copy = response_text_copy.replace('|\n', '|2\n')
|
||||
try:
|
||||
data = yaml.safe_load(response_text_copy)
|
||||
get_logger().info(f"Successfully parsed AI prediction after replacing | with |2")
|
||||
return data
|
||||
except:
|
||||
# if it fails, we can try to add spaces to the lines that are not indented properly, and contain '}'.
|
||||
response_text_lines_copy = response_text_copy.split('\n')
|
||||
for i in range(0, len(response_text_lines_copy)):
|
||||
initial_space = len(response_text_lines_copy[i]) - len(response_text_lines_copy[i].lstrip())
|
||||
if initial_space == 2 and '|2' not in response_text_lines_copy[i] and '}' in response_text_lines_copy[i]:
|
||||
response_text_lines_copy[i] = ' ' + response_text_lines_copy[i].lstrip()
|
||||
try:
|
||||
data = yaml.safe_load('\n'.join(response_text_lines_copy))
|
||||
get_logger().info(f"Successfully parsed AI prediction after replacing | with |2 and adding spaces")
|
||||
return data
|
||||
except:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
# second fallback - try to extract only range from first ```yaml to the last ```
|
||||
snippet_pattern = r'```yaml([\s\S]*?)```(?=\s*$|")'
|
||||
# second fallback - try to extract only range from first ```yaml to ````
|
||||
snippet_pattern = r'```(yaml)?[\s\S]*?```'
|
||||
snippet = re.search(snippet_pattern, '\n'.join(response_text_lines_copy))
|
||||
if not snippet:
|
||||
snippet = re.search(snippet_pattern, response_text_original) # before we removed the "```"
|
||||
if snippet:
|
||||
snippet_text = snippet.group()
|
||||
try:
|
||||
@ -816,7 +782,6 @@ def try_fix_yaml(response_text: str,
|
||||
# fifth fallback - try to remove leading '+' (sometimes added by AI for 'existing code' and 'improved code')
|
||||
response_text_lines_copy = response_text_lines.copy()
|
||||
for i in range(0, len(response_text_lines_copy)):
|
||||
if response_text_lines_copy[i].startswith('+'):
|
||||
response_text_lines_copy[i] = ' ' + response_text_lines_copy[i][1:]
|
||||
try:
|
||||
data = yaml.safe_load('\n'.join(response_text_lines_copy))
|
||||
@ -825,47 +790,16 @@ def try_fix_yaml(response_text: str,
|
||||
except:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
# sixth fallback - replace tabs with spaces
|
||||
if '\t' in response_text:
|
||||
response_text_copy = copy.deepcopy(response_text)
|
||||
response_text_copy = response_text_copy.replace('\t', ' ')
|
||||
# sixth fallback - try to remove last lines
|
||||
for i in range(1, len(response_text_lines)):
|
||||
response_text_lines_tmp = '\n'.join(response_text_lines[:-i])
|
||||
try:
|
||||
data = yaml.safe_load(response_text_copy)
|
||||
get_logger().info(f"Successfully parsed AI prediction after replacing tabs with spaces")
|
||||
data = yaml.safe_load(response_text_lines_tmp)
|
||||
get_logger().info(f"Successfully parsed AI prediction after removing {i} lines")
|
||||
return data
|
||||
except:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
# seventh fallback - add indent for sections of code blocks
|
||||
response_text_copy = copy.deepcopy(response_text)
|
||||
response_text_copy_lines = response_text_copy.split('\n')
|
||||
start_line = -1
|
||||
for i, line in enumerate(response_text_copy_lines):
|
||||
if 'existing_code:' in line or 'improved_code:' in line:
|
||||
start_line = i
|
||||
elif line.endswith(': |') or line.endswith(': |-') or line.endswith(': |2') or line.endswith(':'):
|
||||
start_line = -1
|
||||
elif start_line != -1:
|
||||
response_text_copy_lines[i] = ' ' + line
|
||||
response_text_copy = '\n'.join(response_text_copy_lines)
|
||||
try:
|
||||
data = yaml.safe_load(response_text_copy)
|
||||
get_logger().info(f"Successfully parsed AI prediction after adding indent for sections of code blocks")
|
||||
return data
|
||||
except:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
# # sixth fallback - try to remove last lines
|
||||
# for i in range(1, len(response_text_lines)):
|
||||
# response_text_lines_tmp = '\n'.join(response_text_lines[:-i])
|
||||
# try:
|
||||
# data = yaml.safe_load(response_text_lines_tmp)
|
||||
# get_logger().info(f"Successfully parsed AI prediction after removing {i} lines")
|
||||
# return data
|
||||
# except:
|
||||
# pass
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def set_custom_labels(variables, git_provider=None):
|
||||
if not get_settings().config.enable_custom_labels:
|
||||
@ -933,7 +867,6 @@ def get_max_tokens(model):
|
||||
elif settings.config.custom_model_max_tokens > 0:
|
||||
max_tokens_model = settings.config.custom_model_max_tokens
|
||||
else:
|
||||
get_logger().error(f"Model {model} is not defined in MAX_TOKENS in ./pr_agent/algo/__init__.py and no custom_model_max_tokens is set")
|
||||
raise Exception(f"Ensure {model} is defined in MAX_TOKENS in ./pr_agent/algo/__init__.py or set a positive value for it in config.custom_model_max_tokens")
|
||||
|
||||
if settings.config.max_model_tokens and settings.config.max_model_tokens > 0:
|
||||
@ -945,66 +878,12 @@ def clip_tokens(text: str, max_tokens: int, add_three_dots=True, num_input_token
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Clip the number of tokens in a string to a maximum number of tokens.
|
||||
|
||||
This function limits text to a specified token count by calculating the approximate
|
||||
character-to-token ratio and truncating the text accordingly. A safety factor of 0.9
|
||||
(10% reduction) is applied to ensure the result stays within the token limit.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
text (str): The string to clip. If empty or None, returns the input unchanged.
|
||||
text (str): The string to clip.
|
||||
max_tokens (int): The maximum number of tokens allowed in the string.
|
||||
If negative, returns an empty string.
|
||||
add_three_dots (bool, optional): Whether to add "\\n...(truncated)" at the end
|
||||
of the clipped text to indicate truncation.
|
||||
Defaults to True.
|
||||
num_input_tokens (int, optional): Pre-computed number of tokens in the input text.
|
||||
If provided, skips token encoding step for efficiency.
|
||||
If None, tokens will be counted using TokenEncoder.
|
||||
Defaults to None.
|
||||
delete_last_line (bool, optional): Whether to remove the last line from the
|
||||
clipped content before adding truncation indicator.
|
||||
Useful for ensuring clean breaks at line boundaries.
|
||||
Defaults to False.
|
||||
|
||||
add_three_dots (bool, optional): A boolean indicating whether to add three dots at the end of the clipped
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
str: The clipped string. Returns original text if:
|
||||
- Text is empty/None
|
||||
- Token count is within limit
|
||||
- An error occurs during processing
|
||||
|
||||
Returns empty string if max_tokens <= 0.
|
||||
|
||||
Examples:
|
||||
Basic usage:
|
||||
>>> text = "This is a sample text that might be too long"
|
||||
>>> result = clip_tokens(text, max_tokens=10)
|
||||
>>> print(result)
|
||||
This is a sample...
|
||||
(truncated)
|
||||
|
||||
Without truncation indicator:
|
||||
>>> result = clip_tokens(text, max_tokens=10, add_three_dots=False)
|
||||
>>> print(result)
|
||||
This is a sample
|
||||
|
||||
With pre-computed token count:
|
||||
>>> result = clip_tokens(text, max_tokens=5, num_input_tokens=15)
|
||||
>>> print(result)
|
||||
This...
|
||||
(truncated)
|
||||
|
||||
With line deletion:
|
||||
>>> multiline_text = "Line 1\\nLine 2\\nLine 3"
|
||||
>>> result = clip_tokens(multiline_text, max_tokens=3, delete_last_line=True)
|
||||
>>> print(result)
|
||||
Line 1
|
||||
Line 2
|
||||
...
|
||||
(truncated)
|
||||
|
||||
Notes:
|
||||
The function uses a safety factor of 0.9 (10% reduction) to ensure the
|
||||
result stays within the token limit, as character-to-token ratios can vary.
|
||||
If token encoding fails, the original text is returned with a warning logged.
|
||||
str: The clipped string.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if not text:
|
||||
return text
|
||||
|
||||
@ -22,7 +22,6 @@ def set_parser():
|
||||
- cli.py --pr_url=... ask "write me a poem about this PR"
|
||||
- cli.py --pr_url=... reflect
|
||||
- cli.py --issue_url=... similar_issue
|
||||
- cli.py --pr_url/--issue_url= help_docs [<asked question>]
|
||||
|
||||
Supported commands:
|
||||
- review / review_pr - Add a review that includes a summary of the PR and specific suggestions for improvement.
|
||||
@ -42,8 +41,6 @@ def set_parser():
|
||||
|
||||
- generate_labels
|
||||
|
||||
- help_docs - Ask a question, from either an issue or PR context, on a given repo (current context or a different one)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Configuration:
|
||||
To edit any configuration parameter from 'configuration.toml', just add -config_path=<value>.
|
||||
@ -86,13 +83,7 @@ def run(inargs=None, args=None):
|
||||
if get_settings().litellm.get("enable_callbacks", False):
|
||||
# There may be additional events on the event queue from the run above. If there are give them time to complete.
|
||||
get_logger().debug("Waiting for event queue to complete")
|
||||
tasks = [task for task in asyncio.all_tasks() if task is not asyncio.current_task()]
|
||||
if tasks:
|
||||
_, pending = await asyncio.wait(tasks, timeout=30)
|
||||
if pending:
|
||||
get_logger().warning(
|
||||
f"{len(pending)} callback tasks({[task.get_coro() for task in pending]}) did not complete within timeout"
|
||||
)
|
||||
await asyncio.wait([task for task in asyncio.all_tasks() if task is not asyncio.current_task()])
|
||||
|
||||
return result
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -19,24 +19,22 @@ global_settings = Dynaconf(
|
||||
"settings/pr_questions_prompts.toml",
|
||||
"settings/pr_line_questions_prompts.toml",
|
||||
"settings/pr_description_prompts.toml",
|
||||
"settings/code_suggestions/pr_code_suggestions_prompts.toml",
|
||||
"settings/code_suggestions/pr_code_suggestions_prompts_not_decoupled.toml",
|
||||
"settings/code_suggestions/pr_code_suggestions_reflect_prompts.toml",
|
||||
"settings/pr_code_suggestions_prompts.toml",
|
||||
"settings/pr_code_suggestions_reflect_prompts.toml",
|
||||
"settings/pr_sort_code_suggestions_prompts.toml",
|
||||
"settings/pr_information_from_user_prompts.toml",
|
||||
"settings/pr_update_changelog_prompts.toml",
|
||||
"settings/pr_custom_labels.toml",
|
||||
"settings/pr_add_docs.toml",
|
||||
"settings/custom_labels.toml",
|
||||
"settings/pr_help_prompts.toml",
|
||||
"settings/pr_help_docs_prompts.toml",
|
||||
"settings/pr_help_docs_headings_prompts.toml",
|
||||
"settings/.secrets.toml",
|
||||
"settings_prod/.secrets.toml",
|
||||
]]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_settings(use_context=False):
|
||||
def get_settings():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Retrieves the current settings.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -8,11 +8,9 @@ from pr_agent.git_providers.bitbucket_server_provider import \
|
||||
from pr_agent.git_providers.codecommit_provider import CodeCommitProvider
|
||||
from pr_agent.git_providers.gerrit_provider import GerritProvider
|
||||
from pr_agent.git_providers.git_provider import GitProvider
|
||||
from pr_agent.git_providers.gitea_provider import GiteaProvider
|
||||
from pr_agent.git_providers.github_provider import GithubProvider
|
||||
from pr_agent.git_providers.gitlab_provider import GitLabProvider
|
||||
from pr_agent.git_providers.local_git_provider import LocalGitProvider
|
||||
from pr_agent.git_providers.gitea_provider import GiteaProvider
|
||||
|
||||
_GIT_PROVIDERS = {
|
||||
'github': GithubProvider,
|
||||
@ -23,7 +21,6 @@ _GIT_PROVIDERS = {
|
||||
'codecommit': CodeCommitProvider,
|
||||
'local': LocalGitProvider,
|
||||
'gerrit': GerritProvider,
|
||||
'gitea': GiteaProvider
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -18,10 +18,14 @@ ADO_APP_CLIENT_DEFAULT_ID = "499b84ac-1321-427f-aa17-267ca6975798/.default"
|
||||
MAX_PR_DESCRIPTION_AZURE_LENGTH = 4000-1
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
# noinspection PyUnresolvedReferences
|
||||
# noinspection PyUnresolvedReferences
|
||||
from azure.devops.connection import Connection
|
||||
# noinspection PyUnresolvedReferences
|
||||
from azure.devops.released.git import (Comment, CommentThread, GitPullRequest, GitVersionDescriptor, GitClient, CommentThreadContext, CommentPosition)
|
||||
from azure.devops.v7_1.git.models import (Comment, CommentThread,
|
||||
GitPullRequest,
|
||||
GitPullRequestIterationChanges,
|
||||
GitVersionDescriptor)
|
||||
# noinspection PyUnresolvedReferences
|
||||
from azure.identity import DefaultAzureCredential
|
||||
from msrest.authentication import BasicAuthentication
|
||||
@ -73,13 +77,40 @@ class AzureDevopsProvider(GitProvider):
|
||||
f"relevant_lines_start is {relevant_lines_start}")
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
thread_context = CommentThreadContext(
|
||||
file_path=relevant_file,
|
||||
right_file_start=CommentPosition(offset=1, line=relevant_lines_start),
|
||||
right_file_end=CommentPosition(offset=1, line=relevant_lines_end))
|
||||
comment = Comment(content=body, comment_type=1)
|
||||
thread = CommentThread(comments=[comment], thread_context=thread_context)
|
||||
if relevant_lines_end > relevant_lines_start:
|
||||
post_parameters = {
|
||||
"body": body,
|
||||
"path": relevant_file,
|
||||
"line": relevant_lines_end,
|
||||
"start_line": relevant_lines_start,
|
||||
"start_side": "RIGHT",
|
||||
}
|
||||
else: # API is different for single line comments
|
||||
post_parameters = {
|
||||
"body": body,
|
||||
"path": relevant_file,
|
||||
"line": relevant_lines_start,
|
||||
"side": "RIGHT",
|
||||
}
|
||||
post_parameters_list.append(post_parameters)
|
||||
if not post_parameters_list:
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
for post_parameters in post_parameters_list:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
comment = Comment(content=post_parameters["body"], comment_type=1)
|
||||
thread = CommentThread(comments=[comment],
|
||||
thread_context={
|
||||
"filePath": post_parameters["path"],
|
||||
"rightFileStart": {
|
||||
"line": post_parameters["start_line"],
|
||||
"offset": 1,
|
||||
},
|
||||
"rightFileEnd": {
|
||||
"line": post_parameters["line"],
|
||||
"offset": 1,
|
||||
},
|
||||
})
|
||||
self.azure_devops_client.create_thread(
|
||||
comment_thread=thread,
|
||||
project=self.workspace_slug,
|
||||
@ -87,36 +118,34 @@ class AzureDevopsProvider(GitProvider):
|
||||
pull_request_id=self.pr_num
|
||||
)
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
get_logger().error(f"Azure failed to publish code suggestion, error: {e}", suggestion=suggestion)
|
||||
get_logger().warning(f"Azure failed to publish code suggestion, error: {e}")
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
def reply_to_comment_from_comment_id(self, comment_id: int, body: str, is_temporary: bool = False) -> Comment:
|
||||
# comment_id is actually thread_id
|
||||
return self.reply_to_thread(comment_id, body, is_temporary)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_pr_description_full(self) -> str:
|
||||
return self.pr.description
|
||||
|
||||
def edit_comment(self, comment: Comment, body: str):
|
||||
def edit_comment(self, comment, body: str):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
self.azure_devops_client.update_comment(
|
||||
repository_id=self.repo_slug,
|
||||
pull_request_id=self.pr_num,
|
||||
thread_id=comment.thread_id,
|
||||
comment_id=comment.id,
|
||||
thread_id=comment["thread_id"],
|
||||
comment_id=comment["comment_id"],
|
||||
comment=Comment(content=body),
|
||||
project=self.workspace_slug,
|
||||
)
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
get_logger().exception(f"Failed to edit comment, error: {e}")
|
||||
|
||||
def remove_comment(self, comment: Comment):
|
||||
def remove_comment(self, comment):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
self.azure_devops_client.delete_comment(
|
||||
repository_id=self.repo_slug,
|
||||
pull_request_id=self.pr_num,
|
||||
thread_id=comment.thread_id,
|
||||
comment_id=comment.id,
|
||||
thread_id=comment["thread_id"],
|
||||
comment_id=comment["comment_id"],
|
||||
project=self.workspace_slug,
|
||||
)
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
@ -147,10 +176,13 @@ class AzureDevopsProvider(GitProvider):
|
||||
return []
|
||||
|
||||
def is_supported(self, capability: str) -> bool:
|
||||
if capability in [
|
||||
"get_issue_comments",
|
||||
]:
|
||||
return False
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
def set_pr(self, pr_url: str):
|
||||
self.pr_url = pr_url
|
||||
self.workspace_slug, self.repo_slug, self.pr_num = self._parse_pr_url(pr_url)
|
||||
self.pr = self._get_pr()
|
||||
|
||||
@ -345,31 +377,22 @@ class AzureDevopsProvider(GitProvider):
|
||||
get_logger().exception(f"Failed to get diff files, error: {e}")
|
||||
return []
|
||||
|
||||
def publish_comment(self, pr_comment: str, is_temporary: bool = False, thread_context=None) -> Comment:
|
||||
def publish_comment(self, pr_comment: str, is_temporary: bool = False, thread_context=None):
|
||||
if is_temporary and not get_settings().config.publish_output_progress:
|
||||
get_logger().debug(f"Skipping publish_comment for temporary comment: {pr_comment}")
|
||||
return None
|
||||
comment = Comment(content=pr_comment)
|
||||
# Set status to 'active' to prevent auto-resolve (see CommentThreadStatus docs)
|
||||
thread = CommentThread(comments=[comment], thread_context=thread_context, status='active')
|
||||
thread = CommentThread(comments=[comment], thread_context=thread_context, status=5)
|
||||
thread_response = self.azure_devops_client.create_thread(
|
||||
comment_thread=thread,
|
||||
project=self.workspace_slug,
|
||||
repository_id=self.repo_slug,
|
||||
pull_request_id=self.pr_num,
|
||||
)
|
||||
created_comment = thread_response.comments[0]
|
||||
created_comment.thread_id = thread_response.id
|
||||
response = {"thread_id": thread_response.id, "comment_id": thread_response.comments[0].id}
|
||||
if is_temporary:
|
||||
self.temp_comments.append(created_comment)
|
||||
return created_comment
|
||||
|
||||
def publish_persistent_comment(self, pr_comment: str,
|
||||
initial_header: str,
|
||||
update_header: bool = True,
|
||||
name='review',
|
||||
final_update_message=True):
|
||||
return self.publish_persistent_comment_full(pr_comment, initial_header, update_header, name, final_update_message)
|
||||
self.temp_comments.append(response)
|
||||
return response
|
||||
|
||||
def publish_description(self, pr_title: str, pr_body: str):
|
||||
if len(pr_body) > MAX_PR_DESCRIPTION_AZURE_LENGTH:
|
||||
@ -414,6 +437,7 @@ class AzureDevopsProvider(GitProvider):
|
||||
def publish_inline_comment(self, body: str, relevant_file: str, relevant_line_in_file: str, original_suggestion=None):
|
||||
self.publish_inline_comments([self.create_inline_comment(body, relevant_file, relevant_line_in_file)])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def create_inline_comment(self, body: str, relevant_file: str, relevant_line_in_file: str,
|
||||
absolute_position: int = None):
|
||||
position, absolute_position = find_line_number_of_relevant_line_in_file(self.get_diff_files(),
|
||||
@ -497,7 +521,7 @@ class AzureDevopsProvider(GitProvider):
|
||||
def get_user_id(self):
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
|
||||
def get_issue_comments(self) -> list[Comment]:
|
||||
def get_issue_comments(self):
|
||||
threads = self.azure_devops_client.get_threads(repository_id=self.repo_slug, pull_request_id=self.pr_num, project=self.workspace_slug)
|
||||
threads.reverse()
|
||||
comment_list = []
|
||||
@ -515,59 +539,30 @@ class AzureDevopsProvider(GitProvider):
|
||||
def remove_reaction(self, issue_comment_id: int, reaction_id: int) -> bool:
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
def set_like(self, thread_id: int, comment_id: int, create: bool = True):
|
||||
if create:
|
||||
self.azure_devops_client.create_like(self.repo_slug, self.pr_num, thread_id, comment_id, project=self.workspace_slug)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.azure_devops_client.delete_like(self.repo_slug, self.pr_num, thread_id, comment_id, project=self.workspace_slug)
|
||||
|
||||
def set_thread_status(self, thread_id: int, status: str):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
self.azure_devops_client.update_thread(CommentThread(status=status), self.repo_slug, self.pr_num, thread_id, self.workspace_slug)
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
get_logger().exception(f"Failed to set thread status, error: {e}")
|
||||
|
||||
def reply_to_thread(self, thread_id: int, body: str, is_temporary: bool = False) -> Comment:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
comment = Comment(content=body)
|
||||
response = self.azure_devops_client.create_comment(comment, self.repo_slug, self.pr_num, thread_id, self.workspace_slug)
|
||||
response.thread_id = thread_id
|
||||
if is_temporary:
|
||||
self.temp_comments.append(response)
|
||||
return response
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
get_logger().exception(f"Failed to reply to thread, error: {e}")
|
||||
|
||||
def get_thread_context(self, thread_id: int) -> CommentThreadContext:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
thread = self.azure_devops_client.get_pull_request_thread(self.repo_slug, self.pr_num, thread_id, self.workspace_slug)
|
||||
return thread.thread_context
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
get_logger().exception(f"Failed to set thread status, error: {e}")
|
||||
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
def _parse_pr_url(pr_url: str) -> Tuple[str, str, int]:
|
||||
parsed_url = urlparse(pr_url)
|
||||
|
||||
path_parts = parsed_url.path.strip("/").split("/")
|
||||
num_parts = len(path_parts)
|
||||
if num_parts < 5:
|
||||
raise ValueError("The provided URL has insufficient path components for an Azure DevOps PR URL")
|
||||
|
||||
# Verify that the second-to-last path component is "pullrequest"
|
||||
if path_parts[num_parts - 2] != "pullrequest":
|
||||
raise ValueError("The provided URL does not follow the expected Azure DevOps PR URL format")
|
||||
|
||||
workspace_slug = path_parts[num_parts - 5]
|
||||
repo_slug = path_parts[num_parts - 3]
|
||||
try:
|
||||
pr_number = int(path_parts[num_parts - 1])
|
||||
except ValueError as e:
|
||||
raise ValueError("Cannot parse PR number in the provided URL") from e
|
||||
if "pullrequest" not in path_parts:
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
"The provided URL does not appear to be a Azure DevOps PR URL"
|
||||
)
|
||||
if len(path_parts) == 6: # "https://dev.azure.com/organization/project/_git/repo/pullrequest/1"
|
||||
workspace_slug = path_parts[1]
|
||||
repo_slug = path_parts[3]
|
||||
pr_number = int(path_parts[5])
|
||||
elif len(path_parts) == 5: # 'https://organization.visualstudio.com/project/_git/repo/pullrequest/1'
|
||||
workspace_slug = path_parts[0]
|
||||
repo_slug = path_parts[2]
|
||||
pr_number = int(path_parts[4])
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise ValueError("The provided URL does not appear to be a Azure DevOps PR URL")
|
||||
|
||||
return workspace_slug, repo_slug, pr_number
|
||||
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
def _get_azure_devops_client() -> GitClient:
|
||||
def _get_azure_devops_client():
|
||||
org = get_settings().azure_devops.get("org", None)
|
||||
pat = get_settings().azure_devops.get("pat", None)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -619,21 +614,8 @@ class AzureDevopsProvider(GitProvider):
|
||||
return pr_id
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
if get_settings().config.verbosity_level >= 2:
|
||||
get_logger().info(f"Failed to get PR id, error: {e}")
|
||||
get_logger().error(f"Failed to get pr id, error: {e}")
|
||||
return ""
|
||||
|
||||
def publish_file_comments(self, file_comments: list) -> bool:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
def get_line_link(self, relevant_file: str, relevant_line_start: int, relevant_line_end: int = None) -> str:
|
||||
return self.pr_url+f"?_a=files&path={relevant_file}"
|
||||
|
||||
def get_comment_url(self, comment) -> str:
|
||||
return self.pr_url + "?discussionId=" + str(comment.thread_id)
|
||||
|
||||
def get_latest_commit_url(self) -> str:
|
||||
commits = self.azure_devops_client.get_pull_request_commits(self.repo_slug, self.pr_num, self.workspace_slug)
|
||||
last = commits[0]
|
||||
url = self.azure_devops_client.normalized_url + "/" + self.workspace_slug + "/_git/" + self.repo_slug + "/commit/" + last.commit_id
|
||||
return url
|
||||
|
||||